Transferring photos from your phone to a computer is essential for backing them up, editing them, or simply freeing up storage space on your mobile device. At dfphoto.net, we understand the importance of seamless photo management, so this guide will walk you through various methods to effortlessly transfer your precious memories. Learn everything about image transfers, picture uploads and digital asset management.
1. Why Transfer Photos From Your Phone to a Computer?
There are a lot of reasons to move your photos from your phone to your computer. Here are some of the most common:
1.1. Backup and Security
- Protecting Memories: Phones can be lost, stolen, or damaged. Transferring photos to a computer ensures your memories are safely backed up. According to a study by the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department in July 2023, approximately 30% of smartphone users experience data loss due to device malfunctions or theft annually.
- Multiple Backups: Storing photos on a computer allows for additional backups to external hard drives, cloud storage, or other devices.
1.2. Editing and Enhancement
- Larger Screen: Editing photos on a computer with a larger screen and more powerful software provides a better editing experience.
- Advanced Tools: Desktop photo editing software often offers more advanced features than mobile apps, allowing for detailed enhancements.
1.3. Freeing Up Phone Storage
- Performance Boost: Transferring large photo and video files can free up significant storage space on your phone, improving its performance.
- More Room for New Memories: With more free space, you can capture more photos and videos without worrying about running out of storage.
1.4. Sharing and Printing
- Easy Sharing: Transferring photos to a computer makes it easier to share them on social media, email, or other platforms.
- High-Quality Prints: For high-quality prints, it’s best to transfer photos to a computer and use professional printing services.
2. What Are The 5 Search Intents For Transferring Photos From Phone to Computer?
Understanding the search intent behind “How To Upload Photos From A Phone To A Computer” helps tailor the content to meet users’ needs effectively. Here are five key search intents:
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Users are looking for a detailed, easy-to-follow guide on how to transfer photos. They want clear instructions for different devices and operating systems.
- Troubleshooting: Users encounter problems during the transfer process and need solutions. This includes issues like connection errors, software compatibility, or file format problems.
- Best Method for Specific Devices: Users want to know the most efficient and reliable method for their specific phone model (e.g., iPhone, Android) and computer (e.g., Windows, Mac).
- Wireless Transfer Options: Users are interested in transferring photos without using a USB cable, exploring options like cloud services, Wi-Fi transfer apps, or Bluetooth.
- Understanding Storage and Backup: Users want to understand how transferring photos to a computer helps with backup and storage management, ensuring their photos are safe and accessible.
3. Methods for Transferring Photos From Phone to Computer
There are several ways to transfer photos from your phone to your computer, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common methods:
3.1. Using a USB Cable
The most direct and often fastest method is using a USB cable.
3.1.1. For iPhone to Mac
- Connect Your iPhone: Use a USB cable to connect your iPhone to your Mac.
- Trust This Computer: If prompted on your iPhone, tap “Trust This Computer”.
- Open Photos App: The Photos app on your Mac should automatically open. If it doesn’t, open it manually.
- Import Photos: In the Photos app, select your iPhone from the sidebar. You’ll see an import screen with all the photos and videos on your device. Choose the photos you want to import and click “Import Selected” or “Import All New Photos”.
