This article explores the question of How To Look At Recently Deleted Photos, and dfphoto.net provides comprehensive solutions for both amateur and professional photographers. We will show you how to recover these photos on various devices and platforms. You’ll discover valuable insights into preventing data loss, explore different techniques to see recently deleted pictures, and learn about reliable methods to restore them, ensuring that your precious memories are never truly lost, as well as photography services.
1. What Are The First Steps To Take When You Accidentally Delete Photos?
The first thing you should do when you accidentally delete photos is to immediately stop using the device to prevent overwriting, then check the “Recently Deleted” album and any cloud backups. By quickly acting and looking for options within the device itself or backups, the chance of a successful retrieval is higher.
When you realize you’ve accidentally deleted photos, swift action is crucial. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
-
Stop Using the Device: The moment you realize the error, cease using your device (phone, camera, computer). Each new photo taken, file saved, or app used increases the risk of overwriting the deleted files. Overwriting means the space where the deleted photos were stored is now occupied by new data, making recovery difficult or impossible.
-
Check the ‘Recently Deleted’ Album: Most smartphones and operating systems have a built-in “Recently Deleted” or “Trash” folder. This is the first place to look.
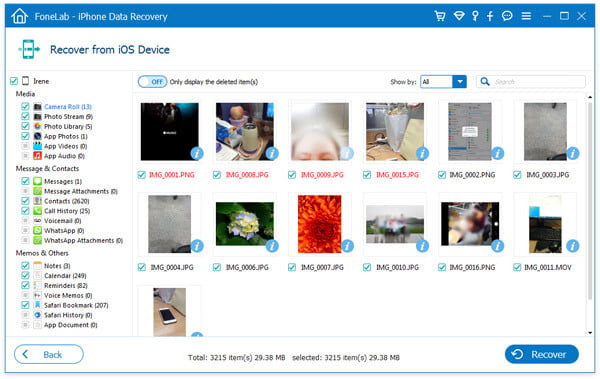
- iPhones/iPads: Open the Photos app, tap on Albums, and scroll down to find the “Recently Deleted” album. Photos remain here for 30 days before permanent deletion. You can select the photos you want to recover and tap “Recover.”
- Android Devices: The process varies depending on the manufacturer. Generally, you can find a “Trash” or “Recently Deleted” folder in the Gallery app. For example, on Samsung devices, open the Gallery app and look for “Trash” in the menu.
- Windows: Check the Recycle Bin on your desktop. Deleted files are stored here until you manually empty the bin.
- macOS: Look in the Trash icon on your dock. You can drag files out of the Trash to restore them.
-
Cloud Backups:
- iCloud (Apple): If you use iCloud Photos, your photos might already be backed up. Sign in to iCloud on your computer or another device to see if the deleted photos are there.
- Google Photos (Android, iOS, Web): Google Photos automatically backs up photos if you’ve enabled the feature. Check the Google Photos app or website for your photos. Look in the “Trash” or “Bin” section. Photos stay in the trash for 60 days.
- Other Cloud Services: If you use other cloud services like Dropbox, OneDrive, or Amazon Photos, check their respective apps or websites for your photos.
Why These Steps Are Important
- Minimizing Overwriting: According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, immediately ceasing device usage significantly minimizes the risk of overwriting, a critical factor in successful data recovery.
- Quick Retrieval: The “Recently Deleted” album and cloud backups offer the quickest and easiest way to recover photos without needing technical expertise or additional software.
2. How Do Data Recovery Tools Work To Restore Deleted Photos?
Data recovery tools work by scanning the device’s storage for traces of deleted photo files and piecing them back together, but their effectiveness decreases if the data has been overwritten. These tools are helpful, but should be used immediately for best results.
Data recovery tools are designed to delve deep into your device’s storage system to find and restore deleted photos. Here’s a breakdown of how they operate:
-
Scanning the Storage: When a file is deleted, it’s not immediately wiped from the storage medium (hard drive, SSD, memory card). Instead, the operating system marks the space it occupied as “available” for new data. The actual data remains until it’s overwritten by new information. Data recovery tools scan the storage sector by sector, looking for these remnants.
