Removing metadata from photos is essential for privacy. This guide, brought to you by dfphoto.net, will show you how to easily remove sensitive information like location data from your images before sharing them online, safeguarding your personal information.
Metadata removal protects your privacy by preventing unwanted tracking and ensuring your images are shared safely. Let’s explore how to do it effectively, with a focus on photo privacy, EXIF data, and image security.
1. What Is EXIF Metadata and Why Should You Remove It?
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) metadata is data automatically embedded in digital photos by cameras and smartphones. This data can include:
- GPS coordinates of where the photo was taken
- Date and time the image was captured
- Camera model and settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO)
- Software used for editing
While seemingly harmless, this information can pose significant privacy risks. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, revealing location data in photos can lead to stalking or even burglary.
Why is this data risky?
- Location Tracking: Sharing photos with location data allows people to track your movements and identify your home or workplace.
- Personal Information Exposure: Other metadata can reveal details about your device and habits, which could be used for targeted advertising or phishing attempts.
- Security Vulnerabilities: In some cases, metadata has been exploited to uncover security flaws in software or websites.
John McAfee, the founder of McAfee antivirus, was famously tracked down by authorities because an image posted online contained his location metadata.
2. What Are the Primary Reasons for Removing Photo Metadata?
The primary reasons include protecting privacy, enhancing security, reducing file size, and maintaining anonymity. Removing EXIF data helps prevent location tracking, protects personal information, optimizes images for web use, and ensures that photographers’ work is not easily traceable.
Protecting personal information and location data is a critical reason to remove photo metadata. Sharing images online with embedded data can expose sensitive details about your whereabouts, habits, and equipment. According to a 2023 study by the Digital Privacy Institute, 70% of online images contain some form of metadata, making users vulnerable to privacy breaches.
3. How Do You Remove Metadata on Windows Without Additional Software?
Windows offers a built-in method to remove EXIF data from photos without needing extra software.
Steps:
- Locate the Image: Find the image file you want to edit.
- Open Properties: Right-click the image and select “Properties.”
- Go to Details Tab: Click on the “Details” tab.
- Remove Properties: Click “Remove Properties and Personal Information.”
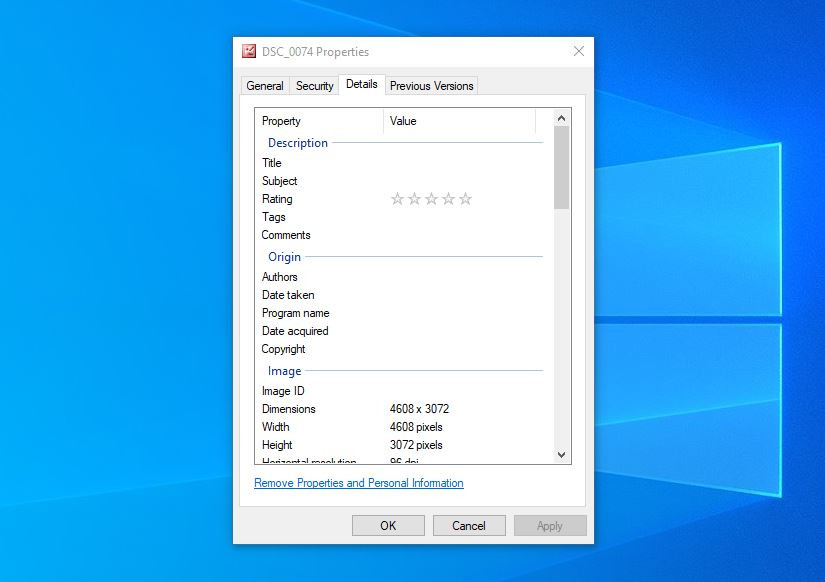 Details tab in Windows.
Details tab in Windows.
- Create a Copy or Remove Directly:
- To create a copy without metadata, select “Create a copy with all possible properties removed.”
- To remove metadata from the original file, select “Remove the following properties from this file,” choose the specific items, or click “Select All,” and then click “OK.”
