Are you wondering how many precious memories you can store on a 32GB flash drive? At dfphoto.net, we understand the importance of preserving your photos, and we’re here to give you a clear, concise answer and help you maximize your storage. Discover the secrets to fitting more photos and explore various file formats for optimal image storage, ensuring you never miss a moment. Optimize your digital storage with our expert advice.
1. Understanding Flash Drive Photo Capacity
How Many Photos Can A 32gb Flash Drive Hold? A 32GB flash drive can typically hold between 2,268 and 2,520 photos, assuming an average file size of 13MB per photo. To understand better, let’s explore the factors influencing storage capacity and how to calculate it accurately.
1.1. Factors Affecting Photo Storage Capacity
Several factors influence the number of photos a 32GB flash drive can store. These include:
- Image Resolution: Higher resolution images contain more detail and require more storage space.
- File Format: Different file formats like JPEG, PNG, and RAW have varying compression levels, affecting file size.
- Camera Settings: Settings like image quality and shooting mode impact the size of the saved photo.
- Flash Drive Formatting: Flash drives lose some capacity during formatting, reducing the available space.
According to a study by the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, the image resolution is the key factor determining the storage capacity of flash drives.
1.2. Understanding Megabytes and Gigabytes
To accurately estimate photo storage, understanding the relationship between megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB) is crucial.
- 1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1,024 Megabytes (MB)
Therefore, a 32GB flash drive has approximately 32,768 MB of storage space.
1.3. The Impact of Image Resolution on Storage
Image resolution significantly affects file size. Higher resolutions mean more pixels, resulting in larger files. Here’s a general guide:
| Resolution | Typical File Size (JPEG) |
|---|---|
| 12MP (4000×3000) | 4-6 MB |
| 24MP (6000×4000) | 8-12 MB |
| 42MP (7952×5304) | 15-25 MB |
As resolution increases, so does the file size, reducing the number of photos that can fit on a 32GB flash drive.
2. Calculating Photo Capacity on a 32GB Flash Drive
How do you calculate how many photos fit on your drive? Calculating photo capacity involves a simple formula that considers the size of the flash drive and the average file size of your photos.
2.1. The Basic Formula for Calculating Photo Capacity
The formula to estimate how many photos a flash drive can hold is:
- Number of Photos = (Flash Drive Size in MB) / (Average Photo Size in MB)
For a 32GB flash drive:
- Flash Drive Size in MB = 32 GB * 1024 MB/GB = 32,768 MB
2.2. Example Calculations for Different File Sizes
Let’s calculate the number of photos a 32GB flash drive can hold for different average file sizes:
- Example 1: Average Photo Size = 5 MB
- Number of Photos = 32,768 MB / 5 MB = Approximately 6,553 photos
- Example 2: Average Photo Size = 10 MB
- Number of Photos = 32,768 MB / 10 MB = Approximately 3,276 photos
- Example 3: Average Photo Size = 15 MB
- Number of Photos = 32,768 MB / 15 MB = Approximately 2,184 photos
These calculations show that the number of photos a 32GB flash drive can hold varies widely based on the average file size.
2.3. How to Determine the Average File Size of Your Photos
To get an accurate estimate, determine the average file size of your photos. Here’s how:
- Select a Sample: Choose 10-20 photos that are representative of your typical shooting conditions and settings.
- Check File Sizes: View the file size of each photo (right-click, select “Properties” on Windows or “Get Info” on macOS).
- Calculate the Average: Add up the file sizes and divide by the number of photos.
This average will help you estimate how many photos you can store on your 32GB flash drive.
3. Understanding Photo File Formats and Their Impact on Storage
What file format should I use? The file format you choose significantly impacts the size of your photos and, consequently, how many you can store on a 32GB flash drive. Let’s compare the most common formats: JPEG, PNG, and RAW.
3.1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is the most common file format for photos due to its efficient compression.
- Pros:
- Small file sizes, allowing more photos to be stored.
- Widely compatible with devices and software.
- Good for everyday photography and sharing.
- Cons:
- Lossy compression reduces image quality, especially with repeated saving.
- Not ideal for professional editing where maximum detail is required.
3.2. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a lossless compression format commonly used for graphics and images with text.
- Pros:
- Lossless compression preserves image quality.
- Good for images with sharp lines, text, and graphics.
