Adding a background to a photo in Photoshop is a common task for photographers and digital artists, and it’s easier than you might think; dfphoto.net explains how. Whether you want to place a product against a pristine white backdrop, create eye-catching composites, or simply enhance your images, mastering background manipulation in Photoshop unlocks a world of creative possibilities. This guide will cover everything from basic techniques to advanced tips, ensuring your photos stand out with seamless background integration and stunning visual effects using digital imaging, image manipulation, and photo enhancements.
1. What Are The Initial Steps To Add A Background To A Photo In Photoshop?
The initial steps involve opening your image in Photoshop and converting it into a layer.
- Open Photoshop and Load an Image: Launch Adobe Photoshop and open the image you wish to edit by selecting File > Open. Navigate to your image and click Open.
- Convert the Image to a Layer: In the Layers panel (usually found in the bottom right corner), check if your image is already a layer. If it appears as “Background,” you need to convert it. Go to Layer > New > Layer from Background. This turns your background into a flexible layer, allowing for transparent background edits. Name your layer, if you desire, and click OK.
These initial steps provide a foundation for seamless background integration and advanced digital image manipulation.
2. How Do I Resize The Canvas In Photoshop For Background Addition?
Resizing the canvas provides the necessary space for adding a new background.
- Open Canvas Size Window: Press Ctrl + Alt + C (Windows) or Option + Cmd + C (Mac) to open the Canvas Size window.
- Set Canvas Dimensions:
- Absolute Size: If you know the specific dimensions you want (e.g., 4500 x 3000 pixels), ensure the “Relative” box is unchecked. Enter your desired width and height in the respective boxes.
- Relative Expansion: Check the “Relative” box to expand the canvas from its current size by a specified amount. Enter the desired amounts in the width and height boxes. For example, to extend the canvas by 100 pixels vertically and 50 pixels horizontally, enter 100 in Width and 50 in Height.
- Anchor Point: Leave the anchor point set in the middle square to ensure the additions are applied equally on all sides of the image.
- Choose Measurement Units: Click the dropdown arrow next to “Pixels” to select a different measurement unit, such as centimeters or inches, if needed.
Resizing the canvas ensures there is ample room to seamlessly integrate the new background, enhancing the overall visual appeal.
3. What Are The Methods To Add A Background Image Or Color In Photoshop?
There are two primary methods: using an image or a solid color as the background.
- Adding an Image Background:
- Drag and Drop: Drag an image from your files directly onto the expanded canvas area in Photoshop. This will place the image as a new layer.
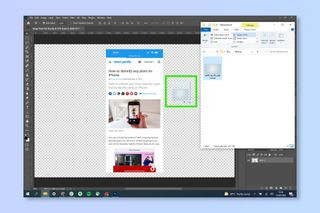 Dragging and dropping an image into Photoshop to use as a background
Dragging and dropping an image into Photoshop to use as a background
- Adding a Solid Color Background:
- Create a New Fill Layer: Go to Layer in the top toolbar, click New Fill Layer, then select Solid Color.
- Name the Layer: Name your new fill layer and click OK.
- Choose a Color: Select your desired color from the Color Picker and click OK.
Using these methods, you can easily add visually striking backgrounds, enhancing your photographs and creating unique digital art.
4. How Do I Resize And Position The Background In Photoshop?
Resizing and positioning the background ensures it fits perfectly within your composition.
- Resizing the Background Image:
- Adjust Anchor Points: If using an image as a background, it may not fit the canvas perfectly. Drag the anchor points (the small squares at the corners and sides of the image) to resize it.
- Maintain Aspect Ratio: To prevent distortion, ensure the aspect ratio lock symbol (usually a chain icon) is activated in the image toolbar. Alternatively, hold the Shift key while dragging the anchor points to resize the image proportionally.
- Confirm Changes: Once you are satisfied with the size and placement, click the checkmark icon in the image toolbar to apply the changes.
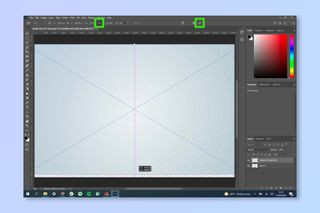 Resizing an image in Photoshop while holding shift to maintain aspect ratio
Resizing an image in Photoshop while holding shift to maintain aspect ratio
- Positioning the Layers:
- Move Image Layer: Your background layer will initially be stacked above your original image. To bring your original image to the forefront, click and hold its layer in the Layers panel (bottom right) and drag it above the background layer.
By resizing and positioning the background correctly, you can achieve a seamless and professional look in your photo manipulations.
