Are you wondering how to recover deleted photos from a digital camera? At dfphoto.net, we understand the panic of losing precious memories. With the right tools and techniques, photo recovery from digital cameras is entirely possible. We’ll guide you through effective methods to restore those irreplaceable images and offer tips to safeguard your photographic treasures, ensuring your cherished moments are not lost forever by using image recovery and data recovery.
1. Understanding Photo Loss Scenarios on Digital Cameras
What are the common reasons for photo loss on digital cameras? Understanding the causes can help you prevent future incidents and choose the right recovery approach.
Photo loss from a digital camera can be a frustrating experience, but understanding the common reasons behind it can empower you to take preventive measures. Here’s a breakdown of typical scenarios:
- Accidental Deletion: The most frequent culprit is unintentionally pressing the delete button.
- Card Formatting: Formatting the memory card without backing up your photos will erase everything.
- Corruption: A corrupted memory card can render your photos inaccessible.
- Physical Damage: Physical damage to the camera or memory card can lead to data loss.
- Interrupted Transfers: Removing the memory card or turning off the camera during a transfer can corrupt files.
- Virus/Malware Infection: Though less common, viruses can target the memory card and cause photo loss.
- Power Failure: Camera shutting down unexpectedly due to a low battery.
Recognizing these potential pitfalls allows you to develop safe habits and implement strategies to protect your valuable images.
2. Immediate Actions to Take After Deleting Photos
What steps should I take immediately after realizing I’ve deleted photos to maximize the chances of recovery? The first few minutes are crucial.
The moment you realize you’ve accidentally deleted photos from your digital camera, time is of the essence. Here’s what you should do immediately to maximize your chances of a successful recovery:
- Stop Using the Camera: Do not take any more photos or videos. Writing new data to the memory card can overwrite the deleted files, making them unrecoverable.
- Remove the Memory Card: Carefully remove the memory card from the camera and store it in a safe place.
- Do Not Format the Card: Resist the urge to format the card, as this will erase all data, including the deleted photos you’re trying to recover.
- Find Recovery Software: Research and download reputable photo recovery software.
- Connect to Computer: Connect the memory card to your computer using a card reader.
- Start Recovery Process: Launch the recovery software and follow the instructions to scan the memory card for deleted photos.
- Save Recovered Files: Save the recovered photos to a different storage device, not back to the original memory card.
Taking these immediate actions will significantly increase your chances of successfully retrieving your deleted photos.
3. Free vs. Paid Photo Recovery Software
What are the differences between free and paid photo recovery software, and which is best for my needs? Consider factors like recovery success rate, file type support, and ease of use.
Choosing the right photo recovery software can be tricky, with both free and paid options available. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences to help you make an informed decision:
| Feature | Free Photo Recovery Software | Paid Photo Recovery Software |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Success Rate | Can be lower than paid software, may not recover all files | Generally higher success rate due to advanced scanning algorithms and more comprehensive file signature databases |
| File Type Support | May support only common image formats (JPEG, PNG) | Typically supports a wider range of image formats, including RAW files (CR2, NEF), video formats (MP4, MOV), and other multimedia files |
| Storage Capacity | Limits on number of files or total data you can recover | No limits on number of files or total data you can recover |
| Advanced Features | Often lacks advanced features like deep scan, corrupted file repair, and RAID recovery | Often includes advanced features like deep scan (for more thorough recovery), corrupted file repair, RAID recovery (for complex storage systems), and hex editing |
| Customer Support | Limited or no customer support | Dedicated customer support via email, phone, or live chat |
| Ease of Use | Can be user-friendly, but may lack clear instructions or intuitive interfaces | Often designed with user-friendliness in mind, providing clear instructions, intuitive interfaces, and helpful wizards |
| Cost | Free, but may contain ads or bundled software | Varies depending on features and licensing terms, but typically involves a one-time purchase or subscription fee |
| Use Cases | Best for simple data loss situations, recovering a few common file types, or trying out recovery before investing in a paid solution | Ideal for complex data loss scenarios, recovering a wide range of file types, repairing corrupted files, or requiring professional customer support. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, paid softwares provides faster data recovery speeds. |
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the severity of your data loss situation, the types of files you need to recover, and your budget. If you’ve lost a few JPEG photos, a free tool might suffice. However, for more complex scenarios, investing in paid software can significantly increase your chances of a successful recovery.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Photo Recovery Using Software
How do I use photo recovery software to retrieve deleted photos from my digital camera’s memory card? This should be a practical, easy-to-follow guide.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you recover deleted photos from your digital camera’s memory card using photo recovery software. For demonstration purposes, we’ll use MiniTool Power Data Recovery, but the general steps apply to most similar programs:
-
Download and Install: Download and install MiniTool Power Data Recovery from dfphoto.net, and launch it on your computer.
