Losing precious photos can be a heart-stopping moment, especially when those memories are irreplaceable. Don’t worry, dfphoto.net is here to guide you through the process of photo recovery, offering practical solutions to retrieve your cherished images and digital artwork. We’ll explore various methods, from checking temporary storage to utilizing data recovery software and cloud backups, ensuring you have the best chance of restoring your lost photos and preventing future data loss.
1. Understanding Photo Deletion and Recovery
1.1. Where Do Deleted Photos Go?
When you delete a photo from your device, it isn’t immediately erased from the storage. Instead, the operating system marks the space occupied by the photo as available for new data. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, deleted files remain recoverable until overwritten by new data. This is why acting quickly after deleting photos is crucial for successful recovery.
1.2. Common Causes of Photo Loss
Photo loss can occur due to various reasons:
- Accidental deletion
- Formatting storage devices
- Software or hardware malfunction
- Virus attacks
- Physical damage to the storage device
1.3. The Importance of Acting Quickly
The sooner you attempt to recover deleted photos, the higher the chance of success. The more you use your device after deletion, the greater the risk of overwriting the deleted files, making them unrecoverable.
2. Immediate Steps After Deletion
2.1. Stop Using the Device
Immediately stop using the device (smartphone, camera, or computer) to prevent new data from overwriting the deleted photos.
2.2. Avoid Installing New Software
Avoid installing new software on the device, as the installation process can also overwrite deleted files.
2.3. Note the Deletion Time
Make a note of the date and time when the photos were deleted, as this information can be helpful when using data recovery software.
3. Checking Temporary Storage Locations
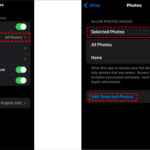
3.1. The ‘Recently Deleted’ Album
Most smartphones and operating systems have a ‘Recently Deleted’ or ‘Trash’ folder where deleted photos are temporarily stored.
How to Check:
- On iPhone: Open the Photos app and tap on the ‘Albums’ tab. Scroll down to find the ‘Recently Deleted’ album.
- On Android: Open the Gallery app and look for a ‘Trash’ or ‘Recently Deleted’ folder.
- On Windows: Check the Recycle Bin on your desktop.
- On macOS: Check the Trash in the Dock.
3.2. Cloud Storage Services
If you use cloud storage services like Google Photos, iCloud, or Dropbox, check their respective trash or recently deleted sections.
How to Check:
- Google Photos: Open the Google Photos app or website, go to ‘Library,’ and check the ‘Trash’ folder.
- iCloud: Sign in to iCloud on a web browser, go to ‘Photos,’ and check the ‘Recently Deleted’ album.
- Dropbox: Open the Dropbox app or website, go to ‘Files,’ and check the ‘Deleted Files’ section.
3.3. Social Media and Messaging Apps
Check social media apps like Facebook, Instagram, and messaging apps like WhatsApp or Telegram, where you might have shared or backed up your photos.
4. Using Data Recovery Software
4.1. Introduction to Data Recovery Tools
Data recovery software can scan your device’s storage for deleted files and attempt to recover them. These tools work by identifying file fragments and reassembling them into usable photos.
4.2. Top Data Recovery Software Options
Here are some of the top data recovery software options:
| Software | Platform | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recuva | Windows | Deep scan mode, secure overwrite, file preview | Free version available, paid version |
| EaseUS Data Recovery | Windows, macOS | Recovers from various storage devices, supports multiple file types, preview before recovery | Free version available, paid version |
| Stellar Data Recovery | Windows, macOS | Recovers from formatted drives, supports RAW photo recovery, advanced filtering | Free version available, paid version |
| Disk Drill | Windows, macOS | Data protection tools, partition recovery, supports various file systems | Free version available, paid version |
| PhotoRec | Windows, macOS | Open-source, recovers a wide range of file types, command-line interface | Free |
4.3. How to Use Data Recovery Software
- Download and Install: Download and install a reputable data recovery software on your computer.
- Select the Drive: Launch the software and select the drive or storage device where the photos were deleted.
- Scan for Deleted Files: Start the scanning process. Choose between a quick scan and a deep scan, depending on the software and the extent of data loss.
