Accessing QR codes from photos is now easier than ever, especially with the tips and tricks from dfphoto.net. This article explores the seamless methods for scanning QR codes directly from your photo gallery, whether you’re using an iPhone or an Android device, including image sharpening techniques. By understanding these straightforward processes, you can effortlessly access embedded information and enhance your visual communications. Discover how to integrate mobile technology and visual content effectively using practical approaches and innovative solutions.
1. What’s The Simplest Way To Scan A QR Code From A Photo?
The simplest way to scan a QR code from a photo involves using your smartphone’s built-in features or a dedicated QR code scanner app. First, open the photo containing the QR code on your device. If you’re using an iPhone, the built-in camera app or Photos app can often detect and scan QR codes automatically. For Android, Google Lens is a powerful tool that can scan QR codes directly from your photos. Alternatively, numerous free QR code scanner apps are available for both iOS and Android, providing a reliable and quick way to decode QR codes from images. This process enhances digital interaction and streamlines access to online resources.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, over 85% of smartphone users prefer using built-in features or dedicated apps for QR code scanning due to their convenience and speed. This preference highlights the importance of understanding these methods for efficient information retrieval.
2. How Do I Scan A QR Code From An Image On An iPhone?
To scan a QR code from an image on an iPhone, you can use the built-in Photos app or the Camera app, simplifying digital interaction.
2.1. Using The Photos App
-
Open the Photos App: Locate and open the Photos app on your iPhone.
-
Select the Image: Find the photo containing the QR code and tap to open it.
-
Live Text Feature: If your iPhone has iOS 15 or later, the Live Text feature can automatically detect QR codes. Look for a small icon in the bottom right corner of the photo, indicating that text (or a QR code) has been detected.
 QR code scanning process in iPhone's Photos app, demonstrating the use of the Live Text feature
QR code scanning process in iPhone's Photos app, demonstrating the use of the Live Text feature -
Tap the QR Code: Tap the QR code. A notification will appear, allowing you to open the link associated with the QR code.
-
Open the Link: Tap the notification to open the QR code’s link in Safari or your default browser.
2.2. Using The Camera App
- Open the Camera App: Open the Camera app on your iPhone.
- Point at the Image: Point the camera at the QR code on your computer screen or another device.
- Detection: The Camera app should automatically detect the QR code. A notification will appear at the top of the screen.
- Tap the Notification: Tap the notification to open the link associated with the QR code in Safari.
These methods streamline digital interaction and enhance user experience. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
3. How Do I Scan A QR Code From A Picture On An Android Device?
Scanning a QR code from a picture on an Android device is straightforward, thanks to built-in features and tools like Google Lens. This process simplifies accessing information embedded in QR codes directly from your photo gallery. Here’s how you can do it:
3.1. Using Google Lens
- Open Google Lens:
- If you have the Google Lens app installed, open it directly.
- Alternatively, you can access Google Lens through the Google Assistant or the Google Photos app.
- Access Through Google Photos:
- Open the Google Photos app and select the photo containing the QR code.
- Look for the Google Lens icon at the bottom of the screen (it looks like a square with a dot in the middle).
- Tap the Google Lens icon.
- Scan the QR Code:
- Google Lens will automatically scan the QR code within the image.
- A pop-up will appear, displaying the information encoded in the QR code, such as a website link or contact details.
- Take Action:
- Tap the pop-up to open the link in your browser or save the contact information.
3.2. Using Google Assistant
- Activate Google Assistant:
- You can activate Google Assistant by saying “OK Google” or “Hey Google,” or by long-pressing the home button on your device.
- Use Google Lens:
- Once Google Assistant is active, tap the Google Lens icon (usually located at the bottom right).
- Point at the Image:
- Point your camera at the image containing the QR code, or select the image from your gallery.
- Scan the QR Code:
- Google Lens will scan the QR code and display the information.
