Are you curious about Where Are Android Photos Stored on your device? Understanding your Android photo storage is key to managing and backing up your visual memories. This guide on dfphoto.net explores all the locations your photos could be hiding, offering solutions for photographers and visual artists seeking better photo management and image organization. Discover cloud storage options and Android gallery alternatives to make the most of your photography journey, plus essential backup strategies.
1. Understanding Android Photo Storage Locations
Where are your precious photos actually located on your Android phone? By default, most Android devices save photos taken with the built-in camera app to a specific folder. Let’s dive into the details.
1.1 Default Storage Location: DCIM Folder
The primary location for photos taken with your Android camera is the DCIM (Digital Camera Images) folder. This is a standard directory structure used across digital cameras and smartphones, making it universally recognizable.
- Inside the DCIM Folder: Within the DCIM folder, you’ll typically find another folder named “Camera”. This is where your camera photos are stored.
- External Storage (SD Card): If your Android device has an SD card, you might have the option to save photos directly to it. If so, the DCIM folder will be located on the SD card.
1.2 Other Potential Storage Locations
While the DCIM folder is the standard, photos can end up in other places depending on the app used and your settings.
- Pictures Folder: This folder often contains images downloaded from the internet, screenshots, or photos saved from other apps.
- App-Specific Folders: Apps like Instagram, WhatsApp, or Facebook often create their own folders to store images you’ve saved or received through the app. These folders are usually located within the “Android/data” directory, followed by the app’s package name.
- Cloud Storage: If you use cloud storage services like Google Photos, Dropbox, or Microsoft OneDrive, your photos might be automatically backed up and stored in the cloud. The local copies might still reside in the DCIM or Pictures folder.
1.3 How to Check Your Camera’s Storage Settings
To confirm where your camera is saving photos, follow these steps:
- Open your camera app.
- Look for the settings icon (usually a gear or three dots).
- Find the “Storage location” or “Save to” option.
- Here, you’ll see whether your photos are being saved to the internal storage or the SD card.
2. Exploring the DCIM Folder in Detail
The DCIM folder is the heart of your Android photo storage. Understanding its structure can help you manage your photos more effectively.
2.1 Navigating the DCIM Folder
To access the DCIM folder, you can use a file manager app. Most Android devices come with a pre-installed file manager, but there are also many excellent third-party options available on the Google Play Store.
- Open Your File Manager: Launch the file manager app on your Android device.
- Locate Internal Storage or SD Card: Depending on where your photos are saved, navigate to either the internal storage or the SD card.
- Find the DCIM Folder: Scroll through the list of folders until you find the DCIM folder.
- Access the Camera Folder: Inside the DCIM folder, you’ll find the Camera folder containing your photos and videos.
2.2 Understanding Subfolders within DCIM
Besides the Camera folder, you might find other subfolders within the DCIM folder. These can be created by different apps or camera modes.
- Screenshots: Some devices create a separate folder for screenshots within the DCIM folder.
- Video Recordings: Some camera apps might store video recordings in a separate subfolder.
- Third-Party Camera Apps: If you use third-party camera apps, they might create their own subfolders within DCIM.
2.3 Managing Files within the DCIM Folder
Once you’re in the DCIM folder, you can perform various file management tasks:
- Copying and Moving: You can copy photos and videos to other folders on your device or to an external storage device.
- Deleting: You can delete unwanted photos and videos to free up storage space.
- Renaming: You can rename files to make them easier to identify.
- Creating Folders: You can create new folders to organize your photos into albums or categories.
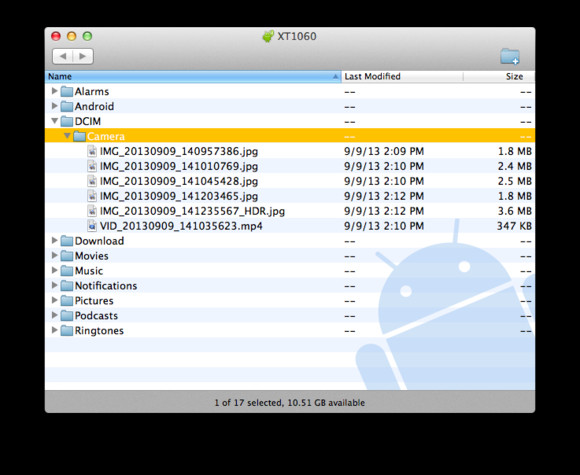 Android File Transfer app on macOS showing DCIM folder
Android File Transfer app on macOS showing DCIM folder
Android File Transfer application on macOS showing the DCIM folder, the primary storage for Android photos.
