Photos consume a significant amount of storage space on our devices and in the cloud, but this is due to several key factors. This article from dfphoto.net delves into the reasons behind large photo file sizes and provides practical strategies to manage and optimize your photo storage. By understanding these factors, you can take control of your digital photo library, ensuring you never run out of space while maintaining high-quality visuals.
1. What Factors Contribute to Large Photo File Sizes?
Several factors contribute to the large size of photo files.
The primary factors are resolution, file format, and bit depth. Higher resolution captures more detail, leading to larger files. Uncompressed formats like TIFF retain all image data, resulting in significantly larger files than compressed formats like JPEG. Bit depth determines the number of colors an image can contain; higher bit depths create larger files with richer color information.
- Resolution: The number of pixels in an image directly affects its file size. A higher resolution means more pixels, resulting in a larger file. For instance, a 12-megapixel photo will be smaller than a 48-megapixel one.
- File Format: Different file formats use various compression algorithms. JPEG is a lossy compression format, reducing file size by discarding some image data. TIFF is a lossless format that retains all image data, resulting in larger file sizes but better quality.
- Bit Depth: Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent each color in a pixel. Higher bit depths allow for more color information, increasing file size. Common bit depths include 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit.
- Image Complexity: Images with many details, textures, and colors will generally have larger file sizes than simpler images with flat colors and minimal details.
- Metadata: Information such as camera settings, date, time, and location are embedded in the image file, contributing to its overall size.
2. How Does Camera Resolution Affect Photo Storage Needs?
Camera resolution is a critical determinant of photo file size and, consequently, your storage requirements.
Higher resolutions capture more detail, leading to larger file sizes. For example, a photo taken with a 48-megapixel camera will require significantly more storage space than one taken with a 12-megapixel camera. Understanding the impact of resolution helps in making informed decisions about storage solutions.
| Resolution (Megapixels) | Typical File Size (JPEG) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 12 MP | 4-6 MB | Social media, small prints |
| 24 MP | 8-12 MB | Medium-sized prints, detailed social media |
| 48 MP | 15-25 MB | Large prints, professional photography |
| 100+ MP | 50+ MB | High-end photography, billboards, extensive cropping capabilities |
3. What Are the Differences Between JPEG, RAW, and TIFF File Formats and Their Impact on Storage?
Different file formats significantly impact photo storage due to their varying compression methods and data retention.
JPEG, RAW, and TIFF formats have distinct characteristics affecting file size and image quality. JPEG is a lossy format that reduces file size by discarding some data. RAW retains all data captured by the camera sensor, resulting in larger files and greater editing flexibility. TIFF is a lossless format that preserves all image data without compression artifacts.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): This is the most common format for photos due to its small file size. JPEG uses lossy compression, which reduces file size by discarding some image data. While this makes JPEG files easy to store and share, it can also lead to a loss of quality, especially with repeated saving and editing.
- RAW: RAW files contain all the data captured by the camera sensor, without any compression. This results in significantly larger files than JPEGs but offers the highest image quality and the greatest flexibility for editing. RAW files are ideal for professional photographers and enthusiasts who want to maximize their editing capabilities.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): TIFF is a lossless format commonly used for archiving and professional printing. It retains all image data without any loss of quality. TIFF files are larger than JPEGs but smaller than RAW files. They are a good choice when you need high-quality images without the massive file sizes of RAW.
4. How Does Bit Depth Influence Photo File Size and Quality?
Bit depth significantly influences both photo file size and quality.
Higher bit depths provide more color information, leading to richer, more accurate colors and smoother tonal transitions. However, this increased color information also results in larger file sizes. Understanding the trade-offs between bit depth, image quality, and file size is essential for optimizing your photo storage.
| Bit Depth | Number of Colors | File Size Impact | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-bit | 256 | Smaller | Web images, social media, general use |
| 16-bit | 65,536 | Larger | Professional photography, detailed editing, large prints |
| 32-bit | Millions | Largest | High-end imaging, scientific applications, specialized color requirements |
5. What Role Does Metadata Play in Photo Storage Requirements?
Metadata, while essential for organization and information, adds to the overall file size of photos, thus affecting storage requirements.