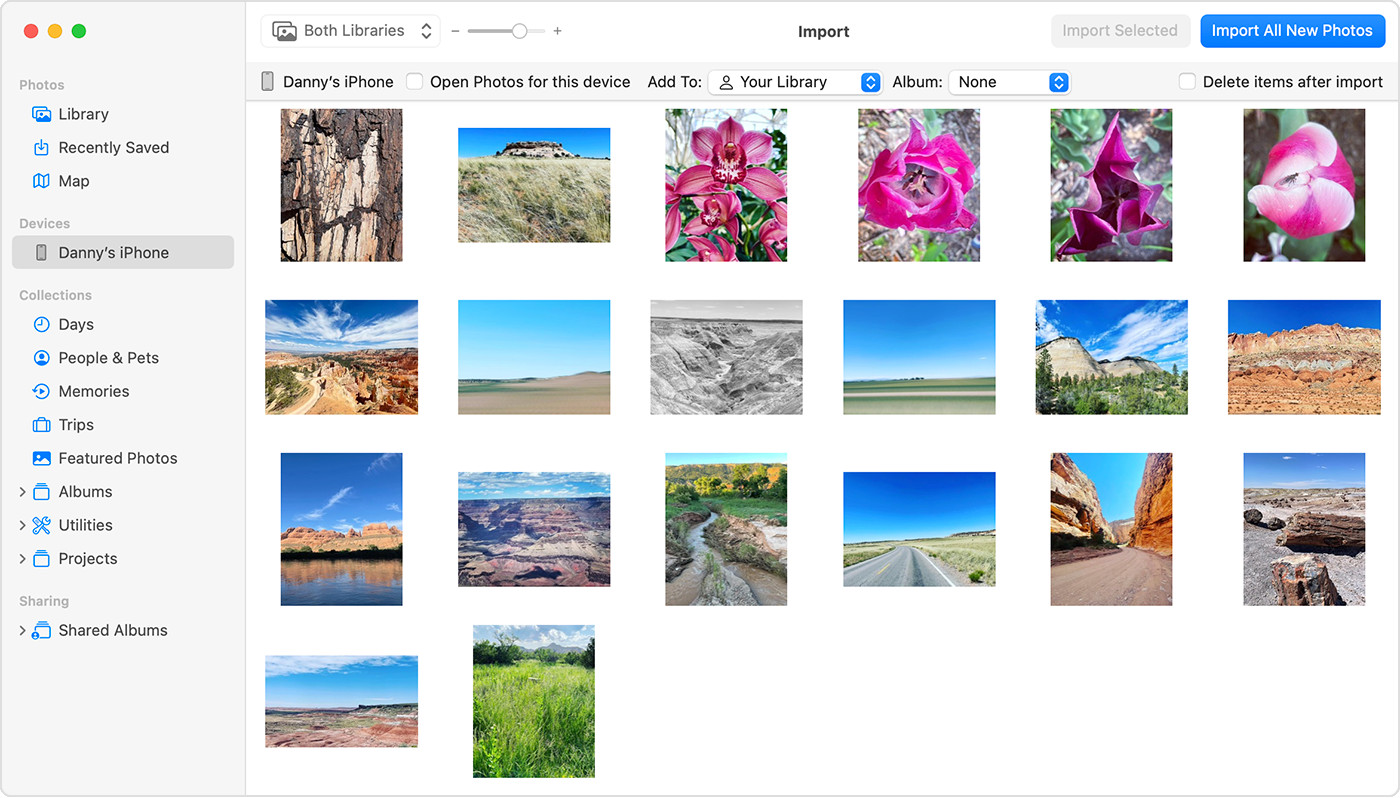 iPhone connected to Mac showing import screen
iPhone connected to Mac showing import screen
3.1.2. For iPhone to Windows PC
- Install Apple Devices App: Download and install the Apple Devices app from the Microsoft Store.
- Connect Your iPhone: Use a USB cable to connect your iPhone to your PC.
- Trust This Computer: If prompted on your iPhone, tap “Trust This Computer”.
- Open Photos App: Open the Photos app on your Windows PC.
- Import Photos: In the Photos app, click “Import” and select your iPhone. Choose the photos you want to import and click “Import Selected” or “Import All New Photos”.
- Compatibility: To ensure the best compatibility with Windows, go to Settings > Camera > Formats on your iPhone and select “Most Compatible”. This will capture photos in JPEG and H.264 formats.
3.1.3. For Android to Mac
- Install Android File Transfer: Download and install Android File Transfer on your Mac.
- Connect Your Android Phone: Use a USB cable to connect your Android phone to your Mac.
- Select USB Connection Type: On your Android phone, swipe down from the top and tap the USB notification. Select “File Transfer” or “MTP”.
- Open Android File Transfer: Android File Transfer will open, showing the files on your phone.
- Copy Photos: Copy the photos you want to transfer to a folder on your Mac.
3.1.4. For Android to Windows PC
- Connect Your Android Phone: Use a USB cable to connect your Android phone to your PC.
- Select USB Connection Type: On your Android phone, swipe down from the top and tap the USB notification. Select “File Transfer” or “MTP”.
- Open File Explorer: Open File Explorer on your Windows PC and find your Android phone in the list of devices.
- Copy Photos: Navigate to the DCIM folder (where photos are stored) and copy the photos you want to transfer to a folder on your PC.
3.2. Using Cloud Storage
Cloud storage services like iCloud, Google Photos, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive offer convenient wireless transfer options.
