Converting a black and white photo to color might seem like a complex task, but with the right tools and techniques, you can breathe new life into your monochrome images. At dfphoto.net, we provide comprehensive guides and resources to help you master the art of photo editing, including transforming black and white photos into vibrant color images. This process involves understanding color theory, utilizing advanced software features, and applying creative techniques to achieve realistic and stunning results. Dive in to discover how to bring your black and white photos to life.
1. Understanding the Basics of Black and White to Color Conversion
To effectively convert a black and white photo to color, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts involved. This includes understanding how black and white images are created, the role of color channels, and the various methods available for adding color back into these images. Let’s explore these foundational elements to give you a solid base for your colorization journey.
1.1. What Is a Black and White Photo?
A black and white photo, also known as a monochrome image, captures a scene using shades of gray, ranging from pure black to pure white. Unlike color photos that record different wavelengths of light to represent colors, black and white photos record only the intensity of light. This means that the colors present in the original scene are translated into varying levels of gray based on their brightness.
In a black and white image, each pixel is represented by a single value indicating its luminance, or brightness. This value determines whether the pixel appears as black, white, or some shade of gray in between. The absence of color information simplifies the image, allowing the viewer to focus on the composition, texture, and contrast.
1.2. The Role of Color Channels
Color channels are the building blocks of color images. In the RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color model, which is commonly used in digital photography, each color channel represents the intensity of one of these primary colors. When combined, these channels create the full spectrum of colors that we see in a photograph.
- Red Channel: Represents the intensity of red light in the image.
- Green Channel: Represents the intensity of green light in the image.
- Blue Channel: Represents the intensity of blue light in the image.
In a black and white image, all three color channels contain the same grayscale information. This is because there is no color variation; each channel simply represents the luminance value of the pixel. When converting to color, the goal is to introduce different values into each channel to simulate the presence of color.
1.3. Methods for Converting Black and White to Color
There are several methods for converting black and white photos to color, each with its own set of techniques and tools. Here are some of the most common approaches:
- Manual Colorization: This involves using photo editing software to manually paint color onto different areas of the black and white image. This method offers the most control but can be time-consuming.
- Semi-Automatic Colorization: This approach combines manual techniques with automated tools that can detect edges and regions, making it easier to apply color accurately.
- Automatic Colorization: This uses AI-powered algorithms to automatically add color to black and white photos. While it’s the quickest method, the results may not always be accurate and often require manual adjustments.
1.4. Why Convert Black and White to Color?
Converting a black and white photo to color can serve various purposes, depending on the context and desired outcome. Some common reasons include:
- Restoration: Bringing old family photos back to life by adding color can make them more relatable and visually appealing.
- Artistic Expression: Colorizing black and white photos can be a creative way to reimagine historical events or create surreal and dreamlike images.
- Commercial Use: Adding color to black and white images can make them more marketable for advertising, publishing, and other commercial applications.
By understanding these basics, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right method and techniques for converting your black and white photos to color and achieving the desired results.
2. Choosing the Right Software for Color Conversion
Selecting the right software is crucial for effectively converting black and white photos to color. Different software options offer varying levels of control, automation, and user-friendliness. This section will explore some of the best software tools available and their key features.
2.1. Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is widely regarded as the industry-standard software for photo editing and manipulation. Its comprehensive set of tools and features make it a powerful choice for converting black and white photos to color.
-
Key Features:
- Colorization Neural Filter: This AI-powered filter can automatically add color to black and white images with a single click.
- Layers and Masks: Photoshop’s layer-based editing system allows you to work non-destructively, making it easy to experiment with different color combinations and adjustments.
- Selection Tools: Precise selection tools like the Lasso, Magic Wand, and Quick Selection tool enable you to isolate specific areas for colorization.
- Blending Modes: Blending modes allow you to blend colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image, creating natural-looking results.
- Adjustment Layers: Adjustment layers like Color Balance, Hue/Saturation, and Curves provide fine-grained control over the colorization process.
-
Pros:
- Industry-standard software with a vast array of tools and features.
