Are you wondering if deleted photos still hog precious storage space on your iPhone, Android, or computer? This is a common concern among photographers and visual artists. At dfphoto.net, we will explain how deleted photos are handled by different devices and platforms, and provide practical tips for reclaiming storage and improving your photo management practices. We also explore how cloud storage and photo optimization strategies can help keep your digital workspace clutter-free. Let’s dive into the world of photo storage, digital images, and memory management!
1. Understanding Photo Storage Basics
Before exploring how deleted photos affect storage, let’s cover some basics.
1.1. How Devices Store Photos
When you take a photo, your device saves it as a digital file. Digital image files use storage space, and the amount they use depends on several factors.
- File Size: Measured in megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB), this indicates how much space the photo occupies. Larger files (more MB) take up more storage.
- Image Resolution: Higher resolution photos contain more detail and require larger file sizes. Resolution is crucial for editing and printing detailed photographs.
- File Format: Formats like JPEG, PNG, and RAW have different compression and storage characteristics. RAW files, for example, retain all the data captured by the camera sensor, resulting in larger sizes but more editing flexibility.
1.2. Storage Types
Knowing where your photos are stored is essential.
- Internal Storage: The built-in memory of your device (phone, tablet, camera).
- External Storage: Includes SD cards, external hard drives, and USB drives.
- Cloud Storage: Online services like iCloud, Google Photos, and Dropbox store your photos remotely.
Understanding these basics helps you manage your photo storage effectively.
2. What Happens When You Delete a Photo?
Deleting a photo doesn’t always mean it’s gone for good. Here’s what happens on different devices.
2.1. On iPhones and iPads
When you delete a photo on an iPhone or iPad, it goes to the “Recently Deleted” album in the Photos app. This album holds the photos for 30 days, giving you a chance to recover them.
- How It Works:
- Deletion: You delete a photo from your main albums.
- Move to Recently Deleted: The photo moves to the “Recently Deleted” album.
- 30-Day Grace Period: The photo stays here for 30 days.
- Permanent Deletion: After 30 days, the photo is permanently deleted.
- Why It Matters: Photos in the “Recently Deleted” album still take up storage.
2.2. On Android Devices
Android devices usually have a similar system. Deleted photos often go to a “Trash” or “Bin” folder within the Gallery app.
- How It Works:
- Deletion: You delete a photo.
- Move to Trash/Bin: The photo is moved to the trash folder.
- Retention Period: Usually 30 days, but it can vary by device and app.
- Permanent Deletion: The photo is automatically and permanently deleted after the retention period.
- Why It Matters: Like iPhones, photos in the trash folder still consume storage space.
2.3. On Computers (Windows and macOS)
On computers, deleted photos typically go to the Recycle Bin (Windows) or Trash (macOS).
- How It Works:
- Deletion: You delete a photo from a folder.
- Move to Recycle Bin/Trash: The photo is moved to the Recycle Bin or Trash.
- Storage Use: The photo continues to take up space on your hard drive.
- Emptying the Bin/Trash: You need to manually empty the Recycle Bin or Trash to permanently delete the photos and free up space.
- Why It Matters: Simply deleting a photo doesn’t free up storage until you empty the Recycle Bin or Trash.
3. Do Deleted Photos Take Up Storage?
The short answer is yes, at least temporarily. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
3.1. Temporary Storage Consumption
When you delete a photo and it goes to a “Recently Deleted,” “Trash,” or “Recycle Bin” folder, it still takes up storage space on your device. This temporary storage consumption is because the device is holding the photo in case you want to recover it.
3.2. Permanent Deletion and Storage Release
To truly free up storage, you need to permanently delete the photos.
- iPhone/iPad: Go to the “Recently Deleted” album, select the photos, and choose “Delete.”
- Android: Open the “Trash” or “Bin” folder in your Gallery app and empty it.
- Windows: Empty the Recycle Bin.
- macOS: Empty the Trash.
Once you complete these steps, the photos are permanently deleted, and the storage space is released.
3.3. Cloud Storage Considerations
If you use cloud storage services like iCloud or Google Photos, deleting a photo from your device might not immediately remove it from the cloud.
- Synchronization: Cloud services synchronize across devices. Deleting a photo on one device will eventually delete it from all synced devices and the cloud.
- Cloud Trash/Bin: Many cloud services also have a trash or bin folder. Deleted photos go here first and are permanently deleted after a certain period.
- Manual Deletion: To ensure a photo is completely removed, check the cloud service’s trash or bin and empty it as well.
