Enlarging photos in Photoshop is a common task for photographers and graphic designers, and dfphoto.net can help you master this skill with ease. In this guide, we’ll explore various techniques to upscale images while minimizing quality loss, ensuring your photos look their best at any size. Let’s dive into the world of image enlargement, resolution boosting, and preserving image quality, all in one comprehensive article!
1. Understanding Image Enlargement in Photoshop
1.1. Why Enlarge Photos?
Enlarging photos is often necessary for various reasons:
- Printing: Printing requires specific image dimensions to fit the desired print size.
- Web Use: Websites might need larger images for banners or high-resolution displays.
- Detail Enhancement: Enlarging can help bring out finer details in an image for closer inspection.
- Artistic Effects: Sometimes, enlarging is done to create a specific visual effect or artistic style.
1.2. The Challenge of Enlargement
The primary challenge in enlarging photos is maintaining image quality. When you increase the size of an image, you’re essentially asking Photoshop to create new pixels based on the existing ones. This process, known as interpolation, can lead to several issues:
- Pixelation: The image becomes visibly blocky as individual pixels become more apparent.
- Blurring: Fine details can become soft and indistinct.
- Artifacts: Unwanted patterns or distortions can appear in the image.
1.3. Key Concepts
Before diving into the how-to, let’s define some essential concepts:
- Resolution: The number of pixels in an image, typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Higher resolution means more detail.
- Pixel Dimensions: The width and height of an image in pixels (e.g., 3000 x 2000 pixels).
- Document Size: The physical size of an image when printed, measured in inches or centimeters.
- Resampling: The process of changing the pixel dimensions of an image, which involves adding or removing pixels.
2. Preparing Your Image for Enlargement
2.1. Initial Assessment
Before enlarging, it’s crucial to assess the original image. Ask yourself:
- What is the current resolution? Is it high enough for the intended use?
- What is the image quality like? Are there any imperfections that need to be addressed?
- How much enlargement is needed? A small increase is less likely to cause quality issues than a large one.
2.2. Cleaning Up the Image
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, cleaning up your image before enlargement minimizes the magnification of any imperfections. You might have dust, scratches, or noise that could become more noticeable when enlarged. Photoshop offers several tools to address these issues:
- Spot Healing Brush Tool: Quickly removes small blemishes and imperfections.
- Clone Stamp Tool: Replicates areas of the image to cover up unwanted details.
- Noise Reduction Filters: Reduces graininess and noise in the image.
2.3. Saving a Backup
Always save a backup of your original image before making any changes. This ensures you can revert to the original if needed. Simply go to File > Save As and save a copy with a different name.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Enlarging Photos in Photoshop
3.1. Opening the Image
- Launch Photoshop: Open Adobe Photoshop on your computer.
- Open Image: Go to
File > Openand select the image you want to enlarge.
3.2. Accessing the Image Size Dialog Box
- Navigate to Image Size: Go to
Image > Image Size. This will open the Image Size dialog box.
3.3. Understanding the Image Size Dialog Box
The Image Size dialog box is where you’ll control the enlargement process. It displays the following information:
- Dimensions: Shows the current width and height of the image in pixels.
- Document Size: Displays the width and height of the image in inches or centimeters, along with the resolution.
- Resolution: Indicates the current resolution of the image in PPI or DPI.
- Resample: A dropdown menu that allows you to choose a resampling method.
3.4. Setting New Dimensions
-
Enter Desired Dimensions: Type in the new pixel dimensions, document size, or resolution you want for the enlarged image.
- Pixel Dimensions: If you know the exact pixel dimensions you need, enter them directly into the Width and Height fields.
- Document Size: If you need a specific print size, enter the desired width and height in the Document Size fields. Photoshop will automatically adjust the pixel dimensions to maintain the specified resolution.
- Resolution: If you want to increase the resolution, enter the new value in the Resolution field. Photoshop will adjust the pixel dimensions and document size accordingly.