-
Connect the Memory Card: Connect the memory card from your digital camera to your computer using a card reader. Make sure the card reader is properly connected and recognized by your computer.
-
Select the Drive: In the main interface of MiniTool Power Data Recovery, you should see a list of available drives and devices. Locate and select the memory card that contained your deleted photos.
-
Scan the Drive: Click the “Scan” button next to the selected memory card. The software will now begin scanning the drive for deleted files. This process may take some time, depending on the size of the card and the speed of your computer.
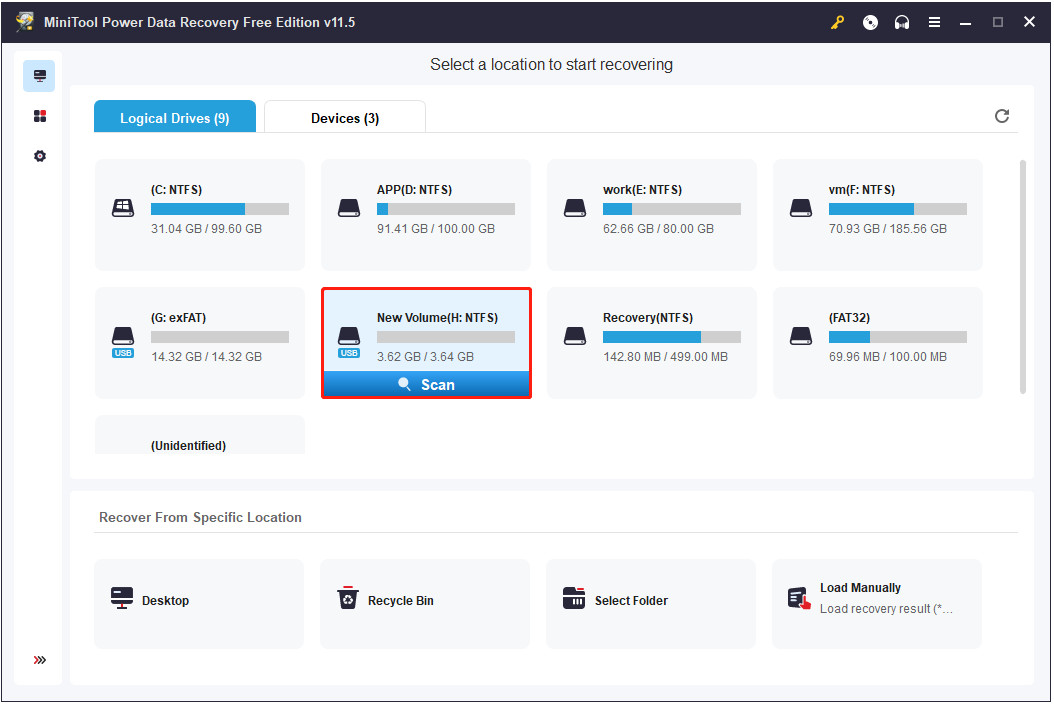 MiniTool Power Data Recovery interface with memory card selected
MiniTool Power Data Recovery interface with memory card selected
- Preview Found Files: Once the scan is complete, the software will display a list of recoverable files. You can use the “Type” category list to filter the results and show only picture files.