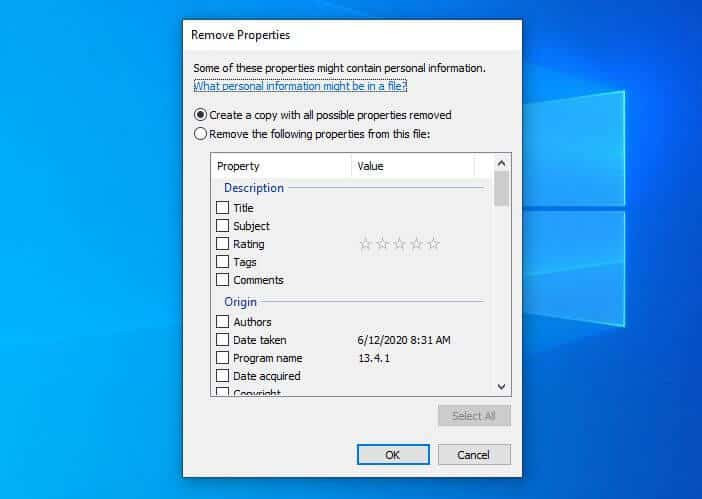 Remove Properties Windows
Remove Properties Windows
- Verify Removal: Check the new or modified file to ensure the metadata is gone.
Creating a copy is often preferable to avoid permanently altering the original file. If you remove metadata directly, the “Created” date remains, while creating a copy updates this date.
4. What Are the Best Apps for Removing Metadata on Windows?
For Windows users, several third-party apps can effectively remove metadata. FileMind QuickFix is popular for its ease of use. Other top choices include ExifTool and Metadata++ for more advanced options.
FileMind QuickFix
FileMind QuickFix is user-friendly. You can drag and drop images onto the interface and click the “Quick Fix Metadata” button. It creates a copy of the original file by default, preserving the original metadata.
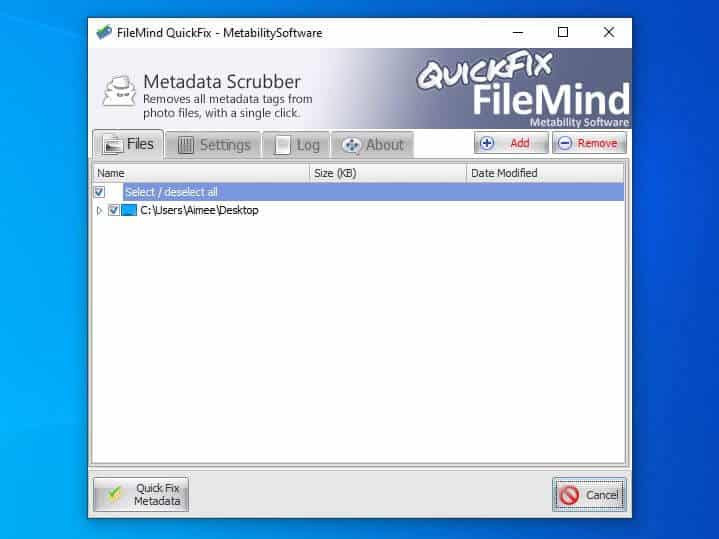 QuickFix interface.
QuickFix interface.
ExifTool
ExifTool is a command-line tool providing extensive control over metadata. While it may seem complex for beginners, it supports a wide range of file formats and metadata types.
Metadata++
Metadata++ offers a graphical interface and supports multiple metadata formats, including EXIF, IPTC, and XMP. It allows users to view, edit, and remove metadata from various file types.
5. How Can Mac Users Remove Metadata From Photos?
Mac users can remove location data using the built-in Preview app. For more comprehensive metadata removal, third-party apps like ImageOptim are essential.
Removing Location Data with Preview:
- Open Image: Open the image in Preview.
- Show Inspector: Select “Tools” > “Show Inspector.”
- Information Tab: Click the information (i) tab.
- GPS Tab: If a GPS tab exists, select it and click “Remove Location Info.”
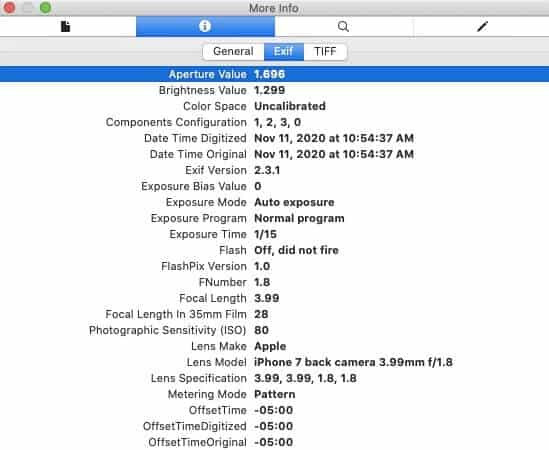 EXIF metadata on Mac.