-
File Signature Recognition: Every file type has a unique “signature,” a specific pattern of bytes at the beginning of the file. Recovery tools use these signatures to identify deleted photo files, even if the file names and directory structure are lost. For example, JPEG files typically start with the bytes
FF D8 FF E0orFF D8 FF E1. -
Reconstructing Files: Once a tool identifies a deleted photo, it attempts to reconstruct the file by piecing together the fragmented data. This process can be complex because deleted files are often scattered across different parts of the storage.
-
Algorithms and Techniques: Data recovery tools employ various algorithms and techniques to improve their chances of success:
- Deep Scan: This thorough scan examines every sector of the storage, which can take a long time but increases the likelihood of finding recoverable files.
- Partition Recovery: If a partition (a section of the hard drive) has been accidentally deleted or formatted, these tools can attempt to rebuild the partition table and recover the data.
- File Carving: This technique involves searching for file signatures and extracting the data based on those signatures, regardless of the file system structure.
-
Preview and Selective Recovery: Most data recovery tools allow you to preview the recovered photos before restoring them. This allows you to select only the files you need, saving time and storage space.
Factors Affecting Success
- Time Elapsed: The longer you wait to use a data recovery tool, the lower your chances of success. The more you use your device after deletion, the greater the risk of overwriting.
- Storage Type: SSDs (Solid State Drives) can be more challenging to recover data from compared to traditional HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). SSDs use a technology called TRIM, which automatically wipes deleted data to improve performance.
- File System: The file system (e.g., NTFS, FAT32, APFS) affects how data is stored and deleted. Some file systems are easier to recover data from than others.
- Overwriting: If the sectors where the deleted photos were stored have been overwritten with new data, recovery is usually impossible.
Popular Data Recovery Tools
- Recuva: A free and user-friendly tool for Windows.
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard: A powerful tool for Windows and macOS.
- Stellar Data Recovery: A comprehensive tool for various storage devices.
- Disk Drill: A popular choice for macOS with a user-friendly interface.
- PhotoRec: A free, open-source tool that specializes in photo recovery.
Remember to download data recovery tools from reputable sources to avoid malware. Install the tool on a separate drive or device to prevent further data loss.
3. What Are Some Top-Rated Data Recovery Tools Recommended by Experts?
Experts recommend tools like Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Stellar Data Recovery, Disk Drill, and PhotoRec, all known for their effectiveness and user-friendly interfaces. Choosing one depends on your operating system and particular data loss situation.
-
Recuva
- Pros: Free, user-friendly, and efficient for basic recovery needs.
- Cons: Less effective for complex data loss scenarios compared to paid options.
- Use Case: Ideal for quick recovery of accidentally deleted photos on Windows systems.
-
EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard
- Pros: Powerful, supports various file types, and has a high success rate. Available for both Windows and macOS.
- Cons: The free version has limited recovery capacity; the full version can be expensive.
- Use Case: Suitable for more complex data loss situations, such as formatted drives or partition loss.
-
Stellar Data Recovery
- Pros: Comprehensive, recovers data from various storage devices, and offers advanced features like corrupted photo repair.
- Cons: Can be pricey, and the interface might be overwhelming for beginners.
- Use Case: Best for professional photographers and users with diverse data recovery needs.
-
Disk Drill
- Pros: User-friendly interface, robust scanning capabilities, and available for macOS and Windows.
- Cons: The free version has limited features, and the full version is relatively expensive.
- Use Case: Excellent for Mac users who need a reliable and easy-to-use data recovery tool.
-
PhotoRec
- Pros: Free, open-source, and supports a wide range of file systems.
- Cons: Command-line interface, which can be intimidating for non-technical users.
- Use Case: Ideal for advanced users who need a powerful and free photo recovery tool.
Here’s a comparison table:
| Tool | Pros | Cons | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recuva | Free, user-friendly | Less effective for complex scenarios | Quick, basic photo recovery on Windows |
| EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard | Powerful, supports various file types | Limited free version, can be expensive | Complex data loss, formatted drives, partition loss |
| Stellar Data Recovery | Comprehensive, recovers from various storage devices, photo repair | Pricey, overwhelming interface | Professional photographers with diverse needs |
| Disk Drill | User-friendly interface, robust scanning | Limited free version, relatively expensive | Mac users needing a reliable and easy-to-use tool |
| PhotoRec | Free, open-source, supports a wide range of file systems | Command-line interface | Advanced users needing a powerful, free photo recovery tool |
When selecting a data recovery tool, consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS) and the type of storage device (HDD, SSD, memory card).