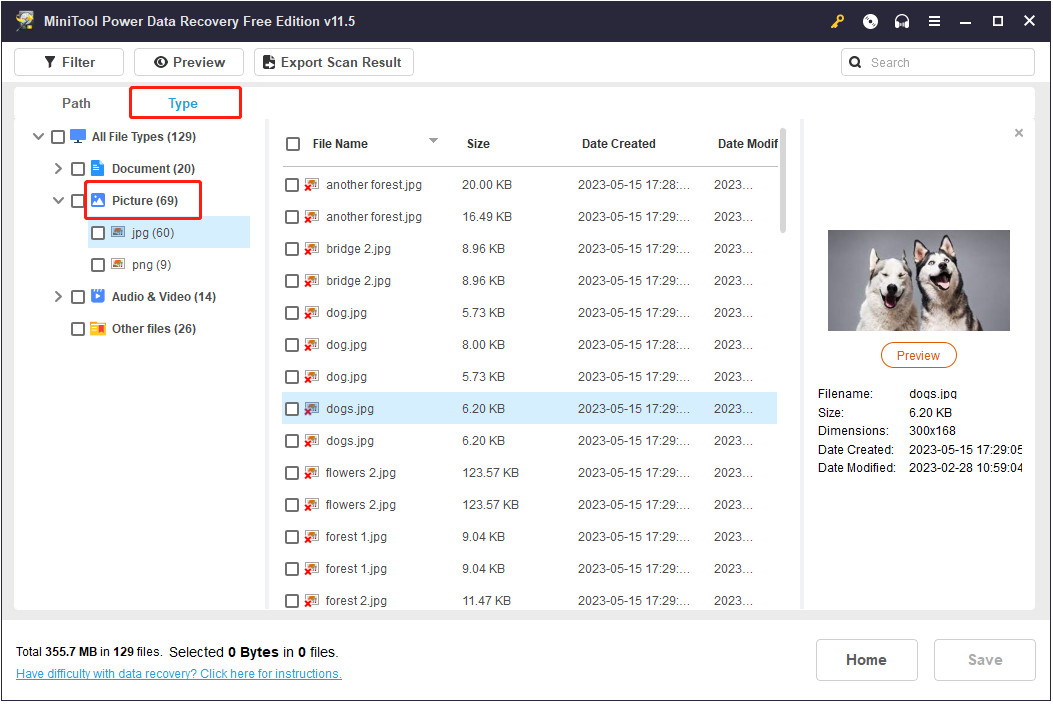 MiniTool Power Data Recovery showing picture files
MiniTool Power Data Recovery showing picture files
- Select and Save: Preview the found photos to identify the ones you want to recover. Check the boxes next to the desired files. Click the “Save” button and choose a safe location on your computer to store the recovered photos. Avoid saving them back to the original memory card, as this could overwrite other deleted files that haven’t been recovered yet.
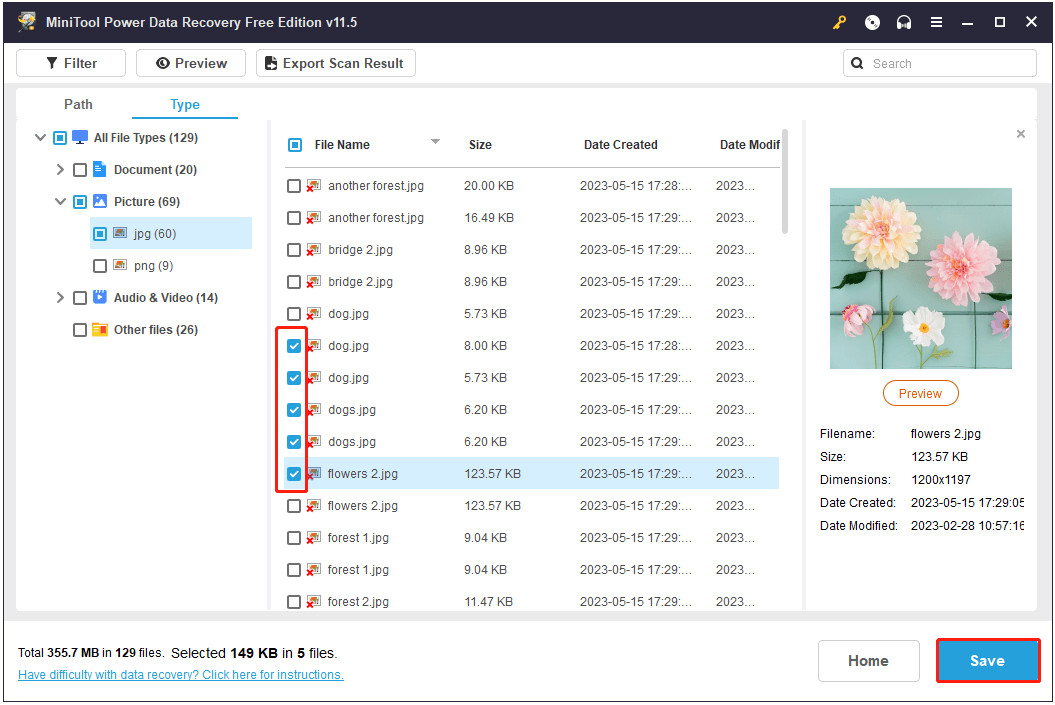 MiniTool Power Data Recovery saving recovered files
MiniTool Power Data Recovery saving recovered files
- Verify Recovery: Once the saving process is complete, navigate to the location where you saved the recovered photos and verify that they are intact and viewable.