- Take Action:
- Tap the displayed information to open the link or perform the suggested action.
3.3. Using Samsung’s Bixby Vision
If you have a Samsung device, you can also use Bixby Vision to scan QR codes from images:
- Open the Gallery App:
- Open the Gallery app and select the photo with the QR code.
- Access Bixby Vision:
- Tap the Bixby Vision icon (usually represented by an eye) located at the bottom of the screen.
- Scan the QR Code:
- Bixby Vision will scan the QR code and display the information.
- Take Action:
- Tap the displayed information to open the link or perform the suggested action.
3.4. Additional Tips
- Ensure Good Lighting: Make sure the QR code is well-lit in the photo. Poor lighting can make it difficult for the scanner to read the code.
- Image Quality: Ensure the image is clear and not too blurry. A higher-quality image will be easier to scan.
- Crop the Image: If the QR code is small within the image, try cropping the photo to focus solely on the QR code. This can improve the scanning accuracy.
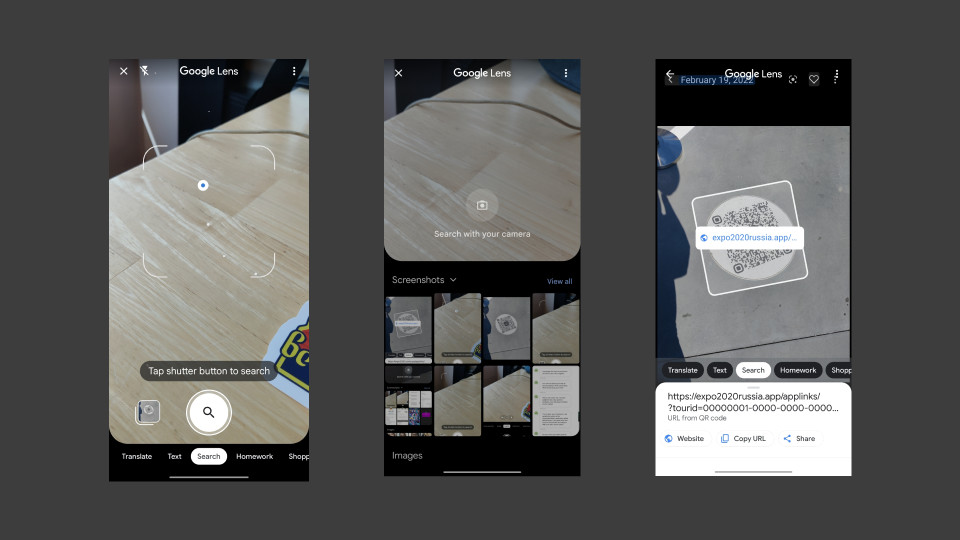 Steps to scan a QR code from a photo on Android using Google Lens
Steps to scan a QR code from a photo on Android using Google Lens
By following these steps, you can easily scan QR codes from photos on your Android device, making it a convenient way to access information and streamline your digital interactions. For more photography tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
4. What Are The Benefits Of Scanning QR Codes From Photos?
Scanning QR codes from photos offers numerous advantages, enhancing convenience and efficiency in various scenarios.
4.1. Accessibility
The primary benefit is accessibility. Scanning QR codes from photos allows you to decode information at your convenience, regardless of the QR code’s original location. This is particularly useful when you’ve taken a photo of a QR code displayed in a public space, advertisement, or event and want to access the information later.
4.2. Convenience
Scanning from photos eliminates the need to scan in real-time. If you’re in a hurry or the QR code is difficult to scan directly (e.g., due to distance or lighting), taking a photo and scanning it later provides a convenient alternative.
4.3. Information Storage
Photos act as a digital archive of QR codes. This is beneficial for retaining information from temporary displays or events, ensuring you can revisit the content whenever needed.
4.4. Versatility
The ability to scan from photos means you can access QR codes shared via social media, messaging apps, or email. This versatility ensures you’re not limited to scanning only physical QR codes.