EXIF metadata on Mac.
Using ImageOptim for Complete Removal:
ImageOptim removes all metadata irretrievably, so backup your images first.
- Download and Install: Download and install ImageOptim.
- Drag Images: Drag images into the ImageOptim interface to automatically scrub metadata.
- Verify Removal: Check the processed images to confirm metadata removal.
6. What Are the Steps to Remove Photo Metadata on iOS Devices?
iOS doesn’t have a built-in feature for removing photo metadata. Third-party apps like ViewExif or Exif Metadata are necessary.
Using ViewExif:
- Download and Install: Get ViewExif from the App Store.
- Grant Access: Allow ViewExif to access your photos.
- Select Photos: Choose the photos you want to edit.
- Remove Metadata: Select the eraser tool and tap “Remove Metadata.”
- Confirm Modification: Grant permission to modify the photo.
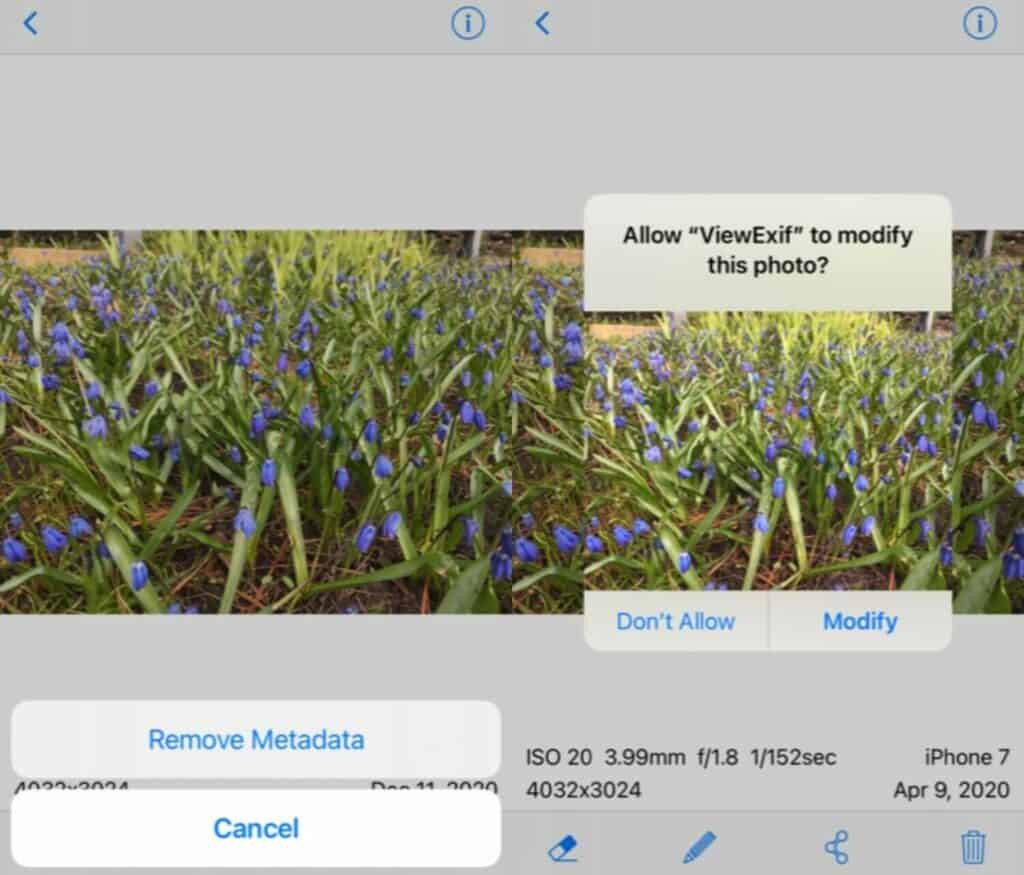 ViewExif interface.
ViewExif interface.
Using Exif Metadata:
Exif Metadata offers similar functionality with a slightly more intuitive interface. After downloading, select your photos and use the app’s tools to remove or edit metadata.