3.2.1. iCloud Photos
- Automatic Sync: iCloud Photos automatically syncs your photos and videos across all your Apple devices, including your Mac and PC (via iCloud for Windows).
- Setup: On your iPhone, go to Settings > [Your Name] > iCloud > Photos and turn on iCloud Photos. On your Mac, open the Photos app, go to Photos > Settings > iCloud, and turn on iCloud Photos.
- Storage: iCloud Photos uses your iCloud storage. Ensure you have enough space to store your entire photo collection.
- Full Resolution: iCloud Photos uploads and stores your original, full-resolution photos.
3.2.2. Google Photos
- Cross-Platform: Google Photos is available on iOS, Android, and web, making it easy to transfer photos between different devices.
- Automatic Backup: Google Photos can automatically back up photos from your phone to the cloud.
- Setup: Download the Google Photos app on your phone and computer. Sign in with your Google account and enable backup and sync.
- Free Storage: Google Photos offers 15 GB of free storage, shared across Google Drive, Gmail, and Google Photos.
- Access: Access your photos on your computer by visiting the Google Photos website or using the desktop app.
3.2.3. Dropbox and Microsoft OneDrive
- Versatile: Dropbox and OneDrive are versatile cloud storage services that can be used to transfer various types of files, including photos and videos.
- Automatic Upload: Both services offer automatic upload features that can be configured to automatically upload photos from your phone to the cloud.
- Setup: Download and install the Dropbox or OneDrive app on your phone and computer. Sign in with your account and configure the app to automatically upload photos.
- Access: Access your photos on your computer by visiting the Dropbox or OneDrive website or using the desktop app.
3.3. Using Wi-Fi Transfer Apps
Several Wi-Fi transfer apps can transfer photos from your phone to your computer without using a USB cable or cloud storage.
3.3.1. Photo Transfer App
- Simple Interface: Photo Transfer App offers a simple and intuitive interface for transferring photos and videos over Wi-Fi.
- Cross-Platform: Available for iOS and Android, as well as Windows and Mac.
- Direct Transfer: Transfers photos directly between your phone and computer without using cloud storage.
3.3.2. Send Anywhere
- Secure Transfer: Send Anywhere uses a unique key to ensure secure photo transfers.
- Cross-Platform: Available for iOS, Android, Windows, and Mac.
- Direct Transfer: Transfers photos directly between your phone and computer without using cloud storage.
3.4. Using Email
While not ideal for transferring large numbers of photos, email can be a quick and easy way to send a few photos to yourself.
- Limitations: Email services often have limitations on the size of attachments, so this method is best for transferring a small number of photos.
- Simplicity: Simply attach the photos to an email and send it to your email address. Open the email on your computer and download the photos.
3.5. Using Bluetooth
Bluetooth can be used to transfer photos wirelessly, but it is generally slower than other methods.
- Pairing: Pair your phone and computer via Bluetooth.
- Transfer: Send the photos from your phone to your computer via Bluetooth.
- Speed: Bluetooth transfer speeds are relatively slow, so this method is best for transferring a small number of photos.
4. Troubleshooting Common Transfer Issues
Even with the best methods, you might encounter some issues during the photo transfer process. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
4.1. Connection Issues
- USB Cable: Ensure the USB cable is properly connected to both your phone and computer. Try using a different USB cable or port.
- Driver Issues: On Windows, ensure that the necessary drivers for your phone are installed. You can usually find these drivers on the manufacturer’s website.
- Trust This Computer: If you see a prompt on your phone asking you to “Trust This Computer”, make sure to tap “Trust”.
4.2. Software Compatibility
- Operating System: Ensure that your computer’s operating system is compatible with your phone. Older operating systems may not support newer phones.
- Software Updates: Make sure that your photo management software (e.g., Photos, Google Photos) is up to date.
- Android File Transfer: If you are using a Mac, ensure that Android File Transfer is installed and up to date.
4.3. File Format Issues
- HEIC Format: iPhones capture photos in HEIC format by default, which may not be compatible with all computers. To change this, go to Settings > Camera > Formats on your iPhone and select “Most Compatible”.
- File Corruption: If you encounter errors when transferring photos, the files may be corrupted. Try transferring the photos again or using a different method.
4.4. Storage Issues
- Insufficient Storage: Ensure that your computer has enough storage space to accommodate the photos you are transferring.
- iCloud Storage: If you are using iCloud Photos, make sure that you have enough iCloud storage to store your entire photo collection.
