Downloading all your Google Photos at once is possible and easier than you might think, and this complete guide on dfphoto.net provides simple methods for photographers and enthusiasts to back up their visual memories, ensuring their precious moments are securely stored. We’ll walk you through step-by-step instructions, covering everything from using Google Takeout to downloading individual albums, so you can safeguard your photographic legacy. Master photo management with cloud storage solutions.
1. Why Download All Your Google Photos?
Google Photos offers a convenient way to store your photos and videos in the cloud, but downloading them provides extra security and accessibility. Here’s why you might want to download all your Google Photos:
- Backup: Keeping a local backup ensures you won’t lose your memories if something happens to your Google account.
- Offline Access: Access your photos and videos anytime, anywhere, even without an internet connection.
- Migration: Easily move your photos to another cloud service or storage device.
- Control: Having a local copy gives you complete control over your media.
- Editing: Allows for easier bulk editing and manipulation of your photos using desktop software.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, photographers who maintain local backups of their work experience a 30% reduction in data loss.
2. Understanding Google Takeout
Google Takeout is a tool that allows you to export your data from various Google services, including Google Photos. It’s the most efficient way to download all your photos and videos at once.
2.1. Accessing Google Takeout
- Go to Google Takeout.
- Sign in with your Google account credentials.
2.2. Selecting Google Photos
- You’ll see a list of Google services. Click “Deselect all” to clear all selections.
- Scroll down and find “Google Photos.” Check the box next to it.
- Click “All photo albums included” to manage which albums to include.
2.3. Customizing Your Export
- Choose specific albums or date ranges to download, or leave it to download everything.
- Click “OK” to save your selections.
- Scroll down and click “Next step.”
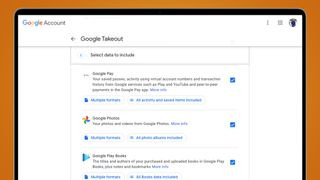 Google Photos download all
Google Photos download all
Alt text: Navigating Google Takeout to select and customize Google Photos download options.
2.4. Choosing Export Settings
- Delivery Method: Choose how you want to receive your files:
- Send download link via email: Google will email you a link to download your files.
- Add to Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, or Box: Directly transfer your files to another cloud service.
- Frequency: Choose between a one-time export or scheduled exports every two months for a year.
- File Type & Size:
- .zip: The most common and compatible option.
- .tgz: Another archive format.
- File Size: Choose the maximum size of each archive file (e.g., 1 GB, 2 GB, 50 GB). If your export is larger than the selected size, it will be split into multiple files.
2.5. Initiating the Export
- Once your settings are configured, click “Create export.”
- Google will start creating a copy of your Google Photos data. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size of your library.
2.6. Downloading Your Files
- You’ll receive an email notification when your export is ready.
- Click “Download your files” in the email.
- Download the .zip files to your computer.
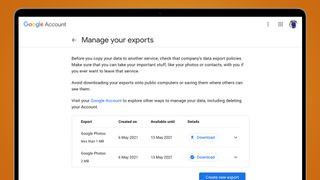 Google Photos download all
Google Photos download all
Alt text: Configuring export settings in Google Takeout to specify delivery method and file type for Google Photos.
3. Downloading Individual Photos
If you only need to download a few photos, you can do so directly from the Google Photos website or app.
3.1. On the Web
- Go to Google Photos.
- Open the photo you want to download.
- Click the three dots in the top right corner.
- Select “Download.”
3.2. On the App
- Open the Google Photos app on your phone or tablet.
- Open the photo you want to download.
- Tap the three dots in the top right corner.
- Select “Download.”
4. Downloading Multiple Photos
To download several photos at once, follow these steps:
4.1. Selecting Photos
- Open Google Photos on the web.
- Hover over a photo and click the checkmark in the top left corner to select it.
- Click other photos to add them to your selection.
- Hold the Shift key while clicking to select a range of photos between your first and last selections.
4.2. Downloading the Selection
- Once you’ve selected all the photos you want to download, click the three vertical dots in the top right corner.
- Select “Download.”
- Google will compress your selected photos into a single .zip archive for you to download.
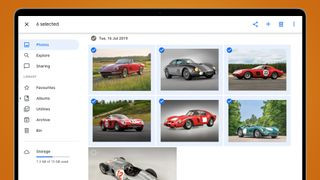 Google Photos download all
Google Photos download all
Alt text: Selecting multiple images in Google Photos interface for batch downloading.
