Face recognition technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, especially with smartphones like iPhones utilizing it for security. This article from dfphoto.net explores the vulnerabilities of face recognition systems, specifically focusing on whether an iPhone photo can bypass this security measure. We’ll delve into the intricacies of Face ID, its strengths, weaknesses, and ways to enhance your digital security, covering photographic security, biometric authentication, and spoofing attacks.
1. Understanding Face ID: Apple’s Biometric Security
Is unlocking your iPhone with a face scan as secure as it seems? Absolutely, Face ID is Apple’s advanced biometric system, available on iPhones and iPads since the iPhone X, that uses facial recognition instead of fingerprints for authentication. It’s designed for secure and convenient device access. Let’s examine how it stacks up.
Face ID analyzes your face using the TrueDepth camera system. This system projects and analyzes over 30,000 invisible dots to create a detailed depth map of your face. This depth map, combined with a 2D infrared image, is used to authenticate your identity. According to Apple, the probability of a random person unlocking your device with Face ID is approximately one in a million, significantly more secure than the one in 50,000 odds with Touch ID.
2. How Does Face ID Technology Actually Work?
How does Apple’s Face ID differentiate between a real face and a photograph? Face ID functions by creating a detailed map of your face using infrared light and a dot projector. It doesn’t store an actual image of your face but rather a mathematical representation of its unique features.
The TrueDepth camera system projects over 30,000 invisible dots onto your face and captures the reflected pattern. This data is then used to construct a 3D model of your facial contours. The system analyzes the depth and shape of various facial features, such as the nose, eyes, and mouth. This 3D model is stored in the Secure Enclave, a dedicated hardware component within the iPhone or iPad.
When you attempt to unlock your device, Face ID compares the newly captured facial data with the stored 3D model. If there’s a sufficient match, the device unlocks. The technology is designed to adapt to changes in your appearance, such as wearing glasses or growing a beard. It even works in low-light conditions thanks to the infrared camera.
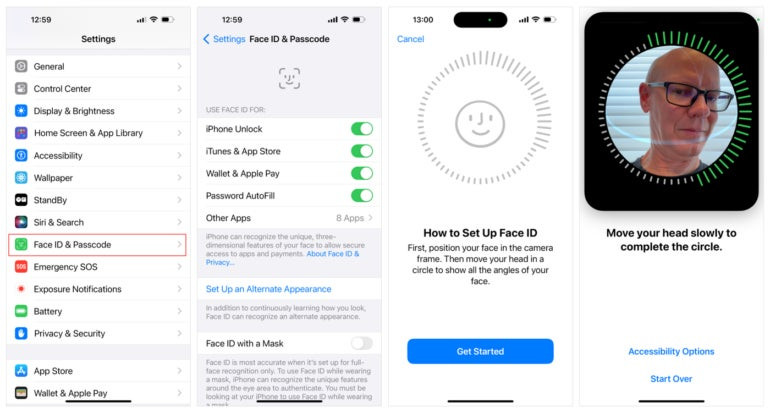 Face ID setup on an iPhone displaying instructions for scanning the user's face.
Face ID setup on an iPhone displaying instructions for scanning the user's face.
3. Can a Photo Fool Face ID? Exploring Potential Vulnerabilities
Can someone really bypass Face ID with just a simple photograph? While Face ID is designed to be secure, it’s not entirely foolproof. Early versions of facial recognition technology were susceptible to being fooled by photographs, but Face ID incorporates several measures to prevent this.
Face ID relies on depth information, which isn’t present in a 2D photograph. The TrueDepth camera system uses infrared light to create a 3D map of your face, making it more difficult to spoof with a simple image. Additionally, Face ID incorporates anti-spoofing neural networks that are trained to detect and prevent attempts to bypass the system using masks or other techniques.
However, determined attackers may still attempt to bypass Face ID using sophisticated methods. For example, they might create a realistic 3D mask of your face or use a high-resolution photograph displayed on a screen with appropriate depth cues. While these attacks are more complex, they demonstrate that Face ID isn’t impenetrable.
According to security researchers at the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, advanced 3D-printed masks combined with sophisticated lighting techniques could potentially fool Face ID.