- Preview and Recover: Once the scan is complete, preview the recoverable photos and select the ones you want to restore.
- Save Recovered Photos: Choose a different storage location to save the recovered photos to avoid overwriting other deleted files.
4.4. Tips for Successful Data Recovery
- Act Fast: The sooner you use data recovery software, the better your chances of recovering the photos.
- Choose Reputable Software: Select a well-known and reputable data recovery software to avoid malware or further data loss.
- Scan the Correct Drive: Ensure you are scanning the correct drive or storage device where the photos were deleted.
- Preview Before Recovering: Always preview the photos before recovering them to ensure they are the ones you need.
- Save to a Different Location: Save the recovered photos to a different drive or storage device to avoid overwriting other deleted files.
5. Recovering Photos from Mobile Devices
5.1. Recovery on iPhones
Checking iCloud Backup:
- Go to Settings: Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Tap on Your Name: Tap on your name at the top of the screen.
- Select iCloud: Tap on iCloud.
- Manage Storage: Tap on Manage Storage.
- Backups: Check if there’s a recent backup available.
Restoring from iCloud Backup:
- Erase All Content: Go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings.
- Restore from iCloud: Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your iPhone from an iCloud backup.
5.2. Recovery on Android Devices
Checking Google Photos Backup:
- Open Google Photos: Open the Google Photos app on your Android device.
- Check the Trash: Go to ‘Library’ and check the ‘Trash’ folder.
- Restore Photos: Select the photos you want to restore and tap on the ‘Restore’ button.
Using Android Data Recovery Apps:
- Download and Install: Download and install a reputable Android data recovery app from the Google Play Store.
- Grant Permissions: Grant the necessary permissions to access your device’s storage.
- Scan for Deleted Photos: Start the scanning process to find deleted photos.
- Preview and Recover: Preview the recoverable photos and select the ones you want to restore.
- Save Recovered Photos: Choose a different storage location to save the recovered photos.
5.3. Avoiding Overwriting Data on Mobile Devices
- Enable Automatic Backup: Enable automatic backup to cloud services like Google Photos or iCloud to prevent data loss.
- Use an SD Card: If your device supports it, use an SD card for storing photos and videos. This allows you to remove the card and use a computer to recover data if needed.
- Minimize Device Usage: Minimize the use of your device after deleting photos to prevent overwriting data.
6. Recovering Photos from Digital Cameras
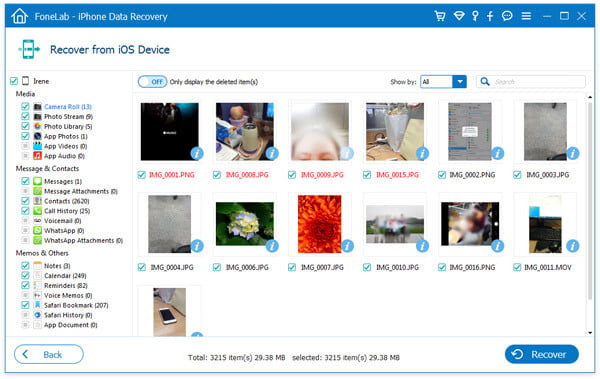
6.1. Using Data Recovery Software for Memory Cards
Memory cards used in digital cameras can also be scanned using data recovery software.
Steps to Recover Photos from Memory Cards:
- Remove the Memory Card: Remove the memory card from the camera.
- Connect to Computer: Connect the memory card to your computer using a card reader.
- Run Data Recovery Software: Launch data recovery software and select the memory card as the drive to scan.
- Scan and Recover: Start the scanning process and recover the deleted photos.
6.2. Preventing Data Loss on Digital Cameras
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your photos from the memory card to a computer or external drive.
- Use Multiple Memory Cards: Use multiple memory cards to avoid storing all your photos on a single card.
- Format Memory Cards Properly: Always format memory cards in the camera before using them to avoid file system errors.
- Handle Memory Cards Carefully: Handle memory cards carefully to avoid physical damage or data corruption.