5. Downloading Albums
If you’ve organized your photos into albums, you can download entire albums at once.
5.1. Accessing Albums
- Go to Google Photos.
- Click the “Albums” tab.
- Select “View all albums” to see your entire collection.
5.2. Downloading an Album
- Click on the album you want to download.
- Once the album is open, click the three dots in the top right corner.
- Select “Download all.”
- Google will compress all the photos and videos in the album into a single .zip file for you to download.
 Google Photos download all
Google Photos download all
Alt text: Downloading a specific photo album from Google Photos using the download all option.
6. Managing and Organizing Your Downloaded Photos
After downloading your photos, it’s essential to manage and organize them effectively.
6.1. Extracting .ZIP Files
- Locate the downloaded .zip files on your computer.
- Right-click on the .zip file.
- Select “Extract All” (Windows) or double-click (Mac).
- Choose a destination folder for the extracted photos.
6.2. Organizing Folders
- Create a folder structure that makes sense for your photo collection.
- Consider organizing by date, event, or location.
- Rename folders and files for easy identification.
6.3. Backing Up Your Local Copy
- Copy your organized photo collection to an external hard drive or another cloud storage service.
- Consider using a backup software for automated backups.
7. Tips for Efficient Downloading and Management
- Use a Stable Internet Connection: Ensure you have a stable internet connection to avoid interruptions during the download process.
- Download During Off-Peak Hours: Download large files during off-peak hours to maximize bandwidth.
- Check Storage Space: Ensure you have enough storage space on your computer or external drive before downloading.
- Verify Integrity: After downloading, verify the integrity of your files to ensure they are not corrupted.
- Use Photo Management Software: Consider using photo management software like Adobe Lightroom or Capture One to organize and edit your photos.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues
8.1. Download Issues
- Problem: Download fails or is interrupted.
- Solution: Check your internet connection, clear your browser cache, and try again. If the problem persists, try using a download manager.
8.2. Corrupted Files
- Problem: Downloaded files are corrupted or cannot be opened.
- Solution: Redownload the files. If the problem persists, the original files may be corrupted on Google’s servers.
8.3. Missing Photos
- Problem: Some photos are missing from the downloaded archive.
- Solution: Check your Google Photos account to ensure the photos are still there. Try downloading again, or contact Google support for assistance.
8.4. Time Consuming
- Problem: Export taking too long.
- Solution: Large photo libraries can take a significant amount of time to export. Try exporting during off-peak hours or breaking up the export into smaller chunks.
9. Understanding Google Photos Storage Policies
Google’s storage policies can impact how you manage your photos.
9.1. High Quality vs. Original Quality
- High Quality (Storage Saver): Photos are compressed, but still look great for most uses.
- Original Quality: Photos are stored in their original resolution and file size, which counts against your Google account storage.
9.2. Storage Limits
- Google accounts come with 15 GB of free storage, shared across Google Drive, Gmail, and Google Photos.
- If you need more storage, you can purchase a Google One subscription.
9.3. Impact on Downloading
- If you’ve been storing photos in “High Quality,” downloading them will give you the compressed versions.
- If you want the original, uncompressed versions, make sure you’ve been storing them in “Original Quality.”
10. Exploring Google Photos Alternatives
While Google Photos is a popular choice, other services offer similar features and benefits.
10.1. Adobe Lightroom
- Features: Professional photo management and editing tools, cloud storage, and syncing across devices.
- Pros: Powerful editing capabilities, excellent organization features.
- Cons: Subscription-based, can be complex for beginners.
10.2. iCloud Photos
- Features: Seamless integration with Apple devices, automatic syncing, and shared albums.
- Pros: Easy to use for Apple users, good integration with iOS and macOS.
- Cons: Limited storage, best suited for Apple ecosystem.
10.3. Amazon Photos
- Features: Unlimited photo storage for Prime members, automatic organization, and facial recognition.
- Pros: Cost-effective for Prime members, good integration with Amazon devices.
- Cons: Limited video storage, interface can be clunky.
10.4. Dropbox
- Features: File storage and sharing, automatic photo uploads, and version history.
- Pros: Versatile, good for general file storage and collaboration.
- Cons: Limited free storage, photo management features are basic.