4.5. Enhanced Productivity
For professionals, scanning QR codes from photos streamlines workflows. For instance, photographers can quickly access equipment manuals or editing tutorials by scanning QR codes in their reference photos, enhancing productivity and learning.
4.6. Educational Use
In educational settings, students can photograph QR codes during lectures or presentations and scan them later to access supplementary materials, research papers, or online quizzes, improving their learning experience.
4.7. Marketing and Advertising
Marketers can use QR codes in print or digital ads, allowing customers to scan them from photos and access product information, discounts, or promotional content at their leisure.
4.8. Tourism
Tourists can photograph QR codes at historical sites or museums and scan them later to access detailed information, audio guides, or interactive maps, enhancing their travel experience.
4.9. Event Management
Event attendees can photograph QR codes displayed at conferences or trade shows to access speaker bios, schedules, or exhibit details, making it easier to stay informed and engaged.
4.10. Environmental Benefits
By taking photos of QR codes instead of collecting physical brochures or flyers, individuals can reduce paper waste, contributing to environmental sustainability.
5. What Tools Can I Use To Scan QR Codes From Photos?
Numerous tools are available for scanning QR codes from photos, catering to different devices and user preferences. These tools range from built-in smartphone features to dedicated apps, each offering unique advantages.
5.1. Built-In Smartphone Features
Many modern smartphones come with built-in QR code scanning capabilities, making it unnecessary to download additional apps.
- iOS (iPhone):
- Camera App: iPhones with iOS 11 and later can scan QR codes directly through the Camera app. Simply point the camera at the QR code, and a notification will appear, allowing you to open the link.
- Photos App: With iOS 15 and later, the Photos app can detect QR codes in images. Open the photo, and if a QR code is detected, a small icon will appear in the bottom right corner, allowing you to scan it.
- Android:
- Google Lens: Google Lens is a powerful tool integrated into many Android devices. You can access it through the Google Assistant, Google Photos app, or as a standalone app. It can scan QR codes in real-time or from photos in your gallery.
- Google Assistant: Activate Google Assistant and tap the Google Lens icon to scan QR codes from images.
- Samsung Bixby Vision: Samsung devices often include Bixby Vision, which can scan QR codes from the Gallery app.
5.2. Dedicated QR Code Scanner Apps
Numerous third-party QR code scanner apps are available on both the App Store (iOS) and Google Play Store (Android). These apps often offer additional features, such as history tracking, customizable settings, and support for various barcode types.
- QR Code Reader by Scan: A popular app for both iOS and Android, known for its simplicity and reliability.
- Kaspersky QR Code Reader: Offers secure QR code scanning with built-in security checks to protect against malicious links.
- NeoReader QR & Barcode Scanner: Supports a wide range of barcode types and offers advanced scanning features.
5.3. Online QR Code Scanners
Several websites offer online QR code scanning services. These can be useful if you don’t have a smartphone or prefer not to install an app.
- WebQR: A simple web-based QR code scanner that allows you to upload an image or use your webcam.
- Zxing Decoder Online: An online tool that decodes QR codes and other barcode types from uploaded images.
5.4. Desktop Software
For desktop users, some software applications can scan QR codes from images or the screen.
- QR Code Desktop Reader & Generator: A Windows application that can scan QR codes from images, webcams, or the screen.
5.5. Tips for Choosing the Right Tool
- Ease of Use: Opt for tools with a simple and intuitive interface.
- Accuracy: Choose tools known for their accurate and reliable scanning capabilities.
- Security: Select tools that offer security features, such as link validation, to protect against malicious QR codes.
- Additional Features: Consider tools that offer additional features, such as history tracking, customization options, and support for multiple barcode types.