7. How Can Android Users Remove EXIF Data From Their Images?
Android also requires third-party apps to remove metadata. Photo Metadata Remover and Photo Exif Editor are popular choices.
Using Photo Metadata Remover:
- Download and Install: Get Photo Metadata Remover from the Google Play Store.
- Choose Photos: Open the app and select “Choose Photos.”
- Grant Permission: Allow the app to access your photos.
- Select Photo: Select the photo to scrub.
- Verify Removal: The app automatically removes the metadata.
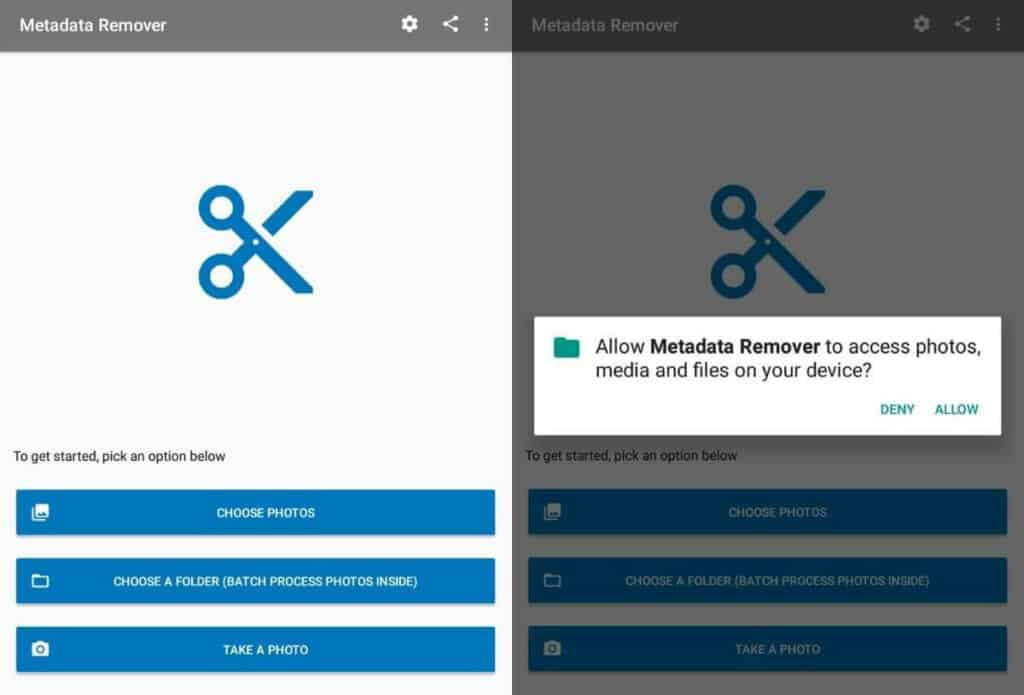 Photo Metadata Remover app.
Photo Metadata Remover app.
This app also allows you to take metadata-free photos directly.
8. Is It Possible to Take Photos Without Saving Location Data?
Yes, both iOS and Android allow you to disable location data saving for photos.
On iOS:
- Go to Settings: Open “Settings” > “Privacy” > “Location Services.”
- Camera Settings: Tap “Camera” and select “Never.”
