Downloading your photos to your computer is a crucial step in managing and preserving your visual memories, and dfphoto.net is here to guide you. Whether you’re a professional photographer or just someone who loves capturing moments, understanding the process of transferring your images is essential for backing them up, editing them, and sharing them with the world. In this guide, we’ll explore different methods of How Do I Download My Photos To My Computer, ensuring your precious memories are safely stored and ready to be enjoyed for years to come. Unlock the art of transferring and optimizing your visual treasures with dfphoto.net, where every pixel tells a story. Embrace the world of photography with knowledge, inspiration, and community.
1. Understanding the Basics of Photo Transfer
Before diving into the technical steps of how do I download my photos to my computer, it’s essential to understand the basic concepts and options available. This section will cover the different methods of transferring photos, the importance of choosing the right method, and the file formats you’ll encounter.
1.1. What Are the Different Methods for Transferring Photos?
There are several ways of how do I download my photos to my computer, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
- USB Cable: Connecting your camera or smartphone to your computer using a USB cable is a direct and reliable way to transfer photos. It’s generally faster than wireless methods and doesn’t require an internet connection.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Photos, Dropbox, and iCloud allow you to automatically back up your photos to the cloud, making them accessible on any device. This method is convenient for syncing photos across multiple devices but requires a stable internet connection and sufficient storage space.
- Memory Card Reader: If you use a digital camera, you can remove the memory card and insert it into a memory card reader connected to your computer. This is a fast and efficient way to transfer photos, especially if you have a large number of files.
- Wireless Transfer: Some cameras and smartphones support wireless transfer via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. This method is convenient for transferring photos without cables, but it can be slower and less reliable than other methods.
- Email: Sending photos as email attachments is a simple way to transfer a few images, but it’s not practical for large numbers of photos due to file size limitations.
1.2. Why Is Choosing the Right Method Important?
Choosing the right method of how do I download my photos to my computer depends on your specific needs and preferences. Factors to consider include:
- Speed: If you need to transfer photos quickly, a USB cable or memory card reader is usually the best option.
- Convenience: Cloud storage and wireless transfer offer the most convenience, allowing you to transfer photos without cables.
- Reliability: USB cables and memory card readers are generally the most reliable methods, as they don’t depend on an internet connection or wireless signal.
- Security: Consider the security implications of each method. Cloud storage services offer encryption and other security measures, but you should still take steps to protect your account.
- File Size: If you’re transferring large files, such as RAW images or videos, a USB cable or memory card reader is usually the best option.
1.3. Understanding File Formats: JPEG, RAW, and More
When downloading photos, you’ll encounter different file formats, each with its own characteristics. The most common file formats include:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): JPEG is a widely used format that offers good image quality with relatively small file sizes. It’s a lossy format, meaning that some image data is lost during compression.
- RAW: RAW formats (such as NEF for Nikon and CR2 for Canon) contain all the data captured by the camera’s sensor, without any compression or processing. This allows for greater flexibility when editing photos, but RAW files are much larger than JPEGs.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): TIFF is a lossless format that preserves all image data. It’s often used for archival purposes and professional printing, but TIFF files are very large.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): PNG is a lossless format that’s often used for web graphics. It supports transparency and is a good choice for images with text or logos.
- HEIF/HEIC (High Efficiency Image File Format): HEIF is a modern format that offers better compression than JPEG, resulting in smaller file sizes with comparable image quality. It’s used by default on newer iPhones and iPads.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, understanding these file formats is crucial for managing your photos effectively and ensuring that you choose the right format for your needs.
2. Step-by-Step Guide: Downloading Photos via USB Cable
Using a USB cable is one of the most reliable and straightforward ways of how do I download my photos to my computer. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide for both Windows and Mac users.
2.1. Downloading Photos to a Windows PC
- Connect Your Device: Use a USB cable to connect your camera or smartphone to your Windows PC.