- Ease of Use: Choose a tool with a user-friendly interface, especially if you’re not technically inclined.
- Features: Look for features like deep scanning, file preview, and selective recovery.
- Price: Consider your budget and whether the free version meets your needs. If not, compare the prices of different paid options.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the tool’s effectiveness and reliability.
4. Is It Possible To Recover Photos From An iPhone Without A Backup?
Yes, it is possible to recover photos from an iPhone without a backup using specialized data recovery software, though success isn’t guaranteed and depends on whether the data has been overwritten. Acting quickly increases the chances of recovery.
Even without a backup, there are ways to attempt to recover deleted photos from an iPhone.
-
Data Recovery Software:
-
How it Works: Data recovery software scans the iPhone’s internal storage for remnants of deleted photo files. These tools use sophisticated algorithms to identify and reconstruct data fragments.
-
Examples: Popular options include Dr.Fone, iMyFone D-Back, and Tenorshare UltData.
-
Success Factors: The success of recovery depends on several factors:
- Time Since Deletion: The sooner you act, the better. The longer you wait, the greater the chance that the deleted data will be overwritten by new data.
- iPhone Usage: Minimizing iPhone usage after deletion is crucial. Avoid taking new photos, downloading apps, or even browsing the internet, as these activities can overwrite the deleted files.
- Storage Type: iPhones use NAND flash memory, which can make data recovery more challenging compared to traditional hard drives.
-
Steps:
- Choose a reputable data recovery software: Research and select a tool that is specifically designed for iPhone data recovery.
- Install the software on your computer: Download and install the software on your Mac or PC.
- Connect your iPhone: Connect your iPhone to your computer using a USB cable.
- Start the scan: Launch the data recovery software and follow the on-screen instructions to scan your iPhone.
- Preview and recover: After the scan is complete, preview the recoverable photos and select the ones you want to restore.
- Save the recovered photos: Save the recovered photos to a safe location on your computer or an external drive.
-
-
Limitations:
- No Guarantee: Data recovery software doesn’t guarantee 100% recovery. The success rate varies depending on the factors mentioned above.
- Overwriting: If the deleted photos have been overwritten, they are likely unrecoverable.
- Cost: Data recovery software can be expensive, and free versions often have limited features.
-
iCloud Considerations:
- Recently Deleted Album: As mentioned earlier, check the “Recently Deleted” album in the Photos app. Photos stay here for 30 days.
- iCloud Photos: If you had iCloud Photos enabled, your photos might be backed up to iCloud. Sign in to iCloud on your computer or another device to see if the deleted photos are there.
-
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Backups: The best way to protect your photos is to create regular backups using iCloud, iTunes, or a third-party backup service.
- iCloud Photos: Enable iCloud Photos to automatically back up your photos to iCloud.
-
DFphoto.net Insights
- Explore dfphoto.net for articles on best practices for iPhone photography and data management. Our tutorials can guide you through setting up reliable backup systems and optimizing your iPhone’s storage for photography.
5. What Should I Consider When Choosing A Data Recovery Service?
When choosing a data recovery service, consider their reputation, success rate, expertise with your device type, data security measures, and pricing transparency. Reading reviews and getting detailed quotes are critical before entrusting them with your data.
Selecting the right data recovery service is essential to ensure the safety and successful retrieval of your deleted photos. Here’s what you should consider:
-
Reputation and Reviews:
- Online Reviews: Look for online reviews and testimonials on sites like Yelp, Google Reviews, and the Better Business Bureau (BBB). Pay attention to both positive and negative feedback.
- Case Studies: Check if the service provider has case studies or success stories that showcase their expertise.
- Referrals: Ask for referrals from friends, family, or colleagues who have used data recovery services in the past.
-
Success Rate and Expertise:
- Device Type: Ensure the service specializes in recovering data from your specific device type (e.g., iPhone, Android, HDD, SSD, memory card).
- Data Loss Scenario: Ask about their experience with similar data loss scenarios (e.g., accidental deletion, formatting, physical damage).
- Success Rate: Inquire about their success rate for data recovery. While no service can guarantee 100% recovery, a higher success rate indicates greater expertise and reliability.
-
Data Security and Confidentiality:
- Privacy Policy: Review the service’s privacy policy to understand how they handle your data.