4.5. Transfer Speed Issues
- USB Cable: Using a USB 3.0 cable and port can significantly improve transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0.
- Wi-Fi Network: If you are using Wi-Fi transfer, ensure that you have a strong and stable Wi-Fi connection.
- File Size: Transferring large files can take a long time. Consider transferring photos in smaller batches.
5. Optimizing Photos for Transfer and Storage
To ensure a smooth transfer process and efficient storage, consider the following tips:
5.1. File Compression
- Lossless Compression: Use lossless compression formats like ZIP or PNG to reduce file size without sacrificing image quality.
- Lossy Compression: Use lossy compression formats like JPEG to significantly reduce file size, but be aware that this will result in some loss of image quality.
5.2. Metadata Management
- EXIF Data: Preserve EXIF data (camera settings, date, time, location) to maintain important information about your photos.
- Keywords and Tags: Add keywords and tags to your photos to make them easier to find and organize.
5.3. File Naming Conventions
- Descriptive Names: Use descriptive file names that include the date, location, and subject of the photo.
- Consistent Format: Follow a consistent file naming format to make it easier to organize and manage your photos.
5.4. Backup Strategy
- 3-2-1 Rule: Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep three copies of your photos on two different media, with one copy offsite.
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups to ensure that your photos are always protected.
6. Understanding Image File Formats for Photography
Different image file formats serve various purposes, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these formats can help you choose the best one for your needs.
6.1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
- Pros:
- Widely Compatible: Supported by almost all devices and software.
- Small File Size: Uses lossy compression to reduce file size, making it ideal for sharing and storage.
- Cons:
- Lossy Compression: Image quality degrades with each save, especially with high compression settings.
- Limited Editing: Not ideal for extensive editing due to quality loss.
- Use Cases: Sharing photos online, everyday snapshots, and general use where file size is a concern.
6.2. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
- Pros:
- Lossless Compression: Preserves image quality during compression, making it suitable for editing.
- Transparency: Supports transparent backgrounds, useful for graphics and logos.
- Cons:
- Larger File Size: Typically larger than JPEGs, which can be a concern for storage and sharing.
- Not Ideal for Photos: Best suited for graphics, logos, and images with text or sharp lines.
- Use Cases: Graphics, logos, images with text, screenshots, and images requiring transparency.
6.3. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
- Pros:
- Lossless: Retains all image data, ideal for professional photography and archiving.
- High Quality: Supports high color depths and bit depths for maximum image quality.
- Cons:
- Very Large File Size: Can be significantly larger than JPEGs and PNGs, requiring substantial storage space.
- Limited Compatibility: Not supported by all devices and software.
- Use Cases: Professional photography, archiving, high-quality printing, and images requiring maximum detail.
6.4. HEIF/HEIC (High Efficiency Image File Format)
- Pros:
- Efficient Compression: Offers better compression than JPEG while maintaining similar image quality.
- Modern Format: Increasingly supported by newer devices and software.
- Cons:
- Compatibility Issues: May not be compatible with older devices and software.
- Conversion Required: May need to be converted to JPEG for wider compatibility.
- Use Cases: Modern smartphones, high-quality photos with efficient storage, and devices supporting HEIF/HEIC.
6.5. RAW
- Pros:
- Unprocessed Data: Contains all the data captured by the camera sensor, allowing for maximum editing flexibility.
- High Dynamic Range: Retains a wide range of tones and details, making it ideal for challenging lighting conditions.
- Cons:
- Very Large File Size: Significantly larger than JPEGs and other formats, requiring substantial storage space.
- Proprietary Formats: Each camera manufacturer uses its own RAW format (e.g., NEF for Nikon, CR2 for Canon), requiring specific software for processing.
- Use Cases: Professional photography, extensive editing, challenging lighting conditions, and images requiring maximum detail and flexibility.
6.6. Comparison Table of Image File Formats
| Feature | JPEG | PNG | TIFF | HEIF/HEIC | RAW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression | Lossy | Lossless | Lossless | Efficient Lossy | Uncompressed/Lossless |
| File Size | Small | Medium | Large | Small | Very Large |
| Image Quality | Good (but degrades with save) | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Transparency | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Compatibility | Widely Supported | Widely Supported | Limited | Increasingly Supported | Limited (Requires Specific Software) |
| Editing | Limited | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Use Cases | Sharing, Snapshots | Graphics, Logos | Archiving, Professional Use | Modern Smartphones | Professional Photography |
7. The Art of Photo Editing: Enhancing Your Images
Photo editing is a powerful tool for enhancing your images and bringing your creative vision to life. Whether you’re a professional photographer or an amateur enthusiast, mastering photo editing techniques can significantly improve the quality and impact of your photos.