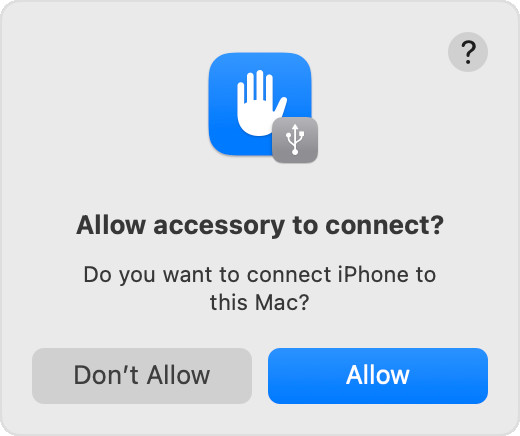 Accessory prompt to allow or don’t allow accessory to connect.
Accessory prompt to allow or don’t allow accessory to connect. - Unlock Your Device: If your device is locked, unlock it using your passcode or biometric authentication.
- Trust This Computer: If prompted, tap “Trust” or “Allow” on your device to allow the computer to access your photos and videos.
- Open the Photos App: The Photos app may open automatically. If not, you can open it manually by searching for “Photos” in the Start menu.
- Import Photos: In the Photos app, click “Import” and select “From a USB device.”
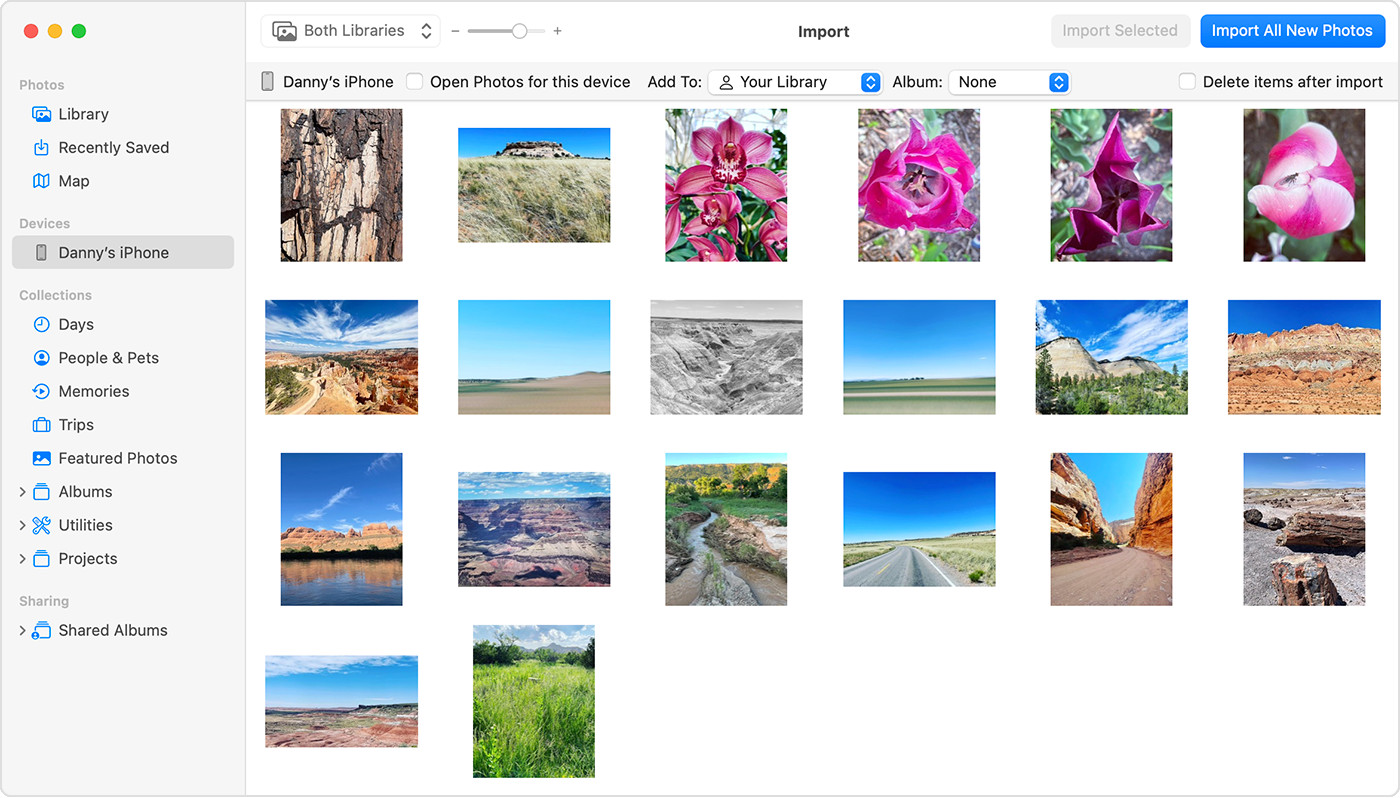 Mac screen showing the photos available for import
Mac screen showing the photos available for import - Select Photos: Choose the photos you want to import. You can select individual photos or click “Select all” to import all photos.
