Where Is My Google Photos? This is a common question, and dfphoto.net is here to provide you with a comprehensive answer, ensuring you can easily access, manage, and safeguard your treasured visual memories. We’ll delve into the various places your photos might be hiding, offering practical solutions to help you locate and organize them, including image search and visual content management.
1. Understanding Google Photos Storage
Google Photos is a powerful tool for storing and managing your photos and videos, but understanding where your content resides is crucial. Your photos are primarily stored in the cloud, but they can also be found on your devices.
1.1. Cloud Storage Basics
Google Photos utilizes cloud storage, meaning your photos are stored on Google’s servers. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, cloud storage provides a secure and accessible way to back up and manage your visual content. This ensures your photos are safe even if your device is lost or damaged. Every Google Account comes with 15 GB of free storage, shared across Google Drive, Gmail, and Google Photos. You can also purchase additional storage through Google One if needed.
1.2. Device Storage and Syncing
Your photos can also be stored locally on your devices (phones, tablets, computers). Google Photos offers a syncing feature that automatically backs up photos from your device to the cloud. To find photos stored locally:
- Android: Use a file manager app to navigate to the “DCIM” (Digital Camera Images) folder.
- iOS: Photos are stored in the Photos app.
- Computers: Check the folders where you typically save your photos (e.g., “Pictures” folder).
2. Accessing Google Photos on Different Devices
Google Photos is accessible on various devices, ensuring you can view and manage your photos from anywhere.
2.1. Web Browser Access
You can access Google Photos through any web browser. Simply go to photos.google.com and sign in with your Google account. This is a straightforward way to view, manage, and share your photos on a larger screen.
2.2. Mobile App Access (Android and iOS)
The Google Photos app is available for both Android and iOS devices. Download it from the Google Play Store or Apple App Store and sign in with your Google account.
2.3. Google Drive Integration
Google Photos integrates with Google Drive, allowing you to access your photos from within Google Drive. To view your photos in Google Drive:
- Go to Google Drive.
- Click on “Settings” (the gear icon).
- Select “Settings.”
- Under the “General” section, check the box next to “Create a Google Photos folder.”
This will create a Google Photos folder in your Google Drive, containing shortcuts to your photos.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, you might encounter issues finding your photos. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
3.1. Photos Not Syncing
If your photos are not syncing, check the following:
- Internet Connection: Ensure you have a stable internet connection (Wi-Fi or cellular data).
- Backup and Sync Settings: Verify that backup and sync are turned on in the Google Photos app settings.
- Storage Space: Make sure you have enough storage space in your Google account.
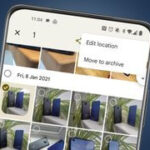
3.2. Missing Photos
If some photos are missing:
- Check the Trash: Deleted photos are stored in the Trash for 60 days before being permanently deleted.
- Search: Use the search feature to look for specific photos by date, location, or keywords.
- Check Different Accounts: Ensure you are signed in to the correct Google account.
3.3. App Permissions
Ensure the Google Photos app has the necessary permissions to access your device’s storage. Go to your device’s settings and check the app permissions for Google Photos.
4. Advanced Search Techniques
Google Photos offers advanced search capabilities to help you quickly find specific photos.
4.1. Using Keywords
You can search for photos using keywords such as “beach,” “birthday,” or “dog.” Google Photos uses AI to analyze your photos and identify objects, people, and places.
4.2. Searching by Location
Search for photos taken at specific locations. Google Photos uses location data embedded in your photos to allow you to search by city, state, or even specific addresses.
4.3. Searching by Date
Find photos taken on a specific date or within a date range. This is useful for finding photos from events or trips.
4.4. Facial Recognition Search
Google Photos uses facial recognition to group photos of the same people together. You can search for photos of specific individuals by labeling their faces. Note: Face grouping is not available in all countries.
5. Managing and Organizing Your Photos
Keeping your photos organized makes it easier to find and enjoy them.
5.1. Creating Albums
Create albums to group photos by event, trip, or theme. This helps you keep your photos organized and makes it easier to share them with others.
5.2. Using Folders
While Google Photos primarily uses albums, you can also use folders in Google Drive to organize your Google Photos folder. This can provide an additional layer of organization.
5.3. Tagging Photos
Tagging photos with relevant keywords can make them easier to find using the search feature. Add descriptive tags to your photos to improve searchability.
5.4. Deleting Unwanted Photos
Regularly deleting unwanted photos can help you free up storage space and keep your library tidy. Remember to check the Trash before permanently deleting photos.