7.1. Basic Adjustments
- Exposure: Adjust the overall brightness of your image. Increasing exposure makes the image brighter, while decreasing it makes it darker.
- Contrast: Adjust the difference between the darkest and brightest areas of your image. Increasing contrast makes the highlights brighter and the shadows darker, while decreasing it reduces the difference between them.
- Highlights: Adjust the brightness of the brightest areas of your image. Reducing highlights can recover details in overexposed areas.
- Shadows: Adjust the brightness of the darkest areas of your image. Increasing shadows can reveal details in underexposed areas.
- Whites: Adjust the brightness of the whitest areas of your image.
- Blacks: Adjust the brightness of the blackest areas of your image.
7.2. Color Correction
- White Balance: Adjust the color temperature of your image to make the colors appear more accurate. Use presets like “Daylight,” “Cloudy,” or “Fluorescent” or adjust the temperature and tint manually.
- Vibrance: Adjust the intensity of the muted colors in your image without affecting the already saturated colors.
- Saturation: Adjust the overall intensity of the colors in your image.
- Hue: Adjust the specific colors in your image. For example, you can change the hue of the blues to make them more green or purple.
7.3. Sharpening and Noise Reduction
- Sharpening: Increase the sharpness of your image to make the details more crisp and clear. Be careful not to over-sharpen, which can create unwanted artifacts.
- Noise Reduction: Reduce the amount of noise (graininess) in your image, especially in low-light situations. Be careful not to over-reduce noise, which can make the image look blurry.
7.4. Retouching
- Spot Removal: Remove small blemishes, dust spots, and other imperfections from your image.
- Cloning: Copy pixels from one area of your image to another to remove larger imperfections or unwanted objects.
- Healing Brush: Blend pixels from the surrounding area to seamlessly remove imperfections.
7.5. Creative Effects
- Filters: Apply pre-designed filters to quickly change the look and feel of your image.
- Presets: Use custom presets to apply a specific set of adjustments to your image with a single click.
- Color Grading: Adjust the colors in your image to create a specific mood or style.
7.6. Popular Photo Editing Software
- Adobe Photoshop: Industry-standard software for professional photo editing. Offers a wide range of tools and features for advanced editing.
- Adobe Lightroom: Designed specifically for photographers. Offers powerful tools for organizing, editing, and exporting photos.
- GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): Free and open-source alternative to Photoshop. Offers many of the same features as Photoshop.
- Capture One: Professional photo editing software known for its color handling and tethered shooting capabilities.
- Affinity Photo: Affordable alternative to Photoshop. Offers a wide range of tools and features for professional photo editing.
8. Exploring Digital Asset Management for Photographers
Digital Asset Management (DAM) is the process of organizing, storing, and retrieving digital assets, such as photos, videos, and documents. For photographers, DAM is essential for managing large collections of images and ensuring that they are easily accessible and properly backed up.
8.1. Key Features of DAM Systems
- Centralized Storage: DAM systems provide a central location for storing all your digital assets, making it easier to find and manage them.
- Metadata Management: DAM systems allow you to add metadata (keywords, tags, descriptions) to your assets, making them easier to search and organize.
- Version Control: DAM systems track changes to your assets, allowing you to revert to previous versions if needed.
- Access Control: DAM systems allow you to control who has access to your assets, ensuring that sensitive information is protected.
- Workflow Automation: DAM systems can automate many of the tasks associated with managing digital assets, such as resizing, converting, and distributing images.
8.2. Benefits of Using a DAM System
- Improved Organization: DAM systems help you organize your photos and other digital assets, making them easier to find and manage.
- Increased Efficiency: DAM systems automate many of the tasks associated with managing digital assets, freeing up your time for other tasks.
- Enhanced Collaboration: DAM systems make it easier to share and collaborate on digital assets with colleagues and clients.
- Better Protection: DAM systems provide better protection for your digital assets, ensuring that they are properly backed up and secured.
- Cost Savings: DAM systems can save you money by reducing the amount of time and effort required to manage your digital assets.