 Connecting a memory card to a computer for photo recovery, highlighting the importance of handling the card with care
Connecting a memory card to a computer for photo recovery, highlighting the importance of handling the card with care
7. Advanced Recovery Techniques
7.1. Forensic Data Recovery
In severe cases of data loss, forensic data recovery services can be used. These services employ advanced techniques and specialized equipment to recover data from damaged or corrupted storage devices.
7.2. Data Recovery Labs
Data recovery labs are equipped with cleanroom environments and experienced technicians who can handle physically damaged storage devices.
7.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- Physically Damaged Device: If the storage device is physically damaged, such as a broken hard drive or a water-damaged smartphone.
- Complex Data Loss Scenarios: If you have attempted data recovery yourself without success and the data is critical.
- Encrypted Storage: If the storage device is encrypted and you have lost the encryption key.
8. Preventing Future Photo Loss
8.1. Implementing a Backup Strategy
3-2-1 Backup Rule:
- 3 Copies of Your Data: Keep at least three copies of your important photos.
- 2 Different Storage Media: Store the copies on at least two different types of storage media, such as a hard drive and a cloud service.
- 1 Offsite Location: Keep one copy of your data offsite, such as in a different physical location or a cloud service.
8.2. Using Cloud Storage Services
Cloud storage services provide automatic backup and synchronization of your photos, ensuring that your data is safe even if your device is lost or damaged.
Popular Cloud Storage Services:
- Google Photos
- iCloud
- Dropbox
- Amazon Photos
- Microsoft OneDrive
8.3. Regular Backups to External Drives
Regularly back up your photos to an external hard drive or NAS (Network Attached Storage) device. This provides an additional layer of protection against data loss.
8.4. Data Redundancy (RAID)
For businesses and professional photographers, implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) system can provide data redundancy and protect against hard drive failures.
8.5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software can help prevent accidental or malicious deletion of photos by monitoring and controlling data access and usage.
9. Understanding File Formats and Corruption
9.1. Common Photo File Formats
Understanding different photo file formats can help you identify potential issues and choose the best format for your needs.
Common Photo File Formats:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): A widely used format for photos, known for its compression capabilities.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): A lossless format that preserves image quality, suitable for graphics and images with text.
- RAW: An uncompressed format that contains all the data captured by the camera sensor, providing maximum flexibility for editing.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): A versatile format that supports both lossless and lossy compression, often used for professional photography and archiving.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): A format commonly used for animated images and simple graphics.
9.2. Causes of File Corruption
File corruption can occur due to various reasons:
- Sudden Power Loss: Sudden power loss during file transfer or saving can corrupt photos.
- Hardware Malfunction: Hardware issues with the storage device or computer can lead to file corruption.
- Software Bugs: Bugs in photo editing software or operating systems can cause file corruption.
- Virus Attacks: Malware and viruses can corrupt or delete photo files.
- Improper File Handling: Incorrectly transferring or saving files can lead to corruption.
9.3. Recovering Corrupted Photo Files
- Use Photo Repair Software: Photo repair software can scan corrupted photo files and attempt to repair them.
- Try Different Software: If one software fails, try using a different photo repair tool.
- Seek Professional Help: In severe cases of corruption, seek professional data recovery services.
10. Photo Management Best Practices
10.1. Organizing Your Photo Library
- Create a Folder Structure: Create a logical folder structure to organize your photos by date, event, or subject.
- Use Descriptive File Names: Use descriptive file names that include the date, location, and subject of the photo.
- Add Metadata: Add metadata such as captions, keywords, and copyright information to your photos.
- Use Photo Management Software: Use photo management software like Adobe Lightroom or Capture One to organize and manage your photo library.
10.2. Tagging and Keywording Photos
Tagging and keywording photos makes it easier to find specific images in your library.
- Use Consistent Keywords: Use a consistent set of keywords to tag your photos.
- Tag People, Places, and Events: Tag photos with the names of people, places, and events.
- Use Hierarchical Keywords: Use hierarchical keywords to create a more organized tagging system.
10.3. Regular Maintenance of Your Photo Library
- Remove Duplicate Photos: Regularly remove duplicate photos to save storage space and keep your library organized.
- Delete Unwanted Photos: Delete unwanted or low-quality photos to keep your library clutter-free.