6. Optimizing Google Photos Settings
Configuring your Google Photos settings correctly can enhance your experience and ensure your photos are backed up and managed effectively.
6.1. Backup Quality Settings
Choose between “High quality” and “Original quality” for your backups. High quality offers compressed versions of your photos, saving storage space, while Original quality backs up your photos in their original resolution. All photos and videos you back up in High quality before June 1, 2021 will not count toward your Google Account storage.
6.2. Sharing Settings
Configure your sharing settings to control who can see your photos. You can share individual photos, albums, or even your entire library with trusted individuals.
6.3. Location Settings
Manage your location settings to control whether Google Photos saves location data with your photos. This can be useful for organizing photos by location, but it also raises privacy concerns.
6.4. Notification Settings
Customize your notification settings to receive alerts about new features, backup status, and sharing activity.
7. Integrating Google Photos With Other Services
Google Photos integrates seamlessly with other Google services, enhancing its functionality and usability.
7.1. Google Drive
As mentioned earlier, Google Photos integrates with Google Drive, allowing you to access your photos from within Google Drive.
7.2. Google Assistant
Use Google Assistant to view your photos on your TV or smart display. Simply say, “Hey Google, show me my photos from last summer.”
7.3. Google Lens
Google Lens is integrated into Google Photos, allowing you to search for information about objects and scenes in your photos. This preview enables you to identify text and objects in your photos to learn more and take action.
7.4. Social Media Integration
Easily share your photos from Google Photos to social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
8. Privacy and Security Considerations
Protecting your privacy and ensuring the security of your photos is crucial when using Google Photos.
8.1. Privacy Settings
Review and adjust your privacy settings to control who can see your photos and how your data is used. Google Photos doesn’t sell your photos, videos, or personal information to anyone and we don’t use your photos and videos for advertising.
8.2. Two-Factor Authentication
Enable two-factor authentication on your Google account to add an extra layer of security. This helps prevent unauthorized access to your photos.
8.3. Regularly Reviewing App Permissions
Regularly review the permissions you have granted to the Google Photos app and revoke any unnecessary permissions.
8.4. Being Mindful of Sharing
Be mindful of who you share your photos with and avoid sharing sensitive or personal information.
9. Tips for Maximizing Google Photos Usage
Here are some additional tips to help you get the most out of Google Photos:
9.1. Utilize the “Free Up Space” Feature
The “Free Up Space” feature removes photos that are safely backed up from your device’s storage in just a tap. This helps you save space on your phone without losing your photos.
9.2. Take Advantage of Automatic Creations
Google Photos automatically creates movies, collages, GIFs, and more from your photos. These can be fun and creative ways to rediscover your memories.
9.3. Create Live Albums
Share your latest photos with Live Albums. Select the people and pets you want to see and Google Photos will automatically add photos of them as you take them, no manual updates needed.
9.4. Rediscover Memories
Get collages of photos you took a year ago on this day – perfect for #tbt. This is a great way to reminisce and share memories with friends and family.
10. Future Trends in Photo Storage and Management
The field of photo storage and management is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to watch:
10.1. AI-Powered Organization
Expect AI to play an even greater role in organizing and managing photos. AI could automatically tag photos, create albums, and even suggest edits.
10.2. Enhanced Privacy Features
Privacy will continue to be a major concern, and photo storage services will likely offer enhanced privacy features to protect user data.
10.3. Integration With AR and VR
Photos may become more integrated with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies, allowing users to experience their memories in new and immersive ways.
10.4. Decentralized Storage Solutions
Decentralized storage solutions, such as blockchain-based photo storage, may become more popular as users seek greater control over their data.
11. Exploring Alternatives to Google Photos
While Google Photos is a popular choice, there are several alternatives to consider.
11.1. Amazon Photos
Amazon Photos offers unlimited photo storage for Amazon Prime members. It also provides features like facial recognition and automatic organization.
11.2. iCloud Photos
iCloud Photos is Apple’s photo storage service, integrated with iOS and macOS devices. It offers seamless syncing and sharing across Apple devices.
11.3. Microsoft OneDrive
Microsoft OneDrive offers cloud storage for photos and other files. It integrates with Windows and Microsoft Office apps.
11.4. Dropbox
Dropbox is a versatile cloud storage service that can be used to store and share photos. It offers a range of features for collaboration and file management.
11.5. Flickr
Flickr is a photo-sharing platform that offers a large amount of free storage and a vibrant community of photographers.
12. Common Photography Terms and Definitions
Understanding common photography terms can enhance your ability to manage and appreciate your photos.