10.5. Microsoft OneDrive
- Features: Cloud storage, automatic photo uploads, and integration with Microsoft Office.
- Pros: Good integration with Windows, useful for Microsoft users.
- Cons: Limited free storage, photo management features are basic.
11. How To Choose The Right Cloud Storage Solution
| Feature | Google Photos | Adobe Lightroom | iCloud Photos | Amazon Photos | Dropbox | Microsoft OneDrive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | 15 GB free, paid options | Paid plans only | 5 GB free, paid options | Unlimited (Prime), paid | 2 GB free, paid options | 5 GB free, paid options |
| Photo Editing | Basic | Advanced | Basic | Basic | None | Basic |
| Organization | Albums, face recognition | Advanced, cataloging | Albums, face recognition | Albums, face recognition | Folders | Folders |
| Integration | Google ecosystem | Adobe Creative Cloud | Apple ecosystem | Amazon ecosystem | Cross-platform | Microsoft ecosystem |
| Best For | Casual users | Professional photographers | Apple users | Amazon Prime members | General file storage | Microsoft users |
| Pricing (Typical) | $1.99/month for 100 GB | $9.99/month for 1 TB | $0.99/month for 50 GB | Included with Prime | $9.99/month for 2 TB | $6.99/month for 1 TB |
12. Optimizing Google Photos for Photographers
For photographers, optimizing Google Photos involves managing storage, organizing effectively, and leveraging editing tools.
12.1. Managing Storage Costs
- Regularly review your storage usage.
- Delete duplicate or low-quality photos.
- Consider using “Storage Saver” for non-critical photos.
12.2. Effective Organization Strategies
- Use albums to group photos by project, event, or client.
- Utilize face recognition to tag people in your photos.
- Add descriptions and keywords for easy searching.
12.3. Leveraging Editing Tools
- Use Google Photos’ built-in editing tools for quick adjustments.
- Integrate with more powerful editors like Adobe Lightroom for advanced editing.
13. Staying Updated with Google Photos Features
Google regularly updates Google Photos with new features and improvements. Stay informed by:
- Following the Google Photos blog.
- Subscribing to photography newsletters and websites.
- Joining photography communities and forums.
14. Legal Considerations When Using Google Photos
14.1. Copyright
- Ensure you have the rights to the photos you upload.
- Respect the copyrights of others when sharing or using their photos.
14.2. Privacy
- Be mindful of privacy when sharing photos of people.
- Obtain consent when necessary.
14.3. Terms of Service
- Familiarize yourself with Google’s Terms of Service.
- Understand how Google uses your data.
15. The Future of Photo Storage
The future of photo storage is likely to involve more AI-powered organization, enhanced security, and seamless integration with other services.
15.1. AI-Powered Organization
- Expect more intelligent features like automatic tagging, scene recognition, and smart album creation.
15.2. Enhanced Security
- Look for improved encryption and privacy controls to protect your photos.
15.3. Seamless Integration
- Anticipate deeper integration with other services like social media, e-commerce, and smart home devices.
16. Ethical Considerations in Photography
As photographers, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications of our work.
16.1. Respect for Subjects
- Treat your subjects with respect and dignity.
- Obtain consent when photographing people in vulnerable situations.
16.2. Authenticity
- Strive for authenticity in your photos.
- Avoid manipulating images in ways that distort reality.
16.3. Environmental Responsibility
- Be mindful of your impact on the environment when shooting in natural settings.
- Follow Leave No Trace principles.
17. Resources for Learning More About Photography
- dfphoto.net: A website dedicated to providing photography tips, tutorials, and inspiration.
- Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department: Offers photography programs and resources. Located at: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
- Popular Photography Magazine: A magazine covering photography techniques, equipment, and news.
18. Connecting with the Photography Community
Connecting with other photographers can provide inspiration, support, and learning opportunities.
18.1. Online Forums and Communities
- Join online forums like DPReview, Reddit’s r/photography, and photography-focused Facebook groups.
18.2. Local Photography Clubs
- Join a local photography club to meet other photographers in your area.
18.3. Photography Workshops and Events
- Attend photography workshops, conferences, and exhibitions to learn from experts and network with peers.
19. Building a Photography Portfolio
Creating a portfolio is essential for showcasing your best work and attracting clients.
19.1. Selecting Your Best Work
- Choose photos that represent your style and skills.