- Powerful AI-powered colorization filter.
- Non-destructive editing with layers and masks.
-
Cons:
- Steep learning curve for beginners.
- Subscription-based pricing model.
2.2. Corel PaintShop Pro
Corel PaintShop Pro is a more affordable alternative to Adobe Photoshop that still offers a robust set of tools for photo editing and colorization.
-
Key Features:
- AI Colorization: Similar to Photoshop, PaintShop Pro includes an AI-powered colorization feature that can automatically add color to black and white images.
- Layers and Masks: PaintShop Pro also supports layer-based editing, allowing you to work non-destructively.
- Selection Tools: A variety of selection tools make it easy to isolate specific areas for colorization.
- Color Adjustment Tools: PaintShop Pro includes a range of color adjustment tools like Hue/Saturation, Color Balance, and Levels.
-
Pros:
- More affordable than Adobe Photoshop.
- User-friendly interface.
- Perpetual license option.
-
Cons:
- Fewer advanced features compared to Photoshop.
- AI colorization may not be as accurate as Photoshop’s.
2.3. GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program)
GIMP is a free and open-source photo editing software that offers a wide range of features for image manipulation and colorization.
-
Key Features:
- Layers and Masks: GIMP supports layer-based editing, allowing you to work non-destructively.
- Selection Tools: A variety of selection tools make it easy to isolate specific areas for colorization.
- Color Adjustment Tools: GIMP includes a range of color adjustment tools like Color Balance, Hue/Saturation, and Curves.
- Plugins: GIMP’s functionality can be extended with a wide range of plugins, including some specifically designed for colorization.
-
Pros:
- Free and open-source.
- Wide range of features for image manipulation.
- Extensible with plugins.
-
Cons:
- Less intuitive interface compared to Photoshop and PaintShop Pro.
- No built-in AI colorization feature.
2.4. Online Colorization Tools
Several online tools use AI-powered algorithms to automatically colorize black and white photos. These tools are often free or offer a limited free trial.
-
Examples:
- MyHeritage In Color: This tool is part of the MyHeritage genealogy platform and is designed to colorize historical photos.
- Colourise.sg: This tool uses AI to automatically colorize black and white photos.
- Algorithmia: This platform offers a variety of AI-powered image processing tools, including a colorization algorithm.
-
Pros:
- Easy to use.
- No software installation required.
- Often free or offer a free trial.
-
Cons:
- Limited control over the colorization process.
- Results may not always be accurate.
- Privacy concerns with uploading photos to online services.
When choosing software for color conversion, consider your budget, skill level, and the level of control you need over the colorization process. For professional results and maximum control, Adobe Photoshop is the best choice. However, Corel PaintShop Pro and GIMP are viable alternatives for those on a budget or who prefer a more user-friendly interface. Online tools are a good option for quick and easy colorization, but they offer limited control and may not produce the best results.
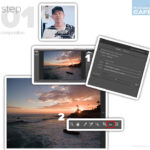
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Manual Colorization in Photoshop
Manual colorization in Photoshop involves using layers, blending modes, and color adjustments to add color to a black and white photo. This method offers the most control over the final result but requires patience and attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
3.1. Setting Up Your Photoshop Workspace
- Open the Black and White Image: Open the black and white photo in Photoshop by going to
File > Openand selecting the image file. - Create a New Layer: Create a new layer by clicking the
Create a New Layericon in the Layers panel or by going toLayer > New > Layer. Name this layer something descriptive, like “Skin Color.” - Set the Blending Mode: In the Layers panel, change the blending mode of the “Skin Color” layer to
Color. This blending mode will apply the color from the layer to the underlying grayscale image without affecting its luminance.
3.2. Selecting and Applying Colors
- Choose a Color: Select a color from the Color Picker panel. For skin tones, start with a warm, slightly reddish hue. You can adjust the color later.
- Select the Brush Tool: Select the Brush tool from the Tools panel. Choose a soft-edged brush with a moderate size.
- Paint the Color: Carefully paint the color onto the areas of the image that you want to colorize. Use a light touch and build up the color gradually. For skin, paint over the face, neck, and any visible skin areas.
