Are you looking for a secure and accessible way to safeguard your precious memories? Figuring out How Do I Backup Photos To Google Drive is the answer, and dfphoto.net is here to guide you through it. This article will explore various methods to ensure your photos are safely stored and easily accessible across all your devices. Learn how to protect your visual memories with simple steps.
Google Drive is a good option for photo backup, providing accessibility and data security. Explore efficient methods for safeguarding your memories and discover expert insights on dfphoto.net with keyword optimization tips, including cloud storage solutions and secure backup strategies, ensuring peace of mind and effortless photo management.
1. Why Use Google Drive to Backup Your Photos?
Google Drive offers a robust and user-friendly solution for backing up your photos. There are several compelling reasons to choose Google Drive as your primary photo backup service:
- Accessibility: Access your photos from any device with an internet connection.
- Security: Google’s infrastructure ensures your photos are stored securely.
- Collaboration: Easily share photos and albums with friends and family.
- Organization: Google Drive allows you to organize your photos into folders and albums.
- Free Storage: Google offers 15 GB of free storage, which is often sufficient for personal use, and you can purchase more if needed.
With Google Drive, your photos are available on all your devices, ensuring they are always within reach.
2. Understanding Google Drive Storage Options
Before diving into the backup process, it’s important to understand the storage options available in Google Drive. Google Drive offers a tiered storage system, allowing you to choose the plan that best fits your needs:
| Storage Plan | Storage Capacity | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 15 GB | Includes Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and basic Drive storage. | Personal use, occasional backups, document storage. |
| Basic | 100 GB | Expanded storage for photos, videos, and files. | Casual photographers, users with moderate storage needs. |
| Standard | 200 GB | Increased storage space with additional features like family sharing. | Families, avid photographers, small businesses. |
| Premium | 2 TB | Substantial storage capacity, advanced security features, and premium support. | Professional photographers, businesses, users with large media collections. |
Understanding these options will help you select the right plan for your photo backup needs.
3. Preparing Your Photos for Backup
Before you begin backing up your photos, it’s essential to prepare them properly. This ensures a smooth and efficient backup process.
3.1. Organizing Your Photo Library
A well-organized photo library makes it easier to manage and locate your photos in Google Drive. Consider organizing your photos into folders based on:
- Dates: Create folders for each year, month, or event.
- Events: Organize photos by specific events like weddings, birthdays, or vacations.
- Themes: Group photos by subject matter, such as landscapes, portraits, or wildlife.
3.2. Choosing the Right Photo Format
Selecting the right photo format is crucial for balancing image quality and storage space. Here are some common photo formats:
- JPEG: A widely used format that offers good compression and reasonable image quality.
- PNG: A lossless format that preserves image quality but results in larger file sizes.
- RAW: An uncompressed format that retains all the original data captured by the camera, providing maximum editing flexibility.
For most users, JPEG is a suitable format for backup. However, if you’re a professional photographer or need to preserve the highest possible image quality, consider using RAW or PNG.
3.3. Resizing Your Photos
Resizing your photos before backing them up can save significant storage space. Google Drive offers options to store photos in “High quality” or “Original quality.” High quality compresses your photos, while Original quality preserves the original resolution and detail.
If you choose to store your photos in Original quality, consider resizing them to a reasonable resolution to reduce file sizes. You can use photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop or free online tools like ResizePixel.
4. How to Backup Photos to Google Drive on iPhone
Backing up photos from your iPhone to Google Drive is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Download and Install Google Drive: If you haven’t already, download the Google Drive app from the App Store and install it on your iPhone.
- Sign In: Open the Google Drive app and sign in with your Google account.
- Enable Backup:
- Tap the Menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top-left corner.
- Select Settings.
- Tap Backup.
- Toggle the Photos option to enable photo backup.
- Start Backup:
- Tap Start Backup to begin backing up your photos to Google Drive.