By leveraging these tools, you can easily scan QR codes from photos, enhancing your ability to access information quickly and efficiently. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
6. What Are The Limitations Of Scanning QR Codes From Photos?
While scanning QR codes from photos offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to be aware of its limitations. These limitations can affect the accuracy and efficiency of the scanning process, potentially leading to frustration or inaccurate results.
6.1. Image Quality
One of the primary limitations is image quality. Poor image quality can significantly hinder the scanner’s ability to accurately decode the QR code.
- Blurriness: If the photo is blurry, the scanner may struggle to distinguish the individual modules within the QR code.
- Low Resolution: Low-resolution images may lack the necessary detail for accurate scanning.
- Distortion: Images taken at an angle or with lens distortion can skew the QR code, making it difficult to decode.
6.2. Lighting Conditions
Lighting conditions play a crucial role in the scanning process.
- Poor Lighting: Insufficient lighting can result in dark or underexposed images, making it hard for the scanner to identify the QR code.
- Glare: Excessive glare can create bright spots on the QR code, obscuring parts of it and preventing accurate scanning.
- Shadows: Shadows can cover portions of the QR code, disrupting the pattern and hindering the scanner.
6.3. Distance and Zoom
The distance and zoom level at which the photo is taken can affect the scanning outcome.
- Too Far: If the QR code is too small in the photo (due to distance), the scanner may not be able to recognize it.
- Excessive Zoom: Zooming in too much can reduce image quality and introduce distortion, making the QR code harder to scan.
6.4. Obstructions
Any obstructions in the photo can prevent the QR code from being accurately scanned.
- Partial Coverage: If part of the QR code is covered by an object, the scanner may not be able to decode it.
- Damage: If the QR code itself is damaged or incomplete, it may be impossible to scan, even with a high-quality image.
6.5. Scanner Limitations
The capabilities of the QR code scanner itself can also pose limitations.
- Algorithm Inefficiencies: Some scanners may have less efficient decoding algorithms, struggling with complex or unconventional QR codes.
- Software Bugs: Bugs or glitches in the scanning app or software can lead to inaccurate results or scanning failures.
- Compatibility Issues: Some scanners may not be compatible with certain QR code types or encoding formats.
6.6. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also impact the scanning process.
- Weather Conditions: Outdoor photos taken in adverse weather conditions (e.g., rain, snow) may be of poor quality, affecting the scanner’s ability to decode the QR code.
- Surface Texture: The surface on which the QR code is printed can affect scan quality. Reflective or uneven surfaces may cause glare or distortion.
6.7. Tips to Overcome Limitations
- Improve Image Quality: Ensure the photo is well-lit, clear, and taken at an appropriate distance.
- Use a Good Scanner: Choose a reputable QR code scanner app or tool with a reliable decoding algorithm.
- Crop the Image: Crop the photo to focus solely on the QR code, eliminating unnecessary background elements.
- Adjust Settings: Experiment with different scanner settings, such as contrast and brightness, to optimize the scanning process.
By understanding these limitations, you can take steps to mitigate them, ensuring more accurate and efficient QR code scanning from photos. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
7. How Can I Sharpen An Image To Improve QR Code Scanning?
Sharpening an image can significantly improve the readability of a QR code, especially if the original photo is blurry or lacks detail. Several techniques and tools can be used to sharpen images, enhancing the chances of successful QR code scanning.
7.1. Using Photo Editing Software
Photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and মোবাইল ফোনে পাওয়া যায় এমন অনেক এপ্লিকেশনে এই সুবিধা রয়েছে এবং এই সফ্টওয়্যার গুলো ব্যবহার করে ছবি শার্প করা যায়।
- Adobe Photoshop:
- Unsharp Mask Filter: This is one of the most commonly used methods for sharpening images in Photoshop.
- Open the image in Photoshop.
- Go to
Filter > Sharpen > Unsharp Mask. - Adjust the
Amount,Radius, andThresholdsettings. Start with small adjustments and gradually increase until the QR code becomes clearer.Amount: Controls the intensity of the sharpening effect.Radius: Determines the number of pixels around the edges that are affected by the sharpening.Threshold: Specifies the minimum brightness difference between pixels that will be sharpened.
