Where Is The Recently Deleted Photos album? The recently deleted photos album is usually located within your phone’s Photos application, allowing you to recover accidentally deleted images and videos. This article, brought to you by dfphoto.net, guides you through locating and using this feature, along with tips for managing your photo storage effectively. Understanding this process will help safeguard your visual memories and keep your digital life organized with proper file management, data recovery strategies, and digital preservation techniques.
1. Understanding the “Recently Deleted” Album
The “Recently Deleted” album acts as a safety net, holding deleted photos and videos for a limited time before they are permanently erased. This gives you a chance to recover items you didn’t mean to delete.
1.1. How Long Do Items Stay in “Recently Deleted”?
Typically, photos and videos remain in the “Recently Deleted” album for 30 days. After this period, they are automatically and permanently deleted from your device.
1.2. Why Use the “Recently Deleted” Album?
The “Recently Deleted” album is crucial for:
- Accidental Deletions: Recovering photos or videos you deleted by mistake.
- Changing Your Mind: Deciding you want to keep a photo you previously deleted.
- Data Security: Ensuring sensitive photos are permanently removed after a set period.
1.3. Impact of Cloud Storage on “Recently Deleted”
If you use cloud storage services like iCloud Photos or Google Photos, deleting a photo on one device will sync the deletion across all devices connected to the same account. The deleted photo will then appear in the “Recently Deleted” or “Trash” folder of the respective cloud service. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, cloud synchronization provides a safety net but requires careful management to prevent unintended data loss.
2. Locating the “Recently Deleted” Album on iOS (iPhone/iPad)
Finding the “Recently Deleted” album on your iPhone or iPad is straightforward. Here’s how:
2.1. Steps to Find the Album
- Open the Photos App: Tap the Photos app icon on your home screen.
- Go to the Albums Tab: At the bottom of the screen, tap the “Albums” tab.
- Scroll Down to “Utilities”: Look for the “Utilities” section, usually at the bottom of the Albums screen.
- Select “Recently Deleted”: Tap the “Recently Deleted” album. You may need to use Face ID, Touch ID, or your passcode to access it.
2.2. What to Do If You Can’t Find the Album
- Ensure iOS is Updated: Make sure your iPhone or iPad is running the latest version of iOS. Go to Settings > General > Software Update to check for updates.
- Check Hidden Albums: In the Albums tab, ensure that “Hidden” albums are visible. Go to Settings > Photos and make sure “Hidden Album” is toggled on.