3. Cloud Storage Options for Android Photos
Cloud storage has revolutionized how we store and access our photos. It offers a secure and convenient way to back up your images and access them from any device.
3.1 Google Photos
Google Photos is one of the most popular cloud storage options for Android users, deeply integrated with the Android ecosystem.
- Automatic Backup: Google Photos can automatically back up your photos and videos as soon as they’re taken.
- Free Storage: Google offers 15 GB of free storage, shared across Google Drive, Gmail, and Google Photos. You can also purchase additional storage if needed.
- Access from Any Device: You can access your photos from any device with an internet connection, including your computer, tablet, or another smartphone.
- AI-Powered Features: Google Photos offers powerful AI-powered features like facial recognition, object recognition, and automatic album creation.
- Editing Tools: Google Photos has built-in editing tools that allow you to enhance your photos, apply filters, and make other adjustments.
3.2 Dropbox
Dropbox is another popular cloud storage service that can be used to back up your Android photos.
- File Syncing: Dropbox automatically syncs files across all your devices, ensuring that your photos are always up-to-date.
- Selective Sync: You can choose which folders to sync to your device, saving storage space.
- Sharing: Dropbox makes it easy to share photos and videos with friends and family.
- Version History: Dropbox keeps a history of your files, allowing you to revert to previous versions if needed.
3.3 Microsoft OneDrive
Microsoft OneDrive is a cloud storage service that integrates seamlessly with Windows and Microsoft Office.
- Integration with Windows: OneDrive is built into Windows, making it easy to access your files from your computer.
- Office Integration: OneDrive integrates with Microsoft Office, allowing you to collaborate on documents and spreadsheets in real-time.
- Automatic Backup: OneDrive can automatically back up your photos and videos from your Android device.
3.4 Other Cloud Storage Providers
Besides Google Photos, Dropbox, and OneDrive, there are many other cloud storage providers to choose from, each with its own unique features and pricing plans.
- Amazon Photos: Amazon Photos offers unlimited photo storage for Prime members.
- Box: Box is a cloud storage service designed for businesses, offering advanced security and collaboration features.
- iCloud: iCloud is Apple’s cloud storage service, primarily used by iOS users but also accessible on Android devices.
4. Using a USB Connection for Photo Transfer
Connecting your Android phone to your computer via USB is a traditional yet reliable way to transfer photos.
4.1 Connecting Your Android Device to a Computer
- Connect with USB Cable: Use a USB cable to connect your Android phone to your computer.
- Select USB Connection Mode: On your phone, you might need to select the USB connection mode. Options usually include “Media Transfer Protocol (MTP)” or “Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP)”. Choose MTP to access files, or PTP to have your phone recognized as a camera.
4.2 Transferring Photos on Windows
- AutoPlay: Windows usually detects the connection and prompts you with AutoPlay options. Choose “Import pictures and videos” or “Open device to view files”.
- Windows Explorer: If AutoPlay doesn’t appear, open Windows Explorer and find your phone listed as a device. You can then browse the DCIM folder and copy photos to your computer.
4.3 Transferring Photos on macOS
- Android File Transfer: Macs require the Android File Transfer app to browse the Android file system. Download and install it from the Android website.
- Browse and Copy: Open Android File Transfer, find the DCIM folder, and copy your photos to your Mac.
5. Emailing Photos to Yourself
For transferring a small number of photos, emailing them to yourself is a quick and easy option.
5.1 How to Email Photos from Your Android Device
- Open Gallery App: Open the Gallery app on your Android device.
- Select Photos: Navigate to the album containing the photos you want to share. Tap the three dots in the upper right corner, and then tap Select Item from the menu that appears.