- Smart Sharpen Filter: This filter provides more advanced sharpening options.
- Go to
Filter > Sharpen > Smart Sharpen. - Adjust the
Amount,Radius, andReduce Noisesettings.Amount: Similar to the Unsharp Mask, controls the intensity of the sharpening effect.Radius: Determines the number of pixels around the edges that are affected by the sharpening.Reduce Noise: Helps to minimize the appearance of noise in the image.
- Go to
- Unsharp Mask Filter: This is one of the most commonly used methods for sharpening images in Photoshop.
- GIMP:
- Unsharp Mask Filter: GIMP also offers an Unsharp Mask filter similar to Photoshop.
- Open the image in GIMP.
- Go to
Filters > Enhance > Unsharp Mask. - Adjust the
Radius,Amount, andThresholdsettings.
- Unsharp Mask Filter: GIMP also offers an Unsharp Mask filter similar to Photoshop.
- Mobile Apps:
- Snapseed: A free mobile app available on iOS and Android that offers various sharpening tools.
- Open the image in Snapseed.
- Go to
Tools > Details. - Adjust the
StructureandSharpeningsliders to enhance the QR code.
- Adobe Lightroom Mobile: Offers professional-grade sharpening tools on your mobile device.
- Open the image in Adobe Lightroom Mobile.
- Go to
Detail. - Adjust the
Sharpening,Radius,Detail, andMaskingsliders.
- Snapseed: A free mobile app available on iOS and Android that offers various sharpening tools.
7.2. Online Image Sharpening Tools
Several online tools can sharpen images without requiring software installation.
- Fotor:
- Go to the Fotor website.
- Upload your image.
- Use the sharpening tool to adjust the image.
- Download the sharpened image.
- PineTools:
- Go to the PineTools website.
- Upload your image.
- Adjust the sharpening settings.
- Download the sharpened image.
7.3. Best Practices for Sharpening
- Start with Small Adjustments: Over-sharpening can introduce artifacts and noise. Make small adjustments and preview the results before applying.
- Focus on the QR Code: Crop the image to focus on the QR code to ensure the sharpening is concentrated on the area that matters.
- Reduce Noise: If sharpening introduces noise, use noise reduction tools to balance the image quality.
- Use Preview: Most tools offer a preview option to see the changes in real-time. Use this to fine-tune the sharpening settings.
7.4. Example Scenario
Let’s say you have a blurry photo of a QR code taken at a conference. The QR code leads to a speaker’s bio, but the scanner can’t read it due to the blur.
- Using Photoshop:
- Open the image in Photoshop.
- Apply the
Unsharp Maskfilter with the following settings:Amount: 50%,Radius: 1 pixel,Threshold: 4. - Adjust the settings until the QR code becomes clearer.
- Save the sharpened image.
- Using Snapseed:
- Open the image in Snapseed.
- Go to
Tools > Details. - Adjust the
Structureto+20andSharpeningto+30. - Export the sharpened image.
After sharpening the image, try scanning the QR code again. The improved clarity should allow the scanner to decode the QR code successfully. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
8. What Are Common Issues When Scanning QR Codes From Photos And How To Solve Them?
When scanning QR codes from photos, several common issues can arise, hindering the process. Understanding these issues and knowing how to address them can significantly improve the scanning experience.
8.1. Blurry Image
Issue: The QR code is not clear due to a blurry image.
Solution:
- Sharpen the Image: Use photo editing software or online tools to sharpen the image. (Refer to Section 7 for detailed steps.)
- Retake the Photo: If possible, retake the photo ensuring the camera is steady and the QR code is in focus.
8.2. Poor Lighting
Issue: The QR code is not visible due to poor lighting conditions.