- Restart Your Device: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve minor software glitches.
2.3. Recovering Photos from “Recently Deleted” on iOS
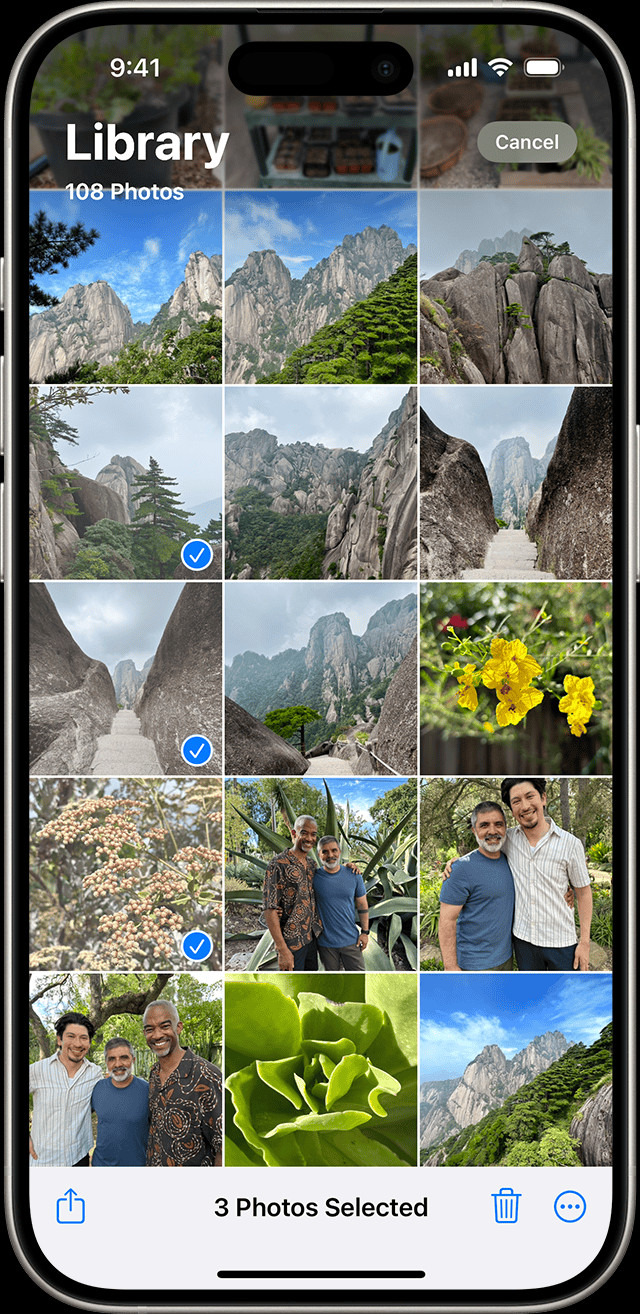 iPhone showing multiple photos selected in the Photos app
iPhone showing multiple photos selected in the Photos app
- Open “Recently Deleted”: Follow the steps above to access the “Recently Deleted” album.
- Select Photos: Tap “Select” in the upper-right corner, then tap the photos or videos you want to recover.
- Recover: Tap “Recover” at the bottom-right corner, then confirm by tapping “Recover Photo” or “Recover Video”.
2.4 Permanently Deleting Photos from “Recently Deleted” on iOS
- Open “Recently Deleted”: Follow the steps above to access the “Recently Deleted” album.
- Select Photos: Tap “Select” in the upper-right corner, then tap the photos or videos you want to permanently delete.
- Delete: Tap “Delete” at the bottom-left corner, then confirm by tapping “Delete Photo” or “Delete Video”.
3. Locating the “Trash” Folder on Android Devices
Android devices also have a similar feature to the “Recently Deleted” album, usually called “Trash” or “Bin”. The exact location and name may vary depending on the device manufacturer and Android version.
3.1. Steps to Find the “Trash” Folder
- Open the Photos App: Launch the Google Photos app on your Android device.
- Access the Menu: Tap on your profile icon (or initial) in the top right corner.
- Look for “Trash” or “Bin”: Find and tap the “Trash” or “Bin” option.
3.2. What to Do If You Can’t Find the Folder
- Check the App Version: Ensure you are using the latest version of the Google Photos app.
- Look in File Manager: Some Android devices may have a “Recently Deleted” folder in the device’s file manager app.
- Device-Specific Instructions: Refer to your device manufacturer’s support documentation for specific instructions.
3.3. Recovering Photos from “Trash” on Android
- Open “Trash”: Follow the steps above to access the “Trash” folder.
- Select Photos: Tap and hold the photos or videos you want to recover.
- Restore: Tap the “Restore” button at the bottom of the screen.
3.4 Permanently Deleting Photos from “Trash” on Android
- Open “Trash”: Follow the steps above to access the “Trash” folder.
- Select Photos: Tap and hold the photos or videos you want to permanently delete.
- Delete: Tap the “Delete” button at the bottom of the screen.
4. Managing Photos in Cloud Storage Services
If you use cloud storage services like iCloud Photos, Google Photos, or Dropbox, managing deleted photos involves understanding how these services handle deleted files.
4.1. iCloud Photos
- Accessing “Recently Deleted”: In the Photos app on your Apple device, the “Recently Deleted” album syncs with iCloud Photos. Deleted photos appear here and are available for recovery for 30 days.