- Refine the Edges: Use the Eraser tool with a soft brush to clean up any areas where the color spills over the edges.
3.3. Using Masks for Precision
- Add a Layer Mask: To further refine the colorization, add a layer mask to the “Skin Color” layer by clicking the
Add Layer Maskicon in the Layers panel. - Paint on the Mask: Select the Brush tool and set the color to black. Paint on the mask to hide the color in areas where it shouldn’t be. Set the color to white to reveal the color. Use a soft brush for smooth transitions.
- Refine the Mask: Use different brush sizes and opacities to refine the mask and create a natural-looking transition between the colorized and uncolored areas.
3.4. Adjusting Colors and Tones
- Add an Adjustment Layer: To adjust the color and tone of the colorized area, add an adjustment layer above the “Skin Color” layer. Go to
Layer > New Adjustment Layerand choose an adjustment layer likeHue/SaturationorColor Balance. - Adjust the Settings: In the Properties panel, adjust the settings of the adjustment layer to fine-tune the color and tone. For skin, you might want to adjust the hue, saturation, and lightness to create a more natural-looking skin tone.
- Clip the Adjustment Layer: To ensure that the adjustment layer only affects the “Skin Color” layer, clip the adjustment layer to the “Skin Color” layer by clicking the
Clip to Layericon in the Properties panel or by going toLayer > Create Clipping Mask.
3.5. Repeating the Process for Other Areas
Repeat the above steps for other areas of the image, such as clothing, hair, and background. Create a new layer for each area and use different colors and blending modes to achieve the desired effect.
- Tips:
- Use reference photos to guide your color choices.
- Pay attention to the lighting and shadows in the original image to create a more realistic colorization.
- Use different blending modes to create different effects. For example, the
Soft Lightblending mode can create a more subtle colorization, while theOverlayblending mode can create a more vibrant colorization. - Don’t be afraid to experiment with different colors and techniques.
3.6. Final Touches and Enhancements
- Sharpening: Apply a slight sharpening filter to the image to enhance the details. Go to
Filter > Sharpen > Unsharp Maskand adjust the settings to achieve the desired level of sharpness. - Noise Reduction: If the image has excessive noise, apply a noise reduction filter to smooth out the image. Go to
Filter > Noise > Reduce Noiseand adjust the settings to reduce the noise without sacrificing too much detail. - Save the Image: Save the colorized image in a high-resolution format like TIFF or JPEG. Go to
File > Save Asand choose the desired format and settings.
By following these steps, you can manually colorize black and white photos in Photoshop and achieve stunning results. Remember to practice and experiment with different techniques to develop your own unique style.
4. Using AI-Powered Colorization Tools
AI-powered colorization tools have revolutionized the process of converting black and white photos to color. These tools use advanced algorithms and machine learning to automatically add color to monochrome images. While they may not offer the same level of control as manual colorization, they can save a significant amount of time and effort. Here’s how to use AI-powered colorization tools effectively:
4.1. Choosing an AI Colorization Tool
Several AI colorization tools are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular options include:
- MyHeritage In Color: This tool is specifically designed for colorizing historical photos and is part of the MyHeritage genealogy platform.
- Colourise.sg: This tool uses AI to automatically colorize black and white photos and is free to use.
- Adobe Photoshop’s Colorize Filter: Photoshop’s Colorize Neural Filter uses AI to add color to black and white images.
When choosing an AI colorization tool, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: How accurately does the tool add color to the image?
- Speed: How quickly does the tool colorize the image?
- Ease of Use: How easy is the tool to use?
- Cost: Is the tool free or paid?
4.2. Preparing Your Image
Before using an AI colorization tool, it’s important to prepare your image for the best results. Here are some tips:
- Resolution: Use a high-resolution image for the best results.
- Clarity: Ensure that the image is clear and well-defined.
- Cropping: Crop the image to remove any unnecessary borders or distractions.
- Adjustments: Make any necessary adjustments to the brightness, contrast, and sharpness of the image.