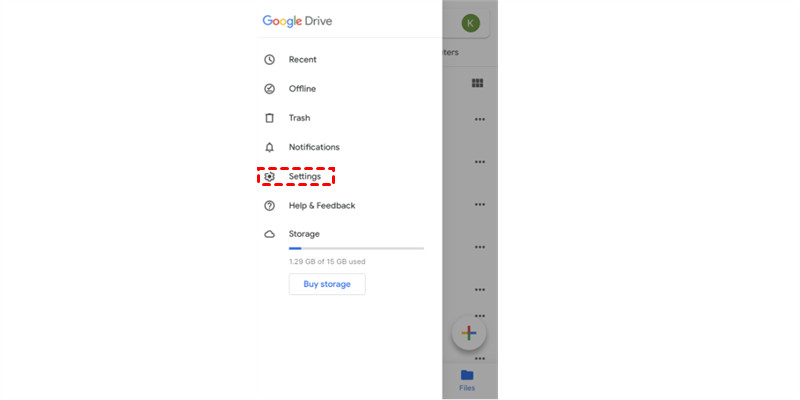 Google Drive iPhone Backup Settings
Google Drive iPhone Backup Settings
Configure your Google Drive app settings on your iPhone to automatically backup your photos.
Pro Tip: Ensure your iPhone is connected to a stable Wi-Fi network to avoid using cellular data during the backup process.
5. How to Backup Photos to Google Drive on Android
Backing up photos from your Android device to Google Drive is equally simple:
- Open Google Drive: Open the Google Drive app on your Android device.
- Access Settings:
- Tap the Menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top-left corner.
- Select Settings.
- Enable Auto-Backup:
- Tap Auto Add to automatically add photos from your Android phone to Google Drive.
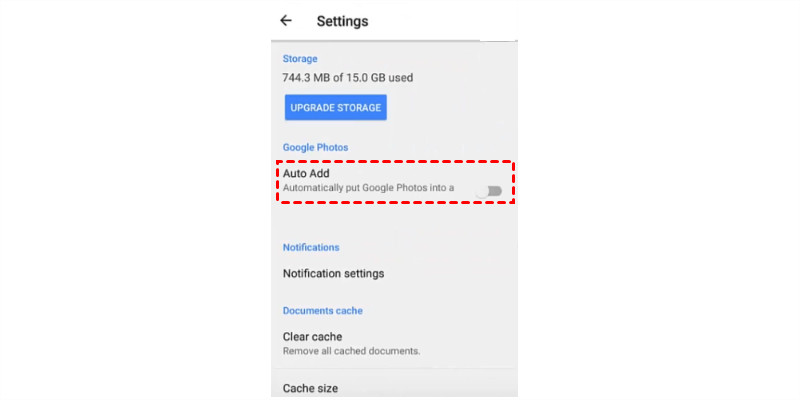 Google Drive Android Auto-Add
Google Drive Android Auto-Add
The Auto Add feature on Android devices ensures that your photos are automatically backed up to Google Drive.
Note: You can also use Google Photos to back up your photos on Android, as it is tightly integrated with Google Drive.
6. How to Backup Photos to Google Drive on Mac/Computer
There are two primary methods for backing up photos from your Mac or computer to Google Drive: using Google Drive for desktop and using a third-party cloud management tool like MultCloud.
6.1. Using Google Drive for Desktop
Google Drive for desktop allows you to sync folders on your computer with Google Drive, ensuring that your photos are automatically backed up.
- Download and Install Google Drive for Desktop: If you haven’t already, download and install Google Drive for desktop from the official Google website.
- Sign In: Open the Google Drive app and sign in with your Google account.
- Configure Sync Settings:
- Click the Google Drive icon in the system tray (Windows) or menu bar (Mac).
- Click the Gear icon and select Preferences.
- Go to My Computer and click Add folder.
- Select the folder containing the photos you want to back up.
- Choose whether to sync the folder with Google Drive or back it up only.
- Click Done and Save to start the backup process.