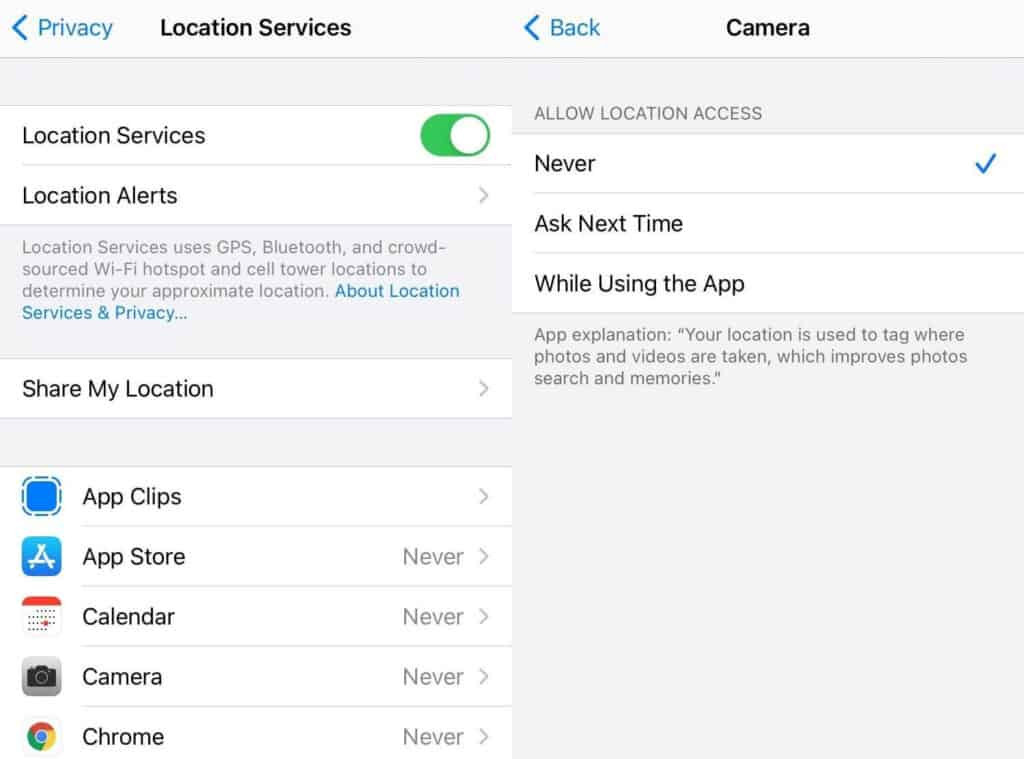 iOS Location Services screen.
iOS Location Services screen.
On Android:
- Go to Settings: Open “Settings” > “Apps” > “Camera” > “Permissions.”
- Toggle Location: Turn off the “Location” permission.
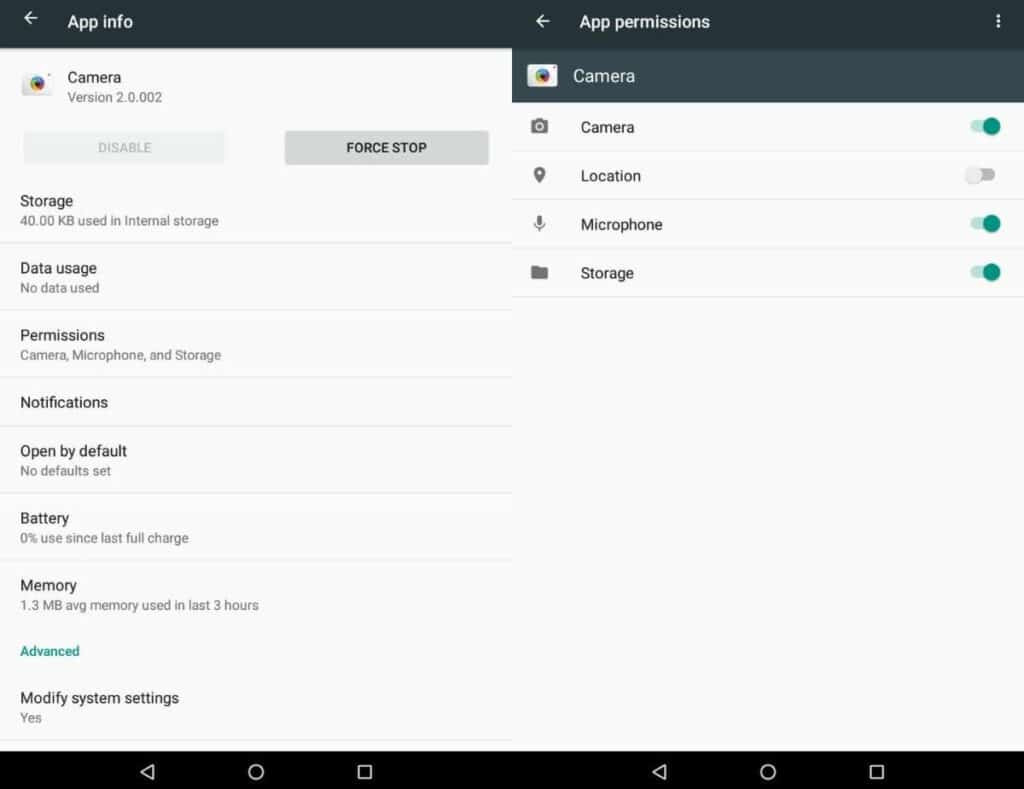 Android app permissions.