5. What Are Some Advanced Techniques For Enhancing Backgrounds In Photoshop?
Advanced techniques can elevate your background editing from simple changes to sophisticated enhancements.
-
Using Layer Masks for Smooth Transitions:
- Add a Layer Mask: Select your image layer and click the “Add Layer Mask” icon at the bottom of the Layers panel (it looks like a rectangle with a circle inside).
- Gradient Tool: Select the Gradient Tool (G) from the toolbar. Choose a black to white gradient.
- Apply Gradient: Click and drag across the layer mask to create a smooth transition between the image and the background. Black hides parts of the layer, white reveals, and shades of gray create partial transparency.
-
Adding Depth of Field to the Background:
- Duplicate Background Layer: Right-click the background layer and select “Duplicate Layer.”
- Apply Gaussian Blur: Go to Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur. Adjust the radius to create the desired amount of blur, simulating depth of field.
- Layer Mask (Again): Add a layer mask to the blurred background layer and use the Gradient Tool to control which parts of the background are blurred.
-
Adjusting Background Color and Tone:
- Adjustment Layers: Use adjustment layers like “Curves,” “Levels,” or “Color Balance” to fine-tune the background’s color and tone. These layers allow non-destructive editing, meaning you can always adjust the settings without permanently altering the original image.
- Clipping Masks: To apply an adjustment layer only to the background, right-click the adjustment layer and select “Create Clipping Mask.”
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can significantly enhance the visual impact of your images, creating professional-quality photo manipulations.
6. How Can I Select Complex Image Elements For Background Changes In Photoshop?
Selecting complex elements accurately is crucial for seamless background changes.
-
Using the Pen Tool:
- Select Pen Tool: Choose the Pen Tool (P) from the toolbar.
- Create Paths: Carefully click and drag to create paths around the complex element. Use Alt/Option to adjust curves and angles precisely.
- Convert to Selection: Right-click inside the path and select “Make Selection.” Adjust the feather radius for softer edges.
-
Utilizing the Select and Mask Workspace:
- Make a Rough Selection: Use a selection tool like the Quick Selection Tool or Lasso Tool to make a rough selection of your element.
- Open Select and Mask: Go to Select > Select and Mask.
- Refine Edges: Use the Refine Edge Brush Tool to paint along the edges of the element, improving the selection around hair, fur, or other fine details.
- Adjust Settings: Adjust the Smooth, Feather, Contrast, and Shift Edge sliders to further refine the selection.
-
Color Range Selection:
- Go to Select > Color Range: This tool allows you to select parts of an image based on color.
- Sample Colors: Click on the colors you want to select. You can add to the selection by holding Shift and clicking, or subtract by holding Alt/Option and clicking.
- Adjust Fuzziness: The Fuzziness slider controls the range of colors selected.
Accurate selections are the foundation of professional-quality background changes, ensuring seamless integration and a polished final result.
7. What Are The Best Practices For Ensuring A Realistic Background Integration In Photoshop?
Achieving a realistic integration requires attention to detail and a nuanced approach.
-
Matching Lighting and Shadows:
- Analyze Lighting: Carefully observe the lighting direction and intensity in both the original image and the new background.
- Adjustment Layers: Use adjustment layers like “Curves” or “Levels” to match the lighting. For example, if the background is brighter, increase the brightness of the foreground element.
- Shadows and Highlights: Add or adjust shadows and highlights using the Dodge and Burn tools to ensure they align with the scene’s overall lighting.
-
Color Grading:
- Color Balance: Use the “Color Balance” adjustment layer to match the color tones between the foreground and background.
- Photo Filter: Apply a “Photo Filter” adjustment layer to add a warming or cooling effect, unifying the color palette.
- Selective Color: Fine-tune specific color ranges with the “Selective Color” adjustment layer for a more cohesive look.
-
Adding Noise and Texture:
- Match Noise Levels: If the background has a certain amount of noise, add a similar level of noise to the foreground element to blend them seamlessly.
- Texture Overlay: Overlay textures (like film grain or subtle patterns) to both the foreground and background to create a unified surface appearance.
By paying close attention to these details, you can ensure that your background integrations appear natural and convincing, enhancing the overall realism of your composite images.
8. How Do I Use Blending Modes Effectively With Backgrounds In Photoshop?
Blending modes offer powerful ways to merge layers and create unique effects.
-
Understanding Blending Modes:
- Location: Blending modes are found in the Layers panel, in a dropdown menu above the layer options.
- Categories: Blending modes are grouped into categories: Normal, Darken, Lighten, Contrast, Inversion, and Component.
