Transferring photos from your phone to your computer is crucial in today’s digital world, and dfphoto.net makes this process easy, enabling you to manage, edit, and share your visual memories effectively. Whether you’re an amateur enthusiast or a professional photographer, understanding the best methods for photo transfer ensures your precious moments are safely backed up and readily accessible for your creative projects. Explore various transfer techniques, understand file formats, and discover how to organize your digital photos with ease.
1. What Are the Primary Methods for Transferring Photos from Phone to Computer?
The primary methods involve using a USB cable, cloud storage services, email, Bluetooth, or third-party apps. USB cables offer a direct and reliable connection, while cloud services like Google Photos or iCloud provide wireless syncing. Email and Bluetooth are suitable for smaller batches of photos, and third-party apps often offer additional features like automatic syncing and organization. Each method has its pros and cons depending on the number of photos, file sizes, and your preferred workflow.
1.1. Using a USB Cable for Direct Transfer
Connecting your phone to your computer via a USB cable is one of the most straightforward methods. It provides a direct connection, ensuring stable and fast transfer speeds.
1.1.1. How to Transfer Photos via USB on Windows
- Connect Your Phone: Use a USB cable to connect your phone to your Windows computer.
- Unlock Your Phone: Ensure your phone is unlocked and you’ve tapped “Trust” or “Allow” when prompted to allow the computer to access your data.
- Access Your Phone’s Storage: Open File Explorer, and your phone should appear as a portable device.
- Copy Photos: Navigate to the DCIM folder (Digital Camera Images) within your phone’s storage, where photos and videos are typically stored.
- Paste to Your Computer: Copy the desired photos and paste them into a folder on your computer.
1.1.2. How to Transfer Photos via USB on macOS
- Connect Your Phone: Connect your iPhone or iPad to your Mac using a USB cable.
- Open the Photos App: The Photos app should automatically open. If it doesn’t, open it manually from your Applications folder.
- Unlock Your Device: Unlock your iOS or iPadOS device using your passcode. If you see a prompt asking you to Trust This Computer, tap Trust to continue.
- Select Photos: The Photos app shows an Import screen with all the photos and videos on your connected device. If the Import screen doesn’t automatically appear, click the device’s name in the Photos sidebar.
- Import Photos: Choose where you want to import your photos. You can select an existing album or create a new one. Click Import Selected, or click Import All New Photos.