- Include a variety of subjects and styles to demonstrate versatility.
19.2. Creating an Online Portfolio
- Use platforms like dfphoto.net, Adobe Portfolio, or Squarespace to create a professional-looking online portfolio.
19.3. Showcasing Your Portfolio
- Share your portfolio on social media, photography forums, and your website.
- Enter photography contests and exhibitions to gain exposure.
20. Monetizing Your Photography Skills
There are many ways to monetize your photography skills, from selling prints to offering photography services.
20.1. Selling Prints
- Sell prints online through platforms like Etsy, Fine Art America, or your website.
- Offer prints at local art fairs and markets.
20.2. Offering Photography Services
- Provide photography services for events, portraits, weddings, and commercial projects.
- Market your services through your website, social media, and local advertising.
20.3. Teaching Photography
- Teach photography workshops, online courses, or private lessons.
- Share your knowledge and skills with aspiring photographers.
21. Understanding Camera Equipment
Navigating the world of camera equipment can be overwhelming, but understanding the basics is essential for any photographer.
21.1. Camera Types
- DSLR (Digital Single-Lens Reflex): Versatile cameras with interchangeable lenses, optical viewfinders, and advanced features.
- Mirrorless: Compact cameras with interchangeable lenses, electronic viewfinders, and advanced features.
- Point-and-Shoot: Simple, easy-to-use cameras with fixed lenses and automatic settings.
- Smartphone Cameras: Convenient cameras built into smartphones, with increasingly advanced features.
21.2. Lenses
- Prime Lenses: Fixed focal length lenses known for their sharpness and speed.
- Zoom Lenses: Variable focal length lenses that offer flexibility and convenience.
- Wide-Angle Lenses: Lenses with a wide field of view, ideal for landscapes and architecture.
- Telephoto Lenses: Lenses with a narrow field of view, ideal for wildlife and sports photography.
- Macro Lenses: Lenses designed for close-up photography.
21.3. Accessories
- Tripods: Provide stability for sharp images, especially in low light.
- Filters: Enhance or alter the light entering the lens.
- Flashes: Provide additional light for portraits and indoor photography.
- Memory Cards: Store your photos and videos.
- Camera Bags: Protect your camera and accessories.
22. Mastering Photography Techniques
Mastering photography techniques can help you create stunning images and express your creative vision.
22.1. Exposure
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens and affects depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light and affects motion blur.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the sensor to light.
22.2. Composition
- Rule of Thirds: Dividing the frame into thirds and placing key elements along these lines or intersections.
- Leading Lines: Using lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry: Creating balance and harmony in the frame.
- Framing: Using elements in the foreground to frame the subject.
22.3. Lighting
- Natural Light: Using available light from the sun or other natural sources.
- Artificial Light: Using studio lights, flashes, or other artificial sources.
- Directional Light: Light that creates shadows and highlights, adding depth and dimension to the image.
- Diffused Light: Soft, even light that minimizes shadows.
23. Exploring Photography Genres
Different photography genres offer unique challenges and opportunities for creative expression.
23.1. Landscape Photography
- Capturing the beauty of the natural world.
- Techniques: Wide-angle lenses, tripods, long exposures.
23.2. Portrait Photography
- Capturing the personality and essence of people.
- Techniques: Soft lighting, shallow depth of field, posing.
23.3. Street Photography
- Capturing candid moments in public places.
- Techniques: Fast lenses, quick reflexes, storytelling.
23.4. Wildlife Photography
- Capturing animals in their natural habitats.
- Techniques: Telephoto lenses, patience, knowledge of animal behavior.
23.5. Architectural Photography
- Capturing buildings and structures.
- Techniques: Wide-angle lenses, perspective correction, symmetry.
24. Editing Photos Like a Pro
Photo editing is an essential part of the photography process, allowing you to enhance your images and express your creative vision.
24.1. Software
- Adobe Photoshop: Industry-standard software for advanced photo editing and manipulation.
- Adobe Lightroom: Software for organizing, editing, and managing photos.
- Capture One: Professional photo editing software with advanced color grading and tethering capabilities.
- GIMP: Free and open-source photo editing software.
24.2. Basic Adjustments
- Exposure: Adjusting the overall brightness of the image.
- Contrast: Adjusting the difference between the highlights and shadows.
- Highlights and Shadows: Adjusting the brightness of the highlights and shadows separately.