-
Commonly Used Blending Modes:
- Multiply: Darkens the image by multiplying the colors of the selected layer with the layer below. Useful for adding shadows and depth.
- Screen: Lightens the image by inverting the colors, multiplying them, and then inverting the result. Ideal for adding highlights and creating a glowing effect.
- Overlay: Combines Multiply and Screen modes. Light areas become lighter, and dark areas become darker, increasing contrast.
- Soft Light: Similar to Overlay, but more subtle. It adds a gentle light or dark effect depending on the layer’s brightness.
- Color: Transfers the color of the selected layer to the layer below, while retaining the luminosity of the underlying layer. Useful for color grading.
-
Applying Blending Modes:
- Experiment: Try different blending modes to see how they affect the interaction between the foreground and background.
- Opacity: Adjust the opacity of the layer to control the strength of the blending mode’s effect.
- Layer Masks: Use layer masks to selectively apply the blending mode to specific areas of the image.
By experimenting with blending modes, you can create stunning visual effects and seamlessly integrate backgrounds into your images, achieving a professional and artistic result.
9. What Tools Are Available For Seamlessly Removing Existing Backgrounds In Photoshop?
Photoshop offers several tools for removing existing backgrounds, each with its strengths.
-
Background Eraser Tool:
- Select the Tool: Choose the Background Eraser Tool from the toolbar (it’s grouped with the Eraser Tool).
- Adjust Settings: Set the brush size, tolerance, and sampling options. A lower tolerance is better for images with distinct foregrounds and backgrounds, while a higher tolerance works well for more complex images.
- Erase Background: Carefully paint over the background to remove it. The tool samples the color at the center of the brush and erases similar colors within the brush area.
-
Magic Eraser Tool:
- Select the Tool: Choose the Magic Eraser Tool from the toolbar (also grouped with the Eraser Tool).
- Click to Erase: Click on the background area you want to remove. The tool erases all contiguous pixels that are similar in color to the pixel you clicked on.
- Adjust Tolerance: Adjust the tolerance setting to control the range of colors that are erased.
-
Remove Background Quick Action:
- Locate the Quick Action: In the Properties panel (Window > Properties), find the Quick Actions section.
- Click Remove Background: Click the “Remove Background” button. Photoshop automatically detects and removes the background.
- Refine the Mask: If necessary, refine the mask by clicking the “Select Subject” button to improve the initial selection, then manually adjust the mask in the Select and Mask workspace.
Using these tools, you can efficiently remove unwanted backgrounds and prepare your images for adding new and exciting backdrops, expanding your creative possibilities.
10. How Can dfphoto.net Help Me Improve My Photoshop Skills?
dfphoto.net is a great resource for enhancing your Photoshop skills and exploring new creative possibilities.
-
Extensive Tutorials and Guides:
- dfphoto.net offers a wide range of tutorials and guides covering various Photoshop techniques, from basic editing to advanced photo manipulation.
- These resources provide step-by-step instructions, ensuring you can easily follow along and master new skills.
-
Inspiration and Creative Ideas:
- The website features stunning photography and digital art, offering a wealth of inspiration for your own projects.
- Explore different styles and techniques to spark your creativity and discover new ways to enhance your images.
-
Community and Collaboration:
- dfphoto.net hosts a vibrant community of photographers and digital artists where you can connect with like-minded individuals.
- Share your work, receive feedback, and collaborate on projects to grow your skills and expand your network.
-
Expert Tips and Advice:
- Benefit from expert tips and advice from seasoned professionals in the field.
- Learn best practices, workflow optimizations, and insider techniques to elevate your Photoshop skills.
By leveraging the resources and community at dfphoto.net, you can unlock your creative potential and transform your images into stunning works of art.
To further enhance your images, dfphoto.net offers in-depth articles on how to remove a background in Photoshop, how to create a GIF in Photoshop, and how to add a drop shadow in Photoshop, along with resources on essential photography skills such as how to edit images on iPhone and understanding optical zoom vs. digital zoom.
11. What Are The Common Mistakes To Avoid When Adding Backgrounds In Photoshop?
Avoiding common mistakes ensures a professional and polished final image.
-
Mismatching Resolution:
- Problem: Using a low-resolution background image with a high-resolution foreground can result in a blurry or pixelated background.
- Solution: Ensure both the foreground and background images have similar resolutions. If the background is low-resolution, consider upscaling it or finding a higher-quality alternative.
-
Inconsistent Lighting:
- Problem: Mismatched lighting between the foreground and background can make the composite look unnatural.