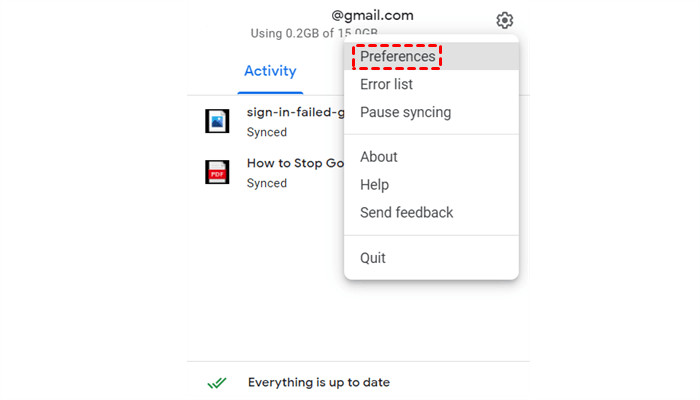 Google Drive Desktop Preferences
Google Drive Desktop Preferences
Adjust the preferences in Google Drive for desktop to sync your photo folders automatically.
6.2. Using MultCloud
MultCloud is a third-party cloud management tool that allows you to manage multiple cloud storage services in one place. It offers a convenient way to backup photos to Google Drive, especially if you use multiple cloud services.
- Create a MultCloud Account: Sign up for a free MultCloud account on their website.
- Add Google Drive:
- Go to Add Cloud on the left navigation bar.
- Select Google Drive and grant MultCloud access to your account.
- Upload Photos:
- Click on Google Drive in the MultCloud interface.
- Click the Upload File button or drag and drop photos to the Google Drive interface.
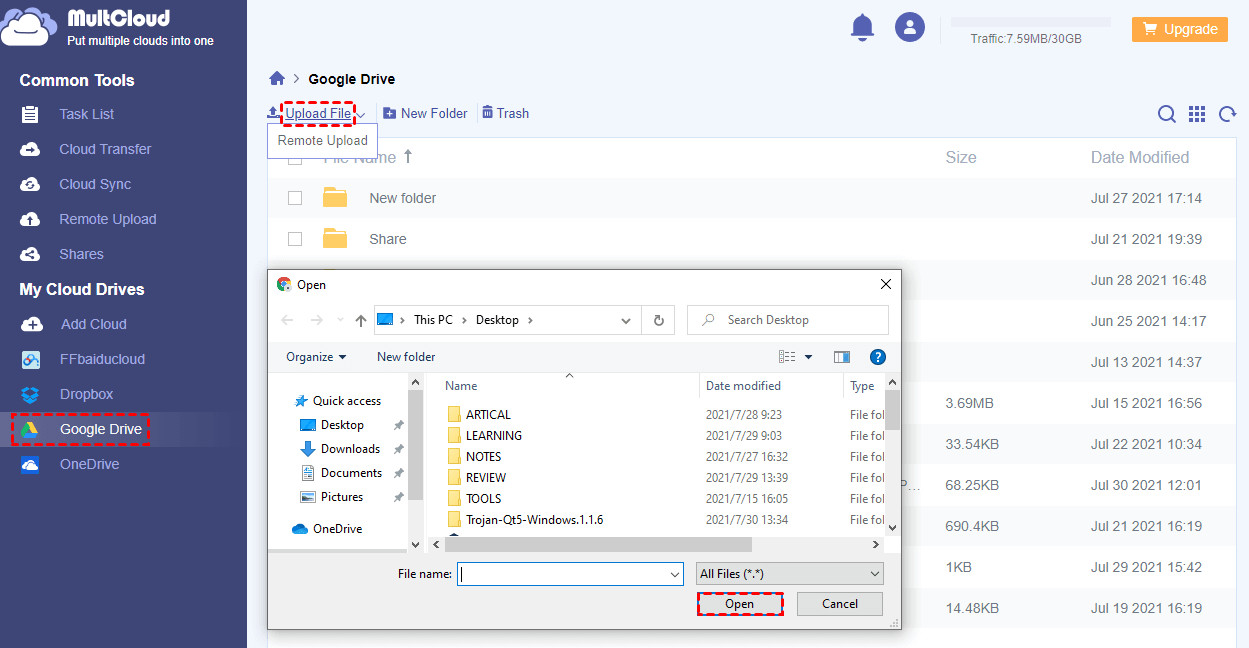 MultCloud Upload to Google Drive
MultCloud Upload to Google Drive
MultCloud simplifies the process of uploading and managing your photos across different cloud services.
