Are you struggling with inaccurate colors and inconsistent brightness in your photo edits? Calibrating your monitor is the key to achieving true-to-life visuals and ensuring your photos look their best, and dfphoto.net is here to guide you through the process. We’ll explore built-in tools, online resources, and professional calibration kits to help you achieve accurate colors, brightness, and contrast. Dive in to discover how monitor screen calibration ensures your images are consistently displayed across devices, leading to professional-quality results in your creative endeavors.
Explore techniques such as gamma adjustment, white point calibration, and color profiling.
1. What is Monitor Calibration and Why is it Essential for Photo Editing?
Monitor calibration is the process of adjusting a display to accurately reproduce colors, brightness, and contrast, ensuring that what you see on your screen is true to life. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, a properly calibrated monitor is crucial for accurate photo editing, as it allows you to make informed decisions about color adjustments and ensures consistency across different devices and print media.
- Why Calibrate? Calibration addresses the natural drift in monitor performance over time, ensuring consistent and accurate color representation.
- Ensuring Accuracy: Calibrating your monitor guarantees that the edits you make are precise and accurately reflect the final output, whether it’s for web display or print.
- For Professionals: Professional photographers rely on calibrated monitors to maintain the integrity of their work, avoiding costly reprints and ensuring client satisfaction.
2. Who Needs Monitor Calibration?
Anyone working with visual content, especially photographers, graphic designers, and video editors, benefits significantly from monitor calibration.
- Photographers: Need accurate color representation for editing and printing photos.
- Graphic Designers: Rely on consistent colors for branding and marketing materials.
- Video Editors: Require precise color grading for a professional look.
3. What are the Different Methods for Monitor Calibration?
There are several ways to calibrate your monitor, ranging from free software solutions to professional hardware calibrators.
- Built-In Calibration Tools: Windows and macOS offer basic calibration tools.
- Online Calibration Tools: Websites provide visual tests to help adjust settings.
- Hardware Calibrators: Devices like X-Rite i1Display Pro or Datacolor SpyderX offer precise measurements and automated adjustments.
4. How Do I Use Built-In Calibration Tools in Windows?
Windows 10 includes a Display Color Calibration tool that guides you through adjusting gamma, brightness, contrast, and color balance.
- Accessing the Tool: Right-click on the desktop, select “Display Settings,” and click “Color Calibration” under “Related Settings.”
- Gamma Adjustment: Follow the prompts to set the gamma level for optimal shadow and highlight detail.
- Brightness and Contrast: Adjust these settings to distinguish subtle differences in shades and tones.
- Color Balance: Fine-tune the color balance to neutralize any color casts.
- Saving the Profile: Save the new calibration as an ICC profile to ensure your settings are retained.
 Screenshot of Windows display color calibration tool
Screenshot of Windows display color calibration tool
5. How Do I Use Built-In Calibration Tools in macOS?
macOS provides a Display Calibrator Assistant to help you adjust white point, gamma, and brightness.
- Accessing the Tool: Go to “System Preferences” > “Displays” > “Color” > “Calibrate.”
- White Point Adjustment: Set the white point to match your ambient lighting conditions for accurate color perception.
- Gamma Adjustment: Adjust the gamma setting to achieve optimal contrast and detail.
- Saving the Profile: Name and save the new color profile to apply your settings.
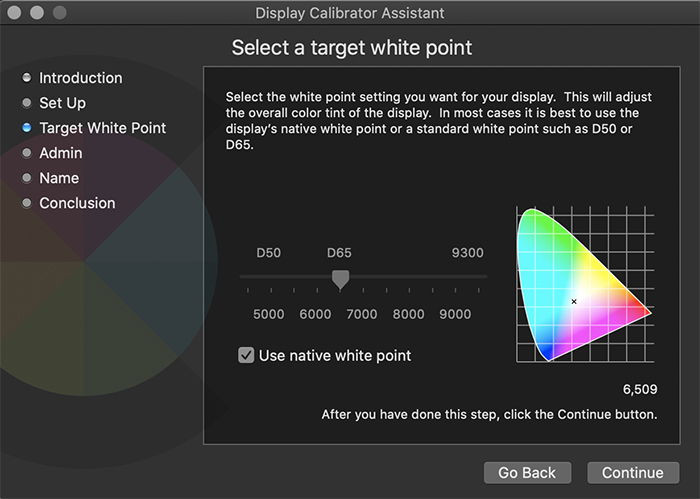 Screenshot of macOS display calibrator assistant tool
Screenshot of macOS display calibrator assistant tool
6. What are the Best Online Monitor Calibration Tools?
Several websites offer tools to help you visually calibrate your monitor. Here are a few top choices:
- Calibrize: A downloadable tool for adjusting brightness, contrast, gamma, and white point.
- Photo Friday: A quick visual check using shapes and tones to assess monitor performance.
- Lagom LCD Monitor Test Pages: A comprehensive set of test images for evaluating black levels, gradients, contrast, and more.