- Solution: Analyze the lighting in both images and use adjustment layers (Curves, Levels) to match the brightness, contrast, and color tones.
-
Poor Selection Quality:
- Problem: Inaccurate selections can result in hard edges or unwanted artifacts around the foreground element.
- Solution: Use advanced selection tools like the Pen Tool or Select and Mask workspace for precise selections. Feather the edges slightly for a smoother transition.
-
Ignoring Shadows:
- Problem: Lack of realistic shadows can make the foreground element appear to float or look pasted on.
- Solution: Add shadows that match the direction and intensity of the light source. Use the Drop Shadow layer style or manually create shadows with the Burn Tool.
-
Overlooking Color Grading:
- Problem: Different color tones between the foreground and background can create a disjointed look.
- Solution: Use color grading techniques (Color Balance, Photo Filter, Selective Color) to unify the color palette and create a cohesive image.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure that your background integrations look seamless and professional.
12. How Do I Create A Seamless White Background For Product Photography In Photoshop?
Creating a seamless white background is essential for professional product photography.
-
Initial Setup:
- Open Image: Open your product photo in Photoshop.
- Duplicate Layer: Duplicate the background layer to preserve the original image.
-
Selection:
- Quick Selection Tool: Use the Quick Selection Tool to roughly select the product.
- Select and Mask: Refine the selection by going to Select > Select and Mask. Use the Refine Edge Brush to clean up the edges, especially around complex areas.
-
Background Removal:
- New Layer with Mask: In the Select and Mask workspace, choose “New Layer with Layer Mask” as the output. This creates a new layer with the product isolated and the background masked out.
-
Creating the White Background:
- New Solid Color Layer: Create a new Solid Color layer (Layer > New Fill Layer > Solid Color).
- Choose White: Select white as the color and click OK.
- Position Layer: Drag the white solid color layer below the product layer.
-
Adjusting Shadows and Highlights:
- Curves Adjustment Layer: Add a Curves adjustment layer above the product layer.
- Adjust Contrast: Use the Curves tool to adjust the contrast and brightness of the product, ensuring it looks natural against the white background.
- Dodge and Burn: Use the Dodge and Burn tools to refine the shadows and highlights, creating a more three-dimensional appearance.
-
Cleaning Up:
- Spot Healing Brush: Use the Spot Healing Brush Tool to remove any remaining blemishes or imperfections on the product.
- Clone Stamp Tool: Use the Clone Stamp Tool to clone clean areas over any distracting spots or reflections.
By following these steps, you can achieve a seamless white background that enhances the presentation of your product, making it ideal for e-commerce and marketing materials.
13. How Do I Add Realistic Shadows To My Subject On A New Background In Photoshop?
Adding realistic shadows is crucial for grounding your subject and creating a believable composite.
-
Assess the Light Source:
- Determine Direction and Intensity: Identify the direction and intensity of the light source in your new background. This will dictate the angle and softness of the shadows.
-
Creating a Basic Shadow:
- Duplicate Subject Layer: Duplicate the layer of your subject.
- Fill with Black: Fill the duplicated layer with black (Edit > Fill > Black).
- Position Shadow: Move the black layer below the subject layer and offset it in the direction opposite the light source.
-
Blurring the Shadow:
- Gaussian Blur: Apply a Gaussian Blur to the shadow layer (Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur). Adjust the radius to soften the edges of the shadow, mimicking the diffusion of light.
-
Distorting the Shadow:
- Distort Tool: Use the Distort tool (Edit > Transform > Distort) to adjust the shape of the shadow, making it follow the contours of the surface it falls on.
-
Adjusting Opacity:
- Reduce Opacity: Reduce the opacity of the shadow layer to make it appear more realistic. The opacity will depend on the intensity of the light source; a brighter light will cast a darker shadow.
-
Adding Contact Shadows:
- Small, Dark Shadows: Create small, dark shadows directly beneath the subject to simulate the contact between the subject and the ground. Use a small, soft brush with low opacity to paint these shadows.
-
Using Perspective:
- Perspective Transform: Use the Perspective transform (Edit > Transform > Perspective) to adjust the shadow’s perspective, making it align with the vanishing points of the background.
By carefully crafting the shadows, you can create a sense of depth and realism, making your subject look naturally integrated into the new background.
14. How Can I Match The Color Grading Of My Subject To The New Background In Photoshop?
Matching color grading ensures that your subject blends seamlessly with the new background, creating a cohesive and professional-looking image.
-
Analyze Color Tones:
- Identify Dominant Colors: Determine the dominant colors and tones in both the subject and the background. Look for differences in hue, saturation, and brightness.