Benefits of Using MultCloud:
- Manage multiple cloud services in one place.
- Transfer, backup, and sync files between cloud services.
- Schedule automatic backups.
- Faster transfer speeds.
7. Advanced Backup Strategies
For users with extensive photo libraries or specific backup requirements, consider these advanced strategies:
7.1. Incremental Backups
Incremental backups only backup the changes made since the last backup. This saves time and storage space, especially for large photo libraries. Google Drive for desktop supports incremental backups by syncing only the files that have been modified.
7.2. Versioning
Versioning allows you to keep multiple versions of your photos, so you can revert to an earlier version if needed. Google Drive automatically keeps a history of file versions, allowing you to restore previous versions of your photos.
7.3. Offsite Backups
In addition to backing up your photos to Google Drive, consider creating an offsite backup. This involves storing your photos in a separate physical location, such as an external hard drive or another cloud storage service. This provides an extra layer of protection in case of a disaster or data loss event.
8. Troubleshooting Common Backup Issues
While backing up photos to Google Drive is generally reliable, you may encounter some issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Slow Backup Speed:
- Check your internet connection speed.
- Close unnecessary applications that may be using bandwidth.
- Schedule backups during off-peak hours.
- Insufficient Storage Space:
- Upgrade to a larger Google Drive storage plan.
- Delete unnecessary files from your Google Drive.
- Compress your photos before backing them up.
- Backup Errors:
- Restart your device and try again.
- Ensure Google Drive is up to date.
- Check for conflicting software or firewall settings.
9. Maintaining Your Photo Library in Google Drive
Once your photos are backed up to Google Drive, it’s important to maintain your library to ensure its longevity and accessibility.
9.1. Regularly Reviewing and Organizing Your Photos
Set aside time each month to review and organize your photos in Google Drive. Delete duplicates, rename files, and move photos into appropriate folders.
9.2. Testing Your Backups
Periodically test your backups by restoring a few photos from Google Drive to your device. This ensures that your backups are working correctly and that you can access your photos when needed.
9.3. Keeping Software Up to Date
Keep your Google Drive app and desktop software up to date to ensure compatibility and access to the latest features and security updates.
10. The Future of Photo Backup: Trends and Technologies
The field of photo backup is constantly evolving with new trends and technologies. Here are some developments to watch:
- AI-Powered Photo Management: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automatically organize, tag, and enhance photos.
- Cloud-Based Photo Editing: Edit your photos directly in the cloud without the need for desktop software.
- Blockchain-Based Photo Storage: Blockchain technology offers decentralized and secure photo storage solutions.
- 5G Connectivity: Faster internet speeds will enable faster and more seamless photo backups.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, AI-powered photo management will be a standard feature in most cloud storage services.
11. Exploring dfphoto.net: Your Photography Resource
Now that you know how to backup your photos to Google Drive, take your photography journey to the next level with dfphoto.net. Here, you’ll find a treasure trove of resources tailored for photography enthusiasts and professionals alike.
11.1. Extensive Learning Materials
Dive into a wide array of tutorials covering various photography techniques. Whether you’re mastering exposure, aperture, shutter speed, or composition, dfphoto.net offers detailed guides to help you excel.
11.2. Inspiring Photo Galleries
Explore stunning photo collections that will ignite your creativity. Discover diverse styles and approaches from talented photographers, providing endless inspiration for your own work.
11.3. Vibrant Community Engagement
Connect with a passionate community of photographers. Share your work, receive feedback, and collaborate on projects to grow your skills and expand your network. You can visit our office located at 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States or call us at +1 (505) 471-6001. Also, you can visit our website dfphoto.net.