Metadata includes information such as camera settings, date, time, location (GPS data), and copyright details. While this data is invaluable for cataloging and searching your photo library, it contributes to the total file size. Managing metadata efficiently can help optimize storage.
| Metadata Type | Description | Impact on File Size |
|---|---|---|
| EXIF Data | Camera settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO), date, time | Small |
| IPTC Data | Copyright information, descriptions, keywords | Small |
| GPS Data | Location coordinates | Small |
| XMP Data | Custom metadata, editing history | Variable |
| Thumbnail Images | Small preview images embedded in the file | Moderate |
6. How Can I Optimize My Camera Settings to Reduce Photo File Sizes Without Sacrificing Too Much Quality?
Optimizing camera settings can significantly reduce photo file sizes without compromising image quality.
Adjusting settings such as resolution, file format, and compression levels can help balance file size and quality. Shooting in JPEG instead of RAW, reducing resolution to match your intended use, and using moderate compression settings can lead to substantial storage savings.
- Shoot in JPEG: If you don’t need the editing flexibility of RAW, shooting in JPEG can significantly reduce file sizes.
- Adjust Resolution: Lower the resolution to match your intended use. For example, if you primarily share photos online, a lower resolution may suffice.
- Use Moderate Compression: When shooting in JPEG, use a moderate compression setting to balance file size and image quality.
- Disable Unnecessary Features: Turn off features like GPS tagging if you don’t need them, as they add to the metadata and increase file size.
- Clean Your Lens: A clean lens will produce sharper images, reducing the need for extensive post-processing that can increase file size.
- Proper Exposure: Achieve proper exposure in-camera to minimize the need for brightness adjustments later, which can degrade image quality and increase file size.
7. What Are the Best Practices for Storing Photos on My Computer to Minimize Storage Usage?
Effective photo storage on your computer involves several best practices to minimize storage usage while maintaining organization and accessibility.
Using external hard drives, cloud storage, and efficient file management techniques can help you manage your photo library effectively. Regularly backing up your photos is also crucial to prevent data loss.
- Use External Hard Drives: Store large photo collections on external hard drives to free up space on your computer’s internal storage.
- Cloud Storage: Utilize cloud storage services like Google Photos, Dropbox, or iCloud to store and access your photos from anywhere.
- File Compression: Compress photo files using ZIP or other compression tools to reduce their size without significant quality loss.
- Organize Your Files: Create a structured folder system to organize your photos by date, event, or project. This makes it easier to find and manage your files.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your photo library to multiple locations, including external drives and cloud storage, to protect against data loss.
- Delete Duplicates: Use software to identify and delete duplicate photo files, which can take up significant storage space.
8. How Can Cloud Storage Solutions Help Manage Large Photo Libraries?
Cloud storage solutions offer a scalable and accessible way to manage large photo libraries.
Services like Google Photos, Dropbox, and iCloud provide ample storage space, automatic backups, and easy sharing options. Cloud storage allows you to access your photos from any device, making it a convenient solution for managing large photo collections.
| Cloud Storage Service | Storage Options | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Google Photos | 15 GB free, additional storage available via Google One | Automatic backups, AI-powered organization, sharing features |
| Dropbox | 2 GB free, paid plans available | File syncing across devices, version history, collaboration tools |
| iCloud Photos | 5 GB free, additional storage available via iCloud+ | Seamless integration with Apple devices, automatic syncing, family sharing |
| Amazon Photos | 5 GB free, unlimited photo storage for Prime members | Integration with Amazon devices, facial recognition, printing options |
| Microsoft OneDrive | 5 GB free, additional storage available via Microsoft 365 | Integration with Microsoft Office apps, file sharing, version history |
9. What Are Some Effective Methods for Compressing Photos Without Losing Significant Quality?
Compressing photos without significant quality loss involves using the right tools and techniques.
Tools like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, and online compression services offer options to reduce file size while preserving visual quality. Understanding compression settings and using optimized file formats can help you strike the right balance between size and quality.
- Adobe Photoshop: Use the “Save for Web” feature to optimize images for online use, reducing file size while maintaining quality.
- Adobe Lightroom: Lightroom’s export settings allow you to control the compression level and file size of your exported photos.
- Online Compression Tools: Services like TinyPNG and ImageOptim use intelligent lossy compression to reduce file sizes without noticeable quality loss.
- Optimize File Format: Convert photos to WebP format, which offers superior compression and quality compared to JPEG.
- Reduce Resolution: Lower the resolution of your images to match their intended use, reducing file size without sacrificing perceived quality.
