Are you looking to unlock the hidden information within your photos and understand How To Find Metadata On A Photo? At dfphoto.net, we delve into the world of image metadata, explaining what it is, why it matters, and how you can access and even edit it, offering a comprehensive guide for photographers, marketers, and anyone managing digital images. By mastering metadata, you can organize your photos effectively, protect your copyrights, and enhance your search engine optimization (SEO).
1. Unveiling Photo Metadata: The Hidden Secrets
Photo metadata is the embedded information within a digital image file, akin to a digital fingerprint. It offers a wealth of details about the photo, ranging from technical data to descriptive information and copyright details. Think of it as the behind-the-scenes story of your image.
1.1. Why Photo Metadata Matters
Photo metadata is the backbone of digital image management for several compelling reasons:
- Organization: It enables you to categorize images using location, keywords, and other criteria.
- Searchability: Descriptive tags and keywords allow you to quickly find specific images.
- Copyright Management: Embedded copyright information protects your rights as the image owner.
- Technical Analysis: Photographers can analyze camera settings to improve future shoots.
- Context: It preserves crucial details like time and location, maintaining the photo’s historical value.
1.2. The Core Components of Photo Metadata
Photo metadata typically includes:
- Creation date
- Author
- File name
- Content
- Size in bits and pixels
- Themes
- GPS coordinates or other location information
- Camera settings (ISO speed, shutter speed, focal length, etc.)
- Copyright information
2. Navigating the Metadata Categories
Metadata is organized into three primary categories, each with distinct roles and types of information:
2.1. Descriptive Metadata
Descriptive metadata focuses on identifying and discovering resources. It includes elements like:
- Title
- Abstract
- Author
- Keywords
This category is vital for finding relevant resources in libraries, museums, and digital asset management systems.
2.2. Structural Metadata
Structural metadata provides insights into a resource’s organization and format. It defines the structure of complex objects, such as:
- The sequence of pages in a book
- Relationships between collections of images, texts, and datasets
This metadata is crucial for presenting and navigating complex data sets effectively.
2.3. Administrative Metadata
Administrative metadata manages resources, including details like:
- Creation time and method
- File format
- Access and rights information
This category can be further divided into:
2.3.1. Technical Metadata
Technical metadata describes the technical aspects of a resource:
- File types
- Compression algorithms
- File sizes
It is essential for digital preservation and ensuring ongoing access to digital files.
2.3.2. Preservation Metadata
Preservation metadata maintains digital resources over time, including:
- The digital object’s history
- Its condition
- Actions taken to preserve it
2.3.3. Rights Metadata
Rights metadata covers intellectual property rights and restrictions:
- Access limitations
- Usage conditions
It helps organizations manage the legal aspects of digital asset usage.
 The three categories of metadata as icons with a woman on a laptop over a green background.
The three categories of metadata as icons with a woman on a laptop over a green background.
3. Diving into Common Photo Metadata Formats
Understanding the various metadata formats can help you better manage and interpret photo information:
3.1. EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format)
EXIF is a standard format for storing interchange information in digital photography. It includes details about camera settings, such as shutter speed, aperture, ISO setting, and date/time the photo was taken, as well as information about the image itself like orientation.
- Key Uses: Storing essential camera settings and image details.
- Benefits: Enhances post-processing analysis and understanding of image capture conditions.
- Limitations: Primarily focused on camera-specific data; may lack extensive descriptive fields.
3.2. IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council)
Developed for the press industry, IPTC metadata includes information to catalog and exchange media. It covers a broad range of details such as copyright information, the creator of the image, contact information, and content description.
- Key Uses: Providing comprehensive details for media cataloging and copyright protection.
- Benefits: Widely used in professional photography and journalism for rights management.
- Limitations: Can be complex to implement fully, requiring specific software tools.
3.3. XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform)
Created by Adobe, XMP serves as a framework for handling and preserving both standardized and proprietary metadata. It is embedded into a digital image file and can include a vast range of information about the file, from basic metadata to rights management information.