By following these steps, you should be able to successfully recover deleted photos from your digital camera’s memory card. Remember to act quickly and avoid using the memory card after deleting photos to maximize your chances of recovery.
5. Advanced Recovery Techniques for Challenging Situations
What if the standard recovery methods don’t work? Are there more advanced techniques to try, such as deep scanning or RAW recovery?
Sometimes, standard photo recovery methods may not be enough to retrieve your lost images, especially in situations involving formatted cards, corrupted files, or severely damaged storage media. In such cases, advanced recovery techniques can significantly improve your chances of success. Here are some options to consider:
Deep Scan
Deep scan thoroughly examines the storage device sector by sector, searching for file signatures and data fragments. This method can recover files that standard scans might miss, but it takes significantly longer.
RAW Recovery
RAW photo recovery specializes in retrieving RAW image files (.CR2, .NEF, .ARW, etc.) from digital cameras. These files are unprocessed and contain more data than JPEGs, making them valuable for photographers.
Hex Editing
Hex editing involves directly examining and modifying the raw data on the storage device. This technique requires advanced technical knowledge and is typically used by data recovery professionals.
Data Recovery Services
If you’ve tried all software-based methods and still can’t recover your photos, consider seeking professional data recovery services. These services have specialized equipment and expertise to handle complex data loss situations.
File Carving
File carving is a technique used to identify and extract files based on their headers and footers. This method can be effective when file system metadata is damaged or missing.
RAID Recovery
If your photos were stored on a RAID array, you might need specialized RAID recovery software or services to reconstruct the data.
Hardware Repair
In cases of physical damage to the memory card or camera, hardware repair might be necessary before attempting data recovery.
Remember that advanced recovery techniques can be complex and potentially risky. If you’re not comfortable performing them yourself, it’s best to consult with a professional data recovery service.
6. Preventing Future Photo Loss: Best Practices
How can I prevent future photo loss from my digital camera and memory cards? Proactive measures are key.
Preventing photo loss is always better than trying to recover lost images. Here are some best practices to help you safeguard your precious memories:
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your photos to multiple locations, such as an external hard drive, cloud storage, or another computer. The 3-2-1 backup rule is a good guideline: keep three copies of your data on two different media, with one copy stored offsite.
- Safe Handling of Memory Cards: Handle memory cards with care to avoid physical damage. Store them in protective cases when not in use and avoid bending or twisting them.
- Proper Ejection: Always use the “safely remove hardware” option on your computer before ejecting a memory card.
- Avoid Interrupting Transfers: Never remove the memory card or turn off the camera during photo transfers.
- Format Cards Regularly: Format your memory cards regularly, preferably in the camera, to maintain their performance and prevent file system corruption.
- Use High-Quality Memory Cards: Invest in reputable memory cards from trusted brands to ensure reliability and data integrity.
- Monitor Battery Life: Keep an eye on your camera’s battery life and avoid shooting when the battery is low.
- Protect Against Viruses: Keep your computer and memory cards protected against viruses and malware by using antivirus software and scanning removable media regularly.
- Write-Protect Switch: Utilize the write-protect switch on SD cards to prevent accidental deletion or overwriting of files.