4. Real-World Tests and Research on Face ID Security
What have researchers and security experts discovered about Face ID’s vulnerability to photos? Several real-world tests and research studies have explored Face ID’s security and vulnerability to spoofing attacks. These tests often involve attempting to unlock a device using photographs, masks, or other techniques.
One notable study conducted by Forbes in 2017 found that Face ID could be fooled by a highly realistic 3D mask created using a 3D printer and makeup. The mask was able to successfully unlock an iPhone X, demonstrating a potential vulnerability. However, the process of creating the mask was complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Other tests have shown that Face ID is generally resistant to unlocking with simple 2D photographs. The system’s depth-sensing capabilities and anti-spoofing measures make it difficult to bypass with a flat image. However, some researchers have found that high-resolution photographs displayed on a screen with appropriate lighting and viewing angles can sometimes fool Face ID under specific conditions.
5. Factors Influencing Face ID’s Susceptibility to Spoofing
What factors can increase or decrease Face ID’s vulnerability to being fooled by a photo or other spoofing methods? Several factors can influence Face ID’s susceptibility to spoofing attacks, including the quality of the photograph or mask used, the lighting conditions, and the settings on the device itself.
5.1 Quality of the Spoofing Attempt
The higher the quality and realism of the photograph or mask used, the more likely it is to fool Face ID. A low-resolution or poorly lit photograph is unlikely to succeed, while a high-resolution image with realistic depth cues may have a better chance.
5.2 Lighting Conditions
Lighting conditions can also play a role. Face ID relies on infrared light to create a 3D map of your face, so extreme lighting conditions (such as bright sunlight or complete darkness) can affect its accuracy.
5.3 Device Settings
Certain device settings can also impact Face ID’s security. For example, disabling the “Require Attention for Face ID” feature can make the system more vulnerable to unlocking while you’re not looking at the device.
5.4 Software Updates
Apple regularly releases software updates that include security improvements and bug fixes. Keeping your device updated to the latest version of iOS or iPadOS can help protect against known vulnerabilities.
6. How to Enhance Your iPhone’s Security Against Photo Spoofing
Want to make your iPhone’s Face ID even more secure? Excellent idea. Here are practical steps you can take to protect your device from photo-based spoofing attempts. These methods enhance biometric security, reduce vulnerability to image spoofing, and ensure device protection.
6.1 Enable “Require Attention for Face ID”
This feature requires you to be looking directly at your device for it to unlock, preventing someone from unlocking it while you’re asleep or distracted. To enable this feature, go to Settings > Face ID & Passcode and toggle on “Require Attention for Face ID.”
6.2 Use a Strong Passcode
While Face ID is convenient, it’s essential to have a strong passcode as a backup. A complex passcode (six or more digits) makes it more difficult for someone to guess or brute-force their way into your device.
6.3 Keep Your Software Updated
Apple regularly releases software updates that include security patches and improvements. Install these updates promptly to protect your device from known vulnerabilities.
6.4 Be Cautious About Your Photos
Avoid posting high-resolution photos of yourself online, especially on social media platforms. Attackers could potentially use these images to create realistic masks or other spoofing attempts.
6.5 Use a Privacy Screen Protector
A privacy screen protector limits the viewing angle of your iPhone’s display, making it more difficult for someone to see your face while you’re using Face ID in public.
7. Alternatives to Face ID: Exploring Other Biometric Options
Are there other biometric security options besides Face ID? Yes, while Face ID is a popular and convenient option, other biometric technologies offer alternative security measures. These methods provide diverse options for user authentication, enhancing biometric authentication and ensuring secure access control.
7.1 Touch ID
Touch ID, Apple’s fingerprint recognition system, is still available on some iPhone and iPad models. Touch ID uses a fingerprint sensor to authenticate your identity, providing a secure and reliable alternative to Face ID.
7.2 Iris Scanning
Iris scanning technology uses the unique patterns in your iris to verify your identity. While not as common as Face ID or Touch ID on smartphones, iris scanning is used in some high-security applications.
7.3 Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology uses your voice to authenticate your identity. While voice recognition can be convenient, it’s generally less secure than Face ID or Touch ID, as it can be susceptible to spoofing attacks.
7.4 Password Authentication
Password authentication is a traditional security measure that requires you to enter a password or PIN to access your device. While passwords can be effective, they can also be forgotten or compromised if not managed properly.