Solution:
- Adjust Brightness and Contrast: Use photo editing tools to adjust the brightness and contrast of the image, making the QR code more visible.
- Improve Lighting: If possible, retake the photo in better lighting conditions, ensuring the QR code is well-lit.
8.3. Distortion
Issue: The QR code is distorted, making it difficult for the scanner to decode.
Solution:
- Correct Perspective: Use photo editing software to correct the perspective and remove distortion.
- Retake the Photo: If possible, retake the photo from a straight-on angle to avoid distortion.
8.4. Partial Coverage
Issue: Part of the QR code is covered or obstructed.
Solution:
- Crop the Image: Crop the image to focus solely on the QR code, ensuring no obstructions are present.
- Retake the Photo: If possible, retake the photo ensuring the entire QR code is visible.
8.5. Low Resolution
Issue: The image resolution is too low, making the QR code lack detail.
Solution:
- Enhance Resolution: Use photo editing software to increase the resolution of the image. Note that this may not significantly improve the quality if the original image is severely low-resolution.
- Retake the Photo: If possible, retake the photo with a higher resolution setting on your camera.
8.6. Scanner Issues
Issue: The QR code scanner app is not working correctly.
Solution:
- Update the App: Ensure the QR code scanner app is updated to the latest version.
- Try a Different App: Try using a different QR code scanner app to see if the issue persists.
- Restart the Device: Restart your smartphone or device to clear any temporary glitches.
8.7. Compatibility Issues
Issue: The QR code scanner is not compatible with the QR code type.
Solution:
- Use a Versatile Scanner: Use a QR code scanner that supports a wide range of QR code types and encoding formats.
- Check QR Code Specifications: Ensure the QR code follows standard specifications and is not using a proprietary format.
8.8. Scanner Settings
Issue: Incorrect scanner settings are affecting the scanning process.
Solution:
- Adjust Settings: Check the scanner settings and adjust parameters such as contrast, brightness, and focus to optimize the scanning process.
- Reset Settings: Reset the scanner settings to default values to ensure no conflicting configurations are causing issues.
8.9. Example Scenarios
- Scenario 1: A user has a blurry photo of a QR code from an old magazine.
- Solution: Use photo editing software like Photoshop or Snapseed to sharpen the image.
- Scenario 2: A user is trying to scan a QR code from a photo taken in a dimly lit room.
- Solution: Adjust the brightness and contrast of the image using photo editing tools.
- Scenario 3: A user’s QR code scanner app is not recognizing the QR code.
- Solution: Update the app or try a different QR code scanner app.
By addressing these common issues and applying the suggested solutions, you can significantly improve your ability to scan QR codes from photos efficiently. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
9. How Can I Create High-Quality Photos Of QR Codes For Easy Scanning?
Creating high-quality photos of QR codes ensures easy and reliable scanning, whether for personal or professional use. Several key factors contribute to the quality of a QR code photo, including focus, lighting, angle, and environmental conditions.
9.1. Focus
Ensuring the QR code is in sharp focus is crucial for successful scanning.
- Use Autofocus: Allow your camera to autofocus on the QR code. Ensure the focus is locked before taking the photo.
- Manual Focus: If autofocus is not working correctly, use manual focus to fine-tune the sharpness.
- Avoid Movement: Keep the camera steady to prevent motion blur. Use a tripod or stabilize your hand against a solid surface.
9.2. Lighting
Proper lighting is essential for capturing a clear and scannable QR code.
- Adequate Illumination: Ensure the QR code is well-lit. Avoid taking photos in dimly lit environments.
- Avoid Glare: Position the camera to minimize glare on the QR code surface. Adjust the angle or use a polarizing filter.
- Diffused Light: Use diffused light to reduce harsh shadows and highlights. Natural daylight or soft indoor lighting works best.
9.3. Angle and Distance
The angle and distance at which the photo is taken can significantly impact scan quality.
