Reducing photo size is key for faster website loading and easier sharing, and at dfphoto.net, we’ll guide you through various techniques using image compression, resizing, and file format optimization to ensure your photos look great while remaining manageable in size. Discover how to strike the perfect balance between image quality and file size with our expert tips, and learn about the semantic keywords image optimization and resolution.
1. Understanding the Need to Shrink Photo Size
Why is it important to reduce the size of a photo?
Shrinking photo size is crucial for several reasons:
- Faster Website Loading: Smaller images lead to quicker page load times, improving user experience.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Smaller files consume less bandwidth, saving on data costs.
- Easier Sharing: Smaller photos are easier to share via email and social media.
- Storage Efficiency: Smaller files take up less storage space on devices and servers.
1.1. Impact on Website Performance
How does photo size affect website loading speed?
Large image files significantly slow down website loading speed, leading to a poor user experience. According to research from Google, 53% of mobile site visitors leave a page that takes longer than three seconds to load. Optimizing images by reducing their file size is essential for keeping visitors engaged and improving SEO.
1.2. Storage Considerations
Why should I be mindful of photo size when storing images?
Large photo files consume significant storage space, whether on your computer, phone, or cloud storage. Regularly shrinking your photos can free up valuable space and make it easier to manage your image library.
2. Key Factors Influencing Photo Size
What factors determine the size of a photo file?
Several factors influence the size of a photo file:
- Dimensions: The width and height of the image in pixels.
- Resolution: The number of pixels per inch (PPI).
- File Format: JPEG, PNG, GIF, and other formats use different compression methods.
- Color Depth: The number of colors stored per pixel.
- Compression: The algorithm used to reduce the file size.
2.1. Dimensions and Resolution
How do dimensions and resolution affect photo size?
Dimensions and resolution play a critical role in determining photo size. Larger dimensions (more pixels) and higher resolution (more pixels per inch) result in larger file sizes. Reducing either of these can significantly shrink the photo’s size.
2.2. The Role of File Format
Which file format is best for smaller photo sizes?
The best file format for smaller photo sizes depends on the image content:
- JPEG: Ideal for photos with many colors and gradations, as it uses lossy compression to reduce file size.
- PNG: Suitable for images with transparency or graphics with few colors, offering lossless compression.
- GIF: Best for simple graphics with few colors and solid areas.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, JPEG remains the most popular choice for photographs on the web due to its ability to achieve significant compression with minimal visual quality loss.
3. Choosing the Right File Format
How do I choose the best file format for my photos?
Choosing the right file format is essential for achieving the desired balance between image quality and file size. Here’s a breakdown of the most common formats:
3.1. JPEG (or JPG)
When should I use JPEG?
JPEG is best for photographs and images with gradients due to its lossy compression, which reduces file size while maintaining acceptable image quality. This makes it ideal for web use and sharing.
Lossy Compression Explained
What is lossy compression and how does it affect image quality?
Lossy compression reduces file size by discarding some image data. While this can result in smaller files, it may also lead to a loss of detail and the introduction of artifacts, especially at high compression levels.
Optimizing JPEG Quality Settings
How do I optimize JPEG quality settings for the best results?
When saving a JPEG, adjust the quality settings to find the lowest acceptable level that still preserves the visual integrity of the image. Experiment with different settings to balance file size and image quality.
3.2. PNG
When should I use PNG?
PNG is ideal for graphics, logos, and images with transparency. It uses lossless compression, which preserves all image data, resulting in higher quality but larger file sizes compared to JPEG.
PNG-8 vs. PNG-24
What is the difference between PNG-8 and PNG-24?
PNG-8 is similar to GIF, limited to 256 colors, and suitable for simple graphics. PNG-24 supports millions of colors and is best for detailed images requiring transparency without quality loss.
Transparency and PNG
How does PNG handle transparency?
PNG supports full transparency, making it perfect for images that need to overlay other content without a visible background.
3.3. GIF
When should I use GIF?
GIF is best for simple animated images and graphics with limited colors. It uses lossless compression but is restricted to a 256-color palette.