-
Constrain Proportions: Make sure the “Constrain Proportions” box is checked to maintain the original aspect ratio of the image. This prevents distortion.
-
Resample: The Resample option must be enabled to add new pixels.
- Automatic: Photoshop chooses the best resample method depending on the changes you make.
3.5. Choosing the Right Resampling Method
The resampling method you choose can significantly impact the quality of the enlarged image. Photoshop offers several options, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
-
Nearest Neighbor: This is the simplest method, but it often produces the worst results. It simply duplicates pixels, which can lead to a blocky, pixelated appearance. Not recommended for enlargement.
-
Bilinear: This method calculates the average color of the surrounding pixels to create new ones. It produces smoother results than Nearest Neighbor but can still cause some blurring.
-
Bicubic: This method uses a more complex algorithm to interpolate new pixels, resulting in smoother and more detailed enlargements than Bilinear. It’s a good all-around choice for most images.
-
Bicubic Smoother: Specifically designed for enlarging images. It produces the smoothest results but can sometimes soften fine details. Best for images that require significant enlargement and have minimal fine detail.
-
Bicubic Sharper: Designed for reducing image size. It emphasizes detail and sharpness.
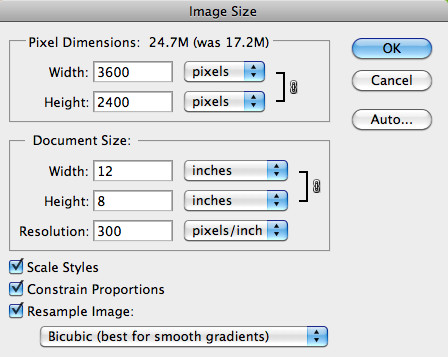 Image Size dialog box in Photoshop
Image Size dialog box in Photoshop
3.6. Clicking OK
Click “OK” to apply the changes. Photoshop will now resample the image according to your settings.
3.7. Reviewing the Results
Carefully examine the enlarged image. Look for any signs of pixelation, blurring, or artifacts. If you’re not satisfied with the results, you can try a different resampling method or reduce the amount of enlargement.
4. Advanced Techniques for High-Quality Enlargements
4.1. Using Step Enlargement
Enlarging an image in small steps can often produce better results than enlarging it all at once. For example, instead of doubling the size of an image, you could increase it by 25% multiple times.
- Open Image Size: Go to
Image > Image Size. - Increase Size Gradually: Increase the width and height by a small percentage (e.g., 25%).
- Choose Resampling Method: Select
Bicubic Smoother. - Click OK: Apply the changes.
- Repeat: Repeat steps 1-4 until you reach the desired size.
4.2. Utilizing Smart Objects
Converting your image to a Smart Object before enlarging allows you to apply transformations non-destructively. This means you can resize the image multiple times without losing quality.
- Convert to Smart Object: Right-click on the image layer in the Layers panel and select “Convert to Smart Object.”
- Enlarge Image: Go to
Image > Image Sizeand enlarge the image as needed. - Re-edit: Double-click the Smart Object thumbnail in the Layers panel to open the Smart Object for editing. Any changes you make to the Smart Object will be reflected in the main image.
4.3. Exploring Third-Party Plugins
Several third-party plugins are designed specifically for image enlargement. These plugins often use more advanced algorithms than Photoshop’s built-in resampling methods, resulting in higher-quality enlargements. Some popular options include:
- Topaz Gigapixel AI: Uses artificial intelligence to upscale images with minimal quality loss. According to Topaz Labs, Gigapixel AI can increase the resolution of an image by up to 600% while preserving detail and sharpness.
- ON1 Resize AI: Another AI-powered plugin that offers excellent results for image enlargement. ON1 claims their plugin uses state-of-the-art technology to maintain image quality during resizing.