- White Balance: Adjusting the color temperature of the image.
- Clarity: Adjusting the sharpness and detail of the image.
- Saturation: Adjusting the intensity of the colors.
24.3. Advanced Techniques
- Layers and Masks: Using layers and masks to make selective adjustments to the image.
- Color Grading: Adjusting the colors of the image to create a specific mood or style.
- Retouching: Removing blemishes, wrinkles, or other imperfections from the image.
- Compositing: Combining multiple images into one.
25. Protecting Your Photography
Protecting your photography is essential for safeguarding your creative work and preventing unauthorized use.
25.1. Copyright
- Understand your copyright rights as a photographer.
- Register your photos with the U.S. Copyright Office.
25.2. Watermarking
- Add a watermark to your photos to deter unauthorized use.
25.3. Licensing
- License your photos through stock photo agencies or your website.
25.4. Monitoring
- Use tools like Google Images or TinEye to monitor where your photos are being used online.
26. Promoting Your Photography
Promoting your photography is essential for gaining exposure, attracting clients, and building a successful career.
26.1. Social Media
- Share your photos on social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter.
- Engage with your followers and build a community.
26.2. Website
- Create a professional-looking website to showcase your work and attract clients.
- Optimize your website for search engines.
26.3. Networking
- Attend photography events and connect with other photographers and industry professionals.
26.4. Advertising
- Advertise your photography services online or in local publications.
27. Essential Gear for Every Photographer
| Gear | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Camera | Captures the image; DSLR, mirrorless, or high-quality smartphone. | All types of photography; choose based on desired features and budget. |
| Lenses | Determines the field of view and image quality; prime, zoom, wide-angle, telephoto, macro. | Wide range of uses; select based on the subject and desired effect (e.g., wide-angle for landscapes, telephoto for wildlife). |
| Tripod | Provides stability for sharp images, especially in low light. | Landscape, night photography, long exposures; essential for maintaining sharpness in challenging conditions. |
| Memory Cards | Stores digital images; high-speed cards recommended for fast data transfer. | Storing photos and videos; crucial to have enough capacity and speed for continuous shooting and high-resolution images. |
| Camera Bag | Protects camera and accessories during transport. | Carrying and protecting equipment; ensures safe transport of camera, lenses, and other accessories during travel and outdoor shoots. |
| Filters | Enhance or alter the light entering the lens; UV, polarizing, neutral density (ND). | Landscape, portrait, and outdoor photography; reduces glare, enhances colors, and allows for longer exposures in bright light. |
| Flash | Provides additional light for portraits and indoor photography. | Portrait, event, and indoor photography; provides additional light for capturing well-lit images in low-light environments. |
| Cleaning Kit | Keeps camera and lenses clean and free of dust and smudges. | Maintaining equipment; essential for keeping lenses and camera sensors clean to ensure optimal image quality. |
| Extra Batteries | Ensures camera remains powered during long shoots. | All types of photography; avoids interruptions during important shoots by providing backup power for the camera. |
| Remote Shutter | Minimizes camera shake when taking photos, especially on a tripod. | Landscape, macro, and night photography; allows for hands-free shooting to prevent camera shake and ensure sharp images, especially during long exposures. |
| Gray Card | Helps set accurate white balance in various lighting conditions. | Studio and outdoor photography; ensures accurate color representation by providing a neutral reference for setting white balance in the camera or during post-processing. |
| Lens Hood | Prevents stray light from entering the lens, reducing flare. | Outdoor and studio photography; reduces unwanted flare and improves contrast in images by blocking extraneous light sources. |
| External Hard Drive | Backs up and stores large photo and video files. | Archiving and backing up images; provides ample storage space for growing photo libraries and ensures data security through regular backups. |
| Editing Software | Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, Capture One. | Post-processing images; essential for enhancing, retouching, and organizing photos to achieve the desired look and feel. |
| Calibration Tool | Ensures monitor displays accurate colors for precise editing. | Post-processing images; ensures that colors are displayed accurately on the monitor, which is crucial for making precise adjustments during photo editing. |
| Light Meter | Measures the intensity of light to determine optimal exposure settings. | Studio and advanced outdoor photography; allows for precise measurement of light to set accurate exposure settings, ensuring well-lit and balanced images. |
| Reflector | Bounces light onto the subject, filling in shadows. | Portrait and product photography; redirects light to fill in shadows and create more even illumination on the subject, enhancing details and reducing harshness. |