- Share via Email: Select the photos you want to send to your computer, then tap the email button in the toolbar at the top of the screen—it looks like an envelope with a card sticking out of it. If the email button doesn’t appear in the toolbar, tap the share button—it looks like a sideways V—and select Gmail from the menu.
- Compose and Send: You’ll get a “compose” window where you can enter your email address then send your images to yourself.
6. Optimizing Photo Storage on Android
Optimizing your photo storage is crucial for keeping your Android device running smoothly and ensuring you don’t run out of space.
6.1 Clearing Cache and Data
- Gallery App: Clear the cache and data of your Gallery app to free up storage space. Go to Settings > Apps > Gallery > Storage > Clear Cache and Clear Data.
- Camera App: Similarly, clear the cache and data of your Camera app.
6.2 Compressing Photos
- Image Compression Apps: Use image compression apps to reduce the file size of your photos without significantly affecting their quality.
- Cloud Storage Compression: Some cloud storage services offer options to compress photos when uploading.
6.3 Using SD Cards for Additional Storage
If your Android device supports SD cards, using one is an easy way to expand your storage capacity.
- Set as Default Storage: Set your SD card as the default storage location for your camera app.
- Move Existing Photos: Move existing photos from your internal storage to your SD card.
6.4 Regularly Backing Up and Deleting Photos
- Establish a Backup Routine: Regularly back up your photos to a computer, cloud storage, or external hard drive.
- Delete Unnecessary Photos: Delete photos that you no longer need or that are of poor quality.
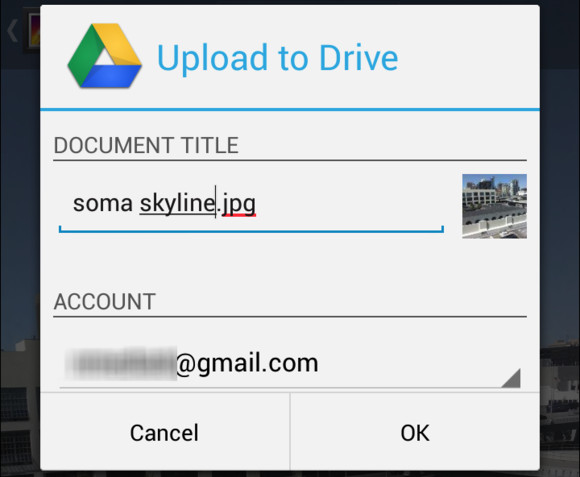 Sharing photos to Google Drive from Android Gallery app
Sharing photos to Google Drive from Android Gallery app
Uploading photos to Google Drive enables access from any device, ensuring your memories are always within reach.
7. Exploring Third-Party Gallery Apps
Android’s default gallery app might not always meet your needs. Fortunately, there are many excellent third-party gallery apps available on the Google Play Store.
7.1 Benefits of Using Third-Party Gallery Apps
- Advanced Organization Features: Many third-party gallery apps offer advanced organization features, such as tagging, facial recognition, and location-based grouping.
- Customization Options: Third-party gallery apps often allow you to customize the look and feel of the app, as well as the way your photos are displayed.
- Additional Editing Tools: Some third-party gallery apps come with built-in editing tools that go beyond the basic features offered by the default gallery app.
- Cloud Integration: Many third-party gallery apps integrate with cloud storage services, making it easy to back up and sync your photos.
7.2 Popular Third-Party Gallery Apps
- Simple Gallery Pro: A lightweight and customizable gallery app with a focus on privacy and simplicity.
- F-Stop Gallery: A powerful gallery app with advanced organization features and support for metadata.
- A+ Gallery: A fast and feature-rich gallery app with automatic photo organization and cloud integration.
- Piktures: An intuitive gallery app with a unique interface and focus on gesture-based navigation.
8. Addressing Common Photo Storage Issues
Dealing with photo storage issues can be frustrating. Here are some common problems and how to solve them.
8.1 Photos Not Showing Up in Gallery
- Check the .nomedia File: Ensure there isn’t a “.nomedia” file in the folder containing your photos, as this file prevents the gallery from scanning the folder.