8.3. Popular DAM Systems for Photographers
- Adobe Bridge: Free DAM software included with Adobe Creative Cloud. Offers basic DAM features for organizing and managing photos.
- Capture One Pro: Professional photo editing software with built-in DAM features. Offers advanced tools for organizing, editing, and exporting photos.
- Photo Mechanic: Fast and efficient photo browser and culling tool. Offers powerful tools for organizing and managing large collections of images.
- Extensis Portfolio: Professional DAM software for managing all types of digital assets. Offers advanced features for metadata management, version control, and workflow automation.
- Canto: Cloud-based DAM software for managing digital assets. Offers advanced features for collaboration, workflow automation, and asset distribution.
8.4. Implementing a DAM System
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your specific needs and requirements for a DAM system.
- Choose a DAM System: Select a DAM system that meets your needs and budget.
- Plan Your Implementation: Develop a plan for implementing the DAM system, including data migration, metadata tagging, and user training.
- Migrate Your Data: Migrate your existing digital assets to the DAM system.
- Tag Your Assets: Add metadata (keywords, tags, descriptions) to your assets.
- Train Your Users: Train your users on how to use the DAM system.
- Maintain Your System: Regularly maintain your DAM system to ensure that it is running smoothly and efficiently.
9. The Importance of Regular Photo Backups
Regular photo backups are crucial for protecting your precious memories from loss or damage. Whether you’re a professional photographer or an amateur enthusiast, it’s essential to have a solid backup strategy in place.
9.1. Risks of Not Backing Up Photos
- Hardware Failure: Hard drives, SSDs, and other storage devices can fail unexpectedly, resulting in the loss of your photos.
- Theft: Computers, phones, and other devices can be stolen, resulting in the loss of your photos.
- Natural Disasters: Fires, floods, and other natural disasters can damage or destroy your storage devices, resulting in the loss of your photos.
- Accidental Deletion: Photos can be accidentally deleted from your computer or phone.
- Software Corruption: Software bugs or viruses can corrupt your photo files, making them unreadable.
9.2. Best Practices for Photo Backups
- 3-2-1 Rule: Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep three copies of your photos on two different media, with one copy offsite.
- Three Copies: Keep three copies of your photos: the original, a local backup, and an offsite backup.
- Two Different Media: Store your photos on two different types of media, such as a hard drive and a cloud storage service.
- One Offsite Backup: Store one copy of your photos offsite, such as in a cloud storage service or at a remote location.
- Automated Backups: Use automated backup software to regularly back up your photos to a local or cloud storage service.
- Cloud Storage: Use cloud storage services like iCloud, Google Photos, Dropbox, or OneDrive to automatically back up your photos to the cloud.
- External Hard Drives: Use external hard drives to create local backups of your photos.
- NAS (Network Attached Storage): Use a NAS device to create a central backup location for all your photos and other digital assets.
- Regular Testing: Regularly test your backups to ensure that they are working properly and that you can restore your photos if needed.
- Encryption: Encrypt your backups to protect your photos from unauthorized access.
9.3. Popular Backup Software
- Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office (formerly Acronis True Image): Comprehensive backup software for Windows and Mac. Offers features like disk imaging, file backup, and cloud backup.
- EaseUS Todo Backup: Easy-to-use backup software for Windows. Offers features like disk imaging, file backup, and system backup.
- Backblaze: Cloud-based backup service for Windows and Mac. Offers unlimited backup storage for a fixed monthly fee.
- Carbonite: Cloud-based backup service for Windows and Mac. Offers unlimited backup storage for a fixed monthly fee.
- Duplicati: Free and open-source backup software for Windows, Mac, and Linux. Offers features like encryption, compression, and remote backup.
10. Exploring the World of Mobile Photography
Mobile photography has revolutionized the way we capture and share our world. With advancements in smartphone camera technology, it’s now possible to take stunning photos with just your phone.
10.1. Advantages of Mobile Photography
- Convenience: Smartphones are always with us, making it easy to capture spontaneous moments.
- Portability: Smartphones are lightweight and easy to carry around, making them ideal for travel and everyday use.
- Accessibility: Smartphones are relatively affordable, making photography accessible to a wider audience.
- Connectivity: Smartphones are connected to the internet, making it easy to share photos on social media and other platforms.
- Editing Apps: Smartphones have a wide range of editing apps that allow you to enhance your photos on the go.
