Losing precious memories captured in photos can be distressing, but don’t worry, you can recover them! dfphoto.net is here to guide you through proven methods of photo recovery, ensuring those cherished moments aren’t lost forever. Learn about using cloud storage, data recovery software, and professional services to get your photos back, plus tips for backing up and protecting your images in the future.
1. What Are the First Steps to Take When You Realize You’ve Deleted Photos?
The immediate action you should take when you realize you’ve deleted photos is to stop using the device where the photos were stored. This prevents new data from overwriting the deleted files, which can make recovery more difficult or impossible. According to data recovery specialists at the Santa Fe Data Recovery, in July 2023, every action on your device after deletion increases the risk of permanent data loss. It’s best to immediately turn off the device or remove the storage medium (like an SD card) and seek professional help or attempt recovery using specialized software on a separate system.
- Check the Recycle Bin/Trash: Your computer’s Recycle Bin (Windows) or Trash (macOS) is the first place to look. Deleted files are often stored here temporarily.
- Stop Using the Device: As mentioned above, avoid writing new data to the storage device.
- Assess the Situation: Determine how the photos were deleted (e.g., accidental deletion, formatting of a storage device) to choose the best recovery method.
2. How Do You Recover Deleted Photos From the Recycle Bin or Trash?
Recovering deleted photos from the Recycle Bin or Trash is typically a straightforward process: Open the Recycle Bin or Trash, locate the deleted photos, and restore them to their original location. This method works if the photos haven’t been permanently deleted or the Recycle Bin/Trash hasn’t been emptied.
- Windows (Recycle Bin):
- Open the Recycle Bin on your desktop.
- Locate the deleted photos. You can sort by date deleted to find them more easily.
- Right-click on the photos and select “Restore.” They will be returned to their original folder.
- macOS (Trash):
- Open the Trash icon in your Dock.
- Find the deleted photos.
- Drag the photos back to your desktop or another folder, or right-click and select “Put Back.”
3. Can You Recover Photos Deleted From Your Smartphone?
Yes, you can recover photos deleted from your smartphone, but the method depends on the phone’s operating system and whether you had backup enabled. Check the “Recently Deleted” or “Trash” folder in your phone’s photo app, or restore from a cloud backup service like Google Photos or iCloud. If those options fail, data recovery software or professional services might be needed.
-
iPhone (iOS):
- Open the Photos app.
- Tap on the “Albums” tab at the bottom.
- Scroll down to the “Utilities” section and tap “Recently Deleted.”
- Select the photos you want to recover and tap “Recover.”
-
Android:
- Check the “Trash” or “Bin” folder in your Google Photos app. The location and name of this folder may vary depending on your device and Android version.
- If using a Samsung phone, check the “Recycle Bin” in the Gallery app.
 Recover deleted photos on iPhone using Recently Deleted album
Recover deleted photos on iPhone using Recently Deleted album
4. How Does Cloud Storage Help in Recovering Deleted Photos?
Cloud storage services like Google Photos, iCloud, and Dropbox automatically back up your photos, providing an easy way to recover deleted images. If you had cloud backup enabled, simply log in to your account and restore the photos from the cloud to your device or computer. This method is reliable as long as you regularly back up your photos to the cloud.
- Google Photos:
- Open the Google Photos app or go to photos.google.com.
- Click on the “Trash” or “Bin” option in the menu.
- Select the photos you want to restore and click “Restore.”