GIF Animation
How does GIF support animation?
GIF supports animation by storing multiple frames in a single file, which are then displayed in sequence to create a short animation.
Limitations of GIF
What are the limitations of GIF?
The main limitations of GIF are its 256-color palette and relatively large file sizes compared to other formats like PNG-8.
4. Image Compression Techniques
What are the most effective image compression techniques?
Image compression techniques reduce file size by removing redundant or unnecessary data. There are two main types:
4.1. Lossy Compression
How does lossy compression work?
Lossy compression permanently removes some image data to reduce file size. This is commonly used in JPEG format and can significantly decrease file size with a potential loss of quality.
Balancing Quality and Size with Lossy Compression
How do I balance quality and size when using lossy compression?
Experiment with different compression settings to find the lowest level that still provides acceptable image quality. Regularly check for artifacts and loss of detail.
Artifacts and Degradation
What are artifacts and how do they affect image quality?
Artifacts are visual distortions that can appear in images compressed with lossy methods, especially at high compression levels. These can include blockiness, color banding, and loss of fine details.
4.2. Lossless Compression
How does lossless compression work?
Lossless compression reduces file size without discarding any image data. This is used in PNG and GIF formats, ensuring no loss of quality but generally resulting in larger file sizes compared to lossy methods.
Preserving Image Quality
How does lossless compression preserve image quality?
Lossless compression identifies and eliminates redundancy in the image data without removing any actual information, ensuring the original image can be perfectly reconstructed.
When to Choose Lossless Compression
When should I choose lossless compression over lossy compression?
Choose lossless compression when image quality is paramount, such as for logos, graphics with text, and images requiring transparency.
5. Resizing Images
How does resizing images help reduce file size?
Resizing images involves changing their dimensions (width and height), which directly affects the number of pixels and, therefore, the file size.
5.1. Understanding Image Dimensions
How do image dimensions relate to file size?
Larger image dimensions mean more pixels, leading to larger file sizes. Reducing dimensions decreases the number of pixels, resulting in smaller files.
Pixel Count
What is a pixel and how does it affect image size?
A pixel is the smallest element of an image. The more pixels an image has, the more detailed it is, but also the larger its file size.
Aspect Ratio
What is aspect ratio and why is it important when resizing?
Aspect ratio is the proportional relationship between the width and height of an image. Maintaining the aspect ratio during resizing prevents distortion and ensures the image looks natural.
5.2. Resizing Tools and Software
What tools can I use to resize images?
Numerous tools and software options are available for resizing images, including:
- Adobe Photoshop: Professional image editing software with advanced resizing capabilities.
- GIMP: A free, open-source image editor.
- Online Image Resizers: Web-based tools like TinyPNG, ImageResizer, and iloveimg.
Adobe Photoshop
How can I resize images using Adobe Photoshop?
In Photoshop, use the “Image Size” dialog box (Image > Image Size) to adjust the width and height of the image. Ensure “Resample” is checked and choose an appropriate resampling method, such as “Bicubic Sharper” for reducing size.
GIMP
How can I resize images using GIMP?
In GIMP, use the “Scale Image” dialog box (Image > Scale Image) to change the width and height. Choose an interpolation method like “Cubic” for good results.
5.3. Maintaining Image Quality While Resizing
How can I maintain image quality while resizing?
To maintain image quality while resizing, use appropriate resampling methods and avoid drastically reducing the dimensions, which can lead to loss of detail.
Resampling Methods
What are resampling methods and how do they affect image quality?
Resampling methods determine how pixels are added or removed during resizing. Common methods include:
- Bicubic: Balances sharpness and smoothness, suitable for general use.
- Bilinear: Faster but less precise than bicubic.
- Nearest Neighbor: Preserves sharp edges but can create a jagged effect.
Avoiding Over-Resizing
Why should I avoid over-resizing images?
Over-resizing (enlarging an image beyond its original dimensions) can lead to pixelation and a loss of sharpness. It’s generally best to avoid enlarging images unless necessary.