12.1. Aperture
The aperture is the opening in the lens that allows light to pass through to the camera sensor. It is measured in f-stops (e.g., f/2.8, f/8). A wider aperture (smaller f-stop number) allows more light in and creates a shallow depth of field, while a narrower aperture (larger f-stop number) allows less light in and creates a greater depth of field.
12.2. Shutter Speed
The shutter speed is the length of time the camera’s shutter is open, exposing the sensor to light. It is measured in seconds or fractions of a second (e.g., 1/1000s, 1s). A faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed allows motion blur.
12.3. ISO
ISO is a measure of the camera sensor’s sensitivity to light. A lower ISO (e.g., ISO 100) is less sensitive to light and produces cleaner images, while a higher ISO (e.g., ISO 3200) is more sensitive to light and allows you to shoot in darker conditions but may introduce noise or grain.
12.4. Exposure
Exposure refers to the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor. It is determined by the combination of aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Proper exposure is essential for creating well-lit and balanced photos.
12.5. White Balance
White balance is the process of adjusting the colors in a photo to ensure that white objects appear white. Different light sources have different color temperatures, and white balance helps to correct for these differences.
12.6. Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within a photo. Good composition can help to create visually appealing and engaging images. Common composition techniques include the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry.
12.7. Depth of Field
Depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a photo that appear acceptably sharp. A shallow depth of field isolates the subject from the background, while a large depth of field keeps both the subject and background in focus.
13. Finding Inspiration for Your Photography
Finding inspiration can help you improve your photography skills and develop your unique style.
13.1. Studying the Work of Famous Photographers
Studying the work of famous photographers can provide valuable insights into composition, lighting, and storytelling.
13.2. Visiting Art Galleries and Museums
Visiting art galleries and museums can expose you to a wide range of photographic styles and techniques.
13.3. Participating in Photography Workshops and Classes
Participating in photography workshops and classes can provide hands-on learning and feedback from experienced photographers.
13.4. Joining Photography Communities
Joining photography communities can connect you with other photographers, allowing you to share your work, receive feedback, and find inspiration.
13.5. Exploring Different Genres of Photography
Exploring different genres of photography, such as portrait, landscape, and street photography, can broaden your horizons and help you discover new interests.
14. Essential Photography Equipment for Beginners
Choosing the right equipment can enhance your photography experience and help you capture stunning images.
14.1. Camera
The camera is the most important piece of equipment. For beginners, a mirrorless camera or DSLR with a kit lens is a good starting point.
14.2. Lenses
Lenses determine the field of view and image quality. A versatile zoom lens is a good choice for beginners.
14.3. Tripod
A tripod provides stability and is essential for shooting in low light or capturing long exposures.
14.4. Camera Bag
A camera bag protects your equipment and makes it easy to carry around.
14.5. Memory Cards
Memory cards store your photos. Choose high-capacity cards with fast read and write speeds.
14.6. Cleaning Kit
A cleaning kit helps you keep your equipment clean and free of dust and smudges.
15. Understanding Image File Formats
Understanding different image file formats is important for managing and editing your photos.
15.1. JPEG
JPEG is a widely used file format that offers good compression and image quality. It is suitable for most everyday photography needs.
15.2. PNG
PNG is a lossless file format that preserves image quality. It is often used for graphics and images with text or transparency.
15.3. RAW
RAW is a file format that contains unprocessed data from the camera sensor. It offers the most flexibility for editing but requires more storage space.
15.4. TIFF
TIFF is a lossless file format that is often used for archival purposes. It preserves image quality but results in large file sizes.
16. Basic Photo Editing Techniques
Learning basic photo editing techniques can help you enhance your images and correct any flaws.
16.1. Cropping
Cropping involves removing unwanted areas from a photo to improve composition or focus attention on the subject.
16.2. Adjusting Exposure
Adjusting exposure involves brightening or darkening a photo to achieve the desired level of brightness.
16.3. Adjusting Contrast
Adjusting contrast involves increasing or decreasing the difference between the lightest and darkest areas of a photo.
16.4. Adjusting White Balance
Adjusting white balance involves correcting the colors in a photo to ensure that white objects appear white.
16.5. Sharpening
Sharpening involves increasing the sharpness of a photo to enhance detail.
17. Exploring Different Genres of Photography
Exploring different genres of photography can help you discover new interests and develop your skills.
17.1. Portrait Photography
Portrait photography involves capturing images of people, often focusing on their face and expression.
17.2. Landscape Photography
Landscape photography involves capturing images of natural landscapes, such as mountains, forests, and oceans.
