High-resolution images are crucial for various applications, from crisp website visuals to large-format prints. But what exactly defines a high-resolution photo? Understanding the factors that contribute to image quality is essential for anyone working with visuals. This article delves into the specifics of high-resolution imagery, explaining its importance and how it differs from low-resolution.
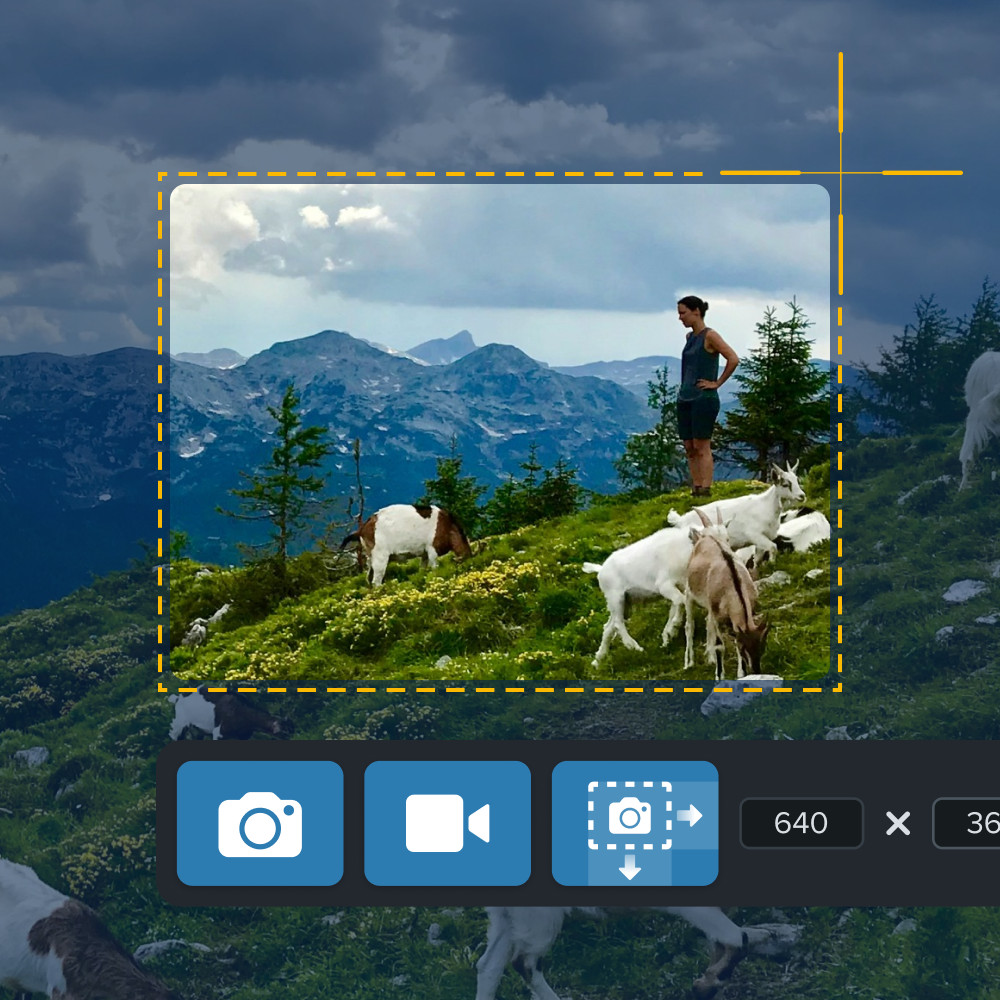 Someone capturing a screenshot of a mountain scene with a person and goats using Snagit, showing cropping tools on the screen.
Someone capturing a screenshot of a mountain scene with a person and goats using Snagit, showing cropping tools on the screen.
Defining High Resolution: Pixels and PPI
High resolution refers to image quality with a denser concentration of pixels. Pixels, short for “picture elements,” are the tiny squares of color that make up a digital image. The more pixels packed into an inch, the sharper and more detailed the image appears. This density is measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI).
![]() small, high resolution image next to the same image, larger but with lower resolution.
small, high resolution image next to the same image, larger but with lower resolution.
A low-resolution image, typically around 72 PPI, is suitable for web use due to its smaller file size, enabling faster loading times. However, enlarging a low-resolution image reveals its pixelated nature, resulting in a blocky or blurry appearance. This is because individual pixels become discernible, compromising clarity.
Conversely, high-resolution images boast at least 300 PPI. This higher density provides the detail necessary for sharp prints, enlargements, and professional-quality visuals. The increased pixel count ensures smooth lines and clarity, even when significantly zoomed in or printed in large formats.
 pixelated image
pixelated image
Identifying High-Resolution Images
Determining if an image is high-resolution requires more than a visual assessment. File size can be misleading, and the aspect ratio provides no information about resolution. The most reliable method involves checking the image properties within an image editing software like Photoshop or TechSmith Snagit. These programs display the PPI and pixel dimensions, allowing for accurate assessment.
When High Resolution is Essential
The need for high resolution depends entirely on the image’s intended use. Different applications have varying resolution requirements:
Screen Display: A Balancing Act
While high-resolution images are visually appealing, using excessively high resolution for screen display is often unnecessary. Screens have a limited pixel density, meaning they can only display a certain level of detail. Using images exceeding the screen’s resolution won’t enhance visual quality and can lead to larger file sizes and slower loading times. Therefore, low to medium resolution often suffices for screen-based content.
Print Media: Detail is Key
Printing demands high-resolution images, especially for large formats like posters. A minimum of 300 DPI is generally recommended to ensure clarity and prevent pixelation when printed. The viewing distance also plays a role: posters viewed from afar may not require ultra-high resolution. However, for materials viewed up close, such as business cards or brochures, high resolution is crucial.
 Screenshot of a document about puffin migration patterns with a section for changing styles highlighted.
Screenshot of a document about puffin migration patterns with a section for changing styles highlighted.
Artwork and Photography: Capturing Nuance
Artwork and fine photography rely on high resolution to capture intricate details and subtle nuances. Whether it’s the texture of a brushstroke or the delicate interplay of light and shadow, high resolution preserves the integrity of the image, allowing for accurate representation and impactful visuals. The intended display medium, whether a physical exhibition or an online portfolio, dictates the necessary resolution.
High Resolution: Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions regarding high-resolution images include how to increase resolution, typical file sizes, and methods for reducing resolution. While software can upscale low-resolution images, the results often lack the sharpness of native high-resolution captures. High-resolution file sizes vary greatly depending on dimensions and PPI. Reducing resolution can be achieved using image editing software or online tools.
In conclusion, understanding what constitutes high resolution is vital for effective visual communication. By considering the intended use and utilizing appropriate resolution, you can ensure optimal image quality across various platforms and mediums. High resolution, defined by its pixel density (PPI), is essential for maintaining clarity, detail, and professional standards in a wide range of applications.