- Key Uses: Handling and preserving metadata across different software platforms.
- Benefits: Highly flexible, supports both standard and custom metadata fields.
- Limitations: Requires software that supports XMP standards for full utilization.
3.4. DNG (Digital Negative)
DNG is a raw image file format created by Adobe, designed for use in digital photography. DNG metadata includes all the information found in EXIF, plus additional details specific to raw files, such as camera calibration data.
- Key Uses: Storing raw image data with comprehensive metadata for advanced processing.
- Benefits: Ensures consistency and compatibility across different editing environments.
- Limitations: Not universally supported by all cameras and editing software.
3.5. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
Primarily used for storing raster graphics and images, TIFF files can include a variety of metadata types stored in tags. These can describe image dimensions, resolution, and image data arrangement, among others.
- Key Uses: Archiving high-quality images with detailed metadata descriptions.
- Benefits: Supports lossless compression and extensive metadata options.
- Limitations: Can result in large file sizes, making it less suitable for web use.
3.6. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a file format for raster graphics that allows for data compression without losing quality. PNG files can contain metadata such as textual information (titles, author, description, etc.) and image-specific data like gamma values, color profiles, and transparency information.
- Key Uses: Web graphics and images requiring lossless compression.
- Benefits: Supports transparency and stores basic metadata efficiently.
- Limitations: Less comprehensive metadata options compared to formats like TIFF or XMP.
3.7. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
The JPEG format is a widely utilized technique for compressing digital images in a lossy manner. JPEG files can include EXIF, XMP, and ICC profile data, providing a wide range of information from camera settings to copyright and licensing information.
- Key Uses: General-purpose image compression for web and print.
- Benefits: Widely compatible and offers a good balance between file size and image quality.
- Limitations: Lossy compression can degrade image quality with repeated edits.
3.8. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
A bitmap image format that supports animations. GIF files can include simple textual metadata, but their support for detailed metadata is limited compared to other formats.
- Key Uses: Simple animations and web graphics.
- Benefits: Supports animation and is widely compatible.
- Limitations: Limited metadata capabilities and color palette.
Each format has unique strengths and limitations, influencing the type and amount of metadata it can store.
4. Accessing Photo Metadata: A Step-by-Step Guide
Gaining access to photo metadata is straightforward, whether you’re using a Mac or a Windows device.
4.1. Accessing Metadata on Mac
- Locate the Image: Find the image you want to examine in ‘Finder’.
- Get Info: Highlight the file, right-click, and select ‘Get Info’.
- Explore Details: A new window opens with relevant details. Cycle through the tabs to find the information you need.
 Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background.
Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background.
4.2. Accessing Metadata on Windows
- Locate the Image: Find and right-click the digital image file.
- Select Properties: Choose ‘Properties’, and a new window will appear.
- View Details: Click the ‘Details’ tab at the top.
- Scroll to Find: Scroll down to find the metadata you need.
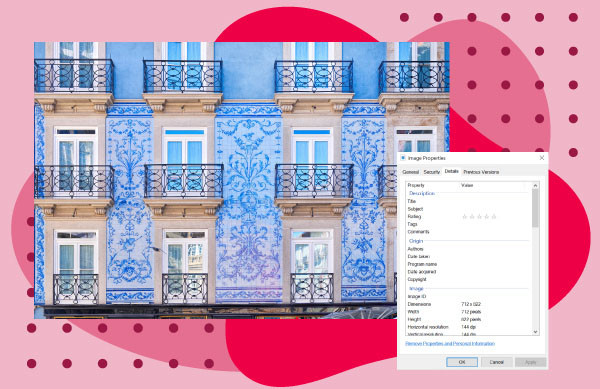 Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background.
Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background.
5. Editing Photo Metadata: Adding Your Personal Touch
Yes, you can easily edit image metadata. Here’s how to do it on both Mac and Windows:
- Navigate to Metadata: Follow the steps above to access the file’s metadata.