- Disconnect: Once the import process is complete, disconnect your device from your Mac.
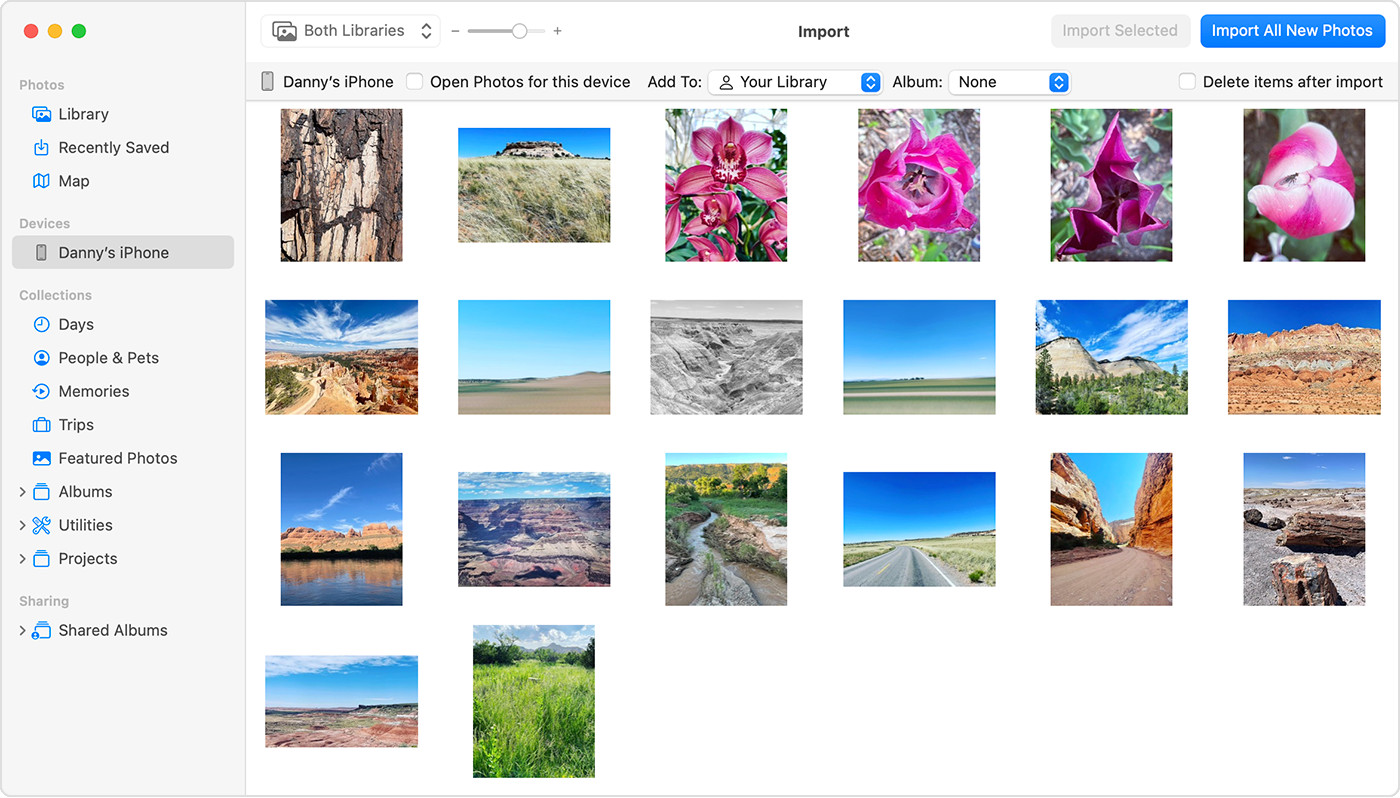 Mac screen showing the photos available for import
Mac screen showing the photos available for import
1.1.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using USB
Advantages:
- Speed: Generally faster than wireless methods, especially for large files.
- Security: Direct connection minimizes the risk of data interception.
- Reliability: Less prone to interruptions compared to Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
Disadvantages:
- Physical Connection: Requires a USB cable, which can be inconvenient if you don’t have one readily available.
- Compatibility Issues: Sometimes, driver issues or compatibility problems can arise, especially with older operating systems.
- Manual Process: Requires manual selection and transfer of files, which can be time-consuming.
1.2. Leveraging Cloud Storage Services
Cloud storage services like Google Photos, iCloud, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive offer a convenient way to automatically back up and transfer photos from your phone to your computer.
1.2.1. How to Use Google Photos
- Install and Set Up: Download the Google Photos app on your phone and sign in with your Google account.
- Enable Backup & Sync: Turn on the “Backup & Sync” feature in the app settings.
- Choose Backup Quality: Select whether to back up photos in “Original Quality” (full resolution, counts against your Google storage) or “Storage Saver” (compressed, offers more storage).
- Access on Computer: On your computer, go to the Google Photos website and sign in with the same Google account.
- Download Photos: Browse your photos and download the ones you need.
1.2.2. How to Use iCloud Photos
- Enable iCloud Photos: On your iPhone, go to Settings > Photos and turn on “iCloud Photos.”
- Choose Storage Option: Select “Optimize iPhone Storage” to save space on your device or “Download and Keep Originals” to keep full-resolution photos on your phone.
- Access on Computer: On your Mac, open the Photos app. If iCloud Photos is enabled, your photos will automatically sync. On a Windows PC, download iCloud for Windows and enable iCloud Photos.
- Download Photos: On your Mac, your photos are already in the Photos app. On Windows, you can access and download photos from the iCloud Photos folder in File Explorer.
1.2.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Storage
Advantages:
- Automatic Backup: Photos are automatically backed up as soon as they are taken.
- Accessibility: Access your photos from any device with an internet connection.