12. Optimizing Your Images for Online Display
Once your photos are safely backed up to Google Drive, you might want to share them online. Optimizing your images for web display ensures they look their best without compromising loading speed.
12.1. Choosing the Right File Format
- JPEG: Ideal for photographs due to its efficient compression.
- PNG: Best for images with text or graphics that require sharp details.
- WebP: A modern image format that provides superior compression and quality compared to JPEG and PNG.
12.2. Resizing Your Images
Large images can slow down website loading times. Resize your images to the appropriate dimensions for their intended display size. A good rule of thumb is to keep images under 2000 pixels in width for most web applications.
12.3. Compressing Your Images
Compressing your images reduces their file size without significantly affecting their visual quality. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress your images before uploading them online.
13. Legal and Ethical Considerations in Photography
As a photographer, it’s essential to be aware of the legal and ethical considerations involved in your work.
13.1. Copyright Laws
Understand copyright laws and respect the intellectual property rights of others. Always obtain permission before using someone else’s work in your photos.
13.2. Model Releases
If you’re photographing people, obtain model releases to ensure you have the right to use their likeness in your photos for commercial purposes.
13.3. Privacy Laws
Respect privacy laws and avoid photographing people in situations where they have a reasonable expectation of privacy.
14. Monetizing Your Photography
If you’re a professional photographer, there are several ways to monetize your work.
14.1. Selling Prints and Digital Downloads
Sell prints and digital downloads of your photos through online platforms like Etsy or your own website.
14.2. Licensing Your Photos
License your photos to stock photography agencies or directly to clients for use in their marketing materials.
14.3. Offering Photography Services
Offer photography services such as portrait photography, event photography, or product photography.
15. Building a Professional Photography Portfolio
A professional photography portfolio is essential for showcasing your work and attracting clients.
15.1. Curating Your Best Work
Select your best photos that represent your style and expertise.
15.2. Designing an Online Portfolio
Create an online portfolio using platforms like WordPress, Squarespace, or специализированные portfolio websites.
15.3. Showcasing Your Portfolio
Promote your portfolio on social media, photography websites, and industry events.
16. Staying Updated with Photography Trends
The world of photography is constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay updated with the latest trends and technologies.
16.1. Following Photography Blogs and Websites
Follow photography blogs and websites like dfphoto.net to stay informed about new techniques, equipment, and trends.
16.2. Attending Photography Workshops and Conferences
Attend photography workshops and conferences to learn from experts and network with other photographers.
16.3. Engaging with the Photography Community
Engage with the photography community on social media and online forums to share your work and learn from others.
17. The Impact of Mobile Photography
Mobile photography has revolutionized the way we capture and share images. With advancements in smartphone camera technology, mobile photography is now a serious contender to traditional photography.
17.1. Advantages of Mobile Photography
- Convenience: Smartphones are always with you, making it easy to capture spontaneous moments.
- Accessibility: Mobile photography is accessible to everyone, regardless of their skill level or budget.
- Sharing: It’s easy to share photos directly from your smartphone to social media and other platforms.
17.2. Tips for Mobile Photography
- Use natural light: Natural light is essential for capturing high-quality photos with your smartphone.
- Focus and exposure: Tap the screen to focus on your subject and adjust the exposure.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds and other composition techniques to create visually appealing photos.
18. The Art of Black and White Photography
Black and white photography is a timeless art form that can evoke emotion and capture the essence of a subject.
18.1. Composition in Black and White Photography
Composition is even more critical in black and white photography, as it is the primary way to create visual interest.
18.2. Lighting in Black and White Photography
Lighting is also essential in black and white photography. Look for strong contrasts and dramatic shadows to create visually stunning images.
18.3. Post-Processing for Black and White Photography
Post-processing is often necessary to enhance the tones and contrast in black and white photos. Use photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom to adjust the levels, curves, and sharpness of your images.