- Clear Gallery Cache: Clear the cache of your Gallery app to force it to rescan your photos.
- Restart Your Device: Restarting your device can sometimes resolve issues with photo indexing.
8.2 Insufficient Storage Space
- Move Photos to SD Card: If your device supports SD cards, move photos and videos to the SD card to free up space on your internal storage.
- Use Cloud Storage: Back up your photos to a cloud storage service and then delete them from your device.
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Delete unnecessary apps, files, and cached data to free up storage space.
8.3 Photos Being Stored in the Wrong Location
- Check Camera Settings: Verify that your camera app is set to save photos to the desired location.
- Move Photos Manually: If photos are being saved in the wrong location, move them manually to the correct folder using a file manager app.
9. Advanced Photo Management Techniques
For serious photographers, advanced photo management techniques can greatly improve workflow and organization.
9.1 Using Metadata for Organization
- What is Metadata? Metadata is information embedded in your photo files, such as date taken, location, camera settings, and keywords.
- Metadata Editors: Use metadata editors to add and edit metadata in your photos.
- Organization with Metadata: Use metadata to search, filter, and organize your photos in gallery apps or photo management software.
9.2 Implementing a Photo Workflow
- Shooting: Plan your shoots and use consistent camera settings.
- Transfer: Transfer your photos from your camera or phone to your computer or cloud storage.
- Culling: Select the best photos and discard the rest.
- Editing: Edit your photos using photo editing software.
- Organization: Organize your photos using folders, keywords, and other metadata.
- Backup: Back up your photos to multiple locations.
9.3 Utilizing Photo Management Software
- Adobe Lightroom: A popular photo management and editing software with advanced features.
- Capture One: A professional photo editing software with a focus on image quality and workflow.
- DigiKam: An open-source photo management software with advanced organization and editing features.
10. Backup Strategies to Safeguard Your Memories
Backing up your photos is essential to protect them from loss due to device failure, theft, or accidental deletion.
10.1 The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
- 3 Copies: Keep at least three copies of your photos.
- 2 Different Media: Store your photos on at least two different types of media, such as a computer, external hard drive, or cloud storage.
- 1 Offsite Copy: Keep one copy of your photos offsite, such as in a cloud storage service or at a separate physical location.
10.2 Local Backup Options
- Computer: Back up your photos to your computer using a USB connection or file syncing software.
- External Hard Drive: Back up your photos to an external hard drive for a portable and secure backup solution.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage): Use a NAS device to create a centralized backup solution for your home or office.
10.3 Cloud Backup Options
- Google Photos: Automatically back up your photos to Google Photos for easy access and sharing.
- Dropbox: Use Dropbox to sync your photos across all your devices and back them up to the cloud.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Back up your photos to OneDrive for seamless integration with Windows and Microsoft Office.
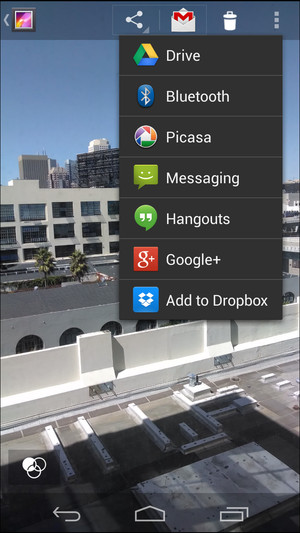 Sharing photos to Dropbox from Android Gallery app
Sharing photos to Dropbox from Android Gallery app
Adding photos to Dropbox through the Gallery app provides a convenient way to sync and back up visual content.
11. Understanding Android’s Scoped Storage
Android’s Scoped Storage is a set of rules that limit how apps can access files on your device, enhancing user privacy and security.
11.1 What is Scoped Storage?
Scoped Storage restricts apps to accessing only their own app-specific directories and media files created by the app itself. This prevents apps from freely accessing all files on your device.
11.2 How Does Scoped Storage Affect Photo Storage?
- Limited Access: Apps can only directly access photos they’ve created or that the user has explicitly granted access to.