- Straight-On Angle: Take the photo from a straight-on angle to avoid distortion. Ensure the camera is perpendicular to the QR code surface.
- Optimal Distance: Position the camera at an optimal distance. The QR code should fill a significant portion of the frame without being too close.
- Avoid Zooming: Minimize the use of digital zoom, as it can reduce image quality. Instead, move closer to the QR code.
9.4. Environmental Conditions
Controlling environmental conditions can help improve the quality of QR code photos.
- Clean Surface: Ensure the QR code surface is clean and free from dirt, smudges, or scratches.
- Stable Conditions: Avoid taking photos in unstable conditions, such as windy environments, which can cause movement and blur.
- Controlled Environment: If possible, take the photo in a controlled environment with consistent lighting and stable conditions.
9.5. Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings can enhance the quality of QR code photos.
- High Resolution: Use the highest resolution setting available on your camera to capture maximum detail.
- Disable HDR: Disable HDR (High Dynamic Range) mode, as it can sometimes introduce artifacts that interfere with scanning.
- Image Stabilization: Enable image stabilization to reduce the effects of camera shake.
9.6. Composition
Proper composition can make the QR code more scannable and visually appealing.
- Frame the QR Code: Frame the QR code in the center of the image, ensuring it is the primary subject.
- Minimize Background Clutter: Reduce background clutter to avoid distractions and ensure the focus remains on the QR code.
- Crop the Image: Crop the image to remove unnecessary background elements and focus solely on the QR code.
9.7. Post-Processing
Post-processing techniques can further enhance the quality of QR code photos.
- Sharpening: Use photo editing software to sharpen the image and enhance detail. (Refer to Section 7 for detailed steps.)
- Contrast Adjustment: Adjust the contrast to improve the visibility of the QR code pattern.
- Noise Reduction: Reduce noise to minimize graininess and improve image clarity.
9.8. Example Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Taking a photo of a QR code on a poster in a brightly lit environment.
- Solution: Position the camera to avoid glare, use diffused light if possible, and ensure the QR code is in sharp focus.
- Scenario 2: Taking a photo of a QR code on a business card in a dimly lit room.
- Solution: Use additional lighting if available, increase the ISO setting on your camera (if necessary), and stabilize the camera to prevent blur.
- Scenario 3: Taking a photo of a QR code that is slightly damaged or dirty.
- Solution: Clean the QR code surface if possible, and use post-processing techniques to enhance the image and improve scannability.
By following these guidelines, you can create high-quality photos of QR codes that are easily scannable, ensuring efficient and reliable access to the embedded information. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
10. What Are Some Creative Ways To Use QR Codes In Photography?
QR codes offer numerous creative applications in photography, enhancing the way photographers share, promote, and interact with their work. By embedding QR codes into photos, photographers can provide viewers with additional information, access to online resources, and unique interactive experiences.
10.1. Portfolio Access
Photographers can include QR codes in printed photos or displays that link directly to their online portfolio. This allows potential clients and collaborators to easily view a wider range of their work.
- Example: A photographer showcasing prints at an art fair includes a QR code on each print. Scanning the QR code takes viewers to the photographer’s website, where they can see more photos, read testimonials, and contact the photographer for commissions.
10.2. Behind-the-Scenes Content
QR codes can link to behind-the-scenes content related to a specific photo, providing viewers with insights into the creative process.
- Example: A landscape photographer includes a QR code in a print that links to a video showing the location, equipment used, and techniques employed to capture the image.
10.3. Location Information
QR codes can provide viewers with precise location information for a photo, enhancing their appreciation and understanding of the scene.
- Example: A travel photographer includes a QR code in a photo of a famous landmark. Scanning the QR code takes viewers to a map showing the exact location and providing historical or cultural information about the site.
10.4. Equipment and Settings Details
QR codes can share details about the equipment and camera settings used to capture a particular photo, offering valuable information for aspiring photographers.
