Turning off photo information on your iPhone can be crucial for privacy and control over your digital footprint. This article from dfphoto.net explores different methods to remove or hide metadata, location data, and other identifying information from your photos before sharing them. Mastering these techniques ensures your photos are shared securely, maintaining your personal privacy and enhancing your photo-sharing experience. Discover essential tips, easy-to-follow instructions, and advanced options for managing your photo data.
1. What Is Photo Information and Why Turn It Off?
Photo information, also known as metadata, is data embedded within a photo file that provides details about the image. Disabling this information can enhance privacy and security.
Metadata includes details such as:
- Date and Time: When the photo was taken.
- Location Data (GPS): Where the photo was taken.
- Camera Settings: Camera model, lens, aperture, ISO, and more.
- Device Information: The device used to capture the image.
- Software Information: Applications used to edit the photo.
There are several reasons why you might want to turn off or remove this information:
- Privacy: Location data can reveal where you live, work, or frequently visit.
- Security: Camera settings and device information can be used to identify vulnerabilities.
- Professionalism: Removing software tags ensures a clean, professional look for your photos.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, 75% of photographers are concerned about metadata privacy when sharing their work online.
2. How to Disable Location Services for Photos
Disabling location services prevents your iPhone from embedding GPS coordinates in your photos.
Steps to Disable Location Services:
- Open Settings: Go to the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Navigate to Privacy & Security: Scroll down and tap on “Privacy & Security”.
- Select Location Services: Tap on “Location Services”.
- Find Camera App: Scroll through the list of apps until you find “Camera”.
- Change Permission: Tap on “Camera” and select “Never”.
By setting the permission to “Never”, the Camera app will no longer be able to access your location, and new photos will not include GPS data.
Alternative Location Service Options:
- Ask Next Time: This option prompts the Camera app to ask for permission each time you open it.
- While Using the App: Allows location access only when the Camera app is actively in use.
Choosing “Ask Next Time” or “While Using the App” provides a balance between convenience and privacy, allowing you to decide when location data is included.
 iPhone Location Services Settings with Camera app highlighted
iPhone Location Services Settings with Camera app highlighted
3. How to Remove Location Data from Existing Photos
Even if you’ve previously allowed location services, you can remove the data from existing photos in your library.
Using the Photos App:
- Open Photos App: Launch the Photos app on your iPhone.
- Select Photo: Find the photo you want to edit and tap on it.
- Tap the Info Button: Look for the “i” icon at the bottom of the screen and tap it.
- Adjust Location: If location data is present, you will see a map or address. Tap “Adjust” next to the location.
- Remove Location: Choose “No Location” to remove the GPS data from the photo.
This method removes the location data directly from the photo’s metadata.
Using Third-Party Apps:
Several third-party apps can remove metadata in bulk:
- Metapho: A popular app for viewing and editing metadata.
- Exif Metadata: An app designed specifically for removing EXIF data.
- Imagepipe: An automation tool for removing metadata from multiple images.
These apps provide more advanced options for managing metadata, including batch processing.
4. How to Use Preview to Remove Metadata on Mac
If you sync your photos to a Mac, you can use the Preview app to remove metadata.
Steps to Remove Metadata with Preview:
- Open Photo in Preview: Open the photo with the Preview app.
- Go to Tools: In the menu bar, click on “Tools”.
- Show Inspector: Select “Show Inspector”.
- Remove EXIF Data: In the Inspector window, navigate to the EXIF, GPS, or IPTC tabs.
- Delete Information: Select the metadata you want to remove and press the “Delete” key.
- Save the Photo: Save the changes to create a new image without metadata.