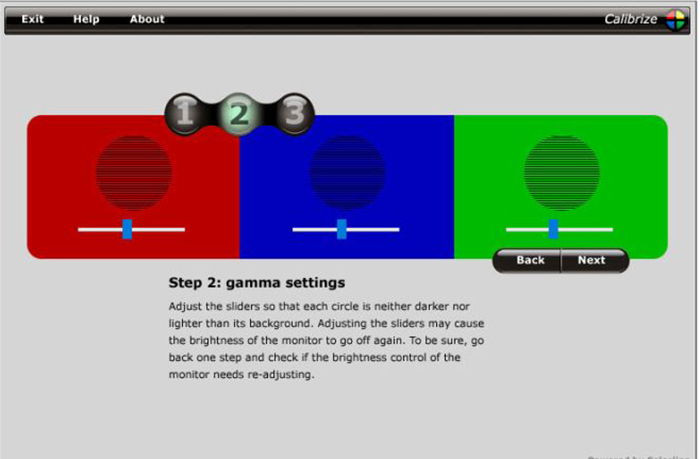 Screenshot of Calibrize calibration tool
Screenshot of Calibrize calibration tool
7. What are the Limitations of Using Online Tools?
While online tools are convenient, they rely on your subjective perception and may not provide the accuracy of hardware calibrators.
- Subjective Perception: Adjustments are based on your interpretation of colors and tones, which can vary.
- Limited Accuracy: Online tools cannot measure actual color output, so they may not correct all inconsistencies.
- Inconsistent Results: Results can vary depending on ambient lighting and viewing conditions.
8. When Should I Consider Using a Hardware Calibrator?
If you require precise color accuracy for professional work, a hardware calibrator is a worthwhile investment.
- Professional Work: Essential for photographers, designers, and video editors who need consistent and accurate results.
- Critical Color Matching: Necessary when matching colors across multiple devices or for print production.
- Time Savings: Automates the calibration process, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
9. What are the Benefits of Using Hardware Calibrators?
Hardware calibrators offer several advantages over software-based methods.
- Accuracy: Measures the actual color output of your monitor for precise adjustments.
- Consistency: Ensures consistent color representation over time and across different devices.
- Automation: Automates the calibration process, making it quick and easy.
- Profiling: Creates a custom color profile that accurately represents your monitor’s capabilities.
10. What are the Top Hardware Monitor Calibrators?
Two leading brands in monitor calibration are X-Rite and Datacolor.
- X-Rite i1Display Pro: Delivers high accuracy and advanced profiling options for professionals.
- Datacolor SpyderX Pro: Offers fast and accurate calibration with user-friendly software.
According to Popular Photography magazine’s review in March 2024, both devices are highly reliable, but the X-Rite i1Display Pro offers more advanced features for experienced users.
 Screenshot of SpyderX calibration tool
Screenshot of SpyderX calibration tool
11. How Does a Hardware Calibrator Work?
A hardware calibrator uses a sensor to measure the colors displayed on your screen and compares them to a known standard.
- Sensor Placement: The sensor is placed on your monitor’s screen to measure color output.
- Software Analysis: The calibrator’s software analyzes the measurements and calculates adjustments.
- Profile Creation: A custom color profile is created to correct any inconsistencies and ensure accurate color representation.
- Automated Adjustments: The software automatically adjusts your monitor’s settings to match the target values.
12. What are the Key Features to Look for in a Hardware Calibrator?
When choosing a hardware calibrator, consider these features:
- Color Accuracy: Ensures precise color measurement and correction.
- Profiling Options: Allows you to create custom color profiles for different workflows.
- Ambient Light Measurement: Adjusts monitor settings based on ambient lighting conditions.
- Software Interface: User-friendly software for easy calibration and profiling.
13. How Often Should I Calibrate My Monitor?
Regular calibration is essential to maintain color accuracy.
- Monthly Calibration: Recommended for critical color work to ensure consistency.
- Quarterly Calibration: Suitable for general use to address gradual color drift.
- After Major Changes: Calibrate after moving your monitor, changing lighting conditions, or upgrading your graphics card.
14. What is the ideal monitor setting for photo editing?
The ideal monitor settings for photo editing prioritize accuracy and consistency. Start by calibrating your monitor to a target gamma of 2.2, a white point of 6500K (D65), and a brightness level between 80-120 cd/m². These settings provide a neutral foundation for critical color assessment, ensuring that the colors you see on screen closely match the final output of your images.
15. How to improve monitor calibration accuracy?
To enhance the accuracy of your monitor calibration, start by ensuring a stable environment with consistent lighting, as suggested by the experts at the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department. Allow your monitor to warm up for at least 30 minutes before calibrating to stabilize its color output. Use a high-quality hardware calibrator and regularly update the calibration profile to maintain accurate color representation over time.
16. What are ICC Profiles and Why are They Important?
ICC (International Color Consortium) profiles are essential for color management, as they ensure consistent color representation across different devices and applications.
- Standardization: ICC profiles provide a standardized way to describe the color characteristics of devices like monitors, printers, and cameras.