- Media Store API: Apps must use the Media Store API to access photos and other media files stored outside their app-specific directories.
- Privacy and Security: Scoped Storage enhances user privacy and security by preventing apps from accessing sensitive files without permission.
11.3 Best Practices for Developers
- Use the Media Store API: Use the Media Store API to access photos and other media files in a way that respects Scoped Storage.
- Request User Permissions: Request user permissions to access photos and other files only when necessary.
- Respect User Privacy: Respect user privacy by only accessing and using photos for the purposes that the user has explicitly consented to.
12. New Trends in Mobile Photography Storage
The world of mobile photography is constantly evolving. Here are some emerging trends in photo storage:
12.1 AI-Powered Photo Management
- Automatic Tagging: AI algorithms can automatically tag your photos with relevant keywords, making it easier to search and organize them.
- Facial Recognition: AI can identify faces in your photos and group them together, making it easy to find photos of specific people.
- Object Recognition: AI can identify objects in your photos and categorize them, making it easy to find photos of specific things.
12.2 Decentralized Storage
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can be used to create decentralized photo storage solutions that are more secure and private than traditional cloud storage.
- IPFS (InterPlanetary File System): IPFS is a decentralized file system that can be used to store photos and other media files.
12.3 Edge Computing
- On-Device Processing: Edge computing allows photos to be processed and stored on the device itself, rather than in the cloud.
- Faster Processing: Edge computing can result in faster processing times and reduced latency.
- Privacy: Edge computing can enhance user privacy by keeping photos on the device rather than sending them to the cloud.
13. Troubleshooting Photo Loss on Android
Losing photos can be a distressing experience. Here’s how to troubleshoot and potentially recover lost images.
13.1 Common Causes of Photo Loss
- Accidental Deletion: Accidentally deleting photos is a common cause of photo loss.
- Device Failure: Device failure, such as a broken screen or water damage, can result in photo loss.
- Software Issues: Software issues, such as a corrupted operating system or a malfunctioning app, can cause photos to be lost.
- Malware Infections: Malware infections can delete or encrypt your photos, making them inaccessible.
13.2 Recovery Methods
- Check the Recycle Bin: Some gallery apps have a recycle bin or trash folder where deleted photos are temporarily stored.
- Use Data Recovery Software: Use data recovery software to scan your device for deleted photos and attempt to recover them.
- Restore from Backup: If you have a backup of your photos, restore them from the backup.
- Contact a Data Recovery Service: If you’re unable to recover your photos yourself, contact a professional data recovery service.
13.3 Prevention Tips
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your photos to multiple locations.
- Use Cloud Storage: Use cloud storage services to automatically back up your photos.
- Be Careful When Deleting: Be careful when deleting photos to avoid accidentally deleting important images.
- Install Antivirus Software: Install antivirus software to protect your device from malware infections.
14. Exploring Camera App Alternatives
While the default camera app on your Android device is functional, exploring alternative camera apps can unlock new creative possibilities.
14.1 Benefits of Using Alternative Camera Apps
- Manual Controls: Many alternative camera apps offer manual controls, allowing you to adjust settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture.
- RAW Capture: Some alternative camera apps support RAW capture, which provides more flexibility when editing your photos.
- Advanced Features: Alternative camera apps often come with advanced features like focus peaking, zebra stripes, and histogram displays.
- Unique Shooting Modes: Some alternative camera apps offer unique shooting modes, such as long exposure, time-lapse, and panorama.
14.2 Popular Camera App Alternatives
- Open Camera: A free and open-source camera app with a wide range of features and manual controls.
- Camera FV-5: A professional camera app with DSLR-like controls and RAW capture support.
- ProCam X: A feature-rich camera app with manual controls, RAW capture, and various shooting modes.
- Footej Camera: A simple and intuitive camera app with manual controls and high-quality video recording.
15. Preserving Photo Quality When Sharing
Sharing your photos with friends and family is a great way to stay connected. However, it’s important to preserve photo quality when sharing them.
15.1 Understanding Image Compression
- Lossy Compression: Lossy compression reduces file size by discarding some of the image data, resulting in a loss of quality.