- Locate Category: Find the category you want to edit (name, date, author, etc.).
- Input New Information: Under the ‘Value’ tab, click and type to enter the new information.
6. Utilizing a Metadata Editor: Simplifying the Process
While manual editing is possible, a metadata editor is preferable for extensive edits. When selecting software, ensure it:
- Supports the image file types you use.
- Can handle the required editing tasks.
Users might edit metadata to fill missing fields or remove sensitive details before sharing images on social media.
Regardless of the reason, ensure a smooth workflow and keep a backup of your original files until satisfied with the changes.
7. Leveraging Digital Asset Management (DAM) Platforms
Digital Asset Management (DAM) is the ongoing process of managing an organization’s digital content, including text, audio files, videos, and images. A DAM platform like Canto stores and manages these assets, allowing users to organize, search, retrieve, and share them easily.
DAM software helps manage, search, and edit metadata, providing thumbnails for quick file content visibility.
8. How to Manage Metadata with Canto
- Search: Type your search criteria into the search bar.
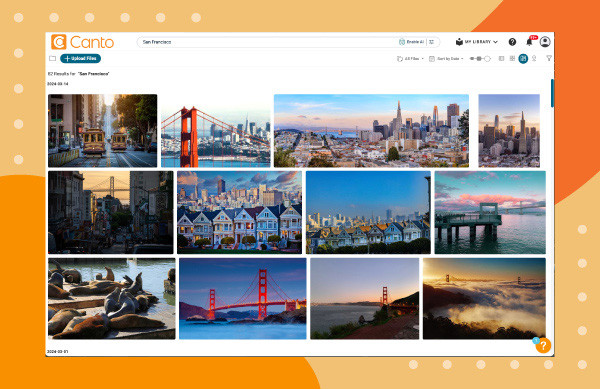 A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background.
A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background.
- Filter: Use the filter pane on the right to narrow your search.
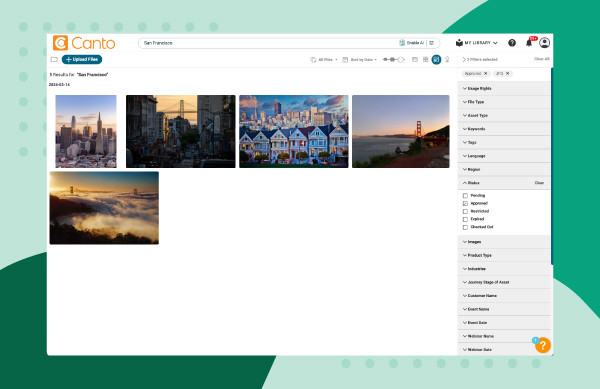 Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background.
Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background.
- View Metadata: Click on the image, and the embedded metadata appears in the right pane. Click the double arrows to display all metadata.
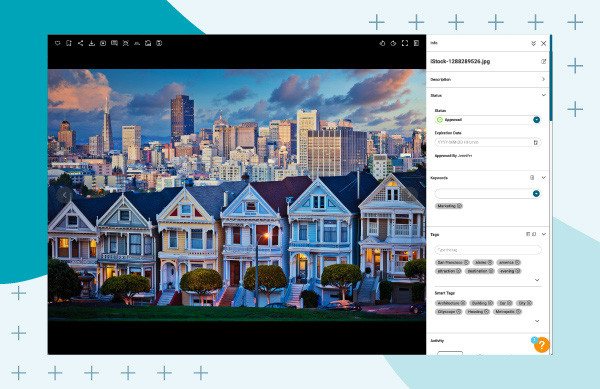 Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background.
Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background.
- Explore Details: Scroll down to find details like creation date, dimensions, and resolution.