19. Mastering Landscape Photography
Landscape photography is a popular genre that involves capturing the beauty of the natural world.
19.1. Composition in Landscape Photography
Composition is crucial in landscape photography. Use elements like leading lines, the rule of thirds, and foreground interest to create visually appealing images.
19.2. Lighting in Landscape Photography
Lighting is also essential in landscape photography. Shoot during the golden hours (sunrise and sunset) for the best light.
19.3. Equipment for Landscape Photography
Essential equipment for landscape photography includes a wide-angle lens, a tripod, and filters (such as a polarizing filter and a neutral density filter).
20. Essential Equipment for Every Photographer
Having the right equipment is essential for capturing high-quality photos. Here’s a list of essential equipment for every photographer:
| Equipment | Description |
|---|---|
| Camera | A DSLR or mirrorless camera is ideal for most types of photography. |
| Lenses | A variety of lenses, including a wide-angle lens, a telephoto lens, and a prime lens. |
| Tripod | A tripod is essential for capturing sharp images, especially in low light. |
| Filters | Filters can enhance your photos and protect your lenses. |
| Memory Cards | High-speed memory cards are essential for capturing photos and videos without lag. |
| Camera Bag | A camera bag is essential for carrying and protecting your equipment. |
21. The Importance of Continuous Learning in Photography
Photography is a constantly evolving field, so it’s important to commit to continuous learning.
21.1. Taking Online Courses
Take online courses to learn new techniques and improve your skills. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Skillshare offer a wide range of photography courses.
21.2. Reading Photography Books
Read photography books to learn about the history of photography, the work of famous photographers, and advanced techniques.
21.3. Joining Photography Clubs
Join photography clubs to connect with other photographers, share your work, and participate in workshops and events.
22. Photo Editing Software: Enhancing Your Images
Photo editing software is an essential tool for enhancing your images and creating a professional look.
22.1. Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is the industry-standard photo editing software. It offers a wide range of tools for retouching, color correction, and compositing.
22.2. Adobe Lightroom
Adobe Lightroom is a popular photo editing software that is designed for photographers. It offers a streamlined workflow for organizing, editing, and exporting photos.
22.3. GIMP
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) is a free and open-source photo editing software. It offers many of the same features as Adobe Photoshop, making it a great option for photographers on a budget.
23. Ethical Considerations in Photo Editing
While photo editing can enhance your images, it’s important to use it ethically.
23.1. Being Transparent About Photo Editing
Be transparent about the amount of photo editing you’ve done. Avoid making significant changes that misrepresent the subject.
23.2. Respecting Cultural Norms
Respect cultural norms and avoid making changes that are offensive or disrespectful.
23.3. Avoiding Plagiarism
Avoid using other people’s work without permission. Always create your own images or obtain the necessary licenses.
24. Common Photography Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced photographers make mistakes. Here are some common mistakes and how to avoid them:
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Not using a tripod | Always use a tripod when shooting in low light or with long exposures. |
| Poor composition | Use the rule of thirds and other composition techniques. |
| Overexposing or underexposing photos | Use your camera’s metering system or a handheld light meter. |
| Not focusing properly | Use autofocus or manual focus to ensure your subject is sharp. |
| Not cleaning your lenses | Clean your lenses regularly with a microfiber cloth. |
25. Backing Up Photos from Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram are great for sharing your photos, but it’s important to back them up as well.
25.1. Downloading Photos from Social Media
Download your photos from social media platforms regularly. This ensures that you have a copy of your photos even if the platform goes down or you lose access to your account.
25.2. Using Third-Party Backup Tools
Use third-party backup tools to automatically back up your photos from social media platforms. These tools can save you time and ensure that your photos are always backed up.
26. The Future of Photography Education
Photography education is evolving with the rise of online learning and new technologies.
26.1. Online Photography Courses
Online photography courses are becoming increasingly popular. They offer a flexible and affordable way to learn photography.
26.2. Photography Workshops and Retreats
Photography workshops and retreats offer hands-on learning experiences and the opportunity to connect with other photographers.