6. Optimizing Images for the Web
How do I optimize images specifically for web use?
Optimizing images for the web involves reducing file size while maintaining acceptable quality, ensuring fast loading times and a good user experience.
6.1. Choosing the Right Dimensions
What are the recommended dimensions for web images?
The recommended dimensions for web images depend on their intended use:
- Full-width Backgrounds: 1920×1080 pixels
- Blog Post Images: 1200×630 pixels
- Product Images: 800×800 pixels
Responsive Images
What are responsive images and how do they improve web performance?
Responsive images automatically adjust their size to fit different screen sizes and devices, ensuring optimal display and performance across all platforms.
Using the <picture> Element
How can I use the <picture> element to serve responsive images?
The <picture> element allows you to specify multiple image sources for different screen sizes and resolutions, enabling the browser to choose the most appropriate image for the user’s device.
6.2. Compressing Images for Faster Loading
How can I compress images for faster loading on websites?
Compressing images reduces their file size, leading to faster loading times. Use online tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel to compress images without significant quality loss.
Online Compression Tools
What are some recommended online image compression tools?
Recommended online image compression tools include:
- TinyPNG: Compresses PNG and JPEG images using lossy compression.
- ImageOptim: A free, open-source tool for Mac that optimizes images by removing unnecessary data.
- ShortPixel: Offers both lossy and lossless compression options.
WordPress Plugins for Image Optimization
What WordPress plugins can help with image optimization?
Popular WordPress plugins for image optimization include:
- Smush: Automatically compresses and optimizes images as you upload them.
- Imagify: Offers various compression levels and integrates with WordPress.
- Optimole: A cloud-based image optimization service.
6.3. Lazy Loading
What is lazy loading and how does it improve website performance?
Lazy loading is a technique that defers the loading of images until they are about to come into view, improving initial page load time and reducing bandwidth usage.
Implementing Lazy Loading
How can I implement lazy loading on my website?
Lazy loading can be implemented using JavaScript libraries like lazysizes or by using the loading="lazy" attribute in HTML.
Benefits of Lazy Loading
What are the benefits of using lazy loading?
The benefits of lazy loading include faster initial page load times, reduced bandwidth consumption, and improved user experience.
7. Software and Tools for Photo Size Reduction
What software and tools can I use to reduce photo size?
Numerous software and tools are available for reducing photo size, each offering different features and capabilities.
7.1. Adobe Photoshop
How can I use Adobe Photoshop to reduce photo size?
Adobe Photoshop provides comprehensive tools for resizing and compressing images. Use the “Image Size” dialog box to adjust dimensions and the “Save for Web” feature to optimize compression settings.
Using “Save for Web”
How does the “Save for Web” feature in Photoshop work?
The “Save for Web” feature allows you to preview different compression settings and file formats, helping you find the best balance between quality and file size.
Batch Processing in Photoshop
How can I use batch processing to resize multiple images in Photoshop?
Batch processing automates the process of resizing and compressing multiple images at once, saving time and effort. Use the “Action” panel to record a series of steps and then apply them to a batch of images.
7.2. GIMP
How can I use GIMP to reduce photo size?
GIMP is a free, open-source image editor that offers similar resizing and compression capabilities to Photoshop. Use the “Scale Image” dialog box to adjust dimensions and the “Export” feature to optimize compression settings.
Export Options in GIMP
What export options are available in GIMP for reducing photo size?
GIMP offers various export options, including JPEG, PNG, and GIF, each with customizable compression settings.
Scripting in GIMP
How can I use scripting to automate image resizing in GIMP?
GIMP supports scripting, allowing you to automate complex tasks like resizing and compressing multiple images.
7.3. Online Image Resizers
What are the advantages of using online image resizers?
Online image resizers are convenient for quick and easy photo size reduction without the need for software installation.
Popular Online Tools
What are some popular online image resizers?
Popular online image resizers include:
- TinyPNG: Compresses PNG and JPEG images.
- ImageResizer: Offers various resizing and compression options.