- Choose Import Settings: Specify where you want to save the photos and whether you want to delete them from your device after importing.
- Start Import: Click “Import selected” to begin the transfer process.
- Disconnect Your Device: Once the import is complete, safely disconnect your device from your computer.
2.2. Downloading Photos to a Mac
- Connect Your Device: Use a USB cable to connect your camera or smartphone to your Mac.
- Unlock Your Device: If your device is locked, unlock it using your passcode or biometric authentication.
- Trust This Computer: If prompted, tap “Trust” on your device to allow the computer to access your photos and videos.
- Open the Photos App: The Photos app may open automatically. If not, you can open it manually by clicking the Photos icon in the Dock or Launchpad.
- Select Your Device: In the Photos app, select your device from the sidebar.
- Import Photos: Choose the photos you want to import and click “Import Selected,” or click “Import All New Photos” to import all new photos.
- Choose an Album: Select an existing album or create a new one to store the imported photos.
- Wait for the Process to Finish: Wait for the import process to complete, then disconnect your device from your Mac.
2.3. Troubleshooting Common USB Transfer Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter issues when transferring photos via USB cable. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Device Not Recognized: Make sure the USB cable is properly connected and that your device is unlocked and trusted. Try using a different USB port or cable.
- Photos App Not Opening: Manually open the Photos app or restart your computer.
- Slow Transfer Speed: Close unnecessary applications and ensure that your USB cable and ports support USB 3.0 for faster transfer speeds.
- Error Messages: Check the error message for specific instructions. It may indicate a problem with the file format or storage space.
3. Utilizing Cloud Storage for Seamless Photo Transfers
Cloud storage services offer a convenient way of how do I download my photos to my computer and keep them synced across multiple devices. This section will explore popular cloud storage options and how to use them effectively.
3.1. Overview of Popular Cloud Storage Options (Google Photos, Dropbox, iCloud)
- Google Photos: Google Photos offers unlimited storage for photos and videos (up to 16MP for photos and 1080p for videos) and integrates seamlessly with other Google services. It also provides automatic organization and search features.
- Dropbox: Dropbox is a versatile cloud storage service that can be used for photos, documents, and other files. It offers automatic syncing across devices and collaboration features.
- iCloud Photos: iCloud Photos is Apple’s cloud storage service for photos and videos. It’s integrated with iOS and macOS and offers automatic syncing across Apple devices.
3.2. Setting Up and Configuring Cloud Storage on Your Devices
- Choose a Service: Select a cloud storage service that meets your needs and budget.
- Create an Account: Sign up for an account on the service’s website or app.
- Install the App: Download and install the app on your computer and mobile devices.
- Configure Sync Settings: Choose which folders or albums you want to sync to the cloud.
- Enable Automatic Upload: Turn on automatic upload to ensure that new photos are automatically backed up to the cloud.
3.3. Downloading Photos from Cloud Storage to Your Computer
- Open the Cloud Storage App: Open the app on your computer.
- Locate Your Photos: Navigate to the folder or album containing the photos you want to download.
- Select Photos: Choose the photos you want to download. You can select individual photos or select all photos in the folder.
- Download Photos: Click the “Download” button to save the photos to your computer.
- Choose a Location: Specify where you want to save the photos on your computer.
- Wait for the Download to Finish: Wait for the download process to complete.
3.4. Tips for Optimizing Cloud Storage Usage
- Choose the Right Storage Plan: Select a storage plan that provides enough space for your photos and videos.