4.4. Focus on Sharpening
Sharpening can help restore some of the detail lost during enlargement. Photoshop offers several sharpening filters:
- Unsharp Mask: This is a classic sharpening filter that allows you to control the amount, radius, and threshold of sharpening.
- Smart Sharpen: This filter offers more advanced controls and can reduce noise while sharpening.
Apply sharpening sparingly, as too much sharpening can create unwanted artifacts.
5. Understanding Different Image Types and Their Enlargement Needs
5.1. Raster Images
Raster images, such as JPEGs, PNGs, and TIFFs, are made up of pixels. When you enlarge a raster image, Photoshop has to create new pixels, which can lead to quality loss. The resampling method you choose is crucial for minimizing this loss.
5.2. Vector Images
Vector images, such as those created in Adobe Illustrator, are made up of mathematical equations rather than pixels. This means they can be scaled infinitely without losing quality. If possible, it’s always best to work with vector images when you need to enlarge something significantly.
5.3. RAW Images
RAW images contain unprocessed data captured directly from your camera’s sensor. They offer the most flexibility for editing and can often be enlarged with better results than JPEGs or other compressed formats. When working with RAW images, use Adobe Camera Raw or Lightroom to make initial adjustments before opening them in Photoshop.
6. Real-World Examples and Use Cases
6.1. Enlarging Photos for Print
Let’s say you have a photo that’s 4×6 inches at 300 DPI, and you want to print it at 8×10 inches. Here’s how you would enlarge it in Photoshop:
- Open Image Size: Go to
Image > Image Size. - Set Document Size: Enter 8 inches for the width and 10 inches for the height in the Document Size fields.
- Check Resolution: Make sure the resolution is set to 300 DPI.
- Choose Resampling Method: Select
Bicubic Smoother. - Click OK: Apply the changes.
6.2. Enlarging Photos for Web Use
If you need to enlarge a photo for a website banner, the process is similar:
- Open Image Size: Go to
Image > Image Size. - Set Pixel Dimensions: Enter the desired pixel dimensions for the banner.
- Choose Resampling Method: Select
Bicubic Smoother. - Click OK: Apply the changes.
- Optimize for Web: Save the image as a JPEG and use the “Save for Web” feature to reduce the file size without sacrificing too much quality.
6.3. Enlarging Scanned Documents
Enlarging scanned documents often requires a slightly different approach. Since scanned documents typically contain text and fine lines, it’s important to preserve sharpness and detail.
- Open Image Size: Go to
Image > Image Size. - Set Pixel Dimensions: Enter the desired pixel dimensions for the document.
- Choose Resampling Method: Select
Bicubic Sharper. - Click OK: Apply the changes.
- Sharpen: Use the Unsharp Mask filter to sharpen the text and lines.
7. The Impact of AI on Image Enlargement
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of image enlargement. AI-powered tools like Topaz Gigapixel AI and ON1 Resize AI use machine learning algorithms to analyze images and create new pixels that are more accurate and detailed than traditional resampling methods.
According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, AI-based image enlargement techniques can produce results that are nearly indistinguishable from the original image, even at high magnification levels. These tools can:
- Preserve Fine Details: AI algorithms can identify and preserve fine details, such as hair strands and textures, that are often lost during traditional enlargement.
- Reduce Artifacts: AI can minimize the appearance of pixelation, blurring, and other artifacts.
- Enhance Realism: AI can add realistic details to the enlarged image, making it look more natural and lifelike.
While AI-powered tools can be more expensive than traditional Photoshop techniques, they can be worth the investment if you need to enlarge images frequently or require the highest possible quality.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
8.1. Over-Enlarging
Enlarging an image too much can lead to severe quality loss, regardless of the resampling method you use. It’s generally best to avoid enlarging an image by more than 200% to 300%.
8.2. Ignoring Image Quality
Starting with a low-quality image will only result in a low-quality enlarged image. Make sure to start with the highest quality image possible.