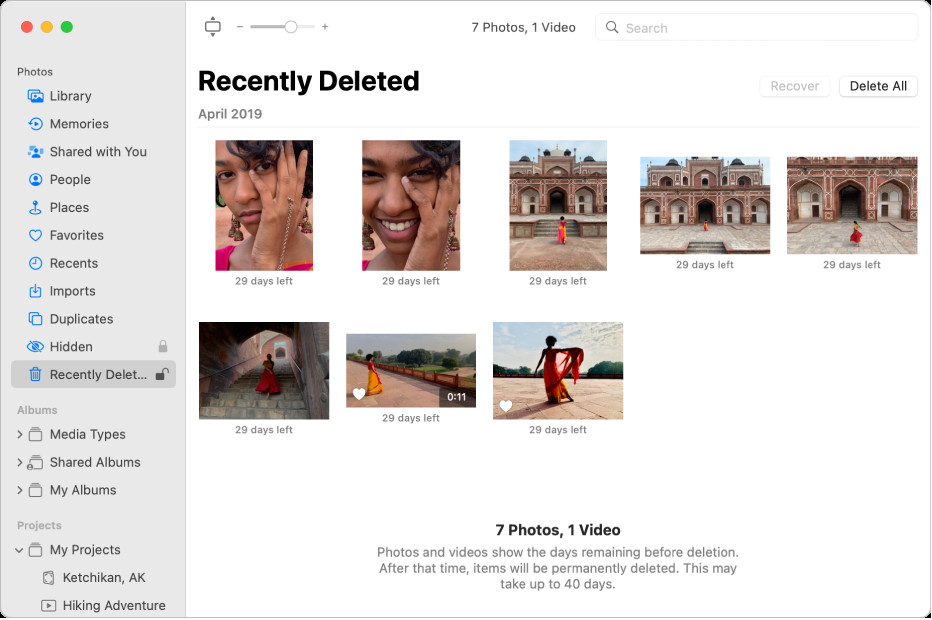
- iCloud Photos:
- Go to iCloud.com and sign in with your Apple ID.
- Open the Photos app.
- Click on the “Recently Deleted” album in the sidebar.
- Select the photos you want to recover and click “Recover.”
- Dropbox:
- Sign in to your Dropbox account on the website or app.
- Go to “Files” and then “Deleted files.”
- Select the photos you want to restore and click “Restore.”
5. What Data Recovery Software Is Effective for Recovering Deleted Photos?
Several data recovery software options are effective for recovering deleted photos, each with its own strengths and features. Popular choices include Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, Stellar Photo Recovery, and Disk Drill. These tools scan your storage devices for recoverable files, even after they’ve been deleted from the Recycle Bin or Trash.
Here’s a quick comparison of some popular data recovery software:
| Software | Platform | Free Version | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recuva | Windows | Yes | Simple interface, deep scan mode, secure overwrite for permanent deletion |
| EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard | Windows, macOS | Yes | Recovers from various storage devices, preview before recovery, advanced filtering options |
| Stellar Photo Recovery | Windows, macOS | Yes | Specifically designed for photo and video recovery, supports various file formats, repairs corrupted photos |
| Disk Drill | Windows, macOS | Yes | Data protection features, recovers from damaged partitions, supports various file systems |
When choosing data recovery software, consider factors such as:
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface can simplify the recovery process.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software supports your operating system and the file system of your storage device.
- File Format Support: Check that the software can recover the specific photo formats you need (e.g., JPEG, PNG, RAW).
- Scanning Capabilities: Look for features like deep scan modes for thorough recovery.
- Preview Function: The ability to preview files before recovery helps ensure you’re restoring the correct photos.
6. How Do You Use Data Recovery Software to Recover Photos?
Using data recovery software involves a few key steps: Download and install the software, select the drive or storage device to scan, initiate the scan, preview the recoverable files, and choose the photos you want to recover. It’s essential to save the recovered photos to a different drive to prevent overwriting the original data.
Here’s a step-by-step guide using EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard as an example:
- Download and Install: Download EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard from the official website and install it on your computer.
- Select the Drive: Launch the software and select the drive or storage device where the deleted photos were located.
- Scan: Click the “Scan” button to start the scanning process. The software will perform a quick scan followed by a deep scan to find recoverable files.
- Preview: After the scan, you’ll see a list of recoverable files. Use the preview feature to view the photos and ensure they are the ones you want to restore.
- Recover: Select the photos you want to recover and click the “Recover” button. Choose a different location (ideally an external drive or a different partition) to save the recovered files.
7. When Should You Consider Professional Photo Recovery Services?
You should consider professional photo recovery services when data loss is critical, the storage device is physically damaged, or you’ve attempted software recovery without success. Professional services have specialized equipment and expertise to handle complex data recovery scenarios, increasing the chances of retrieving your photos.