- Organize Your Photos: Use albums and folders to organize your photos in the cloud.
- Enable Automatic Backup: Turn on automatic backup to ensure that your photos are always protected.
- Review Sync Settings: Regularly review your sync settings to ensure that you’re only syncing the folders you need.
- Use Wi-Fi for Uploading: Upload photos and videos over Wi-Fi to avoid using up your mobile data.
4. Using Memory Card Readers for Fast and Efficient Transfers
Memory card readers offer a fast and efficient way of how do I download my photos to my computer, especially if you use a digital camera. This section will cover the benefits of using memory card readers and how to use them effectively.
4.1. Benefits of Using a Memory Card Reader
- Speed: Memory card readers can transfer photos faster than USB cables or wireless methods.
- Convenience: You can transfer photos directly from the memory card without connecting the camera to your computer.
- Compatibility: Memory card readers support a wide range of memory card formats, including SD, microSD, and CompactFlash.
- Reliability: Memory card readers don’t depend on an internet connection or wireless signal.
4.2. Types of Memory Card Readers Available
- USB Memory Card Readers: These readers connect to your computer via USB and support various memory card formats.
- Internal Memory Card Readers: Some computers have built-in memory card readers that support SD cards.
- Multi-Card Readers: These readers support multiple memory card formats simultaneously.
4.3. Step-by-Step Guide to Transferring Photos with a Memory Card Reader
- Insert the Memory Card: Remove the memory card from your camera and insert it into the memory card reader.
- Connect the Reader: Connect the memory card reader to your computer via USB.
- Open File Explorer (Windows) or Finder (Mac): The memory card should appear as a removable drive in File Explorer or Finder.
- Locate Your Photos: Open the memory card drive and navigate to the folder containing your photos.
- Copy Photos: Copy the photos you want to transfer to a folder on your computer.
- Eject the Memory Card: Safely eject the memory card from the reader before removing it.
4.4. Tips for Maintaining Your Memory Cards and Readers
- Use High-Quality Memory Cards: Invest in reputable brands known for their reliability and performance.
- Format Memory Cards Regularly: Format your memory cards in your camera to ensure optimal performance.
- Protect Memory Cards from Damage: Store memory cards in a protective case to prevent physical damage.
- Keep Memory Card Readers Clean: Clean the memory card reader slots regularly to remove dust and debris.
- Safely Eject Memory Cards: Always safely eject memory cards from the reader before removing them to prevent data corruption.
5. Wireless Transfer Options: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Wireless transfer options like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer a cable-free way of how do I download my photos to my computer. This section will explore how to use these methods and their advantages and disadvantages.
5.1. How to Transfer Photos via Wi-Fi
- Check Camera Compatibility: Ensure your camera supports Wi-Fi transfer.
- Connect to Wi-Fi: Connect your camera to your home Wi-Fi network.
- Install Camera Software: Install the camera manufacturer’s software on your computer.
- Pair Devices: Follow the instructions in the camera software to pair your camera with your computer.
- Transfer Photos: Use the camera software to browse and transfer photos from your camera to your computer.
5.2. How to Transfer Photos via Bluetooth
- Enable Bluetooth: Enable Bluetooth on your camera and computer.
- Pair Devices: Put your camera in pairing mode and search for it on your computer. Enter the pairing code if prompted.
- Transfer Photos: Use the Bluetooth file transfer option on your computer to browse and transfer photos from your camera to your computer.
5.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Wireless Transfer
Advantages:
- Convenience: No cables required.
- Remote Transfer: You can transfer photos from a distance.
Disadvantages:
- Slower Speed: Wireless transfer is generally slower than USB or memory card readers.
- Reliability: Wireless transfer can be less reliable due to signal interference.
- Battery Drain: Wireless transfer can drain your camera’s battery quickly.
5.4. Best Practices for Wireless Photo Transfers
- Use a Strong Wi-Fi Signal: Ensure that your camera and computer are connected to a strong Wi-Fi signal for faster and more reliable transfer.
- Keep Devices Close Together: Keep your camera and computer close together when using Bluetooth to improve the connection.
- Charge Your Camera Battery: Ensure that your camera battery is fully charged before starting a wireless transfer.