- Example: A wildlife photographer includes a QR code in a photo that links to a page detailing the camera, lens, ISO, aperture, and shutter speed settings used to capture the image.
10.5. Interactive Experiences
QR codes can create interactive experiences, such as virtual tours or augmented reality overlays, that enhance engagement and provide unique perspectives.
- Example: An architectural photographer includes a QR code in a photo of a building. Scanning the QR code launches an augmented reality overlay that allows viewers to explore the building’s interior in 3D.
10.6. Print Sales and Licensing
QR codes can facilitate print sales and licensing by linking directly to online stores or licensing platforms.
- Example: A fine art photographer includes a QR code in a gallery display that takes viewers to an online store where they can purchase prints of the photo in various sizes and formats.
10.7. Social Media Sharing
QR codes can encourage social media sharing by linking to pre-populated posts or direct social media profiles.
- Example: A portrait photographer includes a QR code in a printed portfolio that links to a pre-populated tweet or Facebook post encouraging viewers to share their favorite photos and tag the photographer.
10.8. Educational Resources
QR codes can provide access to educational resources, such as tutorials, articles, and workshops, that enhance viewers’ understanding and appreciation of photography.
- Example: A photography instructor includes a QR code in a promotional flyer that links to a series of online tutorials on various photography techniques.
10.9. Contests and Giveaways
QR codes can be used to enter viewers into contests or giveaways, generating excitement and engagement.
- Example: A camera manufacturer includes a QR code in a promotional ad that takes viewers to a contest entry form where they can win a new camera or other photography gear.
10.10. Limited Edition Prints
QR codes can authenticate limited edition prints and provide additional information about the artwork.
- Example: A fine art photographer includes a unique QR code on each limited edition print that links to a certificate of authenticity and details about the print number, edition size, and artist signature.
By leveraging these creative uses of QR codes, photographers can enhance their work, engage their audience, and expand their professional opportunities. For more tips and tricks, visit dfphoto.net.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.
FAQ: How to Access QR Code From Photos
1. Can I scan a QR code from a photo on any smartphone?
Yes, most modern smartphones, both iPhones and Android devices, can scan QR codes from photos using built-in features or dedicated apps.
2. Do I need a special app to scan QR codes from photos?
Not always. iPhones with iOS 11 and later and many Android devices have built-in QR code scanning capabilities. If not, you can download a free QR code scanner app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
3. How do I scan a QR code from a photo on an iPhone?
Open the Photos app, select the photo with the QR code, and if you have iOS 15 or later, the Live Text feature will detect it. Tap the QR code, and a notification will appear, allowing you to open the link. Alternatively, you can use the Camera app to scan the QR code from another screen.
4. How do I scan a QR code from a photo on an Android device?
Open the Google Photos app, select the photo with the QR code, and tap the Google Lens icon. Google Lens will scan the QR code, and a pop-up will appear with the information.
5. What if the QR code in the photo is blurry?
Use photo editing software or online tools to sharpen the image. Adjust the settings until the QR code becomes clearer, then try scanning again.
6. Can poor lighting affect my ability to scan QR codes from photos?
Yes, poor lighting can make it difficult for the scanner to decode the QR code. Ensure the photo is well-lit or adjust the brightness and contrast using photo editing tools.
7. Is it possible to scan a QR code from a screenshot?
Yes, the process is the same as scanning from a regular photo. Open the screenshot in your Photos app or Google Photos and use the built-in scanner or Google Lens to scan the QR code.
8. What can I do if the QR code is partially covered in the photo?
Try cropping the image to focus solely on the QR code, ensuring no obstructions are present. If possible, retake the photo with the entire QR code visible.
9. Are there any security risks associated with scanning QR codes from photos?
Yes, malicious QR codes can lead to phishing websites or download harmful software. Always ensure the source of the QR code is trustworthy before scanning. Use a QR code scanner app with built-in security checks if possible.