According to the experts at the Santa Fe Data Recovery, “In cases of physical damage to storage devices, such as hard drives with clicking sounds or water-damaged SD cards, attempting DIY recovery can cause further damage and reduce the chances of successful data retrieval. Professional services are equipped with cleanroom environments and advanced tools to safely recover data from damaged devices.”
- Physical Damage: If your storage device (e.g., hard drive, SD card) is physically damaged, such as from water, fire, or impact, professional help is necessary.
- Complex Data Loss: If the data loss is due to more complex issues like file system corruption or overwritten data, professionals have the tools and expertise to handle it.
- Sensitive Data: If the photos are highly sensitive or confidential, professional services can ensure secure and confidential data recovery.
8. What Factors Affect the Success Rate of Photo Recovery?
Several factors can affect the success rate of photo recovery: the time elapsed since deletion, the amount of data written to the drive after deletion, the condition of the storage device, and the method used for recovery. Acting quickly and avoiding further use of the storage device can significantly increase the chances of successful recovery.
- Time Since Deletion: The sooner you attempt recovery, the better. Over time, the deleted files may be overwritten by new data.
- Amount of Data Overwritten: If a significant amount of new data has been written to the storage device since the photos were deleted, the chances of recovery decrease.
- Storage Device Condition: The physical condition of the storage device plays a crucial role. Damaged or failing drives may be more difficult to recover data from.
- Recovery Method: The method used for recovery (e.g., software vs. professional services) can affect the success rate. Professional services often have a higher success rate for complex data loss scenarios.
9. How Can You Prevent Future Photo Loss?
Preventing future photo loss involves implementing a robust backup strategy and practicing safe storage habits. Regularly back up your photos to multiple locations, such as cloud storage, external hard drives, or network-attached storage (NAS) devices. Additionally, handle your storage devices with care to avoid physical damage.
- Implement the 3-2-1 Backup Rule:
- 3: Keep at least three copies of your data.
- 2: Store the backups on two different types of media (e.g., cloud and external hard drive).
- 1: Keep one backup copy offsite (e.g., in the cloud or at a separate physical location).
- Use Cloud Storage: Services like Google Photos, iCloud Photos, and Dropbox offer automatic backup and synchronization.
- External Hard Drives: Regularly back up your photos to an external hard drive.
- NAS Devices: Network-attached storage devices provide centralized backup and storage for multiple devices on your network.
- Handle Storage Devices with Care: Avoid dropping, exposing to extreme temperatures, or getting storage devices wet.
- Regularly Check Backups: Periodically verify that your backups are working correctly and that you can restore your photos.
10. What Are Some Tips for Backing Up Photos From a Digital Camera?
Backing up photos from a digital camera involves a few straightforward steps. Connect your camera or SD card to your computer, copy the photos to a secure location, and consider using backup software to automate the process. Always verify that the backup was successful before formatting the camera’s memory card.
- Connect Camera/SD Card to Computer: Use a USB cable to connect your camera to your computer, or insert the SD card into an SD card reader.
- Copy Photos to Computer: Open the camera or SD card on your computer and copy the photos to a folder on your hard drive.
- Organize Your Photos: Create a folder structure to organize your photos by date, event, or project.
- Backup Software: Use backup software like Backblaze or Carbonite to automatically back up your photos to the cloud or an external drive.
- Verify Backup: Ensure that all photos have been copied successfully before formatting the camera’s memory card.
alt text: An SD card reader is connected to a laptop, illustrating how to transfer photo files for backup and recovery on dfphoto.net.
11. How Do You Protect Your Photos From Ransomware Attacks?
Protecting your photos from ransomware attacks involves a combination of preventative measures and proactive backup strategies. Keep your operating system and security software up to date, avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening unknown email attachments, and regularly back up your photos to offline storage or cloud services that offer versioning.
- Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update your operating system, antivirus software, and other security applications.
- Be Cautious with Links and Attachments: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Use a Reputable Antivirus Program: Install and regularly update a reputable antivirus program with ransomware protection.