17.3. Street Photography
Street photography involves capturing candid images of people and scenes in public places.
17.4. Wildlife Photography
Wildlife photography involves capturing images of animals in their natural habitats.
17.5. Macro Photography
Macro photography involves capturing close-up images of small objects, such as flowers and insects.
18. Understanding Copyright and Usage Rights
Understanding copyright and usage rights is essential for protecting your work and avoiding legal issues.
18.1. Copyright Basics
Copyright is a legal right that protects original works of authorship, including photographs. As the creator of a photograph, you automatically own the copyright to it.
18.2. Usage Rights
Usage rights determine how others can use your photos. You can grant different types of licenses, such as exclusive or non-exclusive, to control how your work is used.
18.3. Creative Commons Licenses
Creative Commons licenses offer a flexible way to allow others to use your work while retaining some control over how it is used.
18.4. Watermarking
Watermarking involves adding a visible or invisible mark to your photos to indicate ownership and deter unauthorized use.
19. Building a Photography Portfolio
Building a strong photography portfolio is essential for showcasing your work and attracting clients or employers.
19.1. Selecting Your Best Work
Choose your best photos to include in your portfolio, focusing on images that demonstrate your skills and style.
19.2. Organizing Your Portfolio
Organize your portfolio in a logical and visually appealing manner, grouping photos by genre or theme.
19.3. Creating an Online Portfolio
Create an online portfolio to showcase your work to a wider audience. Use platforms like dfphoto.net, Behance, or your own website.
19.4. Getting Feedback
Get feedback on your portfolio from other photographers or potential clients to identify areas for improvement.
20. Monetizing Your Photography Skills
There are several ways to monetize your photography skills and turn your passion into a profession.
20.1. Selling Prints
Sell prints of your photos online or at art fairs.
20.2. Stock Photography
Submit your photos to stock photography agencies and earn royalties when they are downloaded.
20.3. Freelance Photography
Offer your photography services to clients for events, portraits, or commercial projects.
20.4. Teaching Photography
Teach photography workshops or classes to share your knowledge and skills with others.
20.5. Selling Photo Products
Create and sell photo products, such as calendars, mugs, or phone cases, using your images.
We at dfphoto.net hope this guide has helped you understand where your Google Photos are located and how to manage them effectively. Whether you’re an amateur enthusiast or a professional photographer, mastering these techniques will undoubtedly enhance your photographic journey.
If you’re eager to elevate your photography skills, seek inspiration, and connect with a vibrant community, visit dfphoto.net today. Explore our rich collection of tutorials, browse stunning photo galleries, and join our community of passionate photographers. Let dfphoto.net be your guide to capturing the world’s beauty through your lens. For further assistance, you can reach us at Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States or Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
FAQ: Where Is My Google Photos?
1. Where are my Google Photos actually stored?
Your Google Photos are primarily stored in the cloud on Google’s servers. This means they are accessible from any device with an internet connection and your Google account credentials.
2. How do I find my Google Photos on my phone?
On your phone, your photos are visible using the Google Photos app. Download the app from the Google Play Store (Android) or the Apple App Store (iOS), sign in with your Google account, and you’ll see all your backed-up photos.
3. Can I access Google Photos on my computer?
Yes, you can access Google Photos on your computer by visiting photos.google.com in a web browser. Sign in with your Google account to view and manage your photos.
4. What if my photos are not syncing to Google Photos?
If your photos aren’t syncing, ensure you have a stable internet connection, backup and sync are turned on in the Google Photos app settings, and you have enough storage space in your Google account.
5. How can I search for specific photos in Google Photos?
You can search for photos using keywords (like “beach” or “birthday”), locations, dates, or even by faces if you’ve labeled them.
6. How do I organize my photos in Google Photos?
You can organize your photos by creating albums to group them by event, trip, or theme. This makes it easier to find and share your photos.
7. What is the “Free Up Space” feature in Google Photos?
The “Free Up Space” feature removes photos from your device’s storage that are safely backed up to Google Photos, helping you save space on your phone without losing your photos.
8. How do I control who can see my photos in Google Photos?
You can control who sees your photos through the sharing settings. You can share individual photos, albums, or your entire library with trusted individuals.
9. What should I do if some of my photos are missing from Google Photos?
First, check the Trash folder, as deleted photos are stored there for 60 days before being permanently deleted. Also, ensure you are signed in to the correct Google account.
10. Is Google Photos safe for storing my personal photos?
Yes, Google Photos is generally safe. It uses encryption to protect your data and offers privacy settings to control who can see your photos. However, enabling two-factor authentication on your Google account is always a good idea for added security.