- Deleting Permanently: After 30 days, photos are permanently deleted from iCloud. You can also manually delete them from the “Recently Deleted” album for immediate removal.
4.2. Google Photos
- Accessing “Trash”: In the Google Photos app or on the Google Photos website, deleted photos are moved to the “Trash” folder.
- Deleting Permanently: Photos remain in the “Trash” for 60 days. After this period, they are automatically deleted. You can also empty the “Trash” manually.
4.3. Dropbox
- Accessing “Deleted Files”: On the Dropbox website or desktop app, deleted files are moved to the “Deleted Files” section.
- Deleting Permanently: Dropbox retains deleted files for 30 days for Basic accounts and 180 days for Plus, Professional, and Business accounts. You can permanently delete files manually before this period.
5. Tips for Managing Your Photo Storage
Effective photo storage management can help you avoid accidental data loss and keep your devices organized.
5.1. Regular Backups
- Importance: Regularly back up your photos and videos to multiple locations, such as an external hard drive, a separate cloud service, or a computer.
- Methods: Use automated backup tools like iCloud Backup, Google Backup and Sync, or third-party backup software.
5.2. Organizing Your Photos
- Albums and Folders: Create albums or folders to categorize your photos by date, event, or subject.
- Tagging: Use tagging features to add keywords and descriptions to your photos for easy searching.
5.3. Review and Delete Regularly
- Culling: Periodically review your photos and delete duplicates, blurry images, and unwanted screenshots.
- Storage Limits: Be mindful of storage limits on your devices and cloud services.
5.4. Using Storage Optimization Features
- iCloud Photos Optimization: On iOS, enable “Optimize iPhone Storage” in Settings > Photos to store full-resolution photos in iCloud and smaller, device-optimized versions on your device.
- Google Photos Storage Saver: In Google Photos, choose the “Storage saver” option to compress photos and videos while maintaining good visual quality.
6. Dealing with Permanently Deleted Photos
If you’ve permanently deleted photos from your device or cloud storage, recovery can be challenging but not always impossible.
6.1. Data Recovery Software
- Use Cases: Data recovery software can sometimes recover deleted files from your device’s internal storage or an external storage device.
- Examples: Popular data recovery software includes Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, and Stellar Data Recovery.
6.2. Professional Data Recovery Services
- When to Use: If the data is critical and data recovery software fails, consider using a professional data recovery service.
- Considerations: These services can be expensive, and success is not guaranteed, especially if the data has been overwritten.
6.3. Prevention is Key
- Regular Backups: The best way to avoid the stress of permanently deleted photos is to maintain regular backups.
- Double-Check Before Deleting: Always double-check before deleting photos, especially when cleaning up storage.
7. Understanding Photo Metadata
Photo metadata is data embedded in a photo file that provides information about the image, such as date, time, location, camera settings, and more.
7.1. What is Metadata?
Metadata is essentially “data about data.” For photos, it includes:
- EXIF Data: Exchangeable Image File Format data contains camera settings, date, time, and GPS coordinates.
- IPTC Data: International Press Telecommunications Council data includes descriptions, keywords, and copyright information.
- XMP Data: Extensible Metadata Platform data is a flexible standard for embedding metadata.
7.2. How to View Metadata
- On iOS: Open a photo in the Photos app, swipe up, and view the information below the photo.
- On Android: Open a photo in Google Photos, tap the three dots in the upper-right corner, and select “Info.”
- On Windows: Right-click the photo, select “Properties,” and go to the “Details” tab.
- On macOS: Open the photo in Preview, go to “Tools” > “Show Inspector,” and select the “i” tab.
7.3. Why Metadata Matters
- Organization: Metadata helps organize and search for photos.
- Copyright: Metadata can store copyright information.
- Legal Evidence: Metadata can provide evidence of when and where a photo was taken.
8. Best Practices for Photo Security
Protecting your photos from unauthorized access is essential, especially with the increasing prevalence of cyber threats.