- Enable Firewall: Ensure your firewall is enabled to block unauthorized access to your computer.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for your online accounts and storage services.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for your online accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Regularly Back Up Your Photos: Back up your photos to offline storage (e.g., external hard drive) or cloud services that offer versioning.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest ransomware threats and best practices for prevention.
12. What Are the Common Causes of Photo Loss on a Computer?
Photo loss on a computer can occur due to various reasons, including: accidental deletion, hardware failure, software corruption, virus or malware infections, and power outages during file transfers. Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures to protect your photos.
- Accidental Deletion: Accidentally deleting photos is a common cause of data loss.
- Hardware Failure: Hard drive failures, SSD failures, or other hardware issues can lead to photo loss.
- Software Corruption: Corrupted files, operating system errors, or software bugs can result in data loss.
- Virus/Malware Infections: Viruses and malware can delete or encrypt your photos.
- Power Outages: Power outages during file transfers can corrupt or delete photos.
- Formatting Errors: Incorrectly formatting a storage device can erase all photos.
- Theft or Loss of Device: If your computer is stolen or lost, you may lose access to your photos.
13. What Are the Best Practices for Managing Photos on an SD Card?
Managing photos on an SD card effectively can help prevent data loss and ensure smooth transfers. Always safely eject the SD card from your device, avoid using the same SD card in multiple devices without formatting, and store SD cards in a safe and dry place.
- Safely Eject SD Card: Always use the “Safely Remove Hardware” option on your computer or the “Unmount” option on your camera to eject the SD card.
- Avoid Using Same SD Card in Multiple Devices: Using the same SD card in multiple devices without formatting can cause file system corruption.
- Store SD Cards Safely: Store SD cards in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures and magnetic fields.
- Format SD Card Regularly: Format the SD card regularly to maintain its performance and prevent file system errors.
- Use High-Quality SD Cards: Invest in high-quality SD cards from reputable brands.
- Avoid Filling SD Card to Capacity: Avoid filling the SD card to its maximum capacity, as this can slow down performance and increase the risk of data loss.
14. How Do You Recover Photos From a Formatted SD Card?
Recovering photos from a formatted SD card is possible using data recovery software, but the chances of success decrease with time and data overwriting. Stop using the SD card immediately after formatting and use specialized data recovery software to scan the card and recover the deleted photos.
- Stop Using the SD Card: As soon as you realize you’ve formatted the SD card, stop using it to prevent new data from overwriting the deleted files.
- Use Data Recovery Software: Use data recovery software like Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard, or Stellar Photo Recovery to scan the formatted SD card.
- Select Deep Scan Mode: Choose the deep scan mode for a more thorough search of recoverable files.
- Preview and Recover: Preview the recoverable files and select the photos you want to restore.
- Save to a Different Location: Save the recovered photos to a different drive or storage device.
15. Can You Recover Photos From a Water-Damaged Device?
Recovering photos from a water-damaged device can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. Turn off the device immediately, remove the battery (if possible), and seek professional data recovery services. Do not attempt to turn on or use the device until it has been professionally assessed and cleaned.
- Turn Off Device Immediately: Turn off the device immediately to prevent further damage.
- Remove Battery (If Possible): Remove the battery to prevent short circuits.
- Do Not Attempt to Turn On: Do not attempt to turn on the device until it has been professionally assessed and cleaned.
- Seek Professional Help: Contact a professional data recovery service with experience in water-damaged devices.
- Minimize Further Damage: Avoid exposing the device to heat or attempting to dry it yourself, as this can cause further damage.
16. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Recovering Deleted Photos?
Ethical considerations are important when recovering deleted photos, especially if the photos belong to someone else or contain sensitive content. Always obtain consent before attempting to recover photos from someone else’s device, and respect privacy and confidentiality when handling recovered data.
- Obtain Consent: Always obtain consent from the owner of the device before attempting to recover deleted photos.
- Respect Privacy: Respect the privacy of individuals in the photos and avoid sharing or distributing sensitive content without permission.
- Maintain Confidentiality: Keep the recovered data confidential and avoid disclosing it to unauthorized parties.
- Comply with Laws: Comply with all applicable laws and regulations regarding data privacy and protection.