- Review Before Deleting: Before deleting any photos, carefully review them to ensure you’re not accidentally deleting valuable images.
By following these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of photo loss and protect your cherished memories.
7. Understanding Memory Card Types and Their Impact on Recovery
How do different types of memory cards (SD, CF, etc.) affect photo recovery? Does the card type influence the success rate or process?
The type of memory card used in your digital camera can influence the photo recovery process and its success rate. Here’s a breakdown of common memory card types and their impact on recovery:
-
SD (Secure Digital) Cards: SD cards are the most common type of memory card used in digital cameras. They are relatively small, inexpensive, and widely compatible. SD cards come in various formats, including SDHC (High Capacity) and SDXC (eXtended Capacity), which offer different storage capacities.
-
CompactFlash (CF) Cards: CF cards are larger and thicker than SD cards and are often used in high-end digital cameras. CF cards are known for their durability and fast data transfer speeds.
-
XQD Cards: XQD cards are a newer type of memory card that offers even faster data transfer speeds than CF cards. They are used in some high-end digital cameras.
-
CFast Cards: CFast cards are another type of high-speed memory card that is similar in size and shape to CF cards but uses a different interface.
Impact on Recovery:
- File System: The file system used on the memory card (e.g., FAT32, exFAT) can affect the recovery process. Some recovery software may work better with certain file systems than others.
- Wear Leveling: Some memory cards use wear leveling algorithms to distribute write operations evenly across the memory cells, which can make data recovery more challenging.
- Controller Chip: The controller chip on the memory card manages the data storage and retrieval process. A damaged or malfunctioning controller chip can make data recovery difficult or impossible.
- Physical Damage: Physical damage to the memory card, such as a cracked case or broken pins, can also affect the recovery process.
8. Using the CHKDSK Command for Memory Card Errors
Can the CHKDSK command help in recovering photos or fixing errors on my memory card? When is it appropriate to use this tool?
The CHKDSK (Check Disk) command is a Windows utility that can be used to check the integrity of a file system and fix certain types of errors on storage devices, including memory cards. While CHKDSK is not specifically designed for photo recovery, it can sometimes help in situations where the memory card has file system errors that are preventing you from accessing your photos.
When to Use CHKDSK:
-
File System Errors: If you suspect that your memory card has file system errors, such as corrupted file allocation tables or directory structures, CHKDSK can help identify and fix these issues.
-
Inaccessible Files: If you’re unable to access certain files on your memory card, CHKDSK might be able to repair the file system and make those files accessible again.
-
Error Messages: If you’re receiving error messages when trying to access your memory card, such as “The file or directory is corrupted and unreadable,” CHKDSK might be able to resolve the underlying issue.
How to Use CHKDSK:
- Connect the Memory Card: Connect the memory card to your computer using a card reader.
- Open Command Prompt: Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. You can do this by typing “cmd” in the Windows search bar, right-clicking on “Command Prompt,” and selecting “Run as administrator.”
- Run CHKDSK: In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
chkdsk X: /f /rReplace “X” with the drive letter assigned to your memory card. The “/f” parameter tells CHKDSK to fix any errors it finds, and the “/r” parameter tells it to locate bad sectors and recover readable information.
9. Professional Data Recovery Services: When to Seek Help
When should I consider using a professional data recovery service for my digital camera photos? What are the benefits and drawbacks?
While software-based photo recovery methods can be effective in many cases, there are situations where seeking professional data recovery services is the best or only option. Here are some factors to consider:
When to Consider Professional Services:
-
Physical Damage: If your memory card or digital camera has suffered physical damage, such as being dropped, crushed, or exposed to water, professional data recovery services have specialized equipment and expertise to recover data from damaged devices.
-
Severe Corruption: If the file system on your memory card is severely corrupted or overwritten, professional services may be able to use advanced techniques to reconstruct the data.
-
Failed Recovery Attempts: If you’ve tried multiple software-based recovery methods without success, professional services may have a higher chance of success due to their advanced tools and expertise.
-
Time Sensitivity: If you need to recover your photos quickly, professional services can often provide faster turnaround times than DIY methods.