8.1. Password Protection
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for your devices and cloud storage accounts.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for added security.
8.2. Privacy Settings
- Cloud Services: Review and adjust the privacy settings in your cloud storage services to control who can access your photos.
- Social Media: Be cautious when sharing photos on social media, and adjust privacy settings accordingly.
8.3. Encryption
- Device Encryption: Enable device encryption to protect your data if your device is lost or stolen.
- Cloud Encryption: Consider using cloud storage services that offer end-to-end encryption for added security.
8.4. Regular Security Audits
- Review Accounts: Periodically review your online accounts and revoke access from any unauthorized apps or services.
- Monitor Activity: Monitor your cloud storage accounts for any suspicious activity.
9. Exploring Different Photography Styles and Techniques
To enhance your photography skills, consider exploring different styles and techniques.
9.1. Portrait Photography
- Techniques: Use shallow depth of field, flattering lighting, and natural poses.
- Equipment: A fast lens (e.g., f/1.8 or f/2.8) and a reflector can be helpful.
9.2. Landscape Photography
- Techniques: Use wide-angle lenses, tripods, and filters (e.g., polarizing filter, neutral density filter).
- Timing: Shoot during the golden hour (shortly after sunrise or before sunset) for the best light.
9.3. Macro Photography
- Techniques: Use a macro lens, a tripod, and artificial lighting if necessary.
- Focus: Focus stacking can help increase the depth of field.
9.4. Street Photography
- Techniques: Be discreet, capture candid moments, and pay attention to composition and lighting.
- Equipment: A small, inconspicuous camera and a versatile lens are ideal.
9.5. Black and White Photography
- Techniques: Focus on contrast, texture, and composition.
- Editing: Use editing software to convert color photos to black and white and adjust tones.
10. Essential Photography Equipment and Software
Having the right equipment and software can significantly improve your photography.
10.1. Cameras
- DSLRs: Digital Single-Lens Reflex cameras offer excellent image quality and versatility.
- Mirrorless Cameras: Mirrorless cameras are lighter and more compact than DSLRs, with comparable image quality.
- Smartphones: Modern smartphones have advanced camera features and are convenient for everyday photography.
10.2. Lenses
- Wide-Angle Lenses: Ideal for landscape and architecture photography.
- Standard Lenses: Versatile lenses for general photography.
- Telephoto Lenses: Used for wildlife and sports photography.
- Macro Lenses: Designed for close-up photography.
10.3. Editing Software
- Adobe Photoshop: Industry-standard software for photo editing and retouching.
- Adobe Lightroom: Designed for organizing and editing large batches of photos.
- GIMP: A free, open-source alternative to Photoshop.
- Capture One: Professional photo editing software with advanced color grading tools.
10.4. Accessories
- Tripods: Essential for landscape and long-exposure photography.
- Filters: Used to enhance colors, reduce glare, and control light.
- External Flash: Provides additional lighting for portraits and indoor photography.
- Memory Cards: Choose high-speed memory cards with sufficient storage capacity.
11. Advanced Photography Techniques
Mastering advanced photography techniques can elevate your skills and creativity.
11.1. High Dynamic Range (HDR) Photography
- Technique: Capture multiple photos of the same scene at different exposure levels and combine them into a single image with a wide dynamic range.
- Software: Use HDR software like Adobe Photoshop, Aurora HDR, or Photomatix.
11.2. Long Exposure Photography
- Technique: Use a slow shutter speed to capture motion blur and create artistic effects.
- Equipment: A tripod and a neutral density filter are essential.
11.3. Focus Stacking
- Technique: Capture multiple photos of the same subject with different focus points and combine them into a single image with increased depth of field.
- Software: Use focus stacking software like Adobe Photoshop or Helicon Focus.
11.4. Time-Lapse Photography
- Technique: Capture a series of photos over a period of time and combine them into a video to create a time-lapse effect.