- Supports transparency.
- Cons:
- Larger file sizes compared to JPEG.
- Not ideal for storing large quantities of photos.
3.3. RAW Formats (e.g., .CR2, .NEF, .ARW)
RAW formats are uncompressed or minimally compressed files that contain all the data captured by the camera’s sensor.
- Pros:
- Maximum image quality and detail.
- Greater flexibility for editing and post-processing.
- Ideal for professional photography.
- Cons:
- Very large file sizes, significantly reducing storage capacity.
- Requires specialized software for viewing and editing.
3.4. File Format Comparison Table
Here’s a comparison table to illustrate the differences:
| Feature | JPEG | PNG | RAW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression | Lossy | Lossless | Uncompressed/Lossless |
| File Size | Small | Medium | Large |
| Image Quality | Reduced | Preserved | Maximum |
| Best Use | Everyday Photos | Graphics, Text | Professional Photography |
3.5. Recommendations Based on Photography Needs
Choosing the right file format depends on your photography needs:
- Casual Photography: JPEG is suitable for everyday photos where storage space is a concern.
- Important Memories: PNG is a good choice for photos you want to preserve with high quality.
- Professional Work: RAW is essential for professional photography where maximum detail and editing flexibility are required.
By understanding the characteristics of each file format, you can make informed decisions to optimize your storage on a 32GB flash drive.
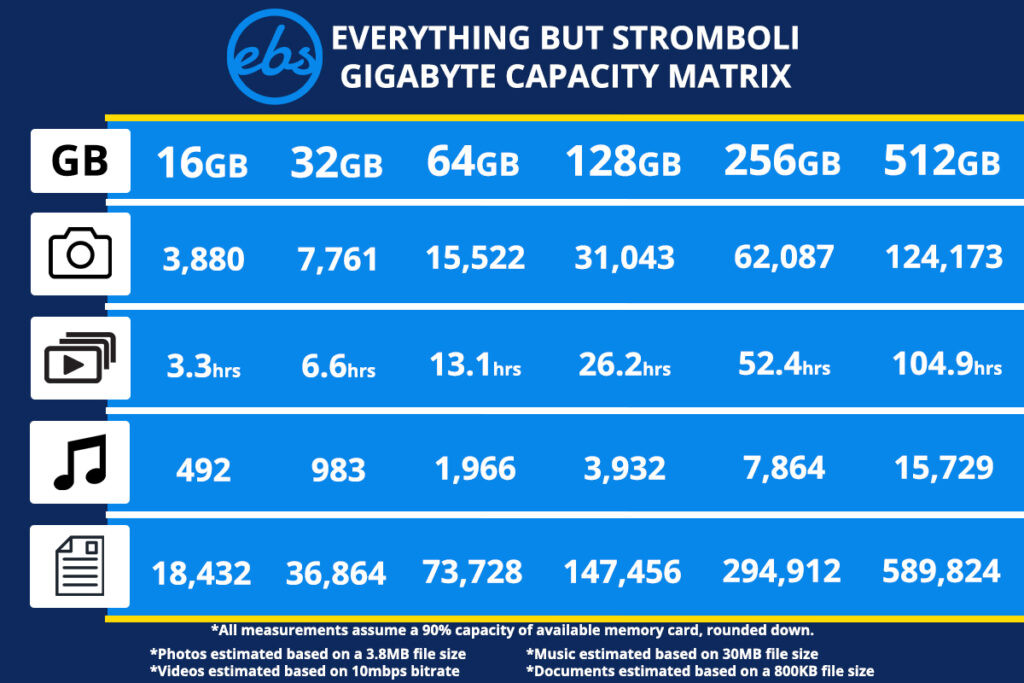 A chart showing how much data can be stored on memory cards.
A chart showing how much data can be stored on memory cards.
4. Optimizing Photo Storage on Your 32GB Flash Drive
How can I fit more photos on my flash drive? Optimizing photo storage involves several strategies to reduce file sizes without significantly compromising image quality.
4.1. Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Storage
Adjusting camera settings can greatly impact file sizes.
- Resolution: Choose a resolution appropriate for your needs. If you don’t need large prints, a lower resolution can save significant space.
- Image Quality: Opt for “Normal” or “Fine” quality settings instead of “Super Fine” to reduce file sizes without noticeable quality loss.