- Use Progressive JPEGs: Progressive JPEGs load gradually in web browsers, providing a better user experience and slightly smaller file sizes.
10. How Can I Identify and Delete Duplicate Photos to Free Up Storage Space?
Identifying and deleting duplicate photos is an effective way to free up storage space.
Software tools like Gemini, Duplicate Cleaner, and Adobe Lightroom can scan your photo library and identify duplicate files. Reviewing and deleting these duplicates can reclaim significant storage space.
- Gemini: A Mac app that quickly scans your hard drive and identifies duplicate files, including photos.
- Duplicate Cleaner: A Windows application that finds and removes duplicate files based on various criteria, such as file name, size, and content.
- Adobe Lightroom: Lightroom can identify and merge duplicate photos in your catalog, helping you keep your library organized.
- manual Review: Manually review your photo library to identify and delete obvious duplicates.
- Cloud Storage Tools: Some cloud storage services, like Google Photos, can automatically detect and remove duplicate uploads.
- Third-Party Apps: Use third-party apps specifically designed for finding and deleting duplicate photos on your computer or mobile device.
11. What Are the Key Considerations When Choosing a Photo Storage Solution for Mobile Devices?
Choosing a photo storage solution for mobile devices requires careful consideration of factors like storage capacity, ease of use, and integration with other devices and services.
Cloud storage services, external storage devices, and built-in device storage are all options to consider. Evaluate your needs and priorities to select the best solution for your mobile photo storage.
- Storage Capacity: Ensure the storage solution offers enough space for your current and future photo needs.
- Ease of Use: Choose a solution that is easy to use and integrates seamlessly with your mobile device.
- Automatic Backups: Opt for a solution that automatically backs up your photos to prevent data loss.
- Accessibility: Select a solution that allows you to access your photos from multiple devices.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the storage solution, including any subscription fees.
- Security: Ensure the storage solution offers adequate security measures to protect your photos from unauthorized access.
12. How Do Photo Editing Software and Their Features Affect Storage Usage?
Photo editing software and their features can significantly impact storage usage.
Software like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom create large temporary files and backups during the editing process. Understanding how these features affect storage can help you manage your editing workflow more efficiently.
| Feature | Impact on Storage Usage |
|---|---|
| Temporary Files | Photo editing software creates temporary files that can take up significant space. |
| Version History | Storing multiple versions of your edits increases storage usage. |
| Cache Files | Cache files speed up performance but can consume storage over time. |
| RAW Processing | RAW files require more storage than JPEG files. |
| High-Resolution Editing | Editing high-resolution images requires more storage space. |
| Export Settings | Export settings can affect the file size of your edited photos. |
13. What Are the Strategies for Archiving Photos Long-Term to Ensure Their Preservation?
Archiving photos long-term requires strategies to ensure their preservation and accessibility.
Using multiple backup locations, storing photos in lossless formats, and periodically migrating your archive to new storage media can help protect your photo collection for future generations.
- Multiple Backups: Store your photos in multiple locations, including external hard drives, cloud storage, and archival discs.
- Lossless Formats: Archive your photos in lossless formats like TIFF or DNG to preserve image quality.
- Metadata Backup: Back up your metadata along with your photo files to retain important information about your images.
- Regular Migration: Periodically migrate your photo archive to new storage media to prevent data loss due to hardware failure or obsolescence.
- Climate Control: Store your archival media in a cool, dry place to prevent damage.
- Checksum Verification: Use checksum verification tools to ensure the integrity of your archived files.
14. How Can I Use External Storage Devices to Expand My Photo Storage Capacity?
External storage devices offer a cost-effective way to expand your photo storage capacity.
External hard drives, SSDs, and NAS devices provide ample storage space and can be easily connected to your computer or network. Consider factors like storage capacity, speed, and portability when choosing an external storage solution.
| Device Type | Storage Capacity | Speed | Portability | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External HDD | Up to 20 TB | Moderate | Moderate | General photo storage, backups |
| External SSD | Up to 4 TB | Fast | High | Editing large photo files, portable storage |
| NAS (Network Attached Storage) | Varies | Network Speed | Low | Centralized photo storage, backups, media streaming |
| USB Flash Drive | Up to 1 TB | Variable | High | Small photo backups, transferring files |
15. What Are the Benefits of Using a Network-Attached Storage (NAS) Device for Photo Storage?
Network-Attached Storage (NAS) devices offer several benefits for photo storage, including centralized access, automatic backups, and media streaming capabilities.