Benefits of Professional Services:
- Expertise: Professional data recovery technicians have extensive knowledge and experience in dealing with various data loss scenarios.
- Specialized Equipment: Professional services have access to specialized equipment, such as cleanroom environments and advanced imaging tools, that can improve the chances of successful recovery.
- Higher Success Rates: In complex data loss situations, professional services often have higher success rates than DIY methods.
- Data Confidentiality: Reputable data recovery services adhere to strict data confidentiality policies and take measures to protect your privacy.
Drawbacks of Professional Services:
- Cost: Professional data recovery services can be expensive, especially for complex cases.
- Turnaround Time: The recovery process can take several days or even weeks, depending on the complexity of the case.
10. Ethical Considerations in Photo Recovery
Are there any ethical considerations when recovering deleted photos, especially if the camera or memory card belongs to someone else?
Yes, there are indeed ethical considerations to keep in mind when recovering deleted photos, especially if the camera or memory card belongs to someone else. Here are some key points:
Respect for Privacy:
- Obtain Consent: If you’re recovering photos from a device that belongs to someone else, always obtain their explicit consent before attempting any recovery.
- Limit Scope: Even with consent, limit your recovery efforts to only the photos that the owner has authorized you to retrieve. Avoid browsing or recovering other files that may be private or confidential.
Data Security:
- Protect Recovered Data: Once you’ve recovered the photos, take steps to protect the data from unauthorized access. This may involve encrypting the files, storing them in a secure location, or deleting them permanently once they’re no longer needed.
- Dispose of Data Securely: If you’re unable to return the recovered data to the owner, dispose of it securely by wiping the storage device or using a data destruction service.
Looking to enhance your photography skills and explore the world of visual artistry? Visit dfphoto.net today to discover insightful tutorials, stunning photography, and a vibrant community of fellow photography enthusiasts. Join us and ignite your passion for photography! Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
Digital Camera Photo Recovery FAQ
1. Can deleted pictures be recovered from a digital camera?
Yes, deleted pictures can often be recovered from a digital camera if you act quickly and use the appropriate recovery methods. The key is to stop using the camera immediately after realizing the photos have been deleted to prevent overwriting.
2. How do I recover deleted pictures from my digital camera memory card?
To recover deleted pictures from your digital camera memory card, connect the card to your computer using a card reader, then use photo recovery software to scan the card and retrieve the deleted files. Save the recovered photos to a different storage device to avoid overwriting.
3. How to recover deleted photos from Canon digital camera for free?
To recover deleted photos from a Canon digital camera for free, you can try using free photo recovery software like MiniTool Power Data Recovery. Connect your camera or memory card to your computer, run the software, scan the device, and recover the deleted photos.
4. How do I recover photos after formatting the SD card?
To recover photos after formatting the SD card, use photo recovery software that specializes in recovering data from formatted drives. Connect the SD card to your computer, run the software, select the SD card, and start the scanning process.
5. What is the best photo recovery software for digital cameras?
The best photo recovery software for digital cameras depends on your specific needs and budget. However, some popular options include MiniTool Power Data Recovery, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, and Stellar Photo Recovery.
6. Can I recover photos from a physically damaged memory card?
Recovering photos from a physically damaged memory card can be challenging and often requires professional data recovery services. These services have specialized equipment and expertise to recover data from damaged storage devices.
7. How does file system type affect photo recovery?
The file system type (e.g., FAT32, exFAT) can affect photo recovery because different file systems have different ways of organizing and storing data. Some recovery software may work better with certain file systems than others.
8. What is deep scan in photo recovery software?
Deep scan is a more thorough scanning mode in photo recovery software that searches for file signatures and data fragments at a sector level. This method can recover files that standard scans might miss, but it takes significantly longer.
9. Is it possible to recover RAW image files from a digital camera?
Yes, it is possible to recover RAW image files from a digital camera using specialized photo recovery software that supports RAW file formats. These programs can identify and extract RAW files based on their unique file signatures.
10. What precautions should I take to prevent photo loss in the future?
To prevent photo loss in the future, regularly back up your photos to multiple locations, handle memory cards with care, use the “safely remove hardware” option, avoid interrupting transfers, format cards regularly, and use high-quality memory cards.