- Shooting Mode: Avoid shooting in RAW unless necessary. Use JPEG for everyday photography.
4.2. Compressing Photos Without Losing Quality
Several software tools can compress photos without significant quality loss.
- Adobe Photoshop: Use “Save for Web” option to optimize JPEG files.
- ImageOptim (Mac): A free tool that optimizes images for web use.
- TinyPNG/TinyJPG (Online): Web-based tools that compress PNG and JPEG files efficiently.
According to Popular Photography, using compression tools can reduce file sizes by 20-50% with minimal quality loss.
4.3. Using Cloud Storage as an Alternative
Consider using cloud storage services to supplement your flash drive storage.
- Google Photos: Offers free storage for photos up to 16MP.
- Dropbox: Provides cloud storage for various file types, including photos.
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Offers cloud storage for photographers and designers.
4.4. Regularly Backing Up and Organizing Your Photos
Regularly backing up and organizing your photos helps manage storage space effectively.
- Backup: Create multiple backups on different devices (flash drive, external hard drive, cloud).
- Organization: Sort photos into folders by date, event, or category.
- Culling: Delete duplicate, blurry, or unwanted photos to free up space.
4.5. Archiving Old or Less Important Photos
Archive old or less important photos to free up space on your flash drive.
- External Hard Drives: Move older photos to an external hard drive for long-term storage.
- Cloud Archives: Use cloud storage services to archive photos you don’t need immediate access to.
By implementing these optimization strategies, you can maximize the storage capacity of your 32GB flash drive and keep your photo collection well-managed.
5. Choosing the Right Flash Drive for Your Photography Needs
What flash drive is best for me? Choosing the right flash drive involves considering several factors, including capacity, speed, and durability.
5.1. Understanding Different Flash Drive Types and Speeds
Flash drives come in various types and speed classes.
- USB 2.0: Older standard, slower transfer speeds.
- USB 3.0: Faster transfer speeds, recommended for larger files.
- USB 3.1/3.2: Even faster transfer speeds, ideal for professional use.
Speed classes indicate the minimum write speed of the flash drive.
- Class 4: Minimum write speed of 4 MB/s.
- Class 10: Minimum write speed of 10 MB/s.
- UHS-I/UHS-II: Ultra High-Speed, much faster than Class 10.
5.2. Factors to Consider When Selecting a Flash Drive
Consider the following factors when selecting a flash drive:
- Capacity: Choose a capacity that meets your storage needs. 32GB is suitable for moderate use, but consider larger capacities for extensive photo collections.
- Speed: Opt for USB 3.0 or higher for faster transfer speeds, especially if you work with large RAW files.
- Durability: Look for rugged, water-resistant flash drives for outdoor photography.
- Brand Reputation: Choose reputable brands known for reliability and performance.
5.3. Recommended Flash Drives for Photographers
Here are some recommended flash drives for photographers:
| Flash Drive | Type | Speed | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| SanDisk Extreme Pro | USB 3.1 | Up to 420MB/s | High |
| Samsung BAR Plus | USB 3.1 | Up to 300MB/s | Medium |
| Kingston DataTraveler | USB 3.0 | Up to 200MB/s | Medium |
5.4. Tips for Maintaining and Protecting Your Flash Drive
Proper maintenance can prolong the life of your flash drive.
- Safely Eject: Always use the “Safely Remove Hardware” option before unplugging the flash drive.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Store the flash drive in a cool, dry place.
- Protect from Physical Damage: Keep the flash drive in a protective case.
- Scan for Viruses: Regularly scan the flash drive for malware.
By choosing the right flash drive and following these maintenance tips, you can ensure reliable storage for your photos.
6. Alternatives to Flash Drives for Photo Storage
Are there other options for photo storage? While flash drives are convenient, several alternatives offer different benefits.
6.1. External Hard Drives
External hard drives provide larger storage capacities and are suitable for archiving large photo collections.
- Pros:
- High storage capacity (1TB and up).
- Relatively low cost per gigabyte.
- Suitable for long-term storage and backups.
- Cons:
- Less portable than flash drives.
- More susceptible to physical damage.
6.2. Cloud Storage Services
Cloud storage services offer remote storage and accessibility from multiple devices.
- Pros:
- Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Automatic backups and data redundancy.
- Easy sharing with others.