4.3. Using MyHeritage In Color
MyHeritage In Color is a popular AI colorization tool that is specifically designed for historical photos. Here’s how to use it:
- Upload Your Image: Go to the MyHeritage In Color website and upload your black and white photo.
- Colorize the Image: The tool will automatically colorize the image.
- View and Download the Results: Once the colorization is complete, you can view and download the results.
4.4. Using Colourise.sg
Colourise.sg is a free AI colorization tool that is easy to use. Here’s how to use it:
- Upload Your Image: Go to the Colourise.sg website and upload your black and white photo.
- Colorize the Image: The tool will automatically colorize the image.
- View and Download the Results: Once the colorization is complete, you can view and download the results.
4.5. Using Adobe Photoshop’s Colorize Filter
Adobe Photoshop’s Colorize Neural Filter is a powerful AI colorization tool that is integrated into Photoshop. Here’s how to use it:
- Open Your Image: Open your black and white photo in Photoshop.
- Apply the Colorize Filter: Go to
Filter > Neural Filters > Colorize. - Adjust the Settings: Adjust the settings of the Colorize filter to fine-tune the colorization. You can use the Smart Portrait sliders to adjust the skin tone, face lighting, and hair color.
- Output the Results: Choose the desired output option, such as
Color,Grayscale, orOriginal. - Click OK: Click OK to apply the Colorize filter.
4.6. Refining the Results
While AI colorization tools can produce impressive results, they may not always be perfect. Here are some tips for refining the results:
- Adjust the Colors: Use color adjustment tools like Hue/Saturation and Color Balance to fine-tune the colors.
- Use Masks: Use masks to isolate specific areas for colorization.
- Add Details: Add details like highlights and shadows to enhance the realism of the colorization.
- Experiment: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different settings and techniques to achieve the desired effect.
By following these steps, you can effectively use AI-powered colorization tools to convert black and white photos to color and achieve stunning results. Remember to experiment and refine the results to create your own unique style.
5. Tips for Achieving Realistic Colorization
Achieving realistic colorization requires attention to detail and a good understanding of color theory. Here are some tips to help you create natural-looking colorized images:
5.1. Researching Color References
Before you start colorizing a black and white photo, it’s important to research color references for the objects and scenes in the image. This will help you choose the most accurate and realistic colors.
- Historical Photos: If you’re colorizing a historical photo, look for color photos from the same period to get an idea of the colors that were common at the time.
- Online Resources: Use online resources like Google Images and Pinterest to find color references for specific objects and scenes.
- Real-Life Observations: Pay attention to the colors in the real world and use them as a reference for your colorization.
5.2. Understanding Color Theory
A good understanding of color theory is essential for achieving realistic colorization. Here are some key concepts:
- Color Harmony: Choose colors that work well together and create a visually appealing image.
- Color Temperature: Use warm colors (red, orange, yellow) to create a sense of warmth and energy, and cool colors (blue, green, purple) to create a sense of calm and serenity.
- Color Contrast: Use contrasting colors to create visual interest and draw attention to specific areas of the image.
5.3. Paying Attention to Lighting and Shadows
The lighting and shadows in the original black and white photo can provide valuable clues about the colors of the objects and scenes in the image.
- Highlights: Highlights are the brightest areas of the image and can indicate the color of the light source.
- Shadows: Shadows are the darkest areas of the image and can indicate the color of the objects and scenes in the image.
- Midtones: Midtones are the areas in between the highlights and shadows and can provide additional information about the colors of the objects and scenes in the image.
5.4. Using Subtle Colors
When colorizing a black and white photo, it’s important to use subtle colors that blend seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image. Avoid using overly saturated or bright colors, as they can look unnatural and distracting.
- Low Saturation: Use colors with low saturation to create a more natural-looking colorization.
- Soft Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
- Gradual Transitions: Use gradual transitions between different colors to create a more natural-looking colorization.
5.5. Adding Details and Textures
Adding details and textures can enhance the realism of the colorization.
- Skin Details: Add details like freckles, wrinkles, and blemishes to create a more realistic skin tone.