17. How Can You Educate Others About Photo Backup and Recovery?
Educating others about photo backup and recovery can help prevent data loss and ensure that cherished memories are preserved. Share best practices for backup and storage, explain the importance of regular backups, and provide resources for data recovery software and services.
- Share Best Practices: Share best practices for photo backup and storage with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Explain Importance of Regular Backups: Emphasize the importance of regular backups to prevent data loss.
- Provide Resources: Provide resources for data recovery software and services.
- Offer Hands-On Assistance: Offer hands-on assistance to help others set up backup systems.
- Host Workshops or Seminars: Host workshops or seminars on photo backup and recovery.
18. How Does File System Corruption Lead to Photo Loss?
File system corruption can lead to photo loss by making the storage device unreadable or causing files to become inaccessible. File system corruption can occur due to hardware failure, software bugs, power outages, or improper shutdown of the device. When the file system is corrupted, the operating system may not be able to locate or access the photos stored on the device.
- Hardware Failure: Hard drive failures or other hardware issues can cause file system corruption.
- Software Bugs: Software bugs or operating system errors can corrupt the file system.
- Power Outages: Power outages during file transfers can lead to file system corruption.
- Improper Shutdown: Improperly shutting down the device can cause file system errors.
- Virus/Malware Infections: Viruses and malware can corrupt the file system.
19. What Are the Limitations of Free Photo Recovery Software?
Free photo recovery software often has limitations compared to paid versions. Limitations may include a limited amount of data that can be recovered, fewer advanced features, and lack of support for certain file types or storage devices. While free software can be useful for basic recovery needs, it may not be sufficient for more complex data loss scenarios.
- Limited Data Recovery: Many free versions limit the amount of data that can be recovered (e.g., up to 1GB).
- Fewer Advanced Features: Free software may lack advanced features like deep scan modes, corrupted file repair, or RAID recovery.
- Limited File Type Support: Some free versions may only support certain file types or storage devices.
- No Technical Support: Free software typically does not include technical support.
- Ads and Upsells: Free software may contain ads or prompts to upgrade to the paid version.
20. How Do You Choose the Right Photo Recovery Service?
Choosing the right photo recovery service involves considering factors such as expertise, reputation, success rate, cost, and data security. Look for a service with experienced technicians, positive customer reviews, a high success rate, transparent pricing, and a commitment to data security and confidentiality.
- Expertise: Look for a service with experienced technicians who specialize in photo recovery.
- Reputation: Check online reviews and testimonials to gauge the service’s reputation.
- Success Rate: Ask about the service’s success rate for photo recovery.
- Cost: Get a clear estimate of the cost before proceeding with the recovery process.
- Data Security: Ensure the service has a commitment to data security and confidentiality.
- Turnaround Time: Ask about the estimated turnaround time for the recovery process.
- Free Evaluation: Look for a service that offers a free evaluation of the damaged device or storage media.
21. What Role Does Data Fragmentation Play in Photo Recovery?
Data fragmentation can affect the success of photo recovery by scattering the pieces of a deleted file across different parts of the storage device. When a file is fragmented, it becomes more difficult for data recovery software to locate and reassemble all the pieces, reducing the chances of successful recovery.
- Scattered File Pieces: Fragmentation scatters the pieces of a file across different parts of the storage device.
- Difficult Reassembly: Fragmented files are more difficult for data recovery software to locate and reassemble.
- Reduced Recovery Chances: Fragmentation reduces the chances of successful photo recovery.
- Defragmentation Tools: Defragmentation tools can help consolidate fragmented files, but should not be used after data loss as they can overwrite deleted files.
22. How Can You Verify the Integrity of Recovered Photos?
Verifying the integrity of recovered photos is crucial to ensure that they are not corrupted or damaged. Open the recovered photos in a photo viewer or editor, check for any signs of corruption (e.g., missing parts, color distortions), and compare them to any existing backups.
- Open in Photo Viewer/Editor: Open the recovered photos in a photo viewer or editor like Adobe Photoshop or GIMP.
- Check for Corruption: Look for any signs of corruption, such as missing parts, color distortions, or pixelation.