- Equipment: A tripod, an intervalometer, and time-lapse software are needed.
12. Resources for Learning Photography
There are numerous resources available to help you learn and improve your photography skills.
12.1. Online Courses
- Coursera: Offers photography courses from top universities and institutions.
- Udemy: Provides a wide range of photography courses for all skill levels.
- Skillshare: Offers creative photography classes taught by industry professionals.
12.2. Photography Blogs and Websites
- dfphoto.net: Provides tutorials, tips, and inspiration for photographers of all levels.
- Petapixel: A leading photography news and resource website.
- Digital Photography School: Offers articles, tutorials, and community forums.
- Fstoppers: A community-driven photography website with articles, reviews, and tutorials.
12.3. Books
- “Understanding Exposure” by Bryan Peterson
- “The Photographer’s Eye” by Michael Freeman
- “Read This If You Want to Take Great Photographs” by Henry Carroll
12.4. Workshops and Seminars
- Local Photography Clubs: Join a local photography club to network with other photographers and attend workshops and events.
- Photography Workshops: Attend photography workshops led by experienced photographers.
- Online Seminars: Participate in online photography seminars and webinars.
13. Building a Photography Portfolio
Creating a strong photography portfolio is essential for showcasing your work and attracting clients or opportunities.
13.1. Selecting Your Best Work
- Curate Carefully: Choose only your best photos that represent your style and skills.
- Variety: Include a variety of subjects, styles, and techniques.
13.2. Portfolio Platforms
- Websites: Create a professional website to showcase your portfolio.
- Behance: A popular platform for showcasing creative work.
- Flickr: A photo-sharing website with portfolio features.
- Instagram: Use Instagram to share your photos and engage with the photography community.
13.3. Presentation
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent style and presentation throughout your portfolio.
- Organization: Organize your photos into categories or themes.
- Captions: Write descriptive captions for your photos to provide context and information.
14. Monetizing Your Photography
There are various ways to monetize your photography skills and turn your passion into a profession.
14.1. Selling Prints
- Online Marketplaces: Sell your photos as prints on online marketplaces like Etsy, Fine Art America, and Redbubble.
- Local Galleries: Exhibit and sell your photos in local art galleries.
- Direct Sales: Sell prints directly to customers through your website or social media.
14.2. Stock Photography
- Stock Agencies: Submit your photos to stock photography agencies like Shutterstock, iStockphoto, and Getty Images.
- Passive Income: Earn royalties when your photos are licensed by customers.
14.3. Freelance Photography
- Events: Photograph weddings, parties, and corporate events.
- Portraits: Offer portrait photography services to individuals and families.
- Commercial Photography: Photograph products, interiors, and food for businesses.
14.4. Teaching Photography
- Workshops: Teach photography workshops and classes.
- Online Courses: Create and sell online photography courses.
- Private Lessons: Offer private photography lessons to individuals.
15. Legal Aspects of Photography
Understanding the legal aspects of photography is crucial for protecting your rights and avoiding legal issues.
15.1. Copyright
- Ownership: As the photographer, you automatically own the copyright to your photos.
- Registration: Register your copyright with the U.S. Copyright Office to protect your rights and enforce your copyright.
15.2. Model Releases
- Requirement: Obtain model releases from individuals who appear in your photos, especially if you plan to use the photos for commercial purposes.
- Content: A model release should include the model’s name, address, and signature, as well as a description of how the photos will be used.
15.3. Property Releases
- Requirement: Obtain property releases from the owners of private property if you plan to photograph their property for commercial purposes.
- Content: A property release should include the property owner’s name, address, and signature, as well as a description of the property and how the photos will be used.
15.4. Public vs. Private Spaces
- Public Spaces: Generally, you can photograph anything in public spaces without permission.
- Private Spaces: You need permission to photograph on private property.
16. The Future of Photography
Photography is constantly evolving with new technologies and trends.