4. How to Check Storage Usage
Knowing how to check your device’s storage usage is vital for managing photos effectively.
4.1. On iPhones and iPads
- Go to Settings.
- Tap General.
- Tap iPhone Storage (or iPad Storage).
This screen shows you how much storage you’ve used and provides recommendations for optimizing storage.
4.2. On Android Devices
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Storage.
This will display a breakdown of storage usage, including photos, videos, apps, and other files.
4.3. On Windows
- Open File Explorer.
- Right-click on your C: drive (or whichever drive your photos are stored on).
- Select Properties.
This shows you the used and free space on the drive.
4.4. On macOS
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner.
- Select About This Mac.
- Click the Storage tab.
This provides a visual overview of your storage usage.
5. Tips for Managing Photo Storage
Effective photo storage management involves several strategies.
5.1. Regularly Empty the “Recently Deleted” or “Trash/Bin” Folder
Make it a habit to regularly clear out these folders on your devices. This simple step can free up a significant amount of storage space.
5.2. Back Up Photos to the Cloud
Use cloud storage services like iCloud, Google Photos, or Dropbox to back up your photos. Once backed up, you can delete them from your device to save space.
 Back up photos to the cloud to ensure you never lose your precious memories
Back up photos to the cloud to ensure you never lose your precious memories
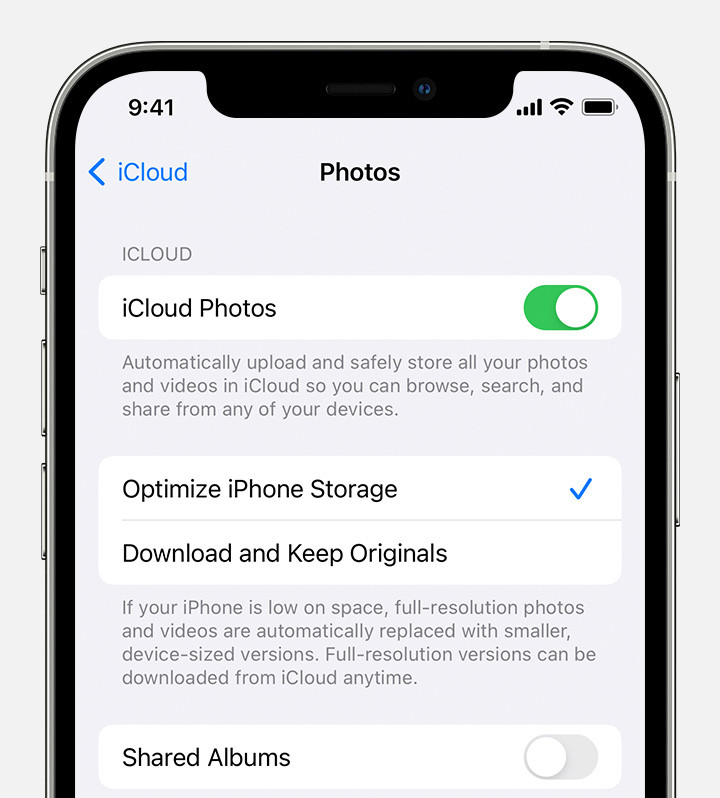
5.3. Optimize Photo Storage Settings
Most devices and cloud services offer options to optimize photo storage. For example, iCloud Photos has an “Optimize iPhone Storage” setting that keeps smaller, space-saving versions of your photos on your device while storing the full-resolution versions in the cloud.
5.4. Use External Storage
Transfer photos to external hard drives or USB drives to free up space on your devices. This is especially useful for archiving older photos that you don’t need immediate access to.
5.5. Compress Photos
Use photo compression tools to reduce the file size of your photos without significantly affecting quality. This can save a considerable amount of storage space, especially if you have a large photo library.
5.6. Delete Unnecessary Photos Promptly
Be diligent about deleting duplicate, blurry, or unwanted photos as soon as you take them. This prevents them from accumulating and taking up valuable storage space.
5.7. Organize Photos into Folders
Organize your photos into folders by date, event, or subject. This makes it easier to find and manage your photos, as well as identify and delete those you no longer need.
5.8. Utilize Photo Management Software
Consider using photo management software like Adobe Lightroom or Capture One. These tools offer advanced features for organizing, editing, and storing photos, helping you keep your photo library in order.
5.9. Regularly Review and Cull Your Photo Collection
Set aside time to review your photo collection and delete photos that are no longer needed or of poor quality. This can be a time-consuming task, but it’s essential for maintaining a manageable and clutter-free photo library.
