In the world of digital imagery, picture resolution is a critical factor that distinguishes between low-resolution (lo-res) and high-resolution (hi-res) photos. This difference can be stark, especially when it comes to visual quality – think of a company logo appearing sharp and professional versus blurry and unprofessional.
To truly appreciate the importance of hi-res images, particularly for applications like printing and enlargement, it’s essential to first understand what “hi-res” actually means.
The Best Snipping Tool for Windows and Mac
Don’t let limited, built-in tools slow you down. Capture and edit screenshots effortlessly with Snagit!
Get Snagit
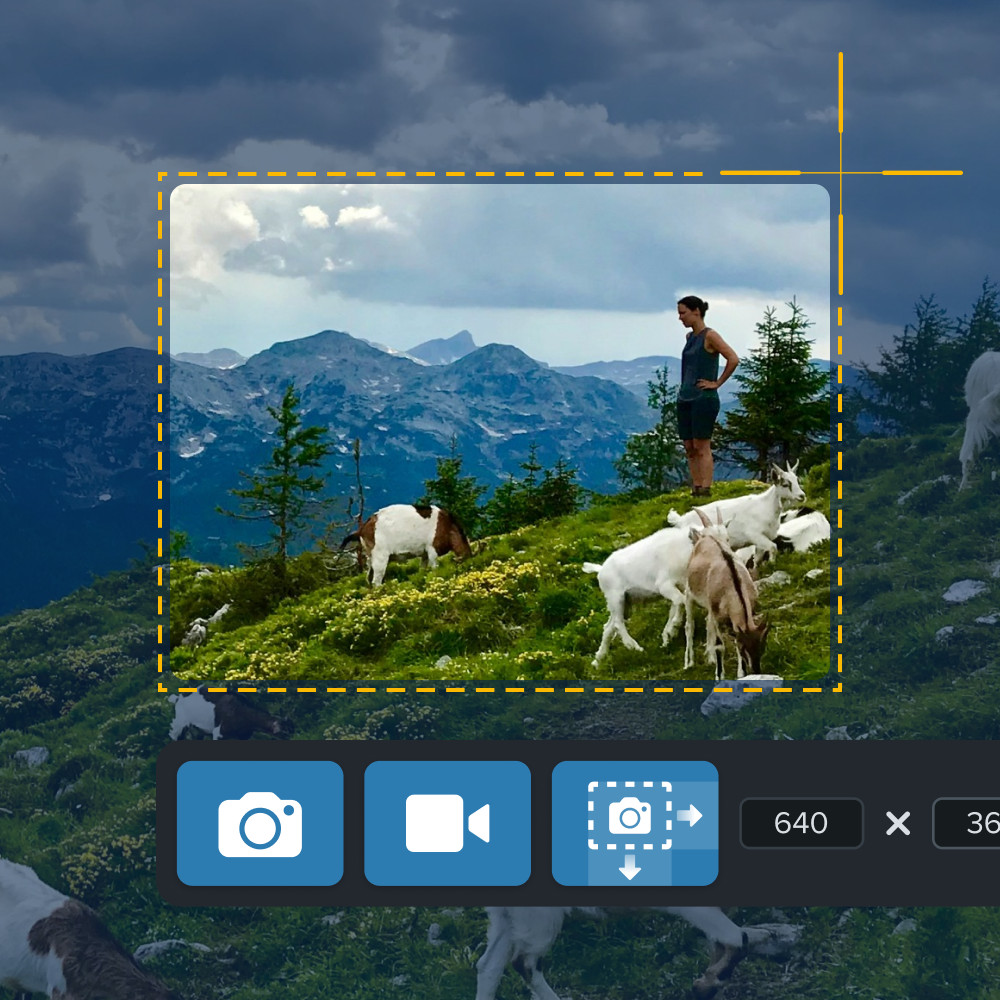 Screenshot of a person using Snagit to capture a mountain scene with goats, highlighting cropping tools for high resolution image selection and editing.