8. The Future of Facial Recognition Security
Where is facial recognition technology headed in the future? The field of facial recognition technology is constantly evolving, with researchers and developers working on new ways to improve its accuracy, security, and privacy. Expect advancements in biometric security, improved spoofing detection, and enhanced user privacy.
8.1 Improved Accuracy
Future facial recognition systems will likely be more accurate and reliable, with improved algorithms and sensors that can better handle variations in lighting, pose, and expression.
8.2 Enhanced Security
Researchers are developing new anti-spoofing techniques to protect facial recognition systems from attacks using photographs, masks, or other methods. These techniques may involve using multiple sensors (such as infrared and depth cameras) to capture more detailed information about the user’s face.
8.3 Greater Privacy
Privacy concerns surrounding facial recognition technology are growing, and developers are working on new ways to protect user privacy. These may include techniques such as federated learning, which allows facial recognition models to be trained on decentralized data without sharing sensitive information.
8.4 Integration with Other Technologies
Facial recognition technology is increasingly being integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things. This integration could lead to new applications in areas such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
9. Face ID vs. Other Facial Recognition Systems: A Comparison
How does Face ID compare to other facial recognition systems in terms of security and accuracy? Face ID stands out from other facial recognition systems due to its advanced technology and security features. It leverages sophisticated algorithms and hardware for superior performance, ensuring reliable biometric authentication.
9.1 Accuracy
Face ID’s use of infrared light and dot projection allows it to create a detailed 3D map of your face, making it more accurate than systems that rely solely on 2D images.
9.2 Security
Face ID incorporates anti-spoofing neural networks that are trained to detect and prevent attempts to bypass the system using photographs, masks, or other techniques.
9.3 Privacy
Apple has implemented several measures to protect user privacy, such as storing facial data securely on the device and not sharing it with third parties.
9.4 Convenience
Face ID is designed to be convenient and easy to use, allowing you to unlock your device with a simple glance.
10. Case Studies: Instances Where Face ID Was Bypassed
Have there been any documented cases where Face ID was successfully bypassed? Yes, while Face ID is generally considered secure, there have been a few documented cases where it was successfully bypassed using sophisticated techniques. These instances highlight the ongoing challenge of maintaining security in the face of determined attackers.
10.1 The 3D Mask Attack
In 2017, researchers at Bkav, a Vietnamese security firm, claimed to have successfully bypassed Face ID using a 3D-printed mask. The mask was created using a combination of 3D printing, makeup, and 2D images of the target’s face. While the attack was successful, it required significant time, resources, and expertise.
10.2 The Twin Study
In 2017, a study by Wired found that identical twins could sometimes fool Face ID. While Face ID is designed to distinguish between different faces, even subtle similarities between identical twins can sometimes lead to false positives.
10.3 The Mask With Eye Cutouts
In 2019, a report by Forbes found that Face ID could be bypassed using a mask with eye cutouts. The mask was designed to mimic the shape and features of the target’s face, while the eye cutouts allowed the system to detect that the user was looking at the device.
11. Ethical Considerations of Facial Recognition Technology
What are the ethical implications of using facial recognition technology, particularly in public spaces? The use of facial recognition technology raises several ethical concerns, particularly regarding privacy, bias, and accountability. These considerations are vital for responsible deployment, addressing privacy concerns, preventing discriminatory practices, and promoting fair application.
11.1 Privacy
Facial recognition technology can be used to track and monitor individuals without their knowledge or consent, raising concerns about privacy and surveillance.
11.2 Bias
Facial recognition systems can be biased against certain demographic groups, such as people of color or women, leading to inaccurate or unfair outcomes.
11.3 Accountability
It can be difficult to hold individuals or organizations accountable for the misuse of facial recognition technology, particularly in cases where the technology is used secretly or without oversight.
11.4 Transparency
The lack of transparency surrounding the development and deployment of facial recognition technology can make it difficult for the public to understand how the technology works and how it is being used.
12. Legal Frameworks Governing Facial Recognition Use
What laws and regulations govern the use of facial recognition technology in the United States? The legal framework governing the use of facial recognition technology in the United States is still evolving, with a mix of federal, state, and local laws addressing various aspects of its use. These frameworks aim to regulate biometric data, prevent misuse, and establish accountability.