- Cons:
- Requires an internet connection.
- Subscription fees for larger storage capacities.
- Privacy and security concerns.
6.3. NAS (Network Attached Storage) Devices
NAS devices are centralized storage solutions accessible over a network.
- Pros:
- Centralized storage for multiple users.
- Remote access and file sharing.
- Customizable RAID configurations for data redundancy.
- Cons:
- Higher initial cost.
- Requires technical knowledge to set up and maintain.
6.4. SD Cards
SD cards are commonly used in cameras and offer a convenient way to transfer photos to other devices.
- Pros:
- Compact and portable.
- Directly compatible with cameras.
- Available in various capacities and speed classes.
- Cons:
- Smaller storage capacities compared to external hard drives.
- Can be easily lost or damaged.
6.5. Comparison Table of Storage Alternatives
| Storage Option | Capacity | Portability | Cost | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Hard Drive | High | Low | Low | Archiving large photo collections |
| Cloud Storage | Variable | High | Variable | Remote access, sharing, and backups |
| NAS Device | High | Low | Medium | Centralized storage for multiple users |
| SD Card | Medium | High | Medium | Direct camera storage and quick transfers |
Each of these alternatives offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different photography needs and workflows.
7. Tips for Long-Term Photo Preservation
How do I keep my photos safe forever? Long-term photo preservation involves strategies to ensure your photos remain accessible and intact for years to come.
7.1. Creating Multiple Backups in Different Locations
Creating multiple backups is crucial for preventing data loss.
- Local Backup: Keep a copy of your photos on a local device (flash drive, external hard drive).
- Offsite Backup: Store a backup in a different location (cloud, second external hard drive at a friend’s house).
- Redundancy: Use a combination of backup methods for maximum protection.
7.2. Choosing Durable Storage Media
Choose durable storage media that can withstand the test of time.
- High-Quality Flash Drives: Opt for reputable brands known for reliability.
- Archival-Grade DVDs/Blu-rays: Use DVDs or Blu-rays specifically designed for archival storage.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): SSDs are more durable and resistant to physical damage compared to traditional hard drives.
7.3. Regularly Checking and Migrating Your Data
Regularly check your storage media and migrate your data to new devices as technology evolves.
- Annual Checkup: Verify that your storage media is still functional and that your files are accessible.
- Data Migration: Transfer your photos to new storage devices every few years to avoid compatibility issues.
7.4. Using Archival File Formats
Use archival file formats to ensure long-term compatibility.
- TIFF: A lossless image format suitable for archiving.
- DNG: Adobe’s open-source RAW format.
7.5. Protecting Your Photos from Physical Damage
Protect your photos from physical damage by storing your storage media in a safe environment.
- Temperature and Humidity: Store your storage media in a cool, dry place.
- Physical Protection: Keep your storage media in protective cases to prevent damage from dust, moisture, and impact.
By following these long-term photo preservation tips, you can safeguard your precious memories for future generations.
8. Troubleshooting Common Flash Drive Issues
What if my flash drive isn’t working? Troubleshooting common flash drive issues can help you resolve problems and recover your photos.
8.1. Flash Drive Not Recognized
If your flash drive is not recognized by your computer, try the following:
- Try a Different USB Port: The USB port may be faulty.
- Update Drivers: Update your USB drivers in Device Manager (Windows) or System Information (macOS).
- Restart Your Computer: A simple restart can often resolve connectivity issues.
8.2. Flash Drive is Write-Protected
If your flash drive is write-protected, you cannot copy or delete files.
- Check the Physical Switch: Some flash drives have a physical write-protection switch.
- Use Diskpart (Windows): Use the Diskpart command-line utility to remove write protection.
- Format the Drive: As a last resort, format the drive to remove write protection. Note that this will erase all data on the drive.
8.3. Flash Drive is Corrupted
If your flash drive is corrupted, you may experience errors when accessing files.
- Run CHKDSK (Windows): Use the CHKDSK utility to scan and repair errors on the drive.
- Use Disk Utility (macOS): Use Disk Utility to repair the drive.
- Data Recovery Software: Use data recovery software to recover files from the corrupted drive.
8.4. Slow Transfer Speeds
If you experience slow transfer speeds, try the following:
- Use a USB 3.0 Port: Ensure you are using a USB 3.0 port for faster transfer speeds.