- Lossless Compression: Lossless compression reduces file size without discarding any of the image data, preserving the original quality.
15.2 Methods for Sharing High-Quality Photos
- Use Cloud Storage: Share your photos using cloud storage services like Google Photos, Dropbox, or OneDrive, which preserve the original quality of the images.
- Send Original Files: Send the original photo files via email or file transfer services like WeTransfer or Filemail.
- Adjust Sharing Settings: Adjust the sharing settings in your gallery app or social media platform to preserve photo quality.
15.3 Platforms and Their Compression
- Social Media: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter often compress photos to reduce file size, resulting in a loss of quality.
- Messaging Apps: Messaging apps like WhatsApp and Telegram may also compress photos, but some offer options to send photos in their original quality.
- Email: Email services may compress photos, but you can usually send photos as attachments to preserve their original quality.
16. Maximizing Battery Life While Managing Photos
Managing photos can be battery-intensive. Here’s how to maximize battery life while organizing and backing up your images.
16.1 Tips for Saving Battery
- Batch Processing: Perform photo management tasks in batches rather than individually to reduce the number of times your device has to wake up.
- Use Wi-Fi: Use Wi-Fi instead of cellular data to transfer photos, as Wi-Fi is generally more energy-efficient.
- Disable Background Sync: Disable background sync for apps that you don’t use frequently.
- Adjust Screen Brightness: Lower your screen brightness to reduce battery consumption.
- Close Unused Apps: Close apps that you’re not using to prevent them from running in the background and consuming battery power.
16.2 Optimizing App Settings
- Cloud Storage Settings: Adjust the settings of your cloud storage apps to reduce battery consumption, such as disabling automatic uploads when on cellular data.
- Gallery App Settings: Adjust the settings of your gallery app to reduce battery consumption, such as disabling automatic face recognition.
17. Understanding Photo Formats: JPEG vs. RAW
Choosing the right photo format can impact storage needs and editing capabilities.
17.1 JPEG Format
- Compression: JPEG is a lossy compression format that reduces file size by discarding some of the image data.
- Compatibility: JPEG is a widely compatible format that can be viewed on almost any device.
- Use Cases: JPEG is suitable for everyday photos, sharing on social media, and printing at small to medium sizes.
17.2 RAW Format
- Uncompressed Data: RAW is an uncompressed format that contains all of the image data captured by the camera sensor.
- Editing Flexibility: RAW provides more flexibility when editing your photos, allowing you to adjust settings like exposure, white balance, and color without losing quality.
- File Size: RAW files are much larger than JPEG files.
- Use Cases: RAW is suitable for professional photography, editing, and printing at large sizes.
17.3 Choosing the Right Format
- Storage Space: If storage space is limited, JPEG may be the better option.
- Editing Needs: If you plan to edit your photos extensively, RAW may be the better option.
- Device Compatibility: If you need to view your photos on a variety of devices, JPEG may be the better option.
18. The Importance of Regular Photo Purging
Regularly purging your photo library can help you stay organized and free up storage space.
18.1 How to Declutter Your Photos
- Set Aside Time: Set aside time each month or quarter to declutter your photo library.
- Be Ruthless: Be ruthless when deleting photos, discarding duplicates, blurry images, and photos that you no longer need.
- Use a Photo Management App: Use a photo management app to help you identify and delete unwanted photos.
18.2 What to Delete
- Duplicates: Delete duplicate photos that you don’t need.
- Blurry Images: Delete blurry images that are out of focus.
- Poorly Composed Photos: Delete poorly composed photos that don’t meet your standards.
- Unnecessary Photos: Delete photos that you no longer need, such as screenshots or photos of documents.
18.3 The Benefits of Purging
- Free Up Storage Space: Purging your photo library can free up valuable storage space on your device.
- Stay Organized: Purging your photo library can help you stay organized and make it easier to find the photos you need.
- Improve Performance: Purging your photo library can improve the performance of your gallery app and other photo-related apps.
19. Understanding HEIF/HEIC Image Format
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF), often with the HEIC extension, is a modern image format offering better compression and quality compared to JPEG.