12.1 Federal Laws
There are currently no comprehensive federal laws regulating the use of facial recognition technology in the United States. However, some existing federal laws, such as the Privacy Act of 1974 and the Electronic Communications Privacy Act, may apply to certain uses of facial recognition technology.
12.2 State Laws
Several states have enacted laws regulating the use of facial recognition technology, particularly in areas such as law enforcement and government surveillance. These laws often require transparency, accountability, and restrictions on the use of facial recognition technology.
12.3 Local Laws
Some cities and counties have also enacted laws regulating the use of facial recognition technology, particularly in areas such as public transportation and public housing.
12.4 International Laws
The use of facial recognition technology is also governed by international laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union.
13. Debunking Common Myths About Face ID Security
Are there common misconceptions about how secure Face ID really is? Absolutely, there are several myths and misconceptions surrounding Face ID security. Let’s clear up some of the common misunderstandings. Understanding the true capabilities and limitations of Face ID can help you make informed decisions about your device’s security.
Myth 1: Face ID can be fooled by any photograph.
Fact: Face ID is designed to be resistant to unlocking with simple 2D photographs. The system’s depth-sensing capabilities and anti-spoofing measures make it difficult to bypass with a flat image.
Myth 2: Face ID doesn’t work in the dark.
Fact: Face ID uses infrared light to create a 3D map of your face, so it can work in low-light conditions and even in complete darkness.
Myth 3: Face ID is less secure than Touch ID.
Fact: Apple claims that Face ID is more secure than Touch ID, with a lower probability of a random person being able to unlock your device.
Myth 4: Face ID stores an image of your face on the device.
Fact: Face ID doesn’t store an actual image of your face but rather a mathematical representation of its unique features.
Myth 5: Face ID can be used to track your location.
Fact: Face ID is a local authentication system that doesn’t transmit any facial data to Apple or third parties.
14. Can Law Enforcement Compel You to Unlock Your Phone With Face ID?
Can law enforcement legally force you to unlock your iPhone using Face ID? This is a complex legal question. In the United States, the Fifth Amendment protects individuals from self-incrimination, while the Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures.
In January 2019, a U.S. judge ruled that forcing users to unlock devices using biometric security methods like Face ID violates both the Fourth and Fifth Amendments to the U.S. constitution. This ruling suggests that law enforcement cannot compel you to unlock your phone with Face ID. However, the legal landscape surrounding this issue is still evolving, and different courts may reach different conclusions.
15. Tips for Protecting Your Digital Identity in the Age of Facial Recognition
How can you protect your digital identity in a world increasingly reliant on facial recognition? Protecting your digital identity is crucial. Follow these tips to enhance digital security and protect personal information in an era of increasing facial recognition technology.
15.1 Use Strong Passwords
Use strong, unique passwords for all of your online accounts. Avoid using easily guessable passwords, such as your birthday or pet’s name.
15.2 Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible. 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your phone.
15.3 Be Careful About Sharing Photos Online
Avoid posting high-resolution photos of yourself online, especially on social media platforms. Attackers could potentially use these images to create realistic masks or other spoofing attempts.
15.4 Use a VPN
Use a virtual private network (VPN) when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept your data.
15.5 Monitor Your Credit Report
Monitor your credit report regularly for any signs of identity theft. You can obtain a free copy of your credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) once per year.
16. The Impact of Face ID on Privacy and Surveillance
How has Face ID impacted our privacy and the potential for surveillance? Face ID, while providing convenient security, has raised concerns about privacy and surveillance. These concerns stem from the potential for misuse of biometric data and the increasing use of facial recognition technology in public spaces.
16.1 Data Collection
Face ID collects and stores facial data, raising concerns about how this data is used and protected.
16.2 Surveillance
Facial recognition technology can be used for mass surveillance, allowing governments and corporations to track and monitor individuals without their knowledge or consent.
16.3 Bias
Facial recognition systems can be biased against certain demographic groups, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
16.4 Lack of Transparency
The lack of transparency surrounding the development and deployment of facial recognition technology can make it difficult for the public to understand how the technology works and how it is being used.
17. How to Disable Face ID on Your iPhone or iPad
Want to turn off Face ID on your iPhone or iPad? It’s easy to do if you prefer other security measures. Here’s a step-by-step guide to disable Face ID and explore alternative authentication methods.
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone or iPad.
- Scroll down and tap on “Face ID & Passcode.”