- Secure Facility: Ensure they have a secure facility with restricted access to protect your data from unauthorized access.
- Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA): Ask if they are willing to sign an NDA to guarantee the confidentiality of your data.
- Data Encryption: Check if they use data encryption to protect your data during transit and storage.
-
Pricing and Transparency:
- Free Evaluation: Look for a service that offers a free evaluation to assess the feasibility of data recovery and provide a cost estimate.
- Fixed Price vs. Hourly Rate: Understand how they charge for their services. A fixed price is preferable to an hourly rate, as it provides greater cost certainty.
- No Data, No Fee Policy: Inquire about their “no data, no fee” policy. This means you only pay if they successfully recover your data.
- Detailed Quote: Get a detailed quote that outlines all costs, including evaluation fees, recovery fees, and any additional charges.
-
Turnaround Time:
- Estimated Timeframe: Ask for an estimated timeframe for data recovery. The turnaround time can vary depending on the complexity of the data loss scenario.
- Expedited Services: Inquire about expedited services if you need your data recovered urgently.
-
Customer Support:
- Availability: Ensure the service offers responsive customer support via phone, email, or chat.
- Communication: Check if they provide regular updates on the progress of your data recovery.
-
Facility and Equipment:
- Cleanroom Environment: For physically damaged devices, ensure the service has a cleanroom environment to prevent further damage during the recovery process.
- Advanced Equipment: Check if they have advanced equipment and tools for data recovery, such as data imagers, logic analyzers, and specialized software.
-
DFphoto.net Recommendation
- At dfphoto.net, we emphasize the importance of data security. Explore our articles on secure data storage practices and encryption methods to protect your valuable photos before a loss occurs.
6. How Can Cloud Storage Help Prevent Permanent Photo Loss?
Cloud storage helps prevent permanent photo loss by automatically backing up your images to a secure, off-site location, ensuring they’re safe even if your primary device is lost, damaged, or stolen. Automatic syncing and version history add extra layers of protection.
Cloud storage provides a reliable and convenient way to safeguard your photos from permanent loss.
-
Automatic Backup:
- Real-time Sync: Cloud storage services automatically sync your photos to the cloud as soon as they are taken or saved on your device. This ensures that your photos are backed up in real-time, minimizing the risk of data loss.
- Background Uploads: Most cloud storage apps run in the background, silently uploading your photos without interrupting your workflow.
-
Off-Site Storage:
- Protection Against Physical Damage: Cloud storage protects your photos from physical damage to your device, such as theft, fire, water damage, or hardware failure.
- Accessibility from Anywhere: You can access your photos from any device with an internet connection, allowing you to view, download, and share your photos from anywhere in the world.
-
Version History:
- Accidental Deletion Recovery: Some cloud storage services offer version history, which allows you to restore previous versions of your photos if you accidentally delete or overwrite them.
- File Corruption Protection: Version history can also protect against file corruption, allowing you to revert to a previous, uncorrupted version of your photo.
-
Redundancy:
- Multiple Copies: Cloud storage providers typically store multiple copies of your data on different servers in different locations. This redundancy ensures that your photos are safe even if one server fails.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud storage providers have disaster recovery plans in place to protect your data from natural disasters, power outages, and other unforeseen events.
-
Scalability:
- Flexible Storage: Cloud storage allows you to easily scale your storage capacity as your photo collection grows.
- Cost-Effective: Cloud storage can be more cost-effective than purchasing and maintaining physical storage devices, especially for large photo collections.
-
Collaboration:
- Easy Sharing: Cloud storage makes it easy to share your photos with friends, family, or colleagues.
- Collaborative Editing: Some cloud storage services offer collaborative editing features, allowing multiple users to work on the same photos simultaneously.
Popular Cloud Storage Services for Photos
- Google Photos: Offers unlimited storage for “high quality” photos and videos, as well as automatic organization and sharing features.
- iCloud Photos: Integrates seamlessly with Apple devices and provides automatic backup and syncing of your photos across all your devices.
- Dropbox: A versatile cloud storage service that offers file syncing, sharing, and version history.
- OneDrive: Microsoft’s cloud storage service that integrates with Windows and Office apps.
- Amazon Photos: Offers unlimited photo storage for Amazon Prime members, as well as automatic organization and sharing features.
Choosing the Right Cloud Storage Service
- Storage Capacity: Consider how much storage space you need for your photo collection.