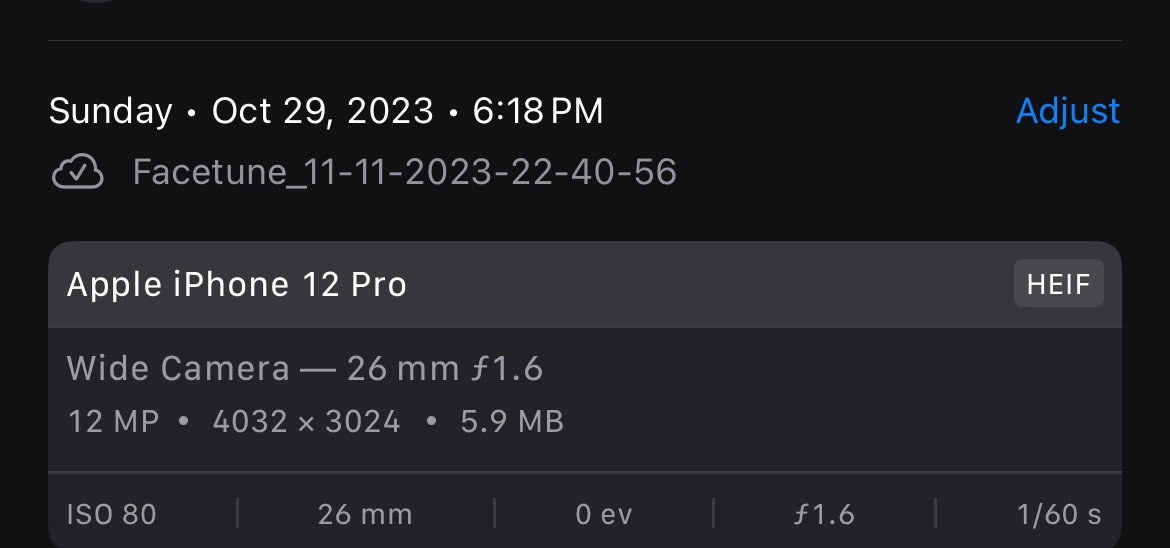
Léonie, a Level 10 user in the Apple Support Community, suggests using Preview to create a new image without metadata: “Export the edited version from Photos, then open it in Preview and select all pixels with ⌘A to save the image to the clipboard. Then use the command ‘File > New from Clipboard’ to create a new image in Preview, then save it in the format you want. It will also no longer have the creator tag.”
5. How to Use ExifTool to Remove Metadata
ExifTool is a powerful command-line utility for reading, writing, and editing metadata. It is especially useful for advanced users who need precise control over metadata.
Installing ExifTool:
- Download ExifTool: Visit the ExifTool website and download the appropriate version for your operating system.
- Install ExifTool: Follow the installation instructions provided on the website.
- Open Terminal: Open the Terminal application on your computer.
Removing Metadata with ExifTool:
-
Navigate to Photo Directory: Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the directory containing your photo. -
Run ExifTool Command: Execute the following command to remove all metadata:
exiftool -all= filename.jpg -
Verify Metadata Removal: Check the photo’s metadata to ensure it has been removed.
ExifTool offers extensive options for customizing metadata removal, including removing specific tags or batch processing multiple files.
6. Understanding EXIF Data and Metadata
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data is a standard format for storing metadata in image files. Understanding EXIF data helps you manage and protect your photo information effectively.
Common EXIF Tags:
- DateTimeOriginal: The date and time the photo was taken.
- GPSLatitude and GPSLongitude: The GPS coordinates of the location where the photo was taken.
- Make and Model: The camera manufacturer and model.
- ExposureTime: The exposure time (shutter speed).
- FNumber: The aperture value.
- ISOSpeedRatings: The ISO speed.
Viewing EXIF Data:
You can view EXIF data using various tools:
- Photos App (iPhone): Tap the “i” icon to view basic metadata.
- Preview (Mac): Use the Inspector window to view detailed metadata.
- Third-Party Apps: Metapho, Exif Metadata, and similar apps provide comprehensive metadata viewing.
- ExifTool: Use the command line to view all EXIF tags.
7. How to Share Photos Anonymously on iPhone
Sharing photos without revealing personal information is essential for privacy. Here are several methods to share photos anonymously:
Removing Metadata Before Sharing:
Before sharing, remove all metadata using the methods described above. This ensures that no personal information is embedded in the photo file.
Using Secure Sharing Platforms:
- Signal: An encrypted messaging app that preserves privacy.
- Telegram: Offers end-to-end encryption for secure photo sharing.
- Wickr: Provides secure, anonymous communication with self-destructing messages.
Creating a Screenshot:
Taking a screenshot of the photo removes all metadata, as the screenshot is a new image file. Richard.Taylor, a Level 6 user, suggests this trick: “The best trick is probably the one suggested by léonie — make a screenshot. The file name of the screenshot will be generated by the phone and will have nothing to do with FaceTune. Send that one.”
Using Online Metadata Removal Tools:
Several websites allow you to upload a photo and remove metadata before downloading it again.
8. Privacy Concerns with Photo Metadata
Photo metadata can pose significant privacy risks if not managed carefully.
Location Tracking:
GPS data can reveal your exact location when the photo was taken. This can be used to track your movements and habits.
Personal Identification:
Camera settings and device information can be used to identify you or your device. This information can be combined with other data to create a detailed profile.
Software Usage:
Metadata can reveal which software you use to edit photos. This information can be used for targeted advertising or other purposes.
Data Breaches:
If photo metadata is not properly secured, it can be exposed in data breaches. This can lead to identity theft or other security risks.
9. How to Prevent Apps from Accessing Photo Metadata
Controlling which apps can access your photo metadata is crucial for maintaining privacy.