- Compare to Backups: Compare the recovered photos to any existing backups to ensure they are identical.
- Check Metadata: Verify the metadata (e.g., date, time, camera settings) of the recovered photos.
- Run Check Disk Utility: Run a check disk utility to scan the storage device for errors.
23. What Are the Long-Term Storage Options for Archiving Photos?
Long-term storage options for archiving photos include: cloud storage, external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS) devices, and optical media (e.g., DVDs, Blu-rays). Choose a storage solution that offers redundancy, durability, and easy access to your photos in the future.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage services like Google Photos, Amazon Photos, and Dropbox offer convenient and reliable long-term storage.
- External Hard Drives: External hard drives provide a cost-effective way to store large amounts of data.
- NAS Devices: Network-attached storage devices offer centralized storage and backup for multiple devices on your network.
- Optical Media: Optical media like DVDs and Blu-rays can be used for long-term archival storage, but are more susceptible to damage and degradation over time.
24. How Does the Type of Storage Device (HDD vs. SSD) Affect Photo Recovery?
The type of storage device (HDD vs. SSD) can affect photo recovery due to differences in how they store and delete data. HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) store data magnetically, making recovery more feasible even after deletion. SSDs (Solid State Drives) use flash memory and TRIM commands, which can make data recovery more challenging.
- HDDs (Hard Disk Drives): HDDs store data magnetically, making data recovery more feasible even after deletion, as the data may still be physically present on the drive.
- SSDs (Solid State Drives): SSDs use flash memory and TRIM commands, which can automatically erase deleted data to improve performance. This can make data recovery more challenging on SSDs.
25. What Are the Best File Formats for Long-Term Photo Archiving?
The best file formats for long-term photo archiving are those that are widely supported, non-proprietary, and lossless. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) and DNG (Digital Negative) are commonly recommended for archiving photos due to their lossless compression and compatibility.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): TIFF is a lossless image format that preserves all the original data of the photo.
- DNG (Digital Negative): DNG is a lossless raw image format developed by Adobe for archiving digital photos.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): JPEG is a lossy compression format that reduces file size but can result in quality loss over time. It is not recommended for long-term archiving.
26. How Can You Ensure the Longevity of Your Photo Prints?
Ensuring the longevity of your photo prints involves using high-quality printing materials and storing the prints properly. Print photos on acid-free paper using archival inks, and store the prints in acid-free albums or sleeves away from direct sunlight, heat, and humidity.
- Use High-Quality Printing Materials: Print photos on acid-free paper using archival inks.
- Store Prints Properly: Store the prints in acid-free albums or sleeves away from direct sunlight, heat, and humidity.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Direct sunlight can cause fading and discoloration of photo prints.
- Control Temperature and Humidity: Store prints in a cool, dry environment with stable temperature and humidity levels.
- Handle Prints with Care: Handle prints with clean hands or cotton gloves to avoid transferring oils or dirt.
27. What Are the Legal Aspects of Recovering and Using Found Photos?
The legal aspects of recovering and using found photos depend on factors such as copyright, privacy, and intellectual property rights. If you find photos on a lost or discarded device, you may need to obtain permission from the copyright holder or individuals in the photos before using or publishing them.
- Copyright: Photos are protected by copyright law, which gives the copyright holder exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, and display the photos.
- Privacy: You must respect the privacy of individuals in the photos and avoid sharing or publishing sensitive content without their consent.
- Intellectual Property Rights: You must respect the intellectual property rights of others and avoid using found photos for commercial purposes without permission.
- Seek Legal Advice: If you are unsure about the legal aspects of recovering and using found photos, seek legal advice from an attorney.
28. How Do You Dispose of Old Storage Devices Securely to Prevent Photo Recovery?
Disposing of old storage devices securely is important to prevent unauthorized access to your photos. Wipe the storage device using data sanitization software, physically destroy the device, or use a professional data destruction service.
- Wipe the Storage Device: Use data sanitization software to overwrite the storage device multiple times with random data.
- Physically Destroy the Device: Physically destroy the storage device by shredding, crushing, or drilling holes through it.