- Defragment the Drive: Defragmenting the drive can improve performance.
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close other programs that may be using system resources.
8.5. Data Recovery Options
If you cannot recover your data using the above methods, consider using professional data recovery services.
- Data Recovery Software: Use data recovery software such as Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, or Stellar Data Recovery.
- Professional Services: Contact professional data recovery services for advanced data recovery options.
By troubleshooting common flash drive issues, you can often resolve problems and recover your valuable photos.
9. The Future of Photo Storage Technology
What’s next for photo storage? The future of photo storage technology is evolving rapidly, with new innovations promising greater capacity, speed, and convenience.
9.1. Advancements in Flash Memory Technology
Advancements in flash memory technology are leading to higher storage capacities and faster transfer speeds.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell) NAND: Offers higher storage density at a lower cost.
- 3D NAND: Stacks memory cells vertically to increase storage capacity.
- PCIe NVMe: Provides significantly faster transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA interfaces.
9.2. The Rise of Cloud-Based Photo Storage
Cloud-based photo storage is becoming increasingly popular, offering remote access, automatic backups, and collaboration features.
- AI-Powered Organization: Cloud services are using AI to automatically organize and tag photos.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers are implementing advanced security measures to protect user data.
9.3. The Potential of DNA Data Storage
DNA data storage is an emerging technology that could revolutionize long-term data storage.
- High Storage Density: DNA can store vast amounts of data in a small space.
- Long-Term Durability: DNA can last for hundreds or thousands of years under the right conditions.
9.4. The Integration of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is being explored for secure and decentralized photo storage.
- Immutable Storage: Blockchain ensures that photos cannot be altered or deleted without authorization.
- Decentralized Networks: Blockchain-based storage solutions distribute data across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of data loss.
9.5. The Impact of 5G and Wi-Fi 6 on Photo Storage
5G and Wi-Fi 6 technologies are improving the speed and reliability of wireless data transfer, making cloud-based photo storage more convenient.
- Faster Upload and Download Speeds: 5G and Wi-Fi 6 enable faster transfer of large photo files.
- Improved Connectivity: These technologies provide more reliable connections, reducing the risk of data loss during transfer.
These advancements in photo storage technology promise to transform the way we store and manage our photos in the years to come.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Photo Storage
Do you have more questions about photo storage? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand how to store your photos.
10.1. How Many High-Resolution Photos Can a 32GB Flash Drive Hold?
A 32GB flash drive can hold approximately 1,000 to 2,000 high-resolution photos, depending on the file size.
10.2. Can I Store RAW Files on a 32GB Flash Drive?
Yes, but you will be limited to around 500 to 1,000 RAW files, depending on the file size.
10.3. What Is the Best File Format for Archiving Photos?
TIFF and DNG are the best file formats for archiving photos due to their lossless compression and long-term compatibility.
10.4. How Often Should I Back Up My Photos?
You should back up your photos regularly, ideally every week or after each significant photo shoot.
10.5. What Is the Best Way to Organize Photos on a Flash Drive?
Organize photos into folders by date, event, or category for easy retrieval.
10.6. How Can I Speed Up Photo Transfers to a Flash Drive?
Use a USB 3.0 or higher port and ensure your flash drive supports fast transfer speeds.
10.7. Is It Safe to Store Photos on a Flash Drive Long Term?
While flash drives are convenient, they are not ideal for long-term storage. Consider using external hard drives or cloud storage for archival purposes.
10.8. What Should I Do If My Flash Drive Fails?
Try troubleshooting common flash drive issues or use data recovery software. If necessary, contact professional data recovery services.
10.9. How Do I Choose the Right Size Flash Drive for My Needs?
Consider the number and size of the photos you need to store and choose a flash drive with sufficient capacity.
10.10. What Are the Advantages of Using Cloud Storage for Photos?
Cloud storage offers remote access, automatic backups, and easy sharing with others.
Discover the perfect blend of knowledge, inspiration, and community at dfphoto.net. Whether you’re seeking expert guidance, visual inspiration, or a place to connect with fellow photographers, dfphoto.net is your ultimate resource.
Visit dfphoto.net today and embark on a journey to elevate your photography skills, discover new creative horizons, and connect with a vibrant community of like-minded individuals. Your next great shot is just a click away! Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.