5.10. Monitor Cloud Storage Usage
Keep an eye on your cloud storage usage to ensure you don’t exceed your storage limits. Many cloud services offer notifications when you’re nearing your limit, allowing you to take action before you run out of space.
6. Understanding Storage Space and Digital Photo Management
Effective management of digital photos involves understanding storage space and digital image manipulation.
6.1. Memory Card and Image Storage
Memory cards are vital for storing digital photos. Different types have varying capacities and speeds. SD cards are the most common, offering ample space for high-resolution images.
- SD Card Types: SD, SDHC, SDXC
- Storage Capacity: Ranges from a few GB to several TB.
- Speed: Measured in MB/s, affecting how quickly photos are saved and accessed.
6.2. Resolution Settings and Storage
Resolution settings affect photo quality and storage. High-resolution photos require more space but offer better detail.
- High Resolution: Ideal for printing and detailed editing.
- Low Resolution: Suitable for online sharing and saving space.
- Choosing the Right Resolution: Depends on your photography needs.
6.3. Photo File Formats
Photo file formats influence storage efficiency and image quality.
- JPEG: Compressed format, good for general use.
- PNG: Lossless format, better for images with text and graphics.
- RAW: Uncompressed format, retains all data for maximum editing flexibility.
6.4. Image Compression
Image compression reduces file size, saving storage space.
- Lossy Compression: Reduces file size by discarding some data (e.g., JPEG).
- Lossless Compression: Reduces file size without losing any data (e.g., PNG).
- Compression Tools: Software and online tools to compress images.
7. Understanding Camera Storage and its Impact
Managing camera storage is crucial for photographers.
7.1. The Role of Camera RAW Files
Camera RAW files contain unprocessed data captured by the camera’s sensor. They provide maximum flexibility for editing but consume significant storage.
- Advantages: Greater dynamic range, more editing options.
- Disadvantages: Larger file sizes, require special software.
- Workflow: Typically converted to other formats after editing.
7.2. Camera Memory Card Types
Different cameras use different memory card types, affecting storage and performance.
- SD Cards: Versatile and widely used in digital cameras.
- CompactFlash (CF) Cards: Older standard, known for durability.
- XQD Cards: High-speed cards, used in professional cameras.
7.3. Maximizing Camera Storage Efficiency
Efficient camera storage management involves several strategies.
- Regularly Transfer Photos: Move photos from the camera to a computer or external drive.
- Use Multiple Cards: Carry multiple memory cards to avoid running out of space.
- Format Cards Regularly: Formatting cards before each shoot ensures optimal performance.
7.4. Camera Storage Limitations
Understanding camera storage limitations is essential for planning your photo shoots.
- Maximum Card Size: Cameras have a maximum card size they can support.
- Battery Life: Frequent writing to memory cards can drain battery life.
- Data Transfer Speed: Slower cards can limit the number of photos you can take in burst mode.
8. Photo Editing and File Size
Photo editing can significantly impact file size and storage requirements.
8.1. How Editing Affects Storage
Editing photos can increase file size, especially when working with RAW files or making extensive changes.
- RAW vs. JPEG: Editing RAW files often results in larger file sizes than editing JPEGs.
- Layered Editing: Using layers in programs like Adobe Photoshop can increase file size.
- Export Settings: The settings you use when exporting your edited photos can affect file size.
8.2. Using External Hard Drives for Photo Storage
External hard drives are essential for storing large photo libraries and backups.
- Types of External Drives: HDD (Hard Disk Drive), SSD (Solid State Drive).
- Storage Capacity: Ranges from a few hundred GB to several TB.
- Backup Strategies: Regular backups to prevent data loss.
8.3. The Best External Hard Drives for Photo Storage
Choosing the right external hard drive is crucial for efficient photo storage.
- SSD vs. HDD: SSDs are faster but more expensive than HDDs.
- Capacity: Choose a drive with enough capacity to store your entire photo library.
- Durability: Look for drives that are rugged and designed to withstand travel.
8.4. Optimizing Digital Image Storage
Optimizing digital image storage involves various techniques to save space without sacrificing quality.
- File Compression: Use compression tools to reduce file size.
- Image Resizing: Resize images to the appropriate dimensions for their intended use.
- Metadata Management: Remove unnecessary metadata to reduce file size.
9. Cloud Storage Options
Exploring various cloud storage options can help you store and manage your photo library effectively.
9.1. Comparing Cloud Services
Different cloud services offer varying features, storage capacities, and pricing.