- Color Conversion: They enable accurate color conversion between different color spaces, ensuring that colors are displayed correctly regardless of the device.
- Workflow Consistency: ICC profiles ensure consistency throughout your digital workflow, from image capture to editing and printing.
17. How Do I Install and Use ICC Profiles?
Installing and using ICC profiles is a straightforward process.
- Installation: On Windows, right-click the ICC profile file and select “Install Profile.” On macOS, copy the profile to the “/Library/ColorSync/Profiles” folder.
- Application Setup: In your photo editing software, select the appropriate ICC profile for your monitor in the color settings.
- Proofing: Use soft proofing to simulate how your images will look on different devices or with different printing profiles.
18. How Does Ambient Lighting Affect Monitor Calibration?
Ambient lighting can significantly impact your perception of colors on your monitor.
- Color Temperature: Different light sources have different color temperatures, which can affect how you perceive colors on your screen.
- Glare: Strong ambient light can cause glare on your monitor, reducing contrast and color accuracy.
- Consistency: Consistent ambient lighting is crucial for accurate color evaluation.
19. How Can I Minimize the Impact of Ambient Lighting?
To minimize the impact of ambient lighting:
- Control Light: Use blinds or curtains to control the amount of light in your editing environment.
- Neutral Light: Use a neutral-colored light source with a color temperature of around 5000K to 6500K.
- Hood: Use a monitor hood to block stray light and reduce glare.
20. How Do I Verify the Accuracy of My Calibration?
After calibrating your monitor, verify the accuracy of your settings.
- Visual Inspection: Compare your images to known standards or reference prints.
- Color Charts: Use color charts to evaluate color accuracy and consistency.
- Soft Proofing: Soft proof your images in your editing software to simulate how they will look on different devices.
21. What Are Common Issues After Monitor Calibration?
Even after calibrating, you may encounter issues:
- Color Casts: If you still see color casts, re-calibrate your monitor and ensure your ambient lighting is neutral.
- Contrast Issues: Adjust brightness and contrast settings to achieve optimal detail in shadows and highlights.
- Profile Conflicts: Ensure you are using the correct ICC profile for your monitor and that there are no conflicts with other color management settings.
22. What are Some Advanced Calibration Techniques?
For advanced users, explore these techniques:
- Hardware Calibration: Use dedicated hardware calibrators for precise color measurement and correction.
- Custom Profiling: Create custom profiles tailored to specific workflows or output devices.
- Ambient Light Compensation: Use calibrators that measure ambient light to adjust monitor settings dynamically.
23. What are the best monitors for photo editing?
Finding the best monitors for photo editing is crucial for achieving accurate and consistent results in your workflow. According to recent reviews in Popular Photography magazine, top-rated monitors include those with high color accuracy, wide color gamut coverage (such as Adobe RGB or DCI-P3), and excellent uniformity across the screen.
24. Where to find additional monitor calibration resources?
For further resources on monitor calibration, explore websites like dfphoto.net, which offers in-depth tutorials, product reviews, and community forums where you can connect with fellow photographers and experts.
25. What are the signs that your monitor needs calibration?
Recognizing the signs that your monitor needs calibration is essential for maintaining the accuracy of your photo editing workflow. If you notice that colors appear dull, inaccurate, or inconsistent across different devices or prints, it’s a clear indication that your monitor’s calibration is off.
26. How to set up monitor calibration workspace?
Setting up an optimal monitor calibration workspace is crucial for achieving accurate and consistent results. Start by selecting a room with controlled lighting conditions to minimize external influences on your monitor’s color perception.
27. How to calibrate a monitor for photo editing on a laptop?
Calibrating a monitor for photo editing on a laptop involves similar steps as calibrating a desktop monitor but may require additional considerations. Begin by ensuring that your laptop is connected to a stable power source and that the battery is fully charged to prevent fluctuations in brightness or color accuracy during the calibration process.
28. What is the difference between monitor calibration vs profiling?
Understanding the distinction between monitor calibration and profiling is essential for achieving accurate color representation in your photo editing workflow. Calibration refers to the process of adjusting a monitor’s settings to meet specific industry standards and achieve a neutral, consistent output.
29. What is color gamut and why is it important for photo editing?
Understanding color gamut is essential for photographers and photo editors who strive for accurate and vibrant color representation in their images. Color gamut refers to the range of colors that a particular device, such as a monitor or printer, can reproduce.
30. What are the common calibration myths to avoid?
Navigating the world of monitor calibration can be confusing, especially with numerous myths circulating about the process. One common myth is that all monitors are accurately calibrated straight out of the box.
Conclusion
Monitor calibration is a fundamental aspect of achieving accurate and consistent results in photo editing. Whether you choose to use built-in tools, online resources, or professional hardware calibrators, taking the time to properly calibrate your monitor will ensure that your images look their best across all devices and print media. Don’t let uncalibrated screens hold back your creative potential. Visit dfphoto.net to discover more tutorials, tips, and community support to elevate your photography skills.
Explore terms such as brightness levels, color accuracy, and color management.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States.
Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001
Website: dfphoto.net.