- iloveimg: Provides a suite of image editing tools, including resizing and compression.
Privacy Considerations
What privacy considerations should I keep in mind when using online image resizers?
Be mindful of the privacy policies of online image resizers, as some may store or use your images. Choose reputable tools with clear privacy practices.
8. Best Practices for Maintaining Image Quality
What are the best practices for maintaining image quality while reducing photo size?
Maintaining image quality while reducing photo size requires careful attention to various factors and techniques.
8.1. Sharpness and Clarity
How can I ensure sharpness and clarity when reducing photo size?
To ensure sharpness and clarity, use appropriate resampling methods, avoid excessive compression, and consider applying a slight sharpening filter after resizing.
Sharpening Filters
What are sharpening filters and how do they improve image quality?
Sharpening filters enhance the edges and details in an image, making it appear sharper and more defined.
Unsharp Masking
What is unsharp masking and how does it work?
Unsharp masking is a sharpening technique that increases the contrast along edges, creating the illusion of greater sharpness.
8.2. Color Accuracy
How can I maintain color accuracy when reducing photo size?
To maintain color accuracy, use a color-managed workflow, avoid converting between color spaces unnecessarily, and use file formats that support the desired color depth.
Color Profiles
What are color profiles and how do they affect color accuracy?
Color profiles are sets of data that define the range of colors a device can reproduce. Using color profiles ensures consistent color reproduction across different devices and applications.
Color Space Conversion
What is color space conversion and why should I be careful when doing it?
Color space conversion involves changing the way colors are represented in an image. Converting between color spaces can sometimes lead to color shifts or loss of information, so it should be done carefully.
8.3. Avoiding Common Mistakes
What are some common mistakes to avoid when reducing photo size?
Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Over-compressing images: Can lead to excessive artifacts and loss of detail.
- Resizing too drastically: Can result in pixelation and blurriness.
- Using the wrong file format: Can lead to larger file sizes or poor image quality.
Over-Compression
Why is over-compression a problem?
Over-compression removes too much image data, resulting in visible artifacts and a significant loss of detail.
Incorrect File Format
How can using the wrong file format affect image quality and size?
Using the wrong file format can lead to larger file sizes or poor image quality. For example, saving a photograph as a GIF can result in a limited color palette and a larger file size than saving it as a JPEG.
9. Advanced Techniques for Photo Optimization
What are some advanced techniques for optimizing photo size?
Advanced techniques for photo optimization include using specialized compression algorithms, optimizing metadata, and employing progressive JPEGs.
9.1. Specialized Compression Algorithms
What are specialized compression algorithms?
Specialized compression algorithms are designed to provide better compression ratios and image quality compared to standard methods.
WebP Format
What is the WebP format and how does it improve image optimization?
WebP is a modern image format developed by Google that offers superior lossless and lossy compression for images on the web. It can reduce file sizes by 25-34% compared to JPEG while maintaining similar image quality.
AVIF Format
What is the AVIF format and how does it compare to WebP?
AVIF (AV1 Image File Format) is an image format based on the AV1 video codec. It offers even better compression than WebP, particularly for complex images with fine details.
9.2. Metadata Optimization
How can optimizing metadata help reduce photo size?
Metadata is information embedded in an image file, such as camera settings, location data, and copyright information. Removing unnecessary metadata can reduce file size without affecting image quality.
Removing EXIF Data
What is EXIF data and how can I remove it?
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data contains detailed information about the camera settings used to capture an image. Removing EXIF data can reduce file size, especially for images shared online.
Tools for Metadata Removal
What tools can I use to remove metadata from images?
Tools for removing metadata from images include:
- ExifTool: A command-line tool for reading, writing, and editing metadata.
- Online Metadata Removers: Web-based tools like Online Exif Remover and Metadata2go.
9.3. Progressive JPEGs
What are progressive JPEGs and how do they improve user experience?
Progressive JPEGs display a low-resolution version of the image first, gradually increasing in detail as the rest of the image loads. This provides a better user experience, as visitors see something quickly rather than waiting for the entire image to load.