- Organization: Cloud services often offer features like facial recognition and automatic album creation.
Disadvantages:
- Storage Limits: Free storage is limited, and you may need to pay for additional space.
- Privacy Concerns: Storing photos on third-party servers may raise privacy concerns for some users.
- Internet Dependency: Requires a stable internet connection for both backup and access.
1.3. Transferring Photos via Email
Emailing photos is a simple method for transferring a small number of images.
1.3.1. Steps to Email Photos
- Select Photos: On your phone, select the photos you want to transfer.
- Share via Email: Tap the share icon and choose your email app (e.g., Gmail, Outlook).
- Compose Email: Enter your own email address as the recipient and add a subject.
- Send Email: Send the email.
- Download on Computer: Open the email on your computer and download the attached photos.
1.3.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Email
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to use and requires no additional software or hardware.
- Accessibility: Works on any device with email access.
Disadvantages:
- File Size Limits: Email providers often have limits on attachment sizes, making it unsuitable for large files or numerous photos.
- Inconvenient for Large Transfers: Not practical for transferring large quantities of photos.
- Quality Reduction: Some email services compress images, reducing their quality.
1.4. Using Bluetooth for Photo Transfer
Bluetooth allows for wireless transfer of photos, but it’s generally slower than other methods.
1.4.1. Steps to Transfer Photos via Bluetooth
- Enable Bluetooth: Turn on Bluetooth on both your phone and your computer.
- Pair Devices: Pair your phone and computer by following the on-screen instructions on both devices.
- Select Photos: On your phone, select the photos you want to transfer.
- Share via Bluetooth: Tap the share icon and choose Bluetooth. Select your computer from the list of available devices.
- Accept Transfer: On your computer, accept the incoming file transfer.
- Receive Photos: The photos will be saved in a default folder, usually the Downloads folder.
1.4.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Bluetooth
Advantages:
- Wireless: No need for cables or internet connection.
- Availability: Bluetooth is a standard feature on most phones and computers.
Disadvantages:
- Slow Speed: Significantly slower than USB or Wi-Fi, making it impractical for large transfers.
- Limited Range: Devices need to be within close proximity to each other.
- Pairing Issues: Sometimes, pairing devices can be problematic.
1.5. Utilizing Third-Party Apps for Photo Transfer
Several third-party apps are designed to simplify and enhance photo transfer, offering features like automatic syncing, file organization, and cross-platform compatibility.
1.5.1. Popular Third-Party Apps
- Dropbox: A cloud storage service that allows for automatic photo uploads and syncing across devices.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Similar to Dropbox, OneDrive offers cloud storage and photo syncing capabilities.
- Send Anywhere: A file transfer app that allows you to send photos and videos directly to another device using a one-time key.
- AirDroid: A comprehensive device management app that allows you to transfer files, manage SMS, and control your phone from your computer.
1.5.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Third-Party Apps
Advantages:
- Additional Features: Often include features like automatic syncing, file organization, and cross-platform compatibility.
- Convenience: Simplify the transfer process with user-friendly interfaces.
- Flexibility: Offer various transfer options, including Wi-Fi Direct, cloud storage, and direct device-to-device transfer.
Disadvantages:
- Security Risks: Using third-party apps may pose security risks if the apps are not reputable or have vulnerabilities.
- Cost: Some apps offer limited free features and require a subscription for full functionality.
- Learning Curve: New apps may require some time to learn and configure.
2. What File Formats Should You Be Aware Of?
Understanding different image file formats is essential for managing and transferring photos effectively. The most common formats are JPEG, PNG, and HEIC, each with its own characteristics and use cases.
2.1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is the most widely used format for photos due to its efficient compression algorithm, which reduces file size while maintaining acceptable image quality.
2.1.1. Characteristics of JPEG
- Lossy Compression: JPEG uses lossy compression, which means some image data is discarded during the compression process.
- Small File Size: JPEGs have relatively small file sizes, making them ideal for sharing online and storing large quantities of images.
- Wide Compatibility: Supported by virtually all devices and software.