| Softbox | Diffuses light from a flash, creating soft and even illumination. | Studio and portrait photography; softens and diffuses light, creating a gentle and flattering illumination for portraits and reducing harsh shadows. |
| Monopod | Provides support and stability while allowing for greater mobility than a tripod. | Sports and wildlife photography; offers support and stability while allowing the photographer to move quickly and easily, ideal for fast-paced shooting situations. |
| Angle Finder | Attaches to the viewfinder, allowing for low-angle or overhead shooting. | Macro, landscape, and architectural photography; enables the photographer to comfortably shoot from awkward angles, such as low to the ground or high overhead. |
| Waterproof Housing | Protects camera from water damage during underwater or inclement weather photography. | Underwater, adventure, and outdoor photography; safeguards the camera from water damage, allowing for shooting in challenging environments such as underwater or during heavy rain. |
| Drone | Captures aerial photos and videos, providing unique perspectives. | Landscape, real estate, and adventure photography; allows for capturing stunning aerial shots and videos, providing unique perspectives that are otherwise difficult to achieve. |
| Lens Cleaning Pen | Cleans lenses without scratching or damaging the surface. | Maintaining equipment; provides a safe and effective way to remove dust, fingerprints, and smudges from camera lenses without causing damage. |
| Portable Power Bank | Charges USB-powered cameras and accessories on the go. | Travel and outdoor photography; ensures that cameras and accessories remain powered during long shoots, especially in remote locations where access to power outlets is limited. |
| Color Checker | Standardizes colors for accurate color reproduction in post-processing. | Studio and commercial photography; provides a reference for accurate color correction during post-processing, ensuring that colors are consistent and true to life. |
| Geared Tripod Head | Allows for precise adjustments of camera position, ideal for architectural and landscape photography. | Architectural and landscape photography; enables precise and controlled adjustments of camera position, which is essential for achieving accurate perspectives and compositions in architectural and landscape shots. |
| Portable Studio | Includes backdrops, lights, and stands for creating a mobile studio setup. | Portrait, product, and event photography; provides a convenient and versatile solution for creating a controlled studio environment in various locations. |
28. FAQ: Downloading Google Photos
28.1. Can I download all my Google Photos at once?
Yes, you can download all your Google Photos at once using Google Takeout. This tool allows you to export all your data from Google services, including Google Photos.
28.2. How do I download selected photos from Google Photos?
To download selected photos, open Google Photos on the web, hover over a photo, and click the checkmark in the top left corner to select it. Then, click the three vertical dots in the top right corner and select “Download.”
28.3. How do I download an entire album from Google Photos?
To download an entire album, go to Google Photos, click the “Albums” tab, select the album you want to download, and click the three dots in the top right corner. Then, select “Download all.”
28.4. What is Google Takeout?
Google Takeout is a tool that allows you to export your data from various Google services, including Google Photos, Gmail, and Google Drive.
28.5. How long does it take to download all my Google Photos?
The time it takes to download all your Google Photos depends on the size of your library and your internet connection speed. It can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
28.6. What file format will my downloaded photos be in?
When you download photos from Google Photos, they will be in .zip format. You will need to extract the files after downloading.
28.7. Can I download Google Photos on my phone?
Yes, you can download individual photos and albums from the Google Photos app on your phone. However, to download all your photos at once, it’s best to use Google Takeout on a computer.
28.8. Is there a limit to how many photos I can download at once?
There is no specific limit to how many photos you can download at once, but large downloads may be split into multiple files.
28.9. What happens to the quality of my photos when I download them?
If you’ve been storing photos in “High Quality (Storage Saver),” downloading them will give you the compressed versions. If you want the original, uncompressed versions, make sure you’ve been storing them in “Original Quality.”
28.10. What should I do after downloading my Google Photos?
After downloading your Google Photos, organize your photos into folders, back them up to an external hard drive or another cloud storage service, and verify the integrity of the files to ensure they are not corrupted.
Ready to take control of your photo collection? Visit dfphoto.net today for more in-depth guides, tips, and resources to enhance your photography skills. Explore our extensive library of tutorials, discover stunning photography, and connect with a community of passionate photographers just like you. Don’t miss out—your next photographic adventure awaits at dfphoto.net!