- Clothing Details: Add details like folds, creases, and textures to create a more realistic clothing appearance.
- Background Details: Add details like trees, buildings, and landscapes to create a more realistic background.
5.6. Getting Feedback and Refining Your Work
Getting feedback from others can help you identify areas where your colorization can be improved.
- Ask for Feedback: Ask friends, family, and other photographers for feedback on your colorization.
- Be Open to Criticism: Be open to criticism and use it to improve your work.
- Refine Your Work: Refine your colorization based on the feedback you receive.
By following these tips, you can achieve realistic colorization and create stunning colorized images that look natural and believable.
6. Advanced Techniques for Colorizing Specific Elements
Colorizing specific elements like skin tones, clothing, and natural landscapes requires specialized techniques to achieve realistic results. Here’s a breakdown of advanced methods for these elements:
6.1. Achieving Natural Skin Tones
Realistic skin tones are crucial for believable colorization. Here’s how to achieve them:
- Base Color: Start with a base color that is close to the natural skin tone. Use a slightly reddish hue for fair skin and a more brownish hue for darker skin.
- Subsurface Scattering: Simulate subsurface scattering by adding a slightly yellowish hue to the highlights and a slightly reddish hue to the shadows. This will create a more realistic skin appearance.
- Color Variations: Add subtle color variations to the skin to create a more natural-looking appearance. Use a slightly greenish hue for veins and a slightly reddish hue for capillaries.
- Details: Add details like freckles, wrinkles, and blemishes to create a more realistic skin tone.
- Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
6.2. Colorizing Clothing with Texture
Colorizing clothing requires attention to texture and detail. Here’s how to do it:
- Base Color: Start with a base color that is close to the natural color of the clothing.
- Texture: Use texture brushes to add texture to the clothing. This will create a more realistic clothing appearance.
- Folds and Creases: Add folds and creases to the clothing to create a more realistic appearance.
- Highlights and Shadows: Add highlights and shadows to the clothing to create depth and dimension.
- Details: Add details like buttons, zippers, and seams to create a more realistic clothing appearance.
- Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
6.3. Capturing Realistic Landscapes
Colorizing landscapes requires attention to detail and a good understanding of natural colors. Here’s how to do it:
- Sky: Use a gradient to colorize the sky. Start with a light blue at the top and gradually transition to a darker blue at the bottom.
- Trees: Use a variety of green colors to colorize the trees. Add details like leaves, branches, and bark to create a more realistic appearance.
- Grass: Use a variety of green colors to colorize the grass. Add details like blades of grass, weeds, and flowers to create a more realistic appearance.
- Water: Use a variety of blue colors to colorize the water. Add details like ripples, waves, and reflections to create a more realistic appearance.
- Mountains: Use a variety of brown and gray colors to colorize the mountains. Add details like rocks, snow, and vegetation to create a more realistic appearance.
- Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
6.4. Restoring Old Photos
Restoring old photos requires a combination of colorization and restoration techniques. Here’s how to do it:
- Remove Scratches and Blemishes: Use the Clone Stamp tool to remove scratches and blemishes from the image.
- Adjust Brightness and Contrast: Adjust the brightness and contrast of the image to improve its overall appearance.
- Colorize the Image: Use the techniques described above to colorize the image.
- Add Details: Add details like skin textures, clothing details, and landscape details to create a more realistic appearance.
- Sharpen the Image: Sharpen the image to enhance the details.
- Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can achieve realistic colorization for specific elements and create stunning colorized images that look natural and believable.
7. Overcoming Common Challenges in Color Conversion
Converting black and white photos to color can present several challenges. Knowing how to address these issues can significantly improve your results. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
7.1. Dealing with Overly Grainy Photos
Grainy photos can make colorization difficult, as the grain can interfere with the color application. Here’s how to deal with grainy photos:
- Noise Reduction: Use noise reduction filters in Photoshop or other photo editing software to reduce the grain. Be careful not to overdo it, as too much noise reduction can make the image look blurry.
- Median Filter: Use the Median filter in Photoshop to smooth out the grain. This filter replaces each pixel with the median color of its surrounding pixels, which can help to reduce the grain.