2.1.2. When to Use JPEG
- Everyday Photos: Suitable for most everyday photos where file size is more important than preserving every detail.
- Online Sharing: Ideal for uploading photos to social media, websites, and email.
- Large Photo Collections: Best for storing large collections of photos on devices with limited storage.
2.2. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a lossless image format that preserves all image data, making it ideal for graphics, logos, and images with text.
2.2.1. Characteristics of PNG
- Lossless Compression: PNG uses lossless compression, which means no image data is lost during compression.
- Larger File Size: PNG files are generally larger than JPEGs due to the preservation of image data.
- Transparency Support: PNG supports transparency, making it suitable for images with transparent backgrounds.
2.2.2. When to Use PNG
- Graphics and Logos: Best for graphics, logos, and illustrations that require sharp details and transparency.
- Images with Text: Ideal for images with text, as PNG preserves the clarity of the text.
- Editing and Archiving: Suitable for images that will be edited multiple times, as lossless compression prevents quality degradation.
2.3. HEIC (High Efficiency Image Container)
HEIC is a modern image format developed by Apple that offers better compression than JPEG while maintaining similar image quality.
2.3.1. Characteristics of HEIC
- Efficient Compression: HEIC uses more efficient compression algorithms than JPEG, resulting in smaller file sizes with comparable image quality.
- Modern Format: HEIC is a relatively new format and may not be supported by all devices and software.
- Metadata Support: HEIC supports advanced metadata, including depth information and dynamic range.
2.3.2. When to Use HEIC
- Modern Devices: Best for use on modern devices that support HEIC, such as iPhones and iPads.
- Space Saving: Ideal for saving storage space on devices with limited capacity.
- High-Quality Images: Suitable for capturing high-quality images without sacrificing storage space.
2.4. Converting Between File Formats
Sometimes, you may need to convert between file formats to ensure compatibility or optimize image quality. Several tools and methods are available for converting image formats.
2.4.1. Using Image Editing Software
Image editing software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and online converters can be used to convert between different image formats.
Steps:
- Open Image: Open the image in your chosen image editing software.
- Save As: Select “Save As” and choose the desired file format from the dropdown menu.
- Adjust Settings: Adjust any necessary settings, such as compression quality or color profile.
- Save Image: Save the converted image to your computer.
2.4.2. Using Online Converters
Online image converters like Zamzar, CloudConvert, and Convertio allow you to convert images directly in your web browser without installing any software.
Steps:
- Upload Image: Upload the image to the online converter.
- Choose Format: Select the desired output format.
- Convert Image: Click the “Convert” button.
- Download Image: Download the converted image to your computer.
2.4.3. Batch Conversion
For converting multiple images at once, batch conversion tools can save time and effort. Software like IrfanView and XnConvert offer batch conversion features.
Steps:
- Open Batch Conversion Tool: Open the batch conversion tool in your chosen software.
- Add Images: Add the images you want to convert to the tool.
- Choose Output Format: Select the desired output format and settings.
- Start Conversion: Start the batch conversion process.
- Save Images: The converted images will be saved to the specified output folder.
3. How to Organize Your Digital Photos?
Organizing your digital photos is crucial for easy access, efficient management, and long-term preservation. Implementing a structured system can save you time and frustration when searching for specific images.
3.1. Creating a Consistent Folder Structure
A well-organized folder structure is the foundation of effective photo management.
3.1.1. Date-Based Folders
Organize photos by date, using a consistent naming convention such as YYYY-MM-DD (e.g., 2024-07-15).
Example:
- 2024
- 2024-01
- 2024-01-01
- 2024-01-05
- 2024-02
- 2024-03
- 2024-01
3.1.2. Event-Based Folders
Organize photos by events, such as vacations, weddings, or birthdays.
Example:
- Vacations
- 2023-Hawaii
- 2024-Italy
- Weddings
- 2022-JohnAndJane
- 2023-AliceAndBob
- Birthdays
- 2023-SarahBirthday
- 2024-MikeBirthday
3.1.3. Combination of Date and Event
Combine date and event-based folders for a more detailed organization.