26.3. Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs provide personalized guidance and support from experienced photographers.
27. Practical Tips for Managing Large Photo Libraries
Managing a large photo library can be overwhelming. Here are some practical tips to help you stay organized:
- Use a consistent naming convention: Use a consistent naming convention for your photo files. This makes it easier to find and organize your photos.
- Use keywords and tags: Use keywords and tags to add metadata to your photos. This makes it easier to search for specific photos.
- Create albums and collections: Create albums and collections to group your photos by subject or event.
- Backup your photo library regularly: Backup your photo library regularly to protect your photos from data loss.
28. Integrating Google Drive with Other Photography Tools
Google Drive integrates seamlessly with other photography tools, making it a valuable asset for photographers.
28.1. Google Photos
Google Photos is a photo management and sharing service that is tightly integrated with Google Drive. You can use Google Photos to automatically back up your photos to Google Drive, organize your photos, and share them with others.
28.2. Adobe Lightroom
Adobe Lightroom is a popular photo editing software that can be integrated with Google Drive. You can use Lightroom to edit your photos and then save them directly to Google Drive.
28.3. Other Cloud Storage Services
Google Drive can be integrated with other cloud storage services like Dropbox and OneDrive. This allows you to easily transfer photos between different cloud storage services.
29. Exploring Different Genres of Photography
Photography is a diverse field with many different genres to explore. Here are some popular genres of photography:
- Portrait photography: Capturing the likeness and personality of a person.
- Landscape photography: Capturing the beauty of the natural world.
- Wildlife photography: Capturing animals in their natural habitat.
- Street photography: Capturing candid moments in public places.
- Macro photography: Capturing extreme close-ups of small objects.
30. Developing Your Unique Photography Style
Developing your unique photography style is essential for standing out in a crowded field.
30.1. Experimenting with Different Techniques
Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you.
30.2. Studying the Work of Other Photographers
Study the work of other photographers to learn from their techniques and styles.
30.3. Practicing Regularly
Practice regularly to hone your skills and develop your unique style.
31. Best Practices for Long-Term Photo Preservation
Preserving your photos for the long term requires careful planning and execution.
31.1. Storing Photos in Multiple Locations
Store your photos in multiple locations, including Google Drive, external hard drives, and optical discs.
31.2. Using Archival-Quality Storage Media
Use archival-quality storage media, such as gold CDs or DVDs, to ensure that your photos last for many years.
31.3. Regularly Migrating Photos to New Storage Media
Regularly migrate your photos to new storage media to prevent data loss due to media degradation.
32. Understanding Metadata and Its Importance in Photo Management
Metadata is data about data. In the context of photography, metadata includes information such as the date and time the photo was taken, the camera settings used, and any keywords or tags that have been added to the photo.
32.1. Benefits of Using Metadata
- Organization: Metadata makes it easier to organize and find your photos.
- Search: Metadata allows you to search for specific photos based on criteria such as date, location, or keywords.
- Copyright: Metadata can be used to embed copyright information in your photos.
32.2. Tools for Managing Metadata
There are many tools available for managing metadata, including Adobe Lightroom, Adobe Bridge, and ExifTool.
33. Maximizing the Free Storage on Google Drive
Google Drive offers 15 GB of free storage, which can be sufficient for personal use. Here are some tips for maximizing your free storage:
- Compress your photos: Compress your photos before backing them up to Google Drive.
- Delete duplicates: Delete duplicate photos from your Google Drive.
- Store photos in “High quality”: Store your photos in “High quality” instead of “Original quality” to save space.
- Remove unnecessary files: Remove unnecessary files from your Google Drive.
34. Collaborating on Photo Projects with Google Drive
Google Drive makes it easy to collaborate on photo projects with other photographers.
34.1. Sharing Folders and Files
Share folders and files with other photographers. This allows them to view, download, and edit your photos.
34.2. Using Google Docs for Project Planning
Use Google Docs for project planning. This allows you to create shared documents for outlining project goals, timelines, and tasks.