- Smart Sharpen: Use the Smart Sharpen filter in Photoshop to sharpen the image after reducing the grain. This will help to restore some of the details that may have been lost during the noise reduction process.
- High-Quality Source: Start with the highest quality source image possible to minimize graininess from the outset.
7.2. Correcting Exposure Issues
Exposure issues can make colorization difficult, as the colors may not look natural if the image is too dark or too bright. Here’s how to correct exposure issues:
- Levels Adjustment: Use the Levels adjustment layer in Photoshop to adjust the brightness and contrast of the image. This will help to correct exposure issues and make the colors look more natural.
- Curves Adjustment: Use the Curves adjustment layer in Photoshop to fine-tune the exposure. This adjustment layer allows you to adjust the brightness and contrast of specific areas of the image.
- Shadows/Highlights Adjustment: Use the Shadows/Highlights adjustment in Photoshop to adjust the brightness of the shadows and highlights in the image. This adjustment can help to bring out details in the shadows and highlights.
7.3. Addressing Blurry or Out-of-Focus Areas
Blurry or out-of-focus areas can make colorization difficult, as it can be hard to determine the colors of the objects and scenes in the image. Here’s how to address blurry or out-of-focus areas:
- Sharpening: Use sharpening filters in Photoshop or other photo editing software to sharpen the image. Be careful not to overdo it, as too much sharpening can make the image look artificial.
- Smart Sharpen: Use the Smart Sharpen filter in Photoshop to sharpen the image. This filter allows you to sharpen specific areas of the image.
- Unsharp Mask: Use the Unsharp Mask filter in Photoshop to sharpen the image. This filter is a classic sharpening tool that can be used to enhance the details in the image.
- Focus Mask: If the blurriness is isolated to specific areas, use a focus mask to selectively sharpen those regions.
7.4. Preserving Original Details
Preserving original details is important for creating a realistic colorization. Here’s how to preserve original details:
- Non-Destructive Editing: Use non-destructive editing techniques like layers and masks to preserve the original details of the image. This will allow you to make changes to the colorization without affecting the original image.
- Blending Modes: Use blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image. This will help to preserve the original details of the image.
- Opacity: Use the opacity setting to adjust the opacity of the color layers. This will allow you to control the intensity of the colors and preserve the original details of the image.
7.5. Avoiding Over-Colorization
Over-colorization can make the image look unnatural and artificial. Here’s how to avoid over-colorization:
- Subtle Colors: Use subtle colors that blend seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image. Avoid using overly saturated or bright colors, as they can look unnatural and distracting.
- Low Saturation: Use colors with low saturation to create a more natural-looking colorization.
- Soft Blending: Use soft blending modes like Soft Light and Overlay to blend the colors seamlessly with the underlying grayscale image.
- Opacity: Use the opacity setting to adjust the opacity of the color layers. This will allow you to control the intensity of the colors and avoid over-colorization.
By addressing these common challenges, you can improve your colorization skills and create stunning colorized images that look natural and believable. Remember to practice and experiment with different techniques to develop your own unique style.
8. Exploring Creative Applications of Colorized Photos
Colorized photos can be used in a variety of creative applications, from restoring historical images to creating unique works of art. Here are some creative applications of colorized photos:
8.1. Restoring Historical Moments
Colorizing historical photos can bring the past to life and make it more accessible to modern audiences.
- Historical Archives: Colorize historical photos from archives and museums to create engaging exhibits and educational materials.
- Documentaries: Use colorized photos in documentaries to illustrate historical events and bring them to life for viewers.
- Genealogy: Colorize old family photos to preserve your family history and make it more meaningful.
8.2. Creating Artistic Interpretations
Colorizing black and white photos can be a creative way to express your artistic vision and create unique works of art.
- Surreal Art: Use unexpected color combinations to create surreal and dreamlike images.
- Abstract Art: Colorize abstract images to create bold and vibrant works of art.
- Photo Manipulations: Combine colorized photos with other images to create unique and imaginative photo manipulations.