- Check for Corruption: Regularly check your photo library for file corruption and repair any damaged files.
- Update Software: Keep your photo management software and operating system up to date to prevent compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities.
11. Legal and Ethical Considerations
11.1. Copyright and Ownership
Understanding copyright and ownership of photos is crucial, especially for professional photographers.
- Copyright Protection: Photos are automatically protected by copyright from the moment they are created.
- Ownership Rights: The photographer typically owns the copyright to their photos unless they have transferred those rights to someone else.
- Usage Rights: Understanding usage rights is essential when using photos for commercial purposes.
11.2. Privacy Issues
Be mindful of privacy issues when taking and sharing photos, especially in public places.
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent when photographing individuals, especially in private settings.
- Respect Privacy: Respect individuals’ privacy and avoid taking photos that could be considered intrusive or offensive.
- Comply with Laws: Comply with local laws and regulations regarding photography in public places.
11.3. Ethical Data Recovery Practices
- Obtain Permission: Obtain permission before attempting to recover data from someone else’s device.
- Respect Privacy: Respect the privacy of the data you recover and avoid sharing or using it without authorization.
- Comply with Laws: Comply with data protection laws and regulations when recovering and handling personal data.
12. Future Trends in Photo Recovery
12.1. AI-Powered Data Recovery
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to enhance data recovery techniques, making it possible to recover data from severely damaged storage devices.
12.2. Cloud-Based Recovery Solutions
Cloud-based data recovery solutions are becoming more popular, allowing users to recover data from anywhere with an internet connection.
12.3. Advanced File System Analysis
Advanced file system analysis techniques are being developed to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data recovery.
13. Conclusion: Your Photos Are Valuable—Protect Them!
Recovering deleted photos can be a stressful experience, but with the right tools and techniques, it’s often possible to restore your precious memories. Remember to act quickly, choose reputable data recovery software, and implement a robust backup strategy to prevent future data loss. dfphoto.net is committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to protect your valuable photos and ensure they are safe for years to come. For more information, explore our extensive collection of photography guides, tips, and community forums at dfphoto.net.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.
Ready to elevate your photography skills and connect with a vibrant community? Visit dfphoto.net today and discover a world of inspiration, learning, and endless possibilities. Explore our expert tutorials, stunning photo galleries, and connect with fellow photography enthusiasts in the USA. Don’t miss out—start your journey with dfphoto.net now.
14. FAQ: How to Retrieve Recently Deleted Photos?
14.1. Can I recover permanently deleted photos from my iPhone?
Yes, you might be able to recover permanently deleted photos from your iPhone by checking iCloud backups or using data recovery software, but the success rate depends on whether the data has been overwritten.
14.2. How long do photos stay in the Recently Deleted album?
Photos typically stay in the Recently Deleted album for 30 days before being permanently deleted.
14.3. Is it possible to recover photos from a formatted memory card?
Yes, it is possible to recover photos from a formatted memory card using data recovery software, as formatting doesn’t completely erase the data.
14.4. What is the best data recovery software for recovering deleted photos?
Some of the best data recovery software options include Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery, Stellar Data Recovery, and Disk Drill.
14.5. How can I prevent future photo loss?
To prevent future photo loss, implement a robust backup strategy, use cloud storage services, and regularly back up your photos to external drives.
14.6. What should I do immediately after deleting photos accidentally?
Immediately stop using the device to prevent overwriting the deleted photos and check the Recently Deleted album or trash folder.
14.7. Can I recover photos from a water-damaged smartphone?
Recovering photos from a water-damaged smartphone is challenging and often requires professional data recovery services.
14.8. What are the legal considerations when recovering someone else’s photos?
When recovering someone else’s photos, obtain permission and respect their privacy to comply with data protection laws and regulations.
14.9. How does AI enhance data recovery techniques?
AI enhances data recovery techniques by improving the accuracy and efficiency of data recovery from damaged storage devices through advanced algorithms.
14.10. What are the benefits of using cloud-based recovery solutions?
Cloud-based recovery solutions allow you to recover data from anywhere with an internet connection and provide automatic backup and synchronization of your photos.