34.3. Providing Feedback and Comments
Provide feedback and comments on other photographers’ photos. This helps them improve their skills and develop their unique style.
35. The Psychology of Photography: Understanding Visual Communication
Photography is more than just capturing images. It’s a form of visual communication.
35.1. Understanding Visual Elements
Understand visual elements such as line, shape, form, color, and texture. These elements can be used to create visually appealing and impactful photos.
35.2. Composing with Intention
Compose your photos with intention. Think about the message you want to convey and use composition techniques to guide the viewer’s eye.
35.3. Evoking Emotion
Evoke emotion with your photos. Use lighting, color, and composition to create photos that resonate with the viewer.
36. Best Cloud Storage Alternatives to Google Drive for Photo Backup
While Google Drive is a popular choice, several other cloud storage services offer excellent photo backup solutions. Here are a few top alternatives:
- Amazon Photos: Integrated with Amazon Prime, offering unlimited photo storage for Prime members.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Seamlessly integrates with Windows and Microsoft Office, providing a convenient backup solution for users in that ecosystem.
- Dropbox: Known for its file syncing and sharing capabilities, Dropbox is also a reliable option for photo backups, especially for those already using it for other file storage needs.
- iCloud Photos: For Apple users, iCloud Photos offers a seamless way to back up and sync photos across all Apple devices.
- Backblaze: Offers unlimited backup for one computer, including connected external drives.
37. Mobile Apps for Streamlining Your Photo Workflow
Mobile apps can significantly streamline your photo workflow, from capturing to editing and backing up. Here are some essential apps for photographers:
- Adobe Lightroom Mobile: A powerful mobile photo editing app with a wide range of features.
- Snapseed: A free and user-friendly photo editing app developed by Google.
- VSCO: A popular app with a variety of filters and editing tools.
- Google Photos: Offers automatic backup and organization of your photos.
- Camera+ 2: A robust camera app with manual controls and advanced features.
38. The Role of AI in Modern Photography
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly significant role in modern photography, offering tools and capabilities that enhance the creative process.
38.1. AI-Powered Editing Tools
AI-powered editing tools can automatically enhance your photos, such as adjusting exposure, color, and sharpness.
38.2. Object Recognition and Tagging
AI can automatically recognize objects and scenes in your photos, making it easier to organize and search your photo library.
38.3. Style Transfer
AI can transfer the style of one photo to another, allowing you to create unique and artistic effects.
FAQ: How Do I Backup Photos to Google Drive?
Here are some frequently asked questions about backing up photos to Google Drive:
-
How much does it cost to backup photos to Google Drive?
- Google Drive offers 15 GB of free storage. If you need more storage, you can purchase a subscription plan.
-
Can I automatically backup photos to Google Drive?
- Yes, you can enable automatic backup in the Google Drive app on your phone or use Google Drive for desktop on your computer.
-
How long does it take to backup photos to Google Drive?
- The backup time depends on the size of your photo library and your internet connection speed.
-
Can I access my photos on Google Drive from any device?
- Yes, you can access your photos on Google Drive from any device with an internet connection.
-
Is Google Drive a secure place to store my photos?
- Yes, Google Drive uses encryption to protect your photos.
-
Can I share my photos on Google Drive with others?
- Yes, you can share your photos on Google Drive with others by creating a shareable link.
-
How do I organize my photos on Google Drive?
- You can organize your photos on Google Drive by creating folders and moving your photos into the appropriate folders.
-
What file formats are supported by Google Drive?
- Google Drive supports a wide range of file formats, including JPEG, PNG, and RAW.
-
Can I edit my photos on Google Drive?
- You can edit your photos on Google Drive using Google Photos or other photo editing apps that integrate with Google Drive.
-
How do I restore my photos from Google Drive?
- You can restore your photos from Google Drive by downloading them to your device.
Ready to safeguard your memories and elevate your photography skills? Visit dfphoto.net today to explore our extensive resources and connect with a community of passionate photographers!