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Close unnecessary applications on your computer to free up resources and improve transfer speed.
6. Addressing Compatibility Issues and File Conversions
Sometimes, you may encounter compatibility issues when trying to open or edit photos on your computer. This section will address common compatibility issues and how to convert files to more compatible formats.
6.1. Common Compatibility Issues with Photo Files
- Unsupported File Format: Your computer may not support the file format of the photo (e.g., HEIF/HEIC).
- Outdated Software: Your photo editing software may be outdated and unable to open certain file formats.
- Missing Codecs: Your computer may be missing the necessary codecs to decode certain video formats.
6.2. Converting Photos to More Compatible Formats (JPEG, PNG)
- Use a Photo Editing Software: Open the photo in a photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, or Paint.NET.
- Save As: Select “Save As” and choose a more compatible format like JPEG or PNG.
- Adjust Quality Settings: Adjust the quality settings to balance file size and image quality.
- Save the File: Save the converted file to your computer.
6.3. Software and Tools for File Conversion
- Adobe Photoshop: A professional photo editing software with powerful file conversion capabilities.
- GIMP: A free and open-source photo editing software that supports various file formats.
- IrfanView: A free image viewer and converter for Windows.
- Online File Converters: Websites like CloudConvert and Zamzar offer online file conversion services.
6.4. Tips for Ensuring File Compatibility
- Update Your Software: Keep your photo editing software and operating system up to date.
- Install Necessary Codecs: Install the necessary codecs to support various video formats.
- Convert Files When Necessary: Convert files to more compatible formats when you encounter compatibility issues.
- Use Standard File Formats: Use standard file formats like JPEG and PNG for maximum compatibility.
7. Optimizing Your Photos for Storage and Sharing
Once you’ve downloaded your photos to your computer, it’s essential to optimize them for storage and sharing. This section will cover techniques for resizing, compressing, and organizing your photos.
7.1. Resizing Photos for Different Purposes (Web, Print, Social Media)
- Web: Resize photos to a smaller size (e.g., 1920×1080 pixels) to reduce file size and improve website loading speed.
- Print: Resize photos to a higher resolution (e.g., 300 DPI) for optimal print quality.
- Social Media: Resize photos to the recommended dimensions for each social media platform.
7.2. Compressing Photos to Reduce File Size
- JPEG Compression: Use JPEG compression to reduce file size while maintaining good image quality.
- PNG Compression: Use PNG compression for images with text or logos to preserve sharpness.
- Online Compression Tools: Websites like TinyPNG and Compressor.io offer online photo compression services.
7.3. Organizing Your Photos with Folders and Metadata
- Create Folders: Create folders for different events, dates, or categories.
- Use Descriptive Filenames: Use descriptive filenames that include the date, location, and subject of the photo.
- Add Metadata: Add metadata like captions, keywords, and copyright information to your photos.
7.4. Backing Up Your Photos for Safekeeping
- Use Multiple Backup Locations: Back up your photos to multiple locations, such as an external hard drive, cloud storage, and a NAS device.
- Automate Your Backups: Use backup software to automate the backup process.
- Test Your Backups Regularly: Test your backups regularly to ensure that they are working properly.
8. Protecting Your Photos: Copyright and Security
Protecting your photos is crucial, especially if you plan to share them online. This section will cover copyright basics and security measures to keep your photos safe.
8.1. Understanding Copyright Basics for Photographers
- Copyright Ownership: As a photographer, you automatically own the copyright to your photos.
- Copyright Protection: Copyright protects your photos from unauthorized use, reproduction, and distribution.
- Copyright Registration: You can register your copyright with the U.S. Copyright Office to strengthen your legal protection.
8.2. Adding Watermarks to Your Photos
- Use a Watermark Tool: Use a photo editing software or online watermark tool to add a watermark to your photos.
- Choose a Subtle Watermark: Choose a subtle watermark that doesn’t detract from the image.
- Position the Watermark Strategically: Position the watermark in a location that’s difficult to remove.
8.3. Security Measures to Protect Your Photos Online
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for your online accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Be Careful What You Share: Be careful about what you share online and who you share it with.