How Progressive JPEGs Work
How do progressive JPEGs load differently than standard JPEGs?
Standard JPEGs load from top to bottom, while progressive JPEGs load in multiple passes, gradually increasing in detail.
Benefits of Using Progressive JPEGs
What are the benefits of using progressive JPEGs?
The benefits of using progressive JPEGs include improved perceived loading speed, a better user experience, and a more visually appealing loading process.
10. Practical Examples and Case Studies
Can you provide practical examples of photo size reduction techniques?
Let’s explore some practical examples and case studies to illustrate the effectiveness of different photo size reduction techniques.
10.1. Reducing JPEG Size for Web Use
How can I effectively reduce JPEG size for web use?
Consider a photograph with an original size of 5MB. By adjusting the JPEG quality setting to 60% and using an online compression tool like TinyPNG, you can reduce the file size to around 500KB without significant quality loss.
Step-by-Step Guide
Can you provide a step-by-step guide for reducing JPEG size?
- Open the image in an image editor: Use Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or an online tool.
- Adjust the JPEG quality: Set the quality to around 60-70% for a good balance between size and quality.
- Preview the image: Check for any visible artifacts or loss of detail.
- Save the image: Save the image with the new settings.
- Use an online compression tool: Upload the image to TinyPNG or a similar tool for further compression.
- Verify the results: Compare the original and compressed images to ensure acceptable quality.
Before and After Comparison
Can you show a before and after comparison of JPEG size reduction?
| Aspect | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| File Size | 5MB | 500KB |
| Visual Quality | High | Slightly Reduced |
| Loading Time | Slow | Fast |
| Compression Method | Standard JPEG | Optimized JPEG with TinyPNG |
10.2. Optimizing PNG Images for Logos
How can I optimize PNG images specifically for logos?
For logos with transparency, save the image as a PNG-24 and use an online compression tool to reduce the file size without losing transparency.
Transparency Considerations
How do I ensure transparency is preserved during PNG optimization?
When compressing PNG images with transparency, ensure that the compression tool supports transparency and that the settings are configured to preserve it.
Color Palette Reduction
How can reducing the color palette help optimize PNG images?
Reducing the color palette in PNG images, especially for logos, can significantly reduce file size without affecting visual quality.
10.3. Resizing Images for Social Media
What are the recommended dimensions for social media images?
Each social media platform has its own recommended image dimensions. Research the specific requirements for each platform and resize your images accordingly.
What are the recommended image dimensions for Facebook?
- Profile Picture: 170×170 pixels
- Cover Photo: 851×315 pixels
- Post Image: 1200×630 pixels
What are the recommended image dimensions for Instagram?
- Profile Picture: 110×110 pixels
- Post Image: 1080×1080 pixels
- Story Image: 1080×1920 pixels
At dfphoto.net, we understand the importance of optimizing your images for various platforms. By following these best practices, you can ensure your photos look their best while remaining manageable in size.
FAQ: Shrinking Photo Size
1. What is the best file format to shrink the size of a photo?
The best file format depends on the image type. JPEG is ideal for photos with many colors, while PNG is better for graphics with transparency.
2. How much can I compress a JPEG image without losing too much quality?
You can often compress a JPEG image to around 60-70% of its original quality without significant visual degradation.
3. What is the difference between lossy and lossless compression?
Lossy compression removes some image data to reduce file size, while lossless compression reduces file size without discarding any data.
4. Can I resize an image without losing quality?
Resizing an image smaller than its original size generally doesn’t result in quality loss. However, enlarging an image can lead to pixelation.
5. What are some good online tools for shrinking photo size?
Some recommended online tools include TinyPNG, ImageOptim, and ShortPixel.
6. How does metadata affect photo size?
Metadata contains information about the image and can increase file size. Removing unnecessary metadata can help reduce file size.
7. What is lazy loading and how does it improve website performance?
Lazy loading defers the loading of images until they are about to come into view, improving initial page load time and reducing bandwidth usage.