NAS devices provide a convenient solution for storing and sharing photos across multiple devices on your network.
- Centralized Storage: Store all your photos in one central location, accessible from any device on your network.
- Automatic Backups: Set up automatic backups to protect your photos from data loss.
- Media Streaming: Stream your photos to TVs, computers, and mobile devices.
- User Access Control: Control who has access to your photo library.
- RAID Protection: Protect your data from hard drive failure with RAID configurations.
- Remote Access: Access your photos remotely over the internet.
16. How Can I Optimize My Photo Workflow to Minimize Storage Usage?
Optimizing your photo workflow can help minimize storage usage and improve efficiency.
From shooting and editing to organizing and archiving, streamlining each step of your workflow can lead to significant storage savings.
- Shoot Strategically: Plan your shoots to minimize unnecessary photos.
- Cull Regularly: Regularly review and delete unwanted photos.
- Edit Efficiently: Edit your photos efficiently to minimize the creation of temporary files.
- Organize Promptly: Organize your photos promptly to prevent clutter and duplicates.
- Archive Smartly: Archive your photos smartly to ensure their long-term preservation.
- Use Presets: Use presets in Lightroom or Photoshop to streamline your editing process and reduce the need for extensive adjustments.
17. What Role Does AI Play in Optimizing Photo Storage and Management?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly significant role in optimizing photo storage and management.
AI-powered tools can automatically identify and tag photos, remove duplicates, and optimize file sizes. These technologies can streamline your workflow and help you manage your photo library more efficiently.
| AI Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Facial Recognition | Automatically identifies and tags faces in photos. | Easier organization and searching. |
| Object Recognition | Identifies objects and scenes in photos, such as landscapes or portraits. | Automatic tagging and categorization. |
| Duplicate Detection | Identifies and removes duplicate photos. | Frees up storage space. |
| Image Optimization | Automatically optimizes file sizes without significant quality loss. | Reduces storage requirements. |
| Smart Curation | Suggests the best photos from a collection based on image quality and content. | Streamlines the selection process. |
18. How Can I Educate Myself Further on Photo Storage and Management Techniques?
Educating yourself on photo storage and management techniques is crucial for maintaining a well-organized and efficient photo library.
Online courses, photography blogs, and books can provide valuable insights and practical tips for managing your photos effectively.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Skillshare, Udemy, and CreativeLive offer courses on photo storage and management.
- Photography Blogs: Websites like PetaPixel, Digital Photography School, and DPReview provide articles and tutorials on photo storage and management.
- Books: Books like “The DAM Book: Digital Asset Management for Photographers” by Peter Krogh offer comprehensive guidance on managing digital photo collections.
- Photography Communities: Join online photography communities and forums to learn from other photographers and share your experiences.
- Software Tutorials: Explore the tutorials and documentation provided by photo editing and storage software.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend photography workshops and seminars to learn from industry experts.
19. What Are the Latest Trends in Photo Storage Technology?
The latest trends in photo storage technology include advancements in cloud storage, AI-powered management tools, and more efficient storage media.
Staying informed about these trends can help you adopt the most effective strategies for managing your photo library.
- AI-Powered Management: AI is increasingly used to automate photo organization, tagging, and optimization.
- Cloud Storage Advancements: Cloud storage services are offering more storage capacity, faster transfer speeds, and improved security features.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is enabling faster and more efficient photo processing and storage on devices.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is being explored for secure and transparent photo storage and copyright protection.
- DNA Storage: DNA storage is being researched as a long-term storage solution for archival data.
- Quantum Storage: Quantum storage is being developed as a next-generation storage technology with the potential for massive storage capacity.
20. How Can dfphoto.net Help Me Better Understand and Manage My Photo Storage Needs?
dfphoto.net offers a wealth of resources to help you understand and manage your photo storage needs effectively.
From in-depth articles and tutorials to community forums and expert advice, dfphoto.net is your go-to resource for all things photography.
- Comprehensive Guides: Access detailed guides on photo storage, optimization, and management techniques.
- Expert Advice: Get insights and tips from experienced photographers and storage professionals.
- Community Forums: Connect with other photographers and share your experiences.
- Product Reviews: Read reviews of photo storage solutions and devices.
- Software Tutorials: Learn how to use photo editing and storage software effectively.