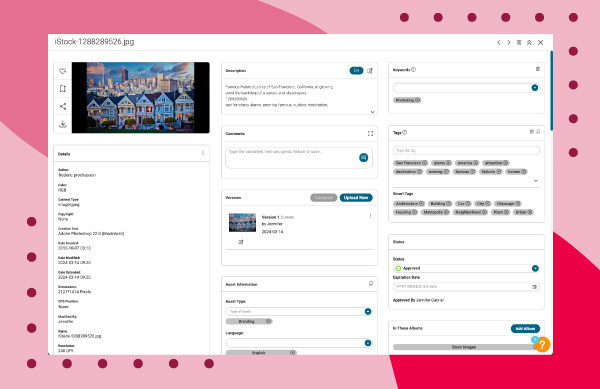 Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background.
Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background.
9. Canto: Simplifying Image Metadata Management
Canto’s AI Visual Search transforms metadata management by using natural language to scan images and find relevant photos without relying on traditional metadata. There’s no need for complex search terms or specific keywords.
AI Visual Search has no learning curve, allowing you to search images as you would on a regular internet search engine.
The best part is rediscovering valuable, forgotten photography that can be reused to create more value for you and your organization.
10. Mastering Photo Metadata for Enhanced SEO
Metadata plays a crucial role in enhancing the SEO of your images, which can significantly improve their visibility and discoverability online. Here’s how you can leverage metadata to optimize your images for search engines:
10.1. Keywords: The Foundation of Image SEO
Keywords are the cornerstone of any SEO strategy, and images are no exception. By incorporating relevant keywords into your image metadata, you make it easier for search engines to understand what your images are about and index them accordingly.
- Title: Use a descriptive title that includes your primary keyword. For example, instead of “IMG_1234.jpg,” use “Santa Fe Landscape Photography.jpg.”
- Description: Write a detailed description that incorporates relevant keywords and provides context about the image.
- Tags: Add multiple tags that cover various aspects of the image, such as location, subject, and style.
10.2. Alt Text: Accessibility and SEO
Alt text (alternative text) is an HTML attribute that provides a text description of an image. It’s essential for accessibility, as it allows screen readers to convey the image’s content to visually impaired users. Additionally, search engines use alt text to understand the context of the image.
- Descriptive: Write alt text that accurately describes the image.
- Keyword-Rich: Include relevant keywords naturally within the description.
- Concise: Keep the alt text brief and to the point.
10.3. File Name: The First Impression
The file name of your image is one of the first things search engines see. Using descriptive file names that include relevant keywords can improve your image SEO.
- Descriptive: Use a file name that clearly describes the image content.
- Keywords: Include your primary keyword in the file name.
- Hyphens: Use hyphens to separate words in the file name.
10.4. Geo-Tagging: Local SEO for Images
If your image is location-specific, adding geo-tagging metadata can boost its visibility in local search results. This is particularly useful for businesses and photographers who want to attract local customers.
- GPS Coordinates: Embed GPS coordinates into the image metadata.
- Location Information: Include the city, state, and country in the description and tags.
10.5. Copyright Information: Protecting Your Images
Adding copyright information to your image metadata not only protects your intellectual property but also helps search engines understand the image’s origin and ownership.
- Copyright Notice: Include a copyright notice with your name and the year of creation.
- Licensing Information: Specify the licensing terms for the image.
10.6. Metadata Consistency: A Holistic Approach
Consistency is key to effective SEO. Ensure that your image metadata is consistent across all platforms, including your website, social media, and image sharing sites.
- Standardized Information: Use the same keywords, descriptions, and tags across all platforms.
- Regular Updates: Keep your metadata up-to-date to reflect any changes in your content strategy.
10.7. Leveraging AI for Metadata Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) can play a significant role in optimizing your image metadata. AI-powered tools can automatically analyze your images and suggest relevant keywords, descriptions, and tags.
- Automated Tagging: Use AI tools to automatically tag your images with relevant keywords.
- Content Analysis: Leverage AI to analyze the content of your images and generate descriptive metadata.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, properly optimized metadata can increase an image’s visibility in search results by up to 70%. This underscores the importance of investing time and effort into optimizing your image metadata for SEO.