8.3. Not Sharpening
Failing to sharpen the enlarged image can result in a soft, blurry appearance. Use sharpening filters sparingly to restore detail.
8.4. Saving in the Wrong Format
Saving the enlarged image in the wrong format can also lead to quality loss. For photos, JPEG is a good choice, but for images with text or fine lines, PNG may be better.
9. Tips for Optimizing Your Workflow
9.1. Use Actions
Photoshop Actions allow you to automate repetitive tasks, such as enlarging images. You can record a series of steps and then play them back with a single click.
9.2. Create Presets
Create presets for different enlargement scenarios. This can save you time and ensure consistent results.
9.3. Batch Processing
Use Photoshop’s batch processing feature to enlarge multiple images at once. This can be a huge time-saver when you have a large number of images to process.
10. Best Practices for Different Photography Genres
10.1. Landscape Photography
For landscape photos, preserving detail and sharpness is crucial. Use the Bicubic Smoother or AI-powered plugins.
10.2. Portrait Photography
For portraits, focus on smoothing skin tones and minimizing artifacts. Use the Bicubic Smoother method and apply gentle sharpening.
10.3. Product Photography
For product photos, preserving detail and sharpness is essential. Use the Bicubic Sharper method or AI-powered plugins.
10.4. Wildlife Photography
For wildlife photos, focus on preserving fine details, such as fur and feathers. Use the Bicubic Smoother method or AI-powered plugins.
11. FAQ: How to Enlarge Photo in Photoshop
1. How do I enlarge a photo in Photoshop without losing quality?
Use the Image Size dialog box (Image > Image Size), choose an appropriate resampling method (Bicubic Smoother for enlargement), and enlarge in small increments. Consider using AI-powered plugins for better results.
2. Which resampling method is best for enlarging images?
Bicubic Smoother is generally the best option for enlarging images, as it produces smooth results with minimal artifacts. AI-powered plugins offer even better quality.
3. What is resampling in Photoshop?
Resampling is the process of changing the pixel dimensions of an image. It involves adding or removing pixels, which can affect image quality.
4. How can I maintain the aspect ratio when enlarging a photo?
Make sure the “Constrain Proportions” box is checked in the Image Size dialog box to maintain the original aspect ratio of the image.
5. Can I enlarge a photo multiple times without losing quality?
Converting the image to a Smart Object before enlarging allows you to resize it multiple times without losing quality.
6. What are the best plugins for enlarging photos?
Topaz Gigapixel AI and ON1 Resize AI are two popular plugins that use artificial intelligence to upscale images with minimal quality loss.
7. How do I sharpen an enlarged photo in Photoshop?
Use the Unsharp Mask or Smart Sharpen filters to sharpen the enlarged image. Apply sharpening sparingly to avoid artifacts.
8. What is the best file format for saving an enlarged photo?
For photos, JPEG is a good choice. For images with text or fine lines, PNG may be better.
9. How much can I enlarge a photo without losing too much quality?
It’s generally best to avoid enlarging an image by more than 200% to 300%.
10. Can I enlarge a RAW image more than a JPEG?
Yes, RAW images offer more flexibility for editing and can often be enlarged with better results than JPEGs or other compressed formats.
12. Conclusion: Mastering Image Enlargement
Enlarging photos in Photoshop doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By understanding the key concepts, choosing the right resampling method, and utilizing advanced techniques, you can achieve high-quality results that meet your specific needs. Remember to start with the highest quality image possible, clean up any imperfections, and sharpen the enlarged image to restore detail. With practice and patience, you’ll master the art of image enlargement and create stunning visuals that showcase your talent.
Ready to take your photography skills to the next level? Visit dfphoto.net to explore our comprehensive tutorials, discover breathtaking images, and connect with a vibrant community of photographers in the USA. Whether you’re looking for inspiration, guidance, or simply a place to share your work, dfphoto.net is your ultimate resource for all things photography. Let’s capture the world together!
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.