Reviewing App Permissions:
Regularly review the permissions you have granted to apps:
- Open Settings: Go to the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Navigate to Privacy & Security: Tap on “Privacy & Security”.
- Select Photos: Tap on “Photos”.
- Review App Access: Review the list of apps and their access levels:
- Limited Access: The app can only access selected photos.
- Full Access: The app can access all photos.
- None: The app cannot access any photos.
- Adjust Permissions: Change the access level for each app as needed.
Using Privacy-Focused Apps:
Choose apps that prioritize privacy and do not require access to your entire photo library.
Disabling Metadata Access:
Some apps allow you to disable metadata access in their settings. Check the app’s documentation for instructions.
10. Best Practices for Protecting Photo Privacy
Protecting your photo privacy requires a combination of technical measures and mindful practices.
Disable Location Services:
Disable location services for the Camera app or use the “Ask Next Time” option.
Remove Metadata Regularly:
Remove metadata from photos before sharing them online or with others.
Review App Permissions:
Regularly review and adjust app permissions to limit access to your photo library.
Use Secure Sharing Platforms:
Use encrypted messaging apps or secure file transfer services for sharing photos.
Be Mindful of What You Share:
Think carefully about the content of your photos and the information they reveal before sharing them.
Educate Yourself:
Stay informed about privacy risks and best practices for protecting your personal information.
11. How to Turn Off Photo Information on Android
While this article focuses on iPhones, it’s worth noting how to manage photo information on Android devices as well.
Disabling Location Services:
- Open Settings: Go to the Settings app on your Android device.
- Navigate to Location: Tap on “Location”.
- App Permissions: Select “App permissions”.
- Find Camera App: Find the Camera app in the list.
- Change Permission: Change the permission to “Deny” or “Ask every time”.
Removing Metadata:
- Google Photos: Open the Google Photos app.
- Select Photo: Select the photo you want to edit.
- Edit: Tap on the “Edit” icon.
- Remove Location: Go to “Info” and remove the location data.
Third-Party Apps:
Use third-party apps like “Photo Exif Editor” to remove metadata in bulk.
12. Impact of Social Media Platforms on Photo Metadata
Social media platforms often strip metadata from photos when you upload them. However, it’s still important to be aware of their policies and practices.
Facebook:
Facebook typically removes EXIF data from photos to reduce file sizes and protect user privacy.
Instagram:
Instagram also strips metadata from photos to optimize performance.
Twitter:
Twitter removes metadata from uploaded images.
LinkedIn:
LinkedIn strips metadata from images to ensure privacy and security.
Be Cautious:
While these platforms generally remove metadata, it’s still a good practice to remove it yourself before uploading photos.
13. How to Configure iPhone Camera Settings for Privacy
Configuring your iPhone camera settings can help you protect your privacy by default.
Disable Location Services:
As mentioned earlier, disable location services for the Camera app.
Turn Off HDR:
High Dynamic Range (HDR) photos can contain more detailed metadata. Turning off HDR can reduce the amount of data stored in the photo.
Use Camera Grid:
The camera grid can help you compose better photos without relying on editing software that adds metadata.
Adjust Image Quality:
Lowering the image quality can reduce the file size and the amount of metadata stored.
14. Tools and Apps for Managing Photo Metadata
Numerous tools and apps are available for managing photo metadata on iPhones and other devices.
Metapho:
A popular iOS app for viewing and editing metadata.
Exif Metadata:
An app specifically designed for removing EXIF data.
Imagepipe:
An automation tool for removing metadata from multiple images.
ExifTool:
A powerful command-line utility for advanced users.
Google Photos:
Provides basic metadata management features.
Preview (Mac):
A built-in tool for viewing and editing metadata on macOS.
15. Legal Aspects of Photo Metadata and Privacy
Understanding the legal aspects of photo metadata and privacy is essential, especially for professional photographers.
Copyright Protection:
Metadata can help protect your copyright by including information about the photographer and the image’s usage rights.
Privacy Laws:
Be aware of privacy laws in your region, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which regulates the collection and use of personal data.
Model Releases:
If your photos include identifiable people, obtain model releases to ensure you have the right to use their images.
Data Security:
Implement measures to protect photo metadata from unauthorized access or disclosure.
16. Ethical Considerations for Sharing Photos Online
Sharing photos online involves ethical considerations, especially when it comes to privacy and consent.
Respecting Privacy:
Obtain consent from individuals before sharing photos of them online.
Avoiding Misrepresentation:
Do not manipulate photos in a way that misrepresents reality or deceives viewers.
Protecting Children:
Be especially careful when sharing photos of children online, and avoid sharing any information that could put them at risk.