11. Best Practices for Photo Metadata Management
To ensure your photo metadata is effective and well-managed, consider these best practices:
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in your metadata practices.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your metadata to prevent data loss.
- Privacy Considerations: Be mindful of privacy when including personal information in metadata.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with metadata standards and regulations.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure data quality and accuracy.
12. Addressing Common Concerns About Metadata
Here are some common questions and concerns about photo metadata:
12.1. How can I ensure that my photo metadata is secure and not exposed when sharing images online?
To avoid sharing unwanted metadata, remove sensitive information like location data before uploading or sharing. Some platforms automatically remove metadata for privacy.
12.2. What are the legal considerations for altering or removing metadata, particularly related to copyright?
Altering or removing metadata, especially copyright information, on images you don’t own can lead to legal issues. Always seek legal advice if unsure about copyright or digital rights issues.
12.3. How does metadata affect the SEO of images when uploaded to websites or social media?
Metadata like keywords, alt text, and titles significantly impact how images are indexed by search engines, enhancing their online discoverability.
13. FAQs: Your Photo Metadata Questions Answered
1. What exactly is photo metadata?
Photo metadata is embedded information within a digital image file that provides details about the photo, including technical data, descriptive information, and copyright details. It’s like a digital fingerprint for your images.
2. Why is photo metadata important for photographers?
Photo metadata is crucial for organizing images, protecting copyright, enabling efficient searches, and providing technical analysis for improving future shoots. It ensures important details about the image are preserved and accessible.
3. What are the main categories of photo metadata?
The main categories are descriptive metadata (title, author, keywords), structural metadata (organization and format), and administrative metadata (creation time, file format, rights information).
4. How can I view photo metadata on my computer?
On a Mac, locate the image in Finder, right-click, select “Get Info,” and cycle through the tabs. On Windows, right-click the image, select “Properties,” and click the “Details” tab.
5. Can I edit photo metadata?
Yes, you can edit photo metadata on both Mac and Windows. Navigate to the metadata, locate the category you want to edit, and input the new information under the “Value” tab.
6. What is a metadata editor, and why should I use one?
A metadata editor is software that simplifies editing metadata. It’s useful for making numerous edits, filling missing fields, or removing sensitive details before sharing images.
7. How does a Digital Asset Management (DAM) platform help with metadata?
A DAM platform like Canto stores and manages digital assets, allowing users to organize, search, retrieve, and share them easily. It helps manage, search, and edit metadata while providing thumbnails for quick file content visibility.
8. How does AI Visual Search in Canto enhance metadata management?
Canto’s AI Visual Search uses natural language to scan images and find relevant photos without relying on traditional metadata. It eliminates the need for complex search terms and helps rediscover valuable, forgotten photography.
9. What are the legal considerations when altering photo metadata?
Altering or removing metadata, especially copyright information, on images you don’t own can lead to legal issues. Always seek legal advice if unsure about copyright or digital rights issues.
10. How does photo metadata affect SEO for images?
Metadata like keywords, alt text, and titles significantly impact how images are indexed by search engines, enhancing their online discoverability. Optimizing this data improves image visibility in search results.
14. Start Organizing Your Photos with dfphoto.net Today
Photo metadata is a powerful tool for organizing, protecting, and optimizing your digital images. By understanding how to find and manage metadata, you can unlock the full potential of your photo library. dfphoto.net is your go-to resource for mastering photo metadata and transforming your digital asset management workflows.
Ready to streamline photo management? Explore our comprehensive guides, discover stunning photography, and connect with a vibrant community of photographers at dfphoto.net.
15. Call to Action (CTA)
Visit dfphoto.net today to explore our detailed tutorials, view beautiful photos, and connect with the American photography community. Enhance your photography skills and discover new sources of inspiration with us!
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States
Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001
Website: dfphoto.net
By mastering the art of metadata, photographers, marketers, and digital asset managers can unlock new levels of organization, efficiency, and creative potential.