- Inspiration and Ideas: Discover creative ways to organize and showcase your photos.
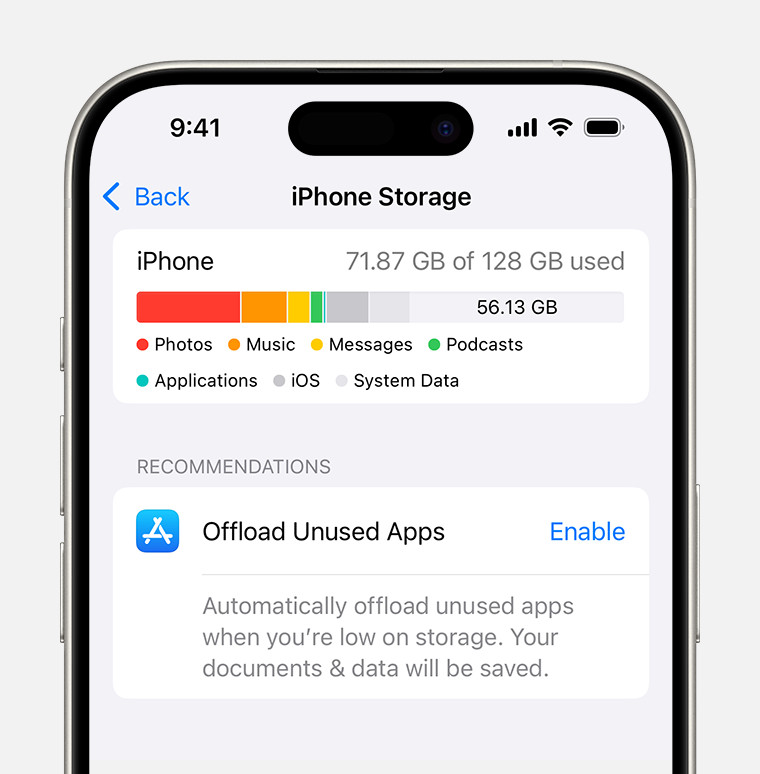 iPhone storage settings showing app usage
iPhone storage settings showing app usage
21. What Are the Environmental Impacts of Digital Photo Storage?
The environmental impacts of digital photo storage are increasingly significant due to the energy consumption of data centers and the manufacturing of storage devices.
Understanding these impacts can help you make more sustainable choices in your photo storage practices.
- Energy Consumption: Data centers consume vast amounts of energy to power servers and cooling systems.
- Carbon Emissions: The energy used by data centers contributes to carbon emissions and climate change.
- Electronic Waste: The disposal of old storage devices generates electronic waste, which can pollute the environment.
- Resource Depletion: The manufacturing of storage devices requires the extraction of raw materials.
- Water Usage: Data centers use large quantities of water for cooling.
- Sustainable Practices: Adopting sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient storage devices and supporting green data centers, can help reduce the environmental impact of digital photo storage.
22. How Can I Minimize the Environmental Impact of My Photo Storage Habits?
Minimizing the environmental impact of your photo storage habits involves adopting sustainable practices and making conscious choices about your storage solutions.
Using energy-efficient devices, optimizing your storage usage, and supporting green data centers can help reduce your carbon footprint.
- Use Energy-Efficient Devices: Choose storage devices with low energy consumption.
- Optimize Storage Usage: Delete unnecessary photos and compress files to reduce storage requirements.
- Support Green Data Centers: Choose cloud storage providers that use renewable energy sources.
- Recycle Old Devices: Properly recycle old storage devices to prevent electronic waste.
- Reduce Data Transfers: Minimize unnecessary data transfers to reduce energy consumption.
- Use Local Storage: Prioritize local storage over cloud storage when possible to reduce the energy consumption of data centers.
23. What Are the Ethical Considerations Related to Photo Storage and Privacy?
Ethical considerations related to photo storage and privacy are paramount in today’s digital age.
Protecting personal data, respecting copyright, and ensuring transparency are essential for responsible photo storage practices.
- Data Privacy: Protect personal data and respect privacy rights when storing and sharing photos.
- Copyright Compliance: Ensure you have the necessary rights and permissions to store and share copyrighted images.
- Transparency: Be transparent about how you collect, use, and share photo data.
- Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to protect photos from unauthorized access and theft.
- Ethical AI Use: Use AI-powered photo management tools ethically and responsibly.