-
Use Adjustment Layers:
- Color Balance: Add a Color Balance adjustment layer above your subject layer. Adjust the sliders to shift the color balance of the subject, matching it to the background.
- Curves: Use a Curves adjustment layer to adjust the overall brightness and contrast of the subject, aligning it with the background’s tones.
- Photo Filter: Apply a Photo Filter adjustment layer to add a warming or cooling filter, unifying the color palette.
-
Selective Color Adjustments:
- Selective Color Layer: Use a Selective Color adjustment layer to fine-tune specific color ranges. For example, adjust the reds, yellows, and blues to match the corresponding colors in the background.
-
Match Black and White Points:
- Levels Adjustment Layer: Use a Levels adjustment layer to set the black and white points of the subject, ensuring they match the dynamic range of the background.
-
Using the Match Color Tool:
- Apply Image > Adjustments > Match Color: Use the Match Color tool to automatically adjust the colors of the subject layer to match a selected source (in this case, the background).
-
Consider Environmental Lighting:
- Environmental Lighting Effects: Add subtle color tints to the subject to simulate the environmental lighting of the background. For example, add a blue tint to simulate sky light or a green tint to simulate foliage.
By carefully adjusting the color grading, you can create a harmonious and visually appealing composite image where the subject and background blend seamlessly.
15. What Are The Best File Formats For Saving Images With Transparent Backgrounds From Photoshop?
Choosing the right file format is crucial for preserving transparency and ensuring optimal image quality.
-
PNG (Portable Network Graphics):
- Best Use: PNG is the preferred format for saving images with transparent backgrounds. It supports lossless compression, meaning no image data is lost during saving.
- Advantages: Excellent for web graphics, logos, and images with text or sharp lines.
- Considerations: PNG files can be larger than JPEG files, especially for images with many colors.
-
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format):
- Best Use: GIF is suitable for simple graphics, animations, and images with limited color palettes.
- Advantages: Supports transparency and animation.
- Considerations: GIF uses lossy compression and is limited to 256 colors, which can result in lower image quality for complex images.
-
PSD (Photoshop Document):
- Best Use: PSD is the native file format for Adobe Photoshop. It preserves all layers, adjustment layers, and transparency.
- Advantages: Ideal for saving work in progress and preserving all editing capabilities.
- Considerations: PSD files can be very large and are not universally supported by all image viewers or web browsers.
-
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):
- Best Use: TIFF is a versatile format that supports both lossless and lossy compression. It is often used for archival purposes and high-quality printing.
- Advantages: Can preserve transparency and supports high bit depths.
- Considerations: TIFF files can be very large and are not ideal for web use.
-
Saving with Transparency:
- Ensure Transparency: When saving in PNG or GIF format, ensure that the “Transparency” option is checked in the save dialog box.
By selecting the appropriate file format, you can ensure that your images with transparent backgrounds retain their quality and transparency, regardless of their intended use.
FAQ: Adding Backgrounds in Photoshop
- How do I quickly remove a background in Photoshop?
- Utilize the “Remove Background” quick action in the Properties panel for a fast, automated solution.
- What’s the best way to select hair for a background change?
- Use the Select and Mask workspace with the Refine Edge Brush for precise hair selection.
- How can I match the lighting of my subject to a new background?
- Employ Curves and Levels adjustment layers to align the brightness and contrast between the subject and background.
- Which blending mode works best for adding shadows?
- The Multiply blending mode is ideal for darkening areas and adding realistic shadows.
- How do I create a smooth transition between layers?
- Apply layer masks with the Gradient Tool for seamless blending.
- What is color grading and how does it help?
- Color grading involves adjusting color tones to unify the foreground and background, creating a cohesive image.
- Which file format should I use for transparent backgrounds?
- Save as PNG to preserve transparency with lossless compression.
- How can I add a depth of field effect to the background?
- Duplicate the background layer, apply Gaussian Blur, and use a layer mask to control the blurred areas.
- What’s the best tool for precise selections?
- The Pen Tool allows for highly accurate selections, especially for complex shapes.
- How does dfphoto.net help improve Photoshop skills?
- dfphoto.net offers tutorials, inspiration, a community, and expert advice to enhance your Photoshop abilities.
Ready to take your Photoshop skills to the next level? Explore dfphoto.net for comprehensive tutorials, inspiring galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers and digital artists. Whether you’re aiming to master background changes or explore advanced photo manipulations, dfphoto.net is your go-to resource. Start your creative journey today at dfphoto.net! Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.