- Pricing: Compare the pricing plans of different cloud storage services to find the best value for your needs.
- Features: Look for features like automatic backup, version history, file sharing, and collaborative editing.
- Integration: Choose a cloud storage service that integrates well with your devices and workflow.
- Security: Ensure the cloud storage service offers robust security measures to protect your photos from unauthorized access.
By using cloud storage, you can protect your precious photos from permanent loss and ensure that they are always accessible, no matter what happens to your device.
7. What Are The Best Practices For Regularly Backing Up Photos?
The best practices for regularly backing up photos include using a combination of local and cloud backups, automating the backup process, organizing your photos logically, and periodically verifying your backups to ensure they are working correctly.
Regularly backing up your photos is crucial for preventing data loss and preserving your memories.
-
Implement a 3-2-1 Backup Strategy:
- Three Copies: Keep at least three copies of your photos.
- Two Different Media: Store the copies on two different types of media (e.g., hard drive, SSD, cloud storage).
- One Off-Site: Keep one copy off-site in case of a disaster at your primary location.
-
Use a Combination of Local and Cloud Backups:
- Local Backup: Use an external hard drive or NAS (Network Attached Storage) device for fast and easy access to your photos.
- Cloud Backup: Use a cloud storage service for off-site backup and protection against physical damage.
-
Automate the Backup Process:
- Backup Software: Use backup software that automatically backs up your photos on a regular schedule.
- Cloud Sync: Enable automatic syncing in your cloud storage app to continuously back up your photos to the cloud.
-
Organize Your Photos Logically:
- Folder Structure: Create a clear and consistent folder structure to organize your photos by date, event, or project.
- Metadata: Use metadata (e.g., tags, captions, keywords) to add additional information to your photos and make them easier to find.
-
Verify Your Backups Regularly:
- Test Restore: Periodically test your backups by restoring a few photos to ensure they are working correctly.
- Check Integrity: Use checksum tools to verify the integrity of your backup files.
-
Use Redundant Storage Solutions:
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Consider using a RAID configuration for your local backup storage to protect against hard drive failure.
-
Encrypt Your Backups:
- Password Protection: Use password protection and encryption to protect your backups from unauthorized access.
-
Keep Your Backup Software Up-to-Date:
- Security Patches: Update your backup software regularly to ensure you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
-
Store Your Backups in a Safe Place:
- Physical Security: Store your local backups in a safe and secure location to protect them from theft, fire, or other physical damage.
-
Document Your Backup Process:
- Backup Plan: Create a written backup plan that outlines your backup strategy, schedule, and procedures.
-
Regularly Review and Update Your Backup Strategy:
- Evolving Needs: As your photo collection grows and your technology changes, regularly review and update your backup strategy to ensure it still meets your needs.
By following these best practices, you can create a robust and reliable backup system that protects your photos from permanent loss and ensures that your memories are always safe.
8. How Do Different File Systems Affect Photo Recovery?
Different file systems (like NTFS, FAT32, APFS, and ext4) affect photo recovery because they manage data storage and deletion differently. Some file systems make it easier to recover deleted files due to their structure and metadata management, while others offer fewer recovery opportunities.
The file system plays a significant role in the feasibility of photo recovery.
-
NTFS (New Technology File System):
- Used by: Windows operating systems.
- Impact on Recovery: NTFS has a complex file system structure that includes a Master File Table (MFT) containing metadata about files and directories. When a file is deleted, its entry in the MFT is marked as “free,” but the file data remains on the disk until overwritten. This makes it possible to recover deleted photos using data recovery tools, which can scan the disk for remnants of deleted files. NTFS also supports file compression and encryption, which can complicate the recovery process.
-
FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32):
- Used by: Older Windows systems, USB drives, and memory cards.
- Impact on Recovery: FAT32 has a simpler file system structure than NTFS. When a file is deleted, its entry in the File Allocation Table (FAT) is marked as “free,” but the file data remains on the disk until overwritten. Data recovery tools can scan the disk for deleted files, but the chances of successful recovery are lower than with NTFS because FAT32 does not store as much metadata. FAT32 also has a file size limit of 4GB, which can be a limitation for large photo files.
-
APFS (Apple File System):
- Used by: macOS operating systems.