- Enter your passcode when prompted.
- Under the “Use Face ID For” section, toggle off the switches next to “iPhone Unlock,” “Apple Pay,” “iTunes & App Store,” and any other options you have enabled.
- To completely remove your facial data from the device, tap on “Reset Face ID.”
18. Future Trends in Biometric Authentication
What are the emerging trends in biometric authentication beyond facial recognition? The field of biometric authentication is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging all the time. Expect advancements beyond facial recognition, ensuring more secure and user-friendly authentication methods.
18.1 Vein Recognition
Vein recognition technology uses the unique patterns of veins in your finger or hand to verify your identity.
18.2 Heart Rate Monitoring
Heart rate monitoring technology uses the unique characteristics of your heartbeat to authenticate your identity.
18.3 Brainwave Scanning
Brainwave scanning technology uses the unique patterns of your brainwaves to verify your identity.
18.4 Behavioral Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics analyze your unique patterns of behavior, such as how you type or swipe on your device, to authenticate your identity.
19. The Role of AI in Improving Facial Recognition Security
How is artificial intelligence (AI) being used to enhance the security of facial recognition systems? AI plays a crucial role in enhancing the security of facial recognition systems. AI algorithms can improve accuracy, detect spoofing attempts, and enhance privacy.
19.1 Improved Accuracy
AI algorithms can be trained to recognize faces with greater accuracy, even under challenging conditions such as low light or partial occlusion.
19.2 Spoofing Detection
AI algorithms can be used to detect spoofing attempts, such as using photographs or masks to bypass facial recognition systems.
19.3 Privacy Enhancement
AI techniques such as federated learning can be used to train facial recognition models on decentralized data without sharing sensitive information.
19.4 Bias Mitigation
AI algorithms can be used to identify and mitigate biases in facial recognition systems, ensuring that the technology is fair and accurate for all demographic groups.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Face ID and Photo Spoofing
Do you still have questions about Face ID and photo spoofing? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand the technology and its security implications.
Q1: Can Face ID be fooled by a photograph?
While Face ID is designed to be resistant to unlocking with simple 2D photographs, sophisticated attacks using high-resolution images or 3D masks may be successful under certain conditions.
Q2: How secure is Face ID compared to Touch ID?
Apple claims that Face ID is more secure than Touch ID, with a lower probability of a random person being able to unlock your device.
Q3: Does Face ID work in the dark?
Yes, Face ID uses infrared light to create a 3D map of your face, so it can work in low-light conditions and even in complete darkness.
Q4: Can law enforcement force me to unlock my phone with Face ID?
The legal landscape surrounding this issue is still evolving, but a U.S. judge has ruled that forcing users to unlock devices using biometric security methods like Face ID violates the Fourth and Fifth Amendments to the U.S. constitution.
Q5: How can I protect my digital identity in the age of facial recognition?
Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be careful about sharing photos online, and use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
Q6: What are the ethical considerations of using facial recognition technology?
The use of facial recognition technology raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, bias, and accountability.
Q7: How can I disable Face ID on my iPhone or iPad?
You can disable Face ID in the Settings app under “Face ID & Passcode.”
Q8: What are the future trends in biometric authentication?
Future trends include vein recognition, heart rate monitoring, brainwave scanning, and behavioral biometrics.
Q9: How is AI being used to improve facial recognition security?
AI is being used to improve accuracy, detect spoofing attempts, and enhance privacy.
Q10: Is Face ID safe to use on business devices?
Yes, Face ID is safe to use on Apple mobile devices you use for work, as it helps reduce the potential that a device might be accessed by anyone other than the authorized user or owner.
 Apple mobile device display with the Swipe up to unlock prompt on highlight.
Apple mobile device display with the Swipe up to unlock prompt on highlight.
Face ID is a convenient and secure way to protect your iPhone or iPad, but it’s essential to understand its limitations and take steps to protect your digital identity. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay safe in the age of facial recognition.
Ready to delve deeper into the world of photography and digital security? Visit dfphoto.net for more insightful articles, tutorials, and resources. Join our community of photography enthusiasts and explore the latest trends and techniques. Whether you’re looking to enhance your photography skills or stay informed about digital security, dfphoto.net has something for everyone. Contact us at Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001 or visit our website at dfphoto.net.