16.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Applications: AI is being used to enhance photo editing, automate tasks, and generate new images.
- Examples: AI-powered photo editing tools, AI-generated art.
16.2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Applications: VR and AR are being used to create immersive photographic experiences.
- Examples: VR photo tours, AR photo filters.
16.3. Drone Photography
- Applications: Drones are being used to capture aerial photos and videos for various purposes.
- Regulations: Be aware of drone regulations and restrictions in your area.
16.4. Mobile Photography
- Advancements: Mobile photography is becoming increasingly sophisticated with advanced camera features and editing apps.
- Accessibility: Mobile photography makes it easier than ever to capture and share photos.
17. How dfphoto.net Can Help You
At dfphoto.net, we are committed to helping you enhance your photography journey. We provide a wealth of resources, from detailed tutorials to inspiring photo collections. Whether you’re looking to master new techniques, discover different photography styles, or find the best equipment, our website offers valuable insights and guidance.
17.1. Comprehensive Tutorials
Our tutorials cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Basic Photography Techniques: Learn about exposure, aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
- Advanced Editing Techniques: Master photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom.
- Specialized Photography Styles: Explore portrait, landscape, macro, and street photography.
17.2. Inspiring Photo Collections
Browse our curated photo collections to find inspiration and discover new perspectives. We showcase the work of talented photographers from around the world, offering a glimpse into various styles and subjects.
17.3. Equipment Reviews
Stay informed about the latest photography equipment with our in-depth reviews. We provide unbiased assessments of cameras, lenses, and accessories to help you make informed purchasing decisions.
17.4. Community Engagement
Connect with fellow photographers in our community forums. Share your work, ask questions, and get feedback from experienced professionals and enthusiasts.
18. FAQ: Where is the Recently Deleted Photos Album?
Here are some frequently asked questions about the “Recently Deleted” album:
- Where is the “Recently Deleted” album on my iPhone?
The “Recently Deleted” album is located in the Photos app, under the “Albums” tab, in the “Utilities” section. - How long do photos stay in the “Recently Deleted” album?
Photos and videos remain in the “Recently Deleted” album for 30 days. - Can I permanently delete photos from the “Recently Deleted” album?
Yes, you can permanently delete photos from the “Recently Deleted” album by selecting them and tapping “Delete.” - Where is the “Trash” folder on my Android device?
The “Trash” folder is typically located in the Google Photos app, accessible through the menu. - How long do photos stay in the “Trash” folder on Google Photos?
Photos and videos remain in the “Trash” folder for 60 days. - Can I recover photos from iCloud Photos after deleting them?
Yes, deleted photos are moved to the “Recently Deleted” album in iCloud Photos and can be recovered for 30 days. - How do I access the “Recently Deleted” album on iCloud?
You can access the “Recently Deleted” album in the Photos app on your Apple device or on the iCloud website. - Is there a way to recover permanently deleted photos?
Recovering permanently deleted photos can be challenging but may be possible with data recovery software or professional data recovery services. - How can I back up my photos to avoid data loss?
You can back up your photos to an external hard drive, a separate cloud service, or a computer using automated backup tools. - What should I do if I can’t find the “Recently Deleted” album on my device?
Ensure your operating system and apps are updated, check hidden album settings, and restart your device.
19. Conclusion: Embrace the Art of Photography
Navigating the world of photography can be both exciting and challenging. Understanding how to manage your photos, recover deleted files, and protect your work are essential skills for any photographer. By leveraging the resources available at dfphoto.net and embracing continuous learning, you can enhance your skills, unleash your creativity, and capture the beauty of the world around you. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting, the journey of photography is a rewarding one filled with endless possibilities.
Ready to take your photography skills to the next level? Visit dfphoto.net today to explore our comprehensive tutorials, discover inspiring photo collections, and connect with a community of passionate photographers. Start your journey now and capture the world through your unique lens. For any inquiries, reach out to us at 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001 or visit our website dfphoto.net.