8. What are progressive JPEGs and why are they useful?
Progressive JPEGs display a low-resolution version of the image first, gradually increasing in detail as the rest of the image loads, providing a better user experience.
9. How do I choose the right dimensions for web images?
The recommended dimensions for web images depend on their intended use. Consider the size and layout of the webpage when choosing dimensions.
10. Why is it important to optimize images for the web?
Optimizing images for the web improves website loading speed, enhances user experience, and reduces bandwidth usage.
We encourage you to explore dfphoto.net for more in-depth tutorials, stunning photography, and a vibrant community of photographers. Discover new techniques, find inspiration, and take your photography to the next level.
Ready to transform your photography skills and share your optimized images with the world? Visit dfphoto.net today to explore our comprehensive guides, view breathtaking photographs, and connect with a passionate community of photographers. Unlock your creative potential and discover the art of photography at Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001. Website: dfphoto.net.
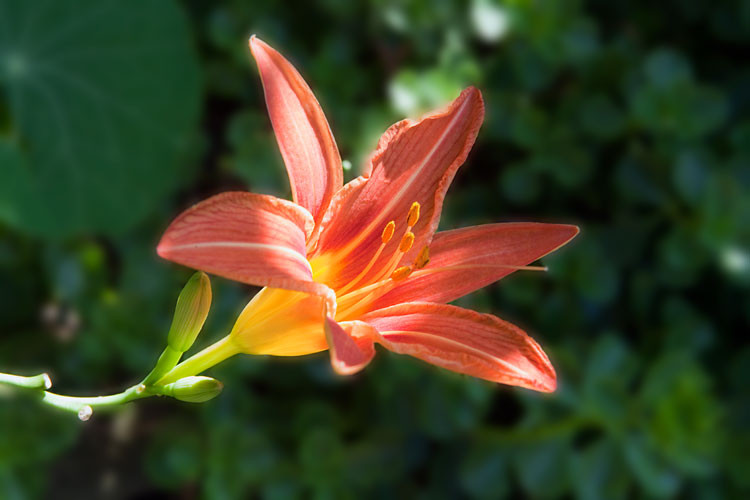 Day lily with background blurred
Day lily with background blurred
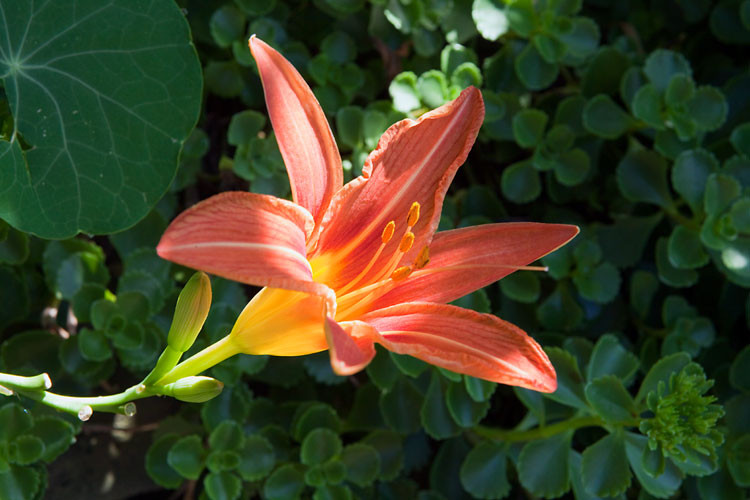 Day lily
Day lily
 Cartoon saved as PNG
Cartoon saved as PNG
 Cartoon saved as GIF
Cartoon saved as GIF
 Photo saved as high quality JGP
Photo saved as high quality JGP
 Photo saved at makimum quality JPG
Photo saved at makimum quality JPG
 Photo saved as PNG
Photo saved as PNG
 Dancing robot
Dancing robot
 daylily flower and buds 0
daylily flower and buds 0
 daylily flower and buds 20
daylily flower and buds 20
 daylily flower and buds 40
daylily flower and buds 40
 daylily flower and buds 60
daylily flower and buds 60
 daylily flower and buds 80
daylily flower and buds 80