- Consent and Notification: Obtain consent from individuals before storing or sharing their photos.
24. How Can I Ensure the Security of My Photos Stored in the Cloud?
Ensuring the security of your photos stored in the cloud requires implementing robust security measures and choosing reputable cloud storage providers.
Using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly backing up your data can help protect your photos from unauthorized access.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for your cloud storage accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Choose Reputable Providers: Select cloud storage providers with a strong track record of security and privacy.
- Encrypt Your Data: Encrypt your photos before uploading them to the cloud.
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your photos to multiple locations.
- Monitor Account Activity: Monitor your cloud storage account activity for suspicious behavior.
25. What Legal Aspects Should I Be Aware of When Storing and Sharing Photos?
When storing and sharing photos, it’s essential to be aware of the legal aspects related to copyright, privacy, and data protection.
Understanding these legal considerations can help you avoid potential legal issues.
- Copyright Law: Understand copyright law and obtain the necessary permissions before storing or sharing copyrighted images.
- Privacy Laws: Comply with privacy laws when storing or sharing photos of individuals.
- Data Protection Laws: Adhere to data protection laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, when collecting, storing, and processing personal data.
- Terms of Service: Review the terms of service of cloud storage providers to understand your rights and responsibilities.
- Model Releases: Obtain model releases when using photos of individuals for commercial purposes.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Respect intellectual property rights and avoid infringing on trademarks or patents.
26. How Can I Future-Proof My Photo Storage Strategy?
Future-proofing your photo storage strategy involves adopting flexible and adaptable solutions that can accommodate evolving technology and changing needs.
Using open file formats, embracing cloud storage, and regularly migrating your data can help ensure the longevity of your photo collection.
- Use Open File Formats: Store your photos in open file formats like TIFF or DNG to ensure compatibility with future software and hardware.
- Embrace Cloud Storage: Cloud storage provides scalability and accessibility, ensuring your photos can be accessed from anywhere.
- Regularly Migrate Your Data: Periodically migrate your photo archive to new storage media to prevent data loss due to hardware failure or obsolescence.
- Metadata Backup: Back up your metadata along with your photo files to retain important information about your images.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about the latest trends in photo storage technology and adapt your strategy accordingly.
- Diversify Storage Locations: Store your photos in multiple locations, including local storage, cloud storage, and archival discs, to protect against data loss.
27. What Resources Are Available to Help Me Choose the Right Photo Storage Solutions?
Numerous resources are available to help you choose the right photo storage solutions.
Online reviews, comparison guides, and expert recommendations can provide valuable insights and guidance.
- Online Reviews: Read reviews of photo storage solutions on websites like PCMag, CNET, and TechRadar.
- Comparison Guides: Consult comparison guides that compare the features, pricing, and performance of different storage solutions.
- Expert Recommendations: Seek recommendations from experienced photographers and storage professionals.
- User Forums: Join online forums and communities to learn from other users and share your experiences.
- Vendor Websites: Visit the websites of storage solution providers to learn about their products and services.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test different storage solutions before making a purchase.
28. How Can I Create a Photo Storage Plan That Meets My Specific Needs?
Creating a photo storage plan that meets your specific needs requires assessing your current and future storage requirements, considering your budget, and evaluating your technical skills.
By taking these factors into account, you can develop a customized storage plan that works for you.
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your current and future storage requirements based on the size of your photo library and your shooting habits.
- Consider Your Budget: Evaluate your budget and choose storage solutions that fit your financial constraints.
- Evaluate Your Technical Skills: Assess your technical skills and choose solutions that are easy for you to use.
- Choose Storage Locations: Select storage locations that meet your needs for accessibility, security, and reliability.
- Implement a Backup Strategy: Develop a backup strategy to protect your photos from data loss.
- Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update your storage plan to ensure it continues to meet your evolving needs.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.