10.2. Tips for Taking Better Mobile Photos
- Clean Your Lens: Regularly clean your phone’s lens to remove smudges and fingerprints that can degrade image quality.
- Use Good Lighting: Good lighting is essential for taking great photos. Avoid shooting in direct sunlight, which can create harsh shadows and overexposed highlights.
- Focus Carefully: Tap the screen to focus on your subject.
- Use Grid Lines: Enable grid lines in your camera app to help you compose your shots.
- Experiment with Angles: Try shooting from different angles to find the most flattering perspective.
- Use HDR Mode: Use HDR (High Dynamic Range) mode to capture a wider range of tones and details in challenging lighting conditions.
- Edit Your Photos: Use editing apps to enhance your photos and bring your creative vision to life.
- Shoot in RAW: If your phone supports it, shoot in RAW format to capture more detail and editing flexibility.
10.3. Popular Mobile Photography Apps
- VSCO: Popular photo editing app with a wide range of filters and editing tools.
- Snapseed: Powerful photo editing app from Google. Offers a wide range of tools and features for advanced editing.
- Adobe Lightroom Mobile: Mobile version of Adobe Lightroom. Offers powerful tools for organizing, editing, and exporting photos.
- ProCamera: Professional camera app for iPhone. Offers manual controls, RAW capture, and other advanced features.
- Filmic Pro: Professional video recording app for iPhone and Android. Offers manual controls, high bitrates, and other advanced features.
10.4. Mobile Photography Accessories
- Tripods: Use a tripod to stabilize your phone and take sharper photos, especially in low-light conditions.
- Lenses: Use external lenses to expand your phone’s capabilities and capture different types of photos.
- Lights: Use external lights to improve the lighting in your photos, especially in low-light conditions.
- Gimbals: Use a gimbal to stabilize your phone and capture smooth videos.
FAQ: How to Upload Photos from a Phone to a Computer
-
What is the easiest way to transfer photos from my phone to my computer?
Using a USB cable is generally the easiest way to transfer photos from your phone to your computer. Simply connect your phone to your computer with a USB cable, and then copy the photos from your phone to your computer. -
How do I transfer photos from my iPhone to my Mac wirelessly?
iCloud Photos is the best way to transfer photos from your iPhone to your Mac wirelessly. Enable iCloud Photos on both your iPhone and your Mac, and your photos will automatically sync between the two devices. -
How do I transfer photos from my Android phone to my Windows PC wirelessly?
Google Photos is a great way to transfer photos from your Android phone to your Windows PC wirelessly. Install the Google Photos app on your phone and computer, sign in with your Google account, and enable backup and sync. -
What if my computer doesn’t recognize my phone when I connect it with a USB cable?
Ensure that the USB cable is properly connected to both your phone and computer. Try using a different USB cable or port. On Windows, ensure that the necessary drivers for your phone are installed. You can usually find these drivers on the manufacturer’s website. -
How do I change the format of photos taken on my iPhone to be more compatible with my Windows PC?
Go to Settings > Camera > Formats on your iPhone and select “Most Compatible”. This will capture photos in JPEG and H.264 formats, which are more compatible with Windows. -
What do I do if my photos are not transferring to my computer in full resolution?
If you are using iCloud Photos, make sure that you have enough iCloud storage to store your entire photo collection. Also, make sure that you have enabled the “Download and Keep Originals” option in the Photos settings on your Mac. -
Is it safe to use third-party apps to transfer photos from my phone to my computer?
Be cautious when using third-party apps to transfer photos. Only use apps from reputable developers and make sure to read the reviews before installing them. -
How can I free up space on my phone after transferring photos to my computer?
After transferring photos to your computer, you can delete them from your phone to free up space. Make sure that you have backed up your photos to a safe location before deleting them from your phone. -
What is the best way to organize my photos on my computer after transferring them?
Use a digital asset management (DAM) system to organize your photos on your computer. DAM systems allow you to add metadata (keywords, tags, descriptions) to your assets, making them easier to search and organize. -
How often should I back up my photos?
You should back up your photos regularly, ideally following the 3-2-1 rule: keep three copies of your photos on two different media, with one copy offsite.
Ready to elevate your photography skills and manage your photos like a pro? Visit dfphoto.net today to discover a wealth of tutorials, stunning photo collections, and a vibrant community of photography enthusiasts! Don’t miss out on the opportunity to enhance your creative journey.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.