Screenshot of a person using Snagit to capture a mountain scene with goats, highlighting cropping tools for high resolution image selection and editing.
Decoding “High Resolution”: What Does Hi-Res Mean?
Simply put, hi-res is shorthand for high resolution, signifying images with a denser pixel arrangement and superior image quality.
Digital images are composed of countless tiny pixels, or picture elements – think of them as minuscule squares of color. Normally, these individual pixels are imperceptible as they seamlessly blend together to form the image you see.
However, these pixels are always there. They become visible when you zoom in excessively or attempt to enlarge an image beyond its inherent capabilities. This is a key reason why understanding how to resize an image correctly is so important.
![]() Comparison of a small, high resolution image beside a larger, lower resolution version demonstrating pixel density and image quality.
Comparison of a small, high resolution image beside a larger, lower resolution version demonstrating pixel density and image quality.
As illustrated above, the lo-res image, while appearing fine at its original size, becomes visibly pixelated and choppy upon zooming or enlargement.
This “pixelation” occurs because you can clearly distinguish each individual pixel, forming a blocky pattern. For those familiar with pre-smartphone technology, this aesthetic might evoke memories of retro video games with their distinct, low-tech visual style.
 Example of a pixelated image reminiscent of retro video games, illustrating the visual effect of low resolution graphics.
Example of a pixelated image reminiscent of retro video games, illustrating the visual effect of low resolution graphics.
Early video games embraced pixelation due to intentional design choices, minimizing colors to conserve memory and processing power. Today, pixelated images are typically encountered when images are:
- Enlarged excessively
- Zoomed-in on too closely
- Printed from a low-resolution file.
Fortunately, preventing blurry pictures is simpler than you might think, and we delve into this topic in detail in our dedicated post on how to prevent blurry pictures.
Defining High-Resolution Images
Low-resolution images generally contain around 72 pixels per inch (PPI). This pixel density makes them well-suited for web use because most computer screens are designed to display images at this resolution. Furthermore, lo-res images are lightweight files due to their lower pixel count, contributing to faster website loading times.
High-resolution images, conversely, boast at least 300 pixels per inch (PPI). This higher resolution is crucial for achieving good print quality and is generally considered the minimum requirement for any printed materials, especially those representing your brand or other important visual assets.
Investing in hi-res photos for printing ensures sharp, clear prints without blurry or jagged edges, ultimately preventing printing disappointments and wasted resources, especially considering the cost of ink.
How to Determine if an Image is High or Low Resolution
Just because an image appears sharp on your computer screen doesn’t automatically mean it’s high-resolution. Aspect ratio is also not an indicator of resolution. While a large file size can suggest a hi-res image, this isn’t always a reliable measure.
The most accurate method for checking image resolution is to open the image in an image editing program, such as Photoshop or TechSmith Snagit, and examine the file properties. While this specific feature is currently exclusive to the Windows version of Snagit, Snagit offers a range of other useful features on both Windows and Mac, including the ability to extract text from images and remove backgrounds from photos.
While Snagit excels in quick photo editing tasks, most operating systems include basic image editing software capable of displaying an image’s resolution, helping you determine if it’s hi-res.
When Do You Need High-Res vs. Low-Res Images?
Now that you understand the fundamental differences between low and high-resolution images and their importance, the next critical step is knowing when each type is appropriate.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on the intended use of the image. Whether you’re an aspiring photographer planning your first exhibition or an entrepreneur building a new website, understanding the context and format in which your image will be viewed is key to selecting the correct resolution.
In this section, we’ll explore common scenarios where low and high-resolution photos are typically required, guiding you to make the best choice for your specific needs.
Optimal Image Resolution for Screens and Monitors
High-resolution images are often lauded for their clarity and sharpness on digital displays, be it computer monitors, mobile devices, or televisions. However, finding the right balance is crucial.
Digital screens have a fixed number of pixels, known as screen resolution, which limits the level of detail they can display. Using an image with a resolution exceeding the screen’s resolution might not enhance visual quality, as the screen is simply incapable of rendering the additional detail.