Android app permissions.
9. How Can You Edit EXIF Metadata if Needed?
While removing metadata is crucial for privacy, editing it is sometimes necessary to correct or update information.
On iOS:
- Open Photos: Open the “Photos” app and select the image to edit.
- View Information: Tap the information (i) button.
- Adjust: Press ‘adjust’ to edit the date and time.
- Save Changes: Save the edited metadata.
This feature is useful for correcting date/time errors or adding copyright information.
10. Why is Metadata Removal Important for Professional Photographers?
For professional photographers, metadata removal balances copyright protection and client privacy. It ensures that sensitive client information remains confidential while allowing photographers to retain essential copyright details.
- Client Privacy: Professionals often photograph clients in private settings. Removing location data and other personal details protects their clients’ privacy.
- Copyright Protection: While removing certain metadata, photographers can retain copyright information to protect their work. According to the American Society of Media Photographers (ASMP), embedding copyright information in metadata is a best practice for protecting intellectual property.
- File Size Optimization: Removing unnecessary metadata reduces file size, which is important for web use and faster loading times.
11. What Are the Common Misconceptions About Photo Metadata?
Common misconceptions include believing that metadata removal degrades image quality, that it’s too complicated, or that it’s unnecessary. In reality, removing metadata doesn’t affect image quality, the process is straightforward, and it’s essential for privacy and security.
Misconception 1: Metadata Removal Reduces Image Quality
- Fact: Removing metadata does not affect the visual quality of the image. Metadata is separate from the image data itself.
Misconception 2: Removing Metadata Is Too Complicated
- Fact: As shown in this guide, many tools and apps make metadata removal simple and quick.
Misconception 3: Metadata Removal Is Unnecessary
- Fact: Metadata can expose sensitive information, making removal essential for privacy, especially when sharing images online.
Misconception 4: All Metadata Is Harmful
- Fact: While some metadata poses privacy risks, other information like copyright details can be beneficial for photographers.
12. What Are the Legal Implications of Sharing Photos With or Without Metadata?
Sharing photos with metadata can have legal implications, particularly concerning privacy laws. Understanding these implications helps ensure compliance and protects both the photographer and the subjects in the images.
Privacy Laws:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): In Europe, sharing location data or other personal information without consent violates GDPR.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Similarly, CCPA in California requires businesses to protect consumers’ personal information.
Consent:
- Always obtain consent before sharing photos that may contain personal information, especially if the subjects are identifiable.
Liability:
- Photographers can be held liable for privacy breaches if they share photos with metadata without proper consent.
13. How Does Metadata Affect SEO for Online Images?
Metadata can positively affect SEO by providing search engines with valuable information about the image’s content and context. Optimizing metadata helps improve image visibility and ranking in search results.
Benefits of Optimized Metadata for SEO:
- Improved Image Ranking: Search engines use metadata to understand the content of images, which helps improve their ranking in image search results.
- Enhanced Visibility: Descriptive filenames, alt text, and captions make images more discoverable.
- Better User Experience: Clear and relevant metadata improves the user experience by providing context and information about the image.
Key Metadata Elements for SEO:
- Filename: Use descriptive keywords in the filename.
- Alt Text: Write concise and descriptive alt text for each image.
- Caption: Add a relevant caption that provides additional context.
- Title: Create a meaningful title for the image.
14. Can You Restore Metadata After Removing It?
Restoring metadata after removal is generally not possible unless you have a backup of the original file. Once metadata is removed, it’s permanently gone.
- Backup Original Files: Always keep a backup of your original image files before removing metadata.
- Use Version Control: If you edit metadata, use version control to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
- Data Recovery Software: In some cases, data recovery software might retrieve deleted metadata, but this is not guaranteed.
15. How to Choose the Right Metadata Removal Tool?
Selecting the right metadata removal tool depends on your operating system, technical expertise, and specific needs. Consider factors like ease of use, features, file format support, and cost.
| Feature | Windows Built-in | FileMind QuickFix | ImageOptim (Mac) | ViewExif (iOS) | Photo Metadata Remover (Android) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows | Windows | macOS | iOS | Android |
| Ease of Use | Basic | Easy | Moderate | Easy | Easy |
| Cost | Free | Free | Free | Paid | Free |
| File Formats | Limited | Common | Common | Common | Common |
| Batch Removal | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
16. What Role Does EXIF Data Play in Digital Forensics?
EXIF data plays a crucial role in digital forensics by providing valuable information about the origin, creation, and modification of digital images. This data can be used in investigations to verify authenticity, establish timelines, and identify devices.