- Impact on Recovery: APFS is a modern file system designed for SSDs and flash storage. It uses a copy-on-write mechanism, which means that when a file is modified, the changes are written to a new location on the disk, and the old version is preserved until it is overwritten. This makes it possible to recover deleted photos using data recovery tools, which can scan the disk for previous versions of files. APFS also supports encryption and snapshots, which can complicate the recovery process.
-
exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table):
- Used by: USB drives, memory cards, and other removable storage devices.
- Impact on Recovery: exFAT is a file system designed for large storage devices. It is similar to FAT32 but does not have the 4GB file size limit. When a file is deleted, its entry in the file allocation table is marked as “free,” but the file data remains on the disk until overwritten. Data recovery tools can scan the disk for deleted files, but the chances of successful recovery are lower than with NTFS or APFS because exFAT does not store as much metadata.
-
ext4 (Fourth Extended Filesystem):
- Used by: Linux operating systems.
- Impact on Recovery: Ext4 is a journaling file system, which means that it keeps a log of changes made to the file system. This can make it possible to recover deleted photos using data recovery tools, which can scan the journal for information about deleted files. Ext4 also supports file compression and encryption, which can complicate the recovery process.
Here’s a summary table:
| File System | Operating System | Metadata Storage | Recovery Difficulty | File Size Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTFS | Windows | High | Medium | No practical limit |
| FAT32 | Older Windows, USB | Low | High | 4GB |
| APFS | macOS | High | Medium | No practical limit |
| exFAT | USB, Memory Cards | Low | High | No practical limit |
| ext4 | Linux | Medium | Medium | No practical limit |
Factors Affecting Recovery
- File System Structure: The complexity of the file system structure affects how easy it is to locate and recover deleted files.
- Metadata Storage: The amount of metadata stored by the file system affects how much information is available about deleted files, such as file names, dates, and locations.
- Journaling: Journaling file systems keep a log of changes made to the file system, which can be helpful for recovering deleted files.
- File Fragmentation: File fragmentation can make it more difficult to recover deleted files, as the file data is scattered across different parts of the disk.
- Overwriting: If the sectors where the deleted photos were stored have been overwritten with new data, recovery is usually impossible.
When attempting to recover photos from a specific file system, it’s important to use data recovery tools that are designed to work with that file system. Some data recovery tools are better suited for certain file systems than others.
9. Can Formatting A Storage Device Impact Photo Recovery?
Yes, formatting a storage device significantly impacts photo recovery by erasing the file system structure and making it more difficult to locate and recover deleted photos. Quick formats offer a slightly better chance of recovery compared to full formats.
Formatting a storage device has a significant impact on photo recovery, and the extent of the impact depends on the type of formatting performed.
-
Quick Format:
- How it Works: A quick format erases the file system structure, but it does not erase the actual data on the disk. It simply marks the space as available for new data.
- Impact on Recovery: A quick format makes it more difficult to recover deleted photos, but it is still possible to recover them using data recovery tools. The chances of successful recovery are higher than with a full format.
-
Full Format:
- How it Works: A full format erases the file system structure and overwrites the entire disk with zeros or random data.
- Impact on Recovery: A full format makes it very difficult or impossible to recover deleted photos. Overwriting the data with zeros or random data effectively destroys the original data, making it unrecoverable.
-
Low-Level Format:
- How it Works: A low-level format is a more intensive process that rewrites the entire disk at the physical level.
- Impact on Recovery: A low-level format makes it virtually impossible to recover deleted photos. It completely erases the original data and rewrites the disk structure.
-
File System Damage:
- Corruption: Formatting a storage device can sometimes cause file system damage, which can make it more difficult to recover deleted photos.
-
Data Overwriting:
- New Data: After formatting a storage device, any new data written to the disk will overwrite the original data, making it unrecoverable.
-
Data Recovery Tools:
- Limitations: Data recovery tools may still be able to recover some data after formatting, but the chances of successful recovery are significantly reduced.
Here’s a summary table:
| Format Type | Data Erasing | Recovery Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Format | File system structure | Medium to High |
| Full Format | File system structure, data overwritten | Very High |
| Low-Level Format | Complete data rewriting | Virtually Impossible |
Factors Affecting Recovery After Formatting
- Type of Format: The type of formatting performed (quick, full, or low-level) has a significant impact on the chances of successful recovery.
- Time Since Formatting: The sooner you attempt to recover data after formatting, the higher your chances of success.