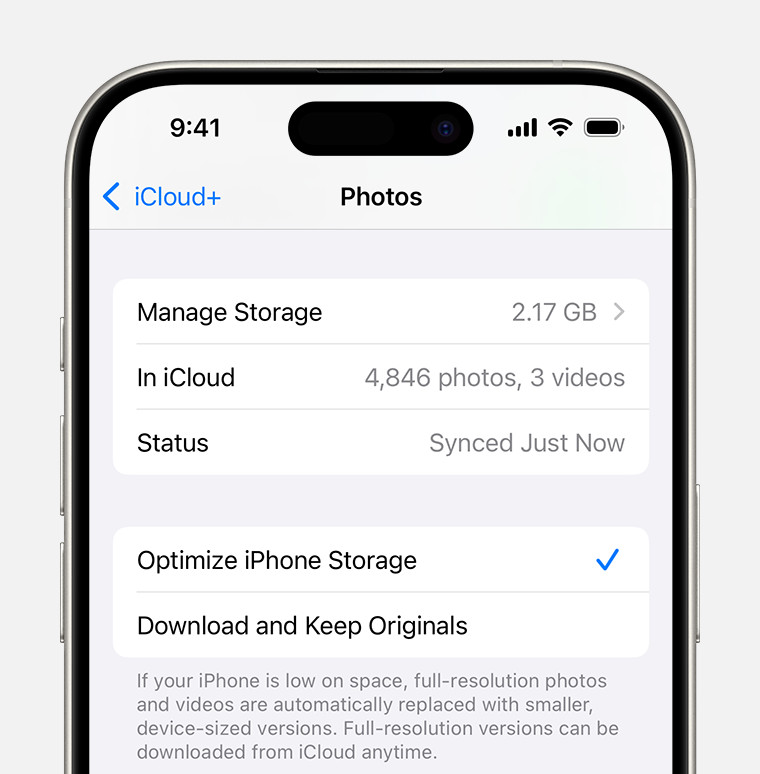 iCloud Photos settings on iPhone
iCloud Photos settings on iPhone
29. What is the Future of Photo Storage?
The future of photo storage is likely to be shaped by advancements in AI, cloud computing, and storage technologies.
Expect to see more automation, greater accessibility, and more sustainable storage solutions in the years to come.
- AI-Driven Automation: AI will automate many aspects of photo storage and management, from tagging and organization to optimization and curation.
- Enhanced Cloud Integration: Cloud storage will become even more seamless and integrated with our devices and workflows.
- Sustainable Storage Solutions: The industry will focus on developing more sustainable storage solutions that minimize environmental impact.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing will enable faster and more efficient photo processing and storage on devices.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain will be used to enhance the security and transparency of photo storage and copyright protection.
- New Storage Technologies: New storage technologies, such as DNA storage and quantum storage, will offer the potential for massive storage capacity and long-term preservation.
30. What Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Photo Storage?
Here are some frequently asked questions about photo storage, along with their answers:
- Why do my photos take up so much space?
- Photos take up a lot of space because of their resolution, file format, and bit depth. Higher resolution and lossless formats like RAW and TIFF result in larger file sizes.
- How can I reduce the file size of my photos?
- You can reduce the file size of your photos by shooting in JPEG, lowering the resolution, using moderate compression settings, and removing unnecessary metadata.
- What is the best file format for storing photos?
- The best file format depends on your needs. JPEG is suitable for general use and sharing, while RAW is ideal for editing, and TIFF is best for archiving.
- How much cloud storage do I need for my photos?
- The amount of cloud storage you need depends on the size of your photo library and your shooting habits. Estimate your current and future storage requirements and choose a plan that meets your needs.
- What are the benefits of using cloud storage for photos?
- Cloud storage offers several benefits, including accessibility from multiple devices, automatic backups, and easy sharing options.
- How can I ensure the security of my photos in the cloud?
- You can ensure the security of your photos in the cloud by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and choosing reputable cloud storage providers.
- What is the best way to organize my photo library?
- The best way to organize your photo library is to create a structured folder system based on date, event, or project. Use consistent naming conventions and add metadata to your photos.
- How often should I back up my photos?
- You should back up your photos regularly, ideally on a daily or weekly basis, to protect against data loss.
- What are the ethical considerations related to photo storage and privacy?
- Ethical considerations include protecting personal data, respecting copyright, ensuring transparency, and obtaining consent when storing or sharing photos of individuals.
- How can dfphoto.net help me manage my photo storage?
- dfphoto.net offers comprehensive guides, expert advice, community forums, product reviews, and software tutorials to help you understand and manage your photo storage effectively.
Call to Action
Ready to master your photo storage and elevate your photography skills? Visit dfphoto.net today to explore our detailed guides, discover inspiring photography, and connect with a vibrant community of photographers in the USA. Start optimizing your photo storage and unlock your creative potential now!