Example:
- 2024
- 2024-01
- 2024-01-01-NewYearsParty
- 2024-07
- 2024-07-15-FamilyVacation
- 2024-01
3.2. Naming Files Effectively
Consistent file naming conventions can make it easier to search and identify photos.
3.2.1. Descriptive File Names
Use descriptive file names that include the date, event, and a brief description of the photo.
Example:
- 2024-07-15-FamilyVacation-BeachSunset.jpg
- 2023-12-25-Christmas-FamilyDinner.png
3.2.2. Sequential Numbering
Add sequential numbers to file names to maintain the order of photos within a folder.
Example:
- 2024-07-15-FamilyVacation-001.jpg
- 2024-07-15-FamilyVacation-002.jpg
3.2.3. Avoiding Special Characters
Avoid using special characters in file names, as they can cause compatibility issues with some operating systems and software. Stick to letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores.
3.3. Using Metadata and Tagging
Metadata is information embedded within a photo file, such as the date taken, camera settings, and location. Tagging involves adding keywords or labels to photos to make them easier to search and categorize.
3.3.1. Adding Metadata
Use photo management software like Adobe Lightroom, Apple Photos, or digiKam to add or edit metadata.
Metadata Fields:
- Date and Time: Automatically recorded by the camera, but can be adjusted if necessary.
- Location: Add location information to photos using GPS data or manual entry.
- Keywords: Add keywords to describe the content of the photo, such as “beach,” “sunset,” “family,” or “vacation.”
- Caption: Write a brief description of the photo.
- Copyright: Add copyright information to protect your work.
3.3.2. Tagging Photos
Tagging photos involves adding keywords or labels to make them easier to search and categorize.
Tagging Strategies:
- People: Tag photos with the names of the people in the image.
- Places: Tag photos with the locations where they were taken.
- Events: Tag photos with the events they depict.
- Subjects: Tag photos with the subjects they contain, such as “animals,” “landscapes,” or “portraits.”
3.3.3. Benefits of Metadata and Tagging
- Improved Searchability: Easily find photos by searching for specific keywords, locations, or people.
- Enhanced Organization: Categorize photos based on various criteria.
- Copyright Protection: Protect your work by embedding copyright information in the metadata.
3.4. Backing Up Your Photo Library
Backing up your photo library is essential to prevent data loss due to hardware failure, theft, or accidental deletion.
3.4.1. Local Backups
Create local backups on external hard drives, NAS devices, or other storage media.
Backup Strategies:
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups to ensure your photo library is always up-to-date.
- Multiple Copies: Keep multiple copies of your backups in different locations.
- Backup Software: Use backup software like Acronis True Image, EaseUS Todo Backup, or Carbon Copy Cloner to automate the backup process.
3.4.2. Cloud Backups
Use cloud storage services like Google Photos, iCloud, Dropbox, or Backblaze to create offsite backups.
Cloud Backup Benefits:
- Offsite Storage: Protects your photos from physical disasters like fire or theft.
- Automatic Backups: Automatically backs up your photos as they are added to your library.
- Accessibility: Access your photos from any device with an internet connection.
3.4.3. Hybrid Backup Strategy
Combine local and cloud backups for maximum protection. A hybrid backup strategy ensures that you have multiple copies of your photos in different locations, protecting you from a wide range of potential data loss scenarios.
4. Troubleshooting Common Transfer Issues
Even with the best methods, you might encounter issues when transferring photos from your phone to your computer. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
4.1. Phone Not Recognized by Computer
If your computer doesn’t recognize your phone when connected via USB, try these solutions.
4.1.1. Check USB Connection
- Use a Different USB Port: Try connecting your phone to a different USB port on your computer.
- Use a Different USB Cable: The USB cable may be faulty. Try using a different cable.
- Clean USB Port: Make sure the USB port on your phone and computer are clean and free of debris.
4.1.2. Update Drivers
- Windows: Open Device Manager, locate your phone under Portable Devices or Other Devices, right-click, and select “Update Driver.”
- macOS: macOS usually handles drivers automatically, but ensure your system is up-to-date.