Moreover, high-res images translate to larger file sizes, which can slow down websites and consume unnecessary storage space on devices. Consequently, low to medium-resolution images are generally optimal for screen-based applications.
Best Image Resolution for Posters
For creating posters, particularly large-format ones, high-resolution images are generally the preferred choice. Large prints demand greater detail to maintain image integrity and prevent pixelation when printed at scale.
However, viewing distance is a significant consideration. If a poster is intended to be viewed from a distance, the need for ultra-high image definition diminishes.
From a distance, the human eye cannot discern the same level of detail as up close. This is where intermediate resolutions become valuable, striking a balance between providing clear, detailed posters without necessitating excessively high resolution.
Ideal Image Resolution for Printing
Whether it’s business cards or glossy magazines, achieving crisp, clear printed images requires the level of detail that only high-resolution images can deliver.
Therefore, images destined for print should have a minimum resolution of 300 DPI (dots per inch). This standard isn’t arbitrary; it’s the resolution benchmark for achieving high-quality images viewed at arm’s length.
Streamline Your Screenshot Process
Stop wasting time with basic snipping tools and experience the efficiency of Snagit!
Learn More
 Screenshot of a document about puffin migration patterns with annotations and style adjustments highlighted, showcasing annotation features for high resolution document editing.
Screenshot of a document about puffin migration patterns with annotations and style adjustments highlighted, showcasing annotation features for high resolution document editing.
Best Image Resolution for Artwork and Fine Photography
In the realm of artwork and fine photography, every detail matters. The texture of a brushstroke, the subtle shading in a charcoal drawing, or the interplay of light and shadow in a photograph can be the defining elements that elevate an image from good to captivating.
As expected, high-resolution images are particularly advantageous in these scenarios, capturing nuanced details with a precision that lo-res images simply cannot match.
Nevertheless, considering the intended use of the image remains important. Are you planning a physical exhibition with large-format prints or building a digital portfolio? While high-resolution images are essential for physical exhibitions, low-res photos might be more suitable for online display.
Optimal Image Resolution for Nature Photography
Nature photography centers around capturing the beauty of the natural world. From the intricate bark of an ancient tree to the vibrant colors of a sunset, countless subtle details contribute to making each photograph a unique testament to nature’s artistry.
Consequently, high-resolution photos are vital for capturing and sharing the richness of nature photography. Consider National Geographic – have you ever seen a blurry image in their publications? Exactly.
High-Resolution Images: FAQs
How to convert a low-res image to high-res? Ideally, it’s always best to recapture an image in high resolution if possible, rather than attempting to upscale a lo-res image. However, software like Adobe Photoshop and online services such as Let’s Enhance utilize sophisticated algorithms to upscale images and enhance resolution while minimizing pixelation. Keep in mind that the result might not achieve the same sharpness as an image originally captured or created in high resolution.
What is the file size of a high-res image? The file size of high-resolution images can vary significantly, but hi-res is primarily defined by pixel dimensions and pixels per inch (PPI or DPI). An image is generally considered high resolution if it has a DPI of 300 or more, with typical dimensions ranging from 2,000 x 2,000 pixels for smaller images to 5,000 x 5,000 pixels (or larger) for larger images. Specific pixel requirements often depend on the intended application of the image.
How to identify a high-res image? You can determine if an image is high resolution by examining its DPI (dots per inch) and pixel dimensions. This information can be found in the image’s properties on your computer or within an image editing program. Generally, an image with 300 DPI or higher and large pixel dimensions (typically in the thousands) is considered high resolution.
How to convert a high-res image to low-res? To reduce a high-res image to low-res, you can use software such as Snagit or Photoshop, or utilize free online tools like PIXLR. These tools allow you to reduce the image’s pixel dimensions or alter its resolution (DPI). By decreasing these parameters, you effectively lower the image’s resolution, creating a smaller, less detailed version of the original.