8.3. Enhancing Storytelling
Colorized photos can be used to enhance storytelling and create more engaging visual narratives.
- Book Illustrations: Use colorized photos to illustrate books and bring the stories to life for readers.
- Magazine Articles: Use colorized photos in magazine articles to illustrate the text and make the articles more visually appealing.
- Websites and Blogs: Use colorized photos on websites and blogs to illustrate the content and make the websites and blogs more engaging.
8.4. Transforming Portraits
Colorizing portraits can enhance the subject’s personality and create more captivating images.
- Family Portraits: Colorize family portraits to create timeless keepsakes that capture the essence of your loved ones.
- Celebrity Portraits: Colorize celebrity portraits to create iconic images that showcase their unique style and personality.
- Self-Portraits: Colorize self-portraits to express your individuality and creativity.
8.5. Reinventing Landscapes
Colorizing landscapes can create stunning visuals that capture the beauty of nature in a new light.
- Travel Photography: Colorize travel photos to create captivating images that showcase the beauty of different destinations.
- Nature Photography: Colorize nature photos to create stunning images that capture the essence of the natural world.
- Urban Landscapes: Colorize urban landscapes to create unique images that showcase the beauty of cities and towns.
By exploring these creative applications, you can unlock the full potential of colorized photos and create stunning images that capture the imagination. Remember to experiment and have fun with the process.
9. Resources for Further Learning and Inspiration
To continue your journey in mastering the art of converting black and white photos to color, here are some valuable resources for further learning and inspiration:
9.1. Online Tutorials and Courses
- Adobe Photoshop Tutorials: Adobe offers a wide range of tutorials on its website that cover various aspects of Photoshop, including colorization techniques.
- YouTube Channels: Numerous YouTube channels offer tutorials on colorizing black and white photos, such as PiXimperfect, Phlearn, and Photoshop Training Channel.
- Skillshare and Udemy: These online learning platforms offer courses on photo editing and colorization taught by experienced professionals.
9.2. Books and Publications
- “The Photoshop Book for Digital Photographers” by Scott Kelby: This book provides comprehensive guidance on using Photoshop for photo editing, including colorization techniques.
- “Adobe Photoshop Classroom in a Book” by Adobe Creative Team: This book offers step-by-step instructions on using Photoshop, including colorization techniques.
- Photography Magazines: Magazines like “Popular Photography” and “Digital Photo Pro” often feature articles on photo editing and colorization.
9.3. Online Communities and Forums
- Photography Forums: Online forums like DPReview and PhotographyTalk offer discussions on various photography topics, including colorization techniques.
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/photoshop and r/colorization provide a platform for sharing and discussing colorized photos.
- Facebook Groups: Numerous Facebook groups are dedicated to photo editing and colorization, where you can share your work and get feedback from others.
9.4. Inspiring Colorization Artists
- Marina Amaral: A Brazilian colorization artist known for her stunningly realistic colorizations of historical photos.
- Sanna Dullaway: A Swedish colorization artist who specializes in colorizing historical photos.
- Jordan Lloyd: A British colorization artist who runs a company called Dynamichrome, which specializes in colorizing historical photos.
9.5. Software and Plugin Resources
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Subscribe to Adobe Creative Cloud to access the latest versions of Photoshop and other photo editing software.
- Nik Collection: A suite of photo editing plugins that includes powerful tools for color correction and enhancement.
- Topaz Labs: Offers AI-powered photo editing software and plugins, including tools for noise reduction and sharpening.
By utilizing these resources, you can expand your knowledge and skills in converting black and white photos to color and create stunning images that capture the imagination.
10. FAQ: Mastering Black and White to Color Conversion
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQ) about converting black and white photos to color:
10.1. Can you turn a black and white photo into color?
Yes, it is possible to convert a black and white photo to color using various techniques and software. Manual colorization involves painting color onto the image, while AI-powered tools automate the process.
10.2. Is there an app to turn black and white photos into color?
Yes, several mobile apps can colorize black and white photos. Some popular options include Colorize, Recolored, and