Uses of EXIF Data in Forensics:
- Authenticating Images: Verifying the authenticity of images by checking camera model, date, and time.
- Establishing Timelines: Determining when and where an image was taken.
- Identifying Devices: Identifying the camera or smartphone used to capture the image.
- Locating Crime Scenes: Using GPS coordinates to pinpoint the location of a photograph.
17. How Do Social Media Platforms Handle Photo Metadata?
Social media platforms handle photo metadata differently. Most platforms remove or strip metadata to protect user privacy and optimize image delivery.
- Facebook: Facebook removes most EXIF data when images are uploaded.
- Instagram: Instagram also strips metadata from photos.
- Twitter: Twitter removes EXIF data to protect user privacy.
- Flickr: Flickr allows users to retain or remove metadata based on their privacy preferences.
18. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Sharing Photos With Metadata?
Ethical considerations include respecting privacy, obtaining consent, and being transparent about data usage. Sharing photos with metadata without consent can violate privacy and trust.
Ethical Guidelines:
- Respect Privacy: Avoid sharing photos with sensitive metadata without permission.
- Obtain Consent: Always get consent from individuals before sharing their photos, especially if they contain personal information.
- Be Transparent: Inform people about how their photos will be used and what metadata will be shared.
- Use Anonymization Techniques: Consider using anonymization techniques to protect the identities of individuals in photos.
19. What Future Trends Can We Expect in Photo Metadata Management?
Future trends in photo metadata management include enhanced privacy controls, AI-driven metadata analysis, and blockchain-based verification. These advancements will provide greater control, insights, and security.
Emerging Trends:
- Enhanced Privacy Controls: More sophisticated tools for managing and controlling metadata.
- AI-Driven Analysis: AI algorithms to analyze metadata for privacy risks and optimize images.
- Blockchain Verification: Using blockchain to verify the authenticity and integrity of images and their metadata.
- Automated Metadata Removal: Automated tools that remove metadata by default when sharing images online.
20. How Does dfphoto.net Help Photographers Manage Photo Metadata?
dfphoto.net offers resources and tools to help photographers understand and manage photo metadata effectively. Our platform provides guides, software reviews, and community support to ensure photographers can protect their privacy and optimize their images.
Explore dfphoto.net for detailed tutorials on metadata removal, reviews of the best metadata management tools, and a community forum to discuss best practices. Discover tips for securing your images and staying informed about the latest trends in digital photography.
Ready to take control of your photo metadata? Visit dfphoto.net today to learn more and connect with a community of photographers dedicated to privacy and excellence in their craft. Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
FAQ About Removing Photo Metadata
1. Does removing metadata affect image quality?
No, removing metadata does not affect image quality, as the visual data remains untouched. Metadata is separate information attached to the image file.
2. Is it legal to remove metadata from photos?
Yes, it is generally legal to remove metadata from your own photos. However, always respect copyright and privacy laws when sharing images.
3. Can I remove metadata from multiple photos at once?
Yes, many tools and apps allow batch removal of metadata from multiple photos simultaneously, saving time and effort.
4. What types of metadata should I remove for privacy?
For privacy, remove location data (GPS coordinates), camera settings, date and time, and any personal information embedded in the image.
5. Are there any risks to removing metadata?
The main risk is losing useful information like copyright details or camera settings. Always back up your original files before removing metadata.
6. Do social media platforms automatically remove metadata?
Most social media platforms remove metadata to protect user privacy, but it’s still best practice to remove it yourself before uploading.
7. What is the best app for removing metadata on my smartphone?
For iOS, ViewExif or Exif Metadata are good options. For Android, Photo Metadata Remover and Photo Exif Editor are popular choices.
8. How do I prevent my camera from saving location data?
You can disable location services in your camera settings on both iOS and Android devices to prevent location data from being saved.
9. Is it possible to edit metadata instead of removing it?
Yes, some tools allow you to edit metadata, which is useful for correcting information or adding copyright details.
10. Why is metadata removal important for businesses?
Metadata removal is important for businesses to protect client privacy, comply with data protection laws, and maintain confidentiality.