- Monitor Your Online Presence: Monitor your online presence to detect unauthorized use of your photos.
8.4. Dealing with Copyright Infringement
- Send a Cease and Desist Letter: Send a cease and desist letter to the infringing party demanding that they stop using your photos.
- File a DMCA Takedown Notice: File a DMCA takedown notice with the website hosting the infringing photos.
- Take Legal Action: If necessary, take legal action to protect your copyright.
9. Exploring Advanced Photo Management Techniques
For serious photographers, advanced photo management techniques can help streamline your workflow and keep your photo library organized. This section will explore advanced techniques like using photo management software and implementing a DAM system.
9.1. Using Photo Management Software (Adobe Lightroom, Capture One)
- Adobe Lightroom: A powerful photo management and editing software with features like cataloging, keyword tagging, and non-destructive editing.
- Capture One: A professional photo editing software with advanced color grading and tethered shooting capabilities.
9.2. Implementing a Digital Asset Management (DAM) System
- Centralized Storage: A DAM system provides a centralized storage location for all your photos and other digital assets.
- Metadata Management: A DAM system allows you to add and manage metadata like captions, keywords, and copyright information.
- Workflow Automation: A DAM system can automate tasks like file conversion, resizing, and watermarking.
9.3. Creating a Photo Archive for Long-Term Storage
- Choose a Storage Medium: Choose a durable storage medium like Blu-ray discs or LTO tape for long-term storage.
- Create Multiple Copies: Create multiple copies of your photo archive and store them in different locations.
- Regularly Migrate Your Archive: Regularly migrate your archive to new storage media to prevent data loss.
9.4. Tips for Efficient Photo Workflow
- Develop a Consistent Workflow: Develop a consistent workflow for importing, editing, and organizing your photos.
- Use Keyboard Shortcuts: Use keyboard shortcuts to speed up your workflow.
- Batch Process Photos: Use batch processing to apply the same edits to multiple photos at once.
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks with scripts or macros.
10. Troubleshooting Advanced Photo Transfer Problems
Even with the best techniques, you may encounter advanced photo transfer problems. This section will cover common issues and how to troubleshoot them.
10.1. Dealing with Corrupted Photo Files
- Use a Photo Repair Tool: Use a photo repair tool to attempt to repair the corrupted photo file.
- Restore from Backup: Restore the photo from a backup if available.
- Accept Data Loss: In some cases, data loss may be unavoidable.
10.2. Resolving Slow Transfer Speeds
- Check Your Hardware: Check your USB cables, memory card readers, and hard drives for damage or wear.
- Update Your Drivers: Update your drivers for your USB ports, memory card readers, and hard drives.
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: Defragment your hard drive to improve performance.
10.3. Fixing Incomplete Photo Transfers
- Check Your Connections: Check your USB cables, memory card readers, and network connections for loose connections.
- Restart Your Devices: Restart your camera, computer, and network devices.
- Try a Different Transfer Method: Try a different transfer method, such as USB cable, memory card reader, or cloud storage.
10.4. Seeking Professional Help
- Consult a Computer Technician: Consult a computer technician for hardware or software issues.
- Contact a Data Recovery Service: Contact a data recovery service for corrupted or lost photo files.
- Join Online Forums: Join online forums and communities to get help from other photographers and experts.
dfphoto.net understands the importance of preserving your visual stories, and we’re here to provide you with the knowledge and resources you need to succeed. We are committed to helping you navigate the world of photography with confidence and creativity.
In conclusion, mastering the art of transferring photos to your computer is crucial for any photographer or visual enthusiast. Whether you opt for the reliability of USB cables, the convenience of cloud storage, the speed of memory card readers, or the freedom of wireless transfer, understanding the nuances of each method ensures your precious memories are safely stored and readily accessible.
Ready to elevate your photography skills and preserve your visual stories? Visit dfphoto.net today to discover a wealth of tutorials, inspiration, and a vibrant community of photographers. Explore our comprehensive guides, showcase your work, and connect with fellow enthusiasts. Join dfphoto.net and transform your passion for photography into a lifelong journey of creativity and discovery. Don’t just capture moments, preserve them with dfphoto.net.