Table: Comparing Cloud Services
| Service | Storage Capacity | Pricing | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| iCloud | 5 GB Free | $0.99/month for 50 GB, $9.99/month for 2 TB | Seamless integration with Apple devices, automatic backups |
| Google Photos | 15 GB Free | $1.99/month for 100 GB, $9.99/month for 2 TB | AI-powered organization, automatic enhancements |
| Dropbox | 2 GB Free | $11.99/month for 2 TB | File sharing, version history |
| Adobe Creative Cloud | Varies | Included with Adobe subscriptions | Integration with Adobe software, collaboration tools |
| OneDrive | 5 GB Free | $1.99/month for 100 GB, $9.99/month for 1 TB | Integration with Microsoft Office, file sharing |
9.2. Cloud Storage Security and Privacy
Ensuring the security and privacy of your photos in the cloud is essential.
- Encryption: Look for services that offer end-to-end encryption.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Privacy Policies: Read the service’s privacy policy to understand how your data is used.
9.3. Cloud Storage for Photographers
Cloud storage offers numerous benefits for photographers.
- Accessibility: Access your photos from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Collaboration: Share photos with clients and collaborators easily.
- Backup: Protect your photos from data loss due to hardware failure.
9.4. Selecting the Right Cloud Storage Solution
Choosing the right cloud storage solution depends on your needs and budget.
- Storage Capacity: Determine how much storage you need.
- Features: Consider the features that are important to you, such as collaboration tools or AI-powered organization.
- Pricing: Compare the pricing of different services to find the best value.
10. Actionable Steps to Optimize Photo Storage
Here’s a list of actionable steps you can take to optimize your photo storage and reclaim space:
- Empty “Recently Deleted”: Regularly empty the “Recently Deleted” or “Trash/Bin” folders on your devices.
- Back Up to Cloud: Back up your photos to a cloud storage service like iCloud, Google Photos, or Dropbox.
- Optimize Storage Settings: Enable photo storage optimization settings on your devices and cloud services.
- Use External Storage: Transfer photos to external hard drives or USB drives.
- Compress Photos: Use photo compression tools to reduce file sizes.
- Delete Unnecessary Photos: Promptly delete duplicate, blurry, or unwanted photos.
- Organize Photos: Organize your photos into folders by date, event, or subject.
- Use Photo Management Software: Consider using photo management software like Adobe Lightroom or Capture One.
- Review Photo Collection: Regularly review your photo collection and delete photos that are no longer needed.
- Monitor Cloud Usage: Keep an eye on your cloud storage usage to avoid exceeding storage limits.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage your photo storage, free up space, and keep your photo library organized.
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, regularly clearing temporary storage locations can free up to 20% of device storage, optimizing performance and reducing data management complexities.
Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States
Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001
Website: dfphoto.net
FAQ Section
1. Do Permanently Deleted Photos Take Up Storage?
No, once photos are permanently deleted from your device and any associated cloud storage, they no longer take up storage space.
2. How Long Do Photos Stay in the “Recently Deleted” Album on iPhone?
Photos remain in the “Recently Deleted” album on iPhone for 30 days before being permanently deleted.
3. Can I Recover Photos After They’ve Been Permanently Deleted?
Recovering permanently deleted photos is generally not possible without specialized data recovery software or services, and success is not guaranteed.
4. Does iCloud Photos Optimize Storage Automatically?
Yes, iCloud Photos can be set to automatically optimize storage by keeping smaller, space-saving versions of your photos on your device while storing the full-resolution versions in the cloud.
5. How Do I Empty the Recycle Bin on Windows?
To empty the Recycle Bin on Windows, right-click on the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop and select “Empty Recycle Bin.”
6. What Is the Best Way to Back Up My Photos?
The best way to back up your photos is to use a combination of cloud storage and external hard drives for redundancy.
7. How Can I Reduce the File Size of My Photos Without Losing Quality?
You can reduce the file size of your photos without significant quality loss by using compression tools or saving them in a compressed format like JPEG with a high-quality setting.
8. What Are the Benefits of Using RAW Format for Photos?
RAW format offers greater dynamic range and more editing options compared to JPEG, but it results in larger file sizes.
9. How Do I Check My Storage Usage on an Android Device?
To check your storage usage on an Android device, go to Settings > Storage.
10. Which Cloud Storage Service Is Best for Photographers?
The best cloud storage service for photographers depends on individual needs and preferences, but popular options include iCloud, Google Photos, Dropbox, and Adobe Creative Cloud.
Ready to master your photography and manage your memories like a pro? Visit dfphoto.net for in-depth tutorials, stunning galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers. Unlock your creative potential and keep your digital world organized – start exploring today!