Being Transparent:
Be transparent about your photo editing practices and disclose any modifications you have made.
17. Future Trends in Photo Metadata and Privacy
The landscape of photo metadata and privacy is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to watch:
AI-Powered Metadata Management:
Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a greater role in automatically identifying and managing metadata.
Blockchain-Based Photo Verification:
Blockchain technology can be used to verify the authenticity and provenance of photos.
Increased Privacy Regulations:
Governments around the world are likely to introduce stricter privacy regulations to protect personal data.
Enhanced Metadata Security:
New technologies will emerge to enhance the security of photo metadata and prevent unauthorized access.
18. How to Back Up Photos Without Metadata
Backing up your photos without metadata can help protect your privacy while still ensuring you have a copy of your images.
Using Cloud Services:
Cloud services like Google Photos and iCloud Photos may strip metadata from photos during the backup process. Check their documentation for details.
Manual Backup:
Manually copy your photos to an external hard drive or other storage device after removing metadata.
Using Backup Software:
Use backup software that allows you to exclude metadata from the backup.
Creating Archives:
Create archives of your photos without metadata for long-term storage.
19. How to Restore Metadata to Photos
If you accidentally remove metadata from your photos, you may be able to restore it using certain tools.
Using Backup Copies:
If you have a backup copy of your photos with metadata, you can restore the metadata from the backup.
Using Metadata Recovery Tools:
Some metadata recovery tools can attempt to recover metadata from photos that have been stripped of it.
Checking Camera Settings:
Make sure your camera settings are configured to include metadata in new photos.
Contacting Support:
If you are unable to restore metadata yourself, contact the support team for your camera or photo editing software for assistance.
20. Practical Examples of Protecting Photo Privacy
Here are some practical examples of how to protect your photo privacy in everyday situations:
Sharing Vacation Photos:
Before sharing vacation photos online, remove location data to prevent others from knowing where you were at specific times.
Posting Photos of Your Home:
Avoid posting photos of your home that reveal identifying details, such as street addresses or unique features.
Sharing Photos of Children:
Obtain consent from parents or guardians before sharing photos of children online, and avoid sharing any personal information about them.
Using Dating Apps:
Be cautious about sharing photos on dating apps, as they may be used to identify you or your location.
Posting Photos on Social Media:
Review the privacy settings on your social media accounts to control who can see your photos and metadata.
21. FAQ: How To Turn Off Photo Information On iPhone
21.1. How do I completely remove location data from my iPhone photos?
To completely remove location data, go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services > Camera and set permission to “Never”. For existing photos, use the Photos app, tap the “i” icon, and select “No Location”.
21.2. Will taking a screenshot remove photo information on my iPhone?
Yes, taking a screenshot creates a new image file without the original metadata, effectively removing photo information.
21.3. What are the best apps for removing metadata from iPhone photos?
Popular apps include Metapho, Exif Metadata, and Imagepipe, which offer comprehensive metadata management features.
21.4. How can I view the metadata of a photo on my iPhone?
Open the photo in the Photos app and tap the “i” icon to view basic metadata. For detailed metadata, use apps like Metapho.
21.5. Does iPhone automatically remove metadata when sharing photos on social media?
While many social media platforms strip metadata, it’s best to manually remove it before sharing to ensure privacy.
21.6. Can I disable location services temporarily for specific photos?
No, you can’t disable location services for specific photos. You can only disable it for the Camera app or remove location data from existing photos.
21.7. Is it possible to restore metadata after removing it from a photo?
If you have a backup copy of the photo with metadata, you can restore it. Otherwise, metadata recovery may not be possible.
21.8. How do I prevent apps from accessing my photo metadata on iPhone?
Go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Photos, and review app access levels. Adjust permissions as needed to limit access.
21.9. What is EXIF data, and why is it important to manage?
EXIF data includes details like date, time, location, and camera settings. Managing it is crucial for privacy and security.
21.10. Are there any legal implications to consider when managing photo metadata?
Yes, be aware of privacy laws like GDPR, copyright protection, and the need for model releases when managing photo metadata.
22. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Photo Privacy
Managing photo metadata is essential for protecting your privacy and security in the digital age. By understanding the risks and implementing the techniques described in this article, you can take control of your photo privacy and share your images with confidence. Whether you’re a professional photographer or a casual iPhone user, these tips will help you safeguard your personal information and maintain control over your digital footprint.
Ready to enhance your photography skills and learn more about photo privacy? Visit dfphoto.net today to discover a wealth of resources, stunning photo galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers! Don’t miss out—explore dfphoto.net and start your journey to photographic excellence.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
Website: dfphoto.net.