- Data Overwriting: Any new data written to the disk after formatting will overwrite the original data, making it unrecoverable.
- Data Recovery Tools: The effectiveness of data recovery tools depends on the type of formatting performed and the condition of the disk.
If you accidentally format a storage device containing important photos, stop using the device immediately and use data recovery tools to attempt to recover the data.
10. How Can DFphoto.net Help Me Learn More About Photo Recovery and Data Backup?
DFphoto.net can help you learn more about photo recovery and data backup by providing comprehensive articles, tutorials, and resources that cover various aspects of digital photography, including data management, backup strategies, and recovery techniques.
DFphoto.net is a valuable resource for learning more about photo recovery and data backup.
-
Comprehensive Articles:
- In-depth Guides: DFphoto.net provides comprehensive articles that cover various aspects of digital photography, including data management, backup strategies, and recovery techniques.
- Expert Advice: The articles are written by experienced photographers and data recovery professionals, offering practical advice and tips.
-
Tutorials:
- Step-by-Step Instructions: DFphoto.net offers step-by-step tutorials that guide you through the process of data recovery and backup.
- Visual Aids: The tutorials include screenshots and videos to help you understand the concepts and follow the instructions.
-
Resource Library:
- Software Recommendations: DFphoto.net provides a resource library that includes recommendations for data recovery software, backup tools, and other useful resources.
- External Links: The resource library also includes links to external websites, forums, and communities where you can find additional information and support.
-
Community Forums:
- Ask Questions: DFphoto.net hosts community forums where you can ask questions, share your experiences, and get advice from other photographers and data recovery professionals.
- Connect with Experts: The forums provide a platform to connect with experts and get personalized assistance.
-
News and Updates:
- Latest Trends: DFphoto.net keeps you up-to-date on the latest trends and technologies in data recovery and backup.
- Software Updates: The website provides news and updates about data recovery software and backup tools, including new releases, bug fixes, and security patches.
-
Case Studies:
- Real-World Examples: DFphoto.net features case studies that showcase real-world examples of data recovery and backup scenarios.
- Lessons Learned: The case studies provide valuable insights and lessons learned from successful and unsuccessful data recovery attempts.
-
Best Practices:
- Backup Strategies: DFphoto.net provides best practices for creating a robust and reliable backup strategy.
- Data Management: The website offers tips for organizing and managing your photos to prevent data loss.
-
DFphoto.net Insights
- Explore dfphoto.net for articles on best practices for iPhone photography and data management. Our tutorials can guide you through setting up reliable backup systems and optimizing your iPhone’s storage for photography.
-
DFphoto.net Recommendation
- At dfphoto.net, we emphasize the importance of data security. Explore our articles on secure data storage practices and encryption methods to protect your valuable photos before a loss occurs.
By utilizing dfphoto.net’s resources, you can enhance your knowledge and skills in photo recovery and data backup, ensuring that your precious photos are always safe and accessible.
 Close up of a phone screen with recently deleted album selected in photo library
Close up of a phone screen with recently deleted album selected in photo library
FAQ: Recovering Recently Deleted Photos
1. Where do deleted photos go on my phone?
Deleted photos typically go into a “Recently Deleted” or “Trash” album within your phone’s photo application, where they remain for a limited time before being permanently erased. This album provides a temporary holding space for deleted photos, allowing you to recover them if you change your mind.
2. How long do photos stay in the “Recently Deleted” album?
Photos usually stay in the “Recently Deleted” album for 30 days on iPhones and 60 days on Google Photos before they are permanently deleted. This timeframe provides a window of opportunity to recover any photos you accidentally deleted.
3. Can I recover permanently deleted photos without a backup?
Yes, it is possible to recover permanently deleted photos without a backup using data recovery software, but the success rate decreases over time and depends on whether the data has been overwritten. Acting quickly and minimizing device usage increases the chances of successful recovery.
4. What is the best data recovery software for iPhones?
Some of the top-rated data recovery software for iPhones include Dr.Fone, iMyFone D-Back, and Tenorshare UltData, known for their effectiveness in scanning and recovering various types of data, including photos, from iOS devices. These tools scan the device’s storage for recoverable files.
5. How does cloud storage prevent photo loss?
Cloud storage prevents photo loss by automatically backing up your photos to a secure, off-site location