4.1.3. Restart Devices
- Restart Phone and Computer: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve connectivity issues.
4.1.4. Trust This Computer
- Trust the Connection: Ensure you have tapped “Trust” or “Allow” on your phone when prompted to allow the computer to access your data.
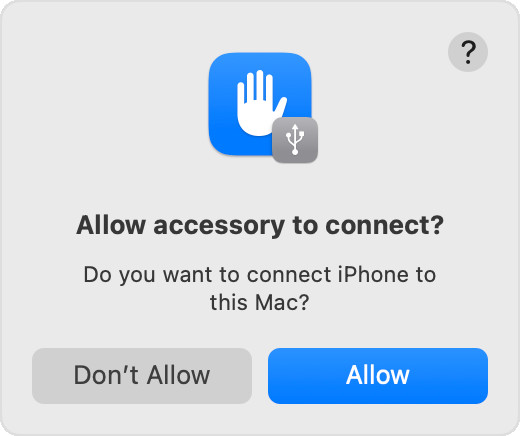 Accessory prompt to allow or don’t allow accessory to connect.
Accessory prompt to allow or don’t allow accessory to connect.
4.2. Slow Transfer Speeds
Slow transfer speeds can be frustrating, especially when transferring large numbers of photos.
4.2.1. Use USB 3.0
- Check USB Ports: Ensure you are using a USB 3.0 port (usually blue) for faster transfer speeds.
- Use USB 3.0 Cable: Use a USB 3.0 compatible cable.
4.2.2. Close Unnecessary Programs
- Free Up Resources: Close any unnecessary programs on your computer to free up system resources.
4.2.3. Transfer in Batches
- Smaller Transfers: Transfer photos in smaller batches to improve speed and stability.
4.2.4. Check Storage Space
- Ensure Adequate Space: Make sure your computer has enough free storage space to accommodate the transferred photos.
4.3. File Compatibility Issues
Sometimes, your computer may not be able to open certain image files, especially if they are in a less common format like HEIC.
4.3.1. Convert File Formats
- Convert Images: Use image editing software or online converters to convert the files to a more compatible format like JPEG.
4.3.2. Install Codecs
- Install HEIC Codecs: For HEIC files, install the HEIF Image Extensions and HEVC Video Extensions from the Microsoft Store.
4.3.3. Use Compatible Software
- Use Updated Software: Ensure your image viewing software is up-to-date and supports the file formats you are trying to open.
4.4. Interrupted Transfers
Transfers can sometimes be interrupted due to various reasons.
4.4.1. Ensure Stable Connection
- Stable USB Connection: Make sure the USB cable is securely connected to both your phone and computer. Avoid moving the devices during the transfer.
4.4.2. Disable Sleep Mode
- Prevent Sleep Mode: Disable sleep mode on your computer to prevent interruptions during the transfer.
4.4.3. Check for Errors
- Monitor Transfer: Keep an eye on the transfer progress and check for any error messages. If an error occurs, try restarting the transfer.
4.5. Cloud Syncing Problems
If you’re using cloud services like Google Photos or iCloud, you may encounter syncing issues.
4.5.1. Check Internet Connection
- Stable Internet: Ensure you have a stable internet connection for both your phone and computer.
4.5.2. Restart App
- Restart the App: Close and reopen the Google Photos or iCloud app on your phone and computer.
4.5.3. Check Account Settings
- Correct Account: Make sure you are signed in to the correct Google or iCloud account on both devices.
4.5.4. Clear Cache
- Clear Cache: Clear the cache and data of the Google Photos or iCloud app on your phone to resolve syncing issues.
5. Security and Privacy Best Practices
When transferring photos, it’s important to consider the security and privacy of your data.
5.1. Secure USB Connections
Ensure that you are using trusted USB cables and ports. Avoid using public charging stations, as they can be compromised.
5.2. Encrypting Data
Encrypt sensitive photos before transferring them, especially if you are using cloud storage or sharing them with others.
5.3. Using Strong Passwords
Use strong, unique passwords for your cloud storage accounts and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
5.4. Reviewing App Permissions
Regularly review the permissions granted to photo management apps on your phone and computer to ensure they only have access to the data they need.