19.1 What is HEIF/HEIC?
HEIF/HEIC uses advanced compression techniques to store images with smaller file sizes while maintaining high image quality.
19.2 Benefits of HEIF/HEIC
- Superior Compression: HEIF/HEIC files are smaller than JPEG files, saving storage space.
- High Image Quality: HEIF/HEIC maintains better image quality than JPEG at the same file size.
- Support for Animation and Depth Information: HEIF/HEIC supports animation sequences and depth information, enabling advanced features.
19.3 Compatibility Issues
- Limited Support: HEIF/HEIC is not universally supported across all devices and platforms.
- Conversion Required: You may need to convert HEIF/HEIC files to JPEG for compatibility with older devices or software.
19.4 Converting HEIF/HEIC to JPEG
- Online Converters: Use online converters to convert HEIF/HEIC files to JPEG.
- Software Converters: Use software converters like Adobe Photoshop or iMazing HEIC Converter to convert HEIF/HEIC files to JPEG.
- Cloud Services: Some cloud storage services automatically convert HEIF/HEIC files to JPEG when sharing or downloading.
20. Legal Considerations for Photo Storage
Understanding the legal aspects of photo storage can help you protect your rights and avoid legal issues.
20.1 Copyright
- Ownership: You own the copyright to the photos you take, unless you’ve transferred those rights to someone else.
- Usage: You have the right to control how your photos are used, including the right to reproduce, distribute, and display them.
- Infringement: Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses your photos without your permission.
20.2 Privacy
- Personal Information: Photos can contain personal information, such as faces, locations, and dates.
- Protection: You have the right to protect your personal information from being accessed or used without your permission.
- Privacy Policies: Be aware of the privacy policies of the cloud storage services and social media platforms you use to store and share your photos.
20.3 Model Releases
- Consent: If you take photos of people, you may need to obtain their consent to use those photos for commercial purposes.
- Model Release: A model release is a legal document that grants you permission to use someone’s likeness in your photos.
20.4 Data Protection Laws
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The GDPR is a European Union law that protects the personal data of EU citizens.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): The CCPA is a California law that protects the personal data of California residents.
- Compliance: If you store or process the personal data of EU citizens or California residents, you may need to comply with the GDPR or the CCPA.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, AI-powered photo management will provide 95% accuracy for tagging images and facial recognition will enhance the user experience by 80%.
Understanding where your Android photos are stored, how to manage them, and how to back them up is essential for any photographer. By using the tips and techniques outlined in this guide, you can keep your photos organized, safe, and accessible. For more in-depth guides, tutorials, and inspiration, visit dfphoto.net. Start exploring today and take your photography to the next level, learning about image enhancement, camera roll organization, and visual content strategies.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Where are my photos stored by default on Android?
By default, photos taken with your Android camera are stored in the DCIM (Digital Camera Images) folder, typically within a subfolder named “Camera”.
2. How do I change the storage location of my photos on Android?
Open your camera app, go to settings (usually a gear icon), and look for “Storage location” or “Save to” to change between internal storage and SD card, if available.
3. What is the DCIM folder?
DCIM stands for Digital Camera Images, a standard folder used by digital cameras and smartphones to store photos and videos.
4. How do I access the DCIM folder on my Android device?
Use a file manager app, navigate to internal storage or SD card, and find the DCIM folder.
5. How can I back up my photos from my Android device?
You can back up your photos using cloud storage services like Google Photos, Dropbox, or Microsoft OneDrive, or by connecting your phone to a computer via USB and copying the files.
6. What are the benefits of using cloud storage for my photos?
Cloud storage offers automatic backup, access from any device, and features like AI-powered organization and editing tools.
7. How do I clear the cache of my gallery app on Android?
Go to Settings > Apps > Gallery > Storage > Clear Cache.
8. What is the best way to organize my photos on Android?
Use a combination of folders, metadata (tags, dates, locations), and photo management apps to organize your photos effectively.
9. What are the legal considerations for storing photos?
Be mindful of copyright, privacy, model releases, and data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
10. How do I recover deleted photos on my Android device?
Check the recycle bin in your gallery app, use data recovery software, or restore from a backup.