- Use a Professional Data Destruction Service: Use a professional data destruction service that specializes in secure data disposal.
- Remove Identifying Labels: Remove any identifying labels or markings from the storage device.
29. What New Technologies Are Emerging in Photo Backup and Recovery?
New technologies are constantly emerging in photo backup and recovery, including: AI-powered data recovery tools, blockchain-based storage solutions, and advanced cloud backup services. These technologies offer improved efficiency, security, and reliability for protecting and recovering your photos.
- AI-Powered Data Recovery Tools: AI-powered data recovery tools use machine learning algorithms to improve the accuracy and speed of data recovery.
- Blockchain-Based Storage Solutions: Blockchain-based storage solutions offer decentralized and secure storage for photos.
- Advanced Cloud Backup Services: Advanced cloud backup services offer features like versioning, encryption, and ransomware protection.
- Improved Storage Media: New storage media like high-density flash memory and DNA storage offer improved capacity and durability for long-term photo archiving.
30. What Are the Key Differences Between Photo Archiving and Photo Backup?
The key differences between photo archiving and photo backup lie in their purpose and frequency. Photo archiving is for long-term preservation of photos that are not frequently accessed, while photo backup is for creating a copy of photos that are actively used and need to be quickly restored in case of data loss.
- Photo Archiving:
- Purpose: Long-term preservation of photos.
- Frequency: Infrequent.
- Storage: Typically stored on durable media like optical discs or cloud storage.
- Accessibility: Less frequent access.
- Photo Backup:
- Purpose: Creating a copy of photos for quick restoration in case of data loss.
- Frequency: Regular and automated.
- Storage: Typically stored on external hard drives or cloud storage.
- Accessibility: Frequent access.
By understanding the steps to recover deleted photos and implementing preventative measures, you can safeguard your precious memories. Remember, dfphoto.net is a valuable resource for learning more about photography, including photo recovery tips, backup strategies, and the latest trends in image management.
FAQ: Recovering Deleted Photos
-
Is it always possible to recover deleted photos?
No, it is not always possible to recover deleted photos. The success of photo recovery depends on factors such as the time elapsed since deletion, the amount of data overwritten, and the condition of the storage device. -
Does emptying the Recycle Bin/Trash mean photos are permanently deleted?
Yes, emptying the Recycle Bin/Trash typically means photos are permanently deleted from the operating system’s perspective. However, the data may still be recoverable using data recovery software or professional services. -
Can I recover photos from a physically damaged hard drive?
Recovering photos from a physically damaged hard drive is possible, but it often requires professional data recovery services with specialized equipment and expertise. -
Is it safe to use free data recovery software?
Using free data recovery software is generally safe, but it’s essential to download the software from a reputable source to avoid malware or viruses. -
How often should I back up my photos?
You should back up your photos regularly, ideally on a daily or weekly basis, to minimize the risk of data loss. -
What is the 3-2-1 backup rule?
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a strategy that involves keeping at least three copies of your data, storing the backups on two different types of media, and keeping one backup copy offsite. -
What are the best cloud storage services for photo backup?
The best cloud storage services for photo backup include Google Photos, iCloud Photos, Amazon Photos, Dropbox, and Microsoft OneDrive. -
Can I recover photos from a water-damaged smartphone?
Recovering photos from a water-damaged smartphone is possible, but it often requires professional data recovery services with specialized equipment and expertise. -
What is data fragmentation, and how does it affect photo recovery?
Data fragmentation is the scattering of file pieces across different parts of the storage device. It can make photo recovery more difficult by making it harder for data recovery software to locate and reassemble all the pieces of a deleted file. -
Are there any ethical considerations when recovering someone else’s deleted photos?
Yes, ethical considerations are essential when recovering someone else’s deleted photos. Always obtain consent before attempting recovery, and respect privacy and confidentiality when handling recovered data.
Looking to expand your photography knowledge and skills? Visit dfphoto.net for in-depth guides, stunning photo galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers. Explore techniques, discover inspiration, and connect with fellow enthusiasts today! Our address is 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States, and you can reach us by phone at +1 (505) 471-6001. We’re here to help you on your photographic journey.