5.5. Privacy Settings
Adjust the privacy settings on your cloud storage services to control who can access your photos.
6. Future Trends in Photo Transfer Technology
The technology for transferring photos is constantly evolving, with new innovations emerging regularly.
6.1. Faster Wireless Transfer
Expect to see faster wireless transfer speeds with the adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7, making wireless transfers as fast as or even faster than USB transfers.
6.2. Improved Cloud Integration
Cloud services will become even more integrated with devices and operating systems, making photo transfer and management seamless.
6.3. AI-Powered Organization
Artificial intelligence will play a greater role in photo organization, with AI algorithms automatically tagging and categorizing photos based on their content. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, AI will be able to automatically identify and tag 95% of the objects and people in a photo.
6.4. Enhanced Security
New security measures will be implemented to protect photos during transfer and storage, including advanced encryption and biometric authentication.
6.5. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Expect to see improved cross-platform compatibility, making it easier to transfer photos between different devices and operating systems.
7. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
7.1. How Do I Transfer Photos From My Phone To My Computer Wirelessly?
You can transfer photos wirelessly using cloud storage services like Google Photos, iCloud, or Dropbox. Simply upload the photos from your phone to the cloud service, and then access and download them on your computer.
7.2. What Is the Fastest Way to Transfer Photos From My Phone to My Computer?
The fastest way is typically using a USB cable, as it provides a direct connection and faster transfer speeds compared to wireless methods.
7.3. How Do I Transfer Photos From My iPhone to My Windows PC Without iCloud?
You can connect your iPhone to your Windows PC using a USB cable and use the Apple Devices app to transfer photos. Alternatively, you can use third-party apps like Dropbox or Send Anywhere.
7.4. How Do I Transfer HEIC Photos From My iPhone to My Computer?
To transfer HEIC photos, you can either convert them to JPEG on your iPhone before transferring or install the HEIF Image Extensions and HEVC Video Extensions from the Microsoft Store on your Windows PC.
7.5. How Do I Transfer Photos From My Android Phone to My Mac?
You can connect your Android phone to your Mac using a USB cable and use Android File Transfer to transfer photos. Alternatively, you can use cloud storage services like Google Photos or third-party apps.
7.6. How Do I Organize My Photos After Transferring Them to My Computer?
Create a consistent folder structure based on date, event, or a combination of both. Use descriptive file names and add metadata and tags to make your photos easier to search and categorize.
7.7. What Should I Do If My Computer Doesn’t Recognize My Phone?
Check the USB connection, update drivers, restart your devices, and ensure you have tapped “Trust” or “Allow” on your phone when prompted.
7.8. How Can I Back Up My Photo Library?
Create local backups on external hard drives or NAS devices and use cloud storage services for offsite backups. A hybrid backup strategy provides the best protection against data loss.
7.9. Is It Safe to Use Third-Party Apps for Photo Transfer?
Using reputable third-party apps is generally safe, but always review the app’s permissions and security practices before using it.
7.10. How Do I Ensure the Privacy of My Photos During Transfer?
Use secure USB connections, encrypt sensitive photos, use strong passwords for your cloud storage accounts, and adjust the privacy settings on your cloud services.
8. Conclusion: Streamlining Your Photo Transfer Process
Transferring photos from your phone to your computer doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By understanding the various methods available, choosing the right file formats, organizing your photos effectively, and following security best practices, you can streamline your photo transfer process and ensure your precious memories are safely backed up and easily accessible. Whether you prefer the directness of a USB connection or the convenience of cloud storage, the key is to find a method that fits your needs and workflow. Remember to regularly back up your photo library to prevent data loss and keep your memories safe for years to come.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of photography? Visit dfphoto.net for a wealth of tutorials, stunning photo collections, and a vibrant community of photographers. Explore expert guides, discover inspirational works, and connect with fellow enthusiasts. Enhance your skills and ignite your passion for capturing the world through your lens! Contact us at Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Let dfphoto.net be your ultimate resource for all things photography.
