A Photo Of The Solar System is more than just a snapshot; it’s a profound visual journey that unveils the beauty and mystery of our cosmic neighborhood, and at dfphoto.net, we celebrate this blend of photography and astronomy, offering resources and inspiration to capture the wonders of the universe. This is achieved through astrophotography techniques, utilizing long exposure settings, and image stacking applications. Dive into the world of cosmic images, celestial photography, and astronomical visuals with us.
1. What Exactly Is A Photo Of The Solar System?
A photo of the solar system is a composite or individual image capturing the planets, moons, asteroids, and other celestial bodies orbiting our Sun. It offers a unique perspective on our place in the cosmos, revealing the scale and beauty of our celestial neighborhood. Capturing a comprehensive photo of the solar system is challenging due to the vast distances and varying brightness of the objects.
1.1 How Are These Photos Typically Taken?
These pictures are often taken using specialized telescopes and cameras. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, advanced imaging techniques have allowed us to capture stunning images of individual planets and even create mosaics that represent the entire solar system. These include long exposure photography, which gathers faint light over extended periods, and stacking multiple images to reduce noise and enhance details.
1.2 What Challenges Do Photographers Face When Capturing Images of the Solar System?
Photographers face significant challenges, including atmospheric distortion, light pollution, and the immense distances involved. Overcoming these hurdles requires sophisticated equipment, precise tracking, and advanced image processing techniques.
- Atmospheric Turbulence: Earth’s atmosphere can blur images, making it difficult to capture sharp details.
- Light Pollution: Artificial lights can overwhelm faint celestial objects.
- Distance: Planets are very far away, meaning very long focal lengths are required.
- Motion: Planets and the Earth are constantly moving, so tracking mounts are required to prevent blurring over long exposures.
1.3 Are There Different Types Of Solar System Photos?
Yes, there are several types, including:
- Wide-field shots: Show the general layout of the planets in their orbits
- Close-ups of individual planets: Reveal surface details and atmospheric phenomena.
- Composite images: Combine multiple exposures to capture a broader range of brightness and detail.
2. Why Is A Photo Of The Solar System Important?
A photo of the solar system is important because it offers a tangible and awe-inspiring view of our cosmic environment, fostering a deeper understanding of our place in the universe and inspiring further exploration. According to Popular Photography Magazine, these images are crucial for scientific study, helping researchers track planetary movements, study atmospheric conditions, and search for potential hazards like asteroids.
2.1 How Do These Images Contribute to Scientific Understanding?
These images provide valuable data for scientists, aiding in the study of planetary atmospheres, surface features, and orbital mechanics. Regular monitoring through photography can reveal changes over time, contributing to our understanding of the solar system’s dynamic nature.
- Atmospheric Analysis: Observing cloud patterns and weather systems on planets like Jupiter and Saturn.
- Surface Mapping: Creating detailed maps of planetary surfaces, identifying geological features and potential landing sites.
- Orbital Tracking: Precisely tracking the movements of planets and asteroids to refine our understanding of orbital mechanics.
2.2 What Role Do They Play in Education and Inspiration?
Photos of the solar system ignite curiosity and inspire the next generation of scientists, engineers, and space explorers. They bring the wonders of the universe into classrooms and homes, making complex concepts more accessible and engaging.
2.3 Can Amateur Photographers Contribute to Solar System Imaging?
Absolutely. With the right equipment and techniques, amateur astronomers can capture stunning images of the solar system, contributing valuable data and insights to the broader scientific community. Many amateur astrophotographers have made significant discoveries.
3. What Equipment Is Needed To Capture A Photo Of The Solar System?
To capture a photo of the solar system, you’ll need a telescope, a specialized camera, and a tracking mount. These tools allow you to gather enough light and compensate for Earth’s rotation, resulting in clear, detailed images.
3.1 What Type Of Telescope Is Best For Solar System Photography?
A telescope with a long focal length is ideal for capturing detailed images of planets. Refractor and reflector telescopes are both popular choices, each offering unique advantages in terms of image quality and cost.
- Refractor Telescopes: Known for their sharp, high-contrast images, ideal for planetary viewing.
- Reflector Telescopes: Offer larger apertures for light gathering, suitable for fainter objects.
3.2 What Kind Of Camera Works Best?
Specialized astronomy cameras, such as CCD or CMOS cameras, are designed to capture faint light with minimal noise. These cameras often feature high resolution and cooling systems to reduce thermal noise, improving image quality.
3.3 What Role Does a Tracking Mount Play?
A tracking mount is essential for long-exposure photography, compensating for Earth’s rotation and keeping celestial objects centered in the frame. This allows for longer exposures without blurring, crucial for capturing faint details.
4. How Do You Process A Photo Of The Solar System?
Processing a photo of the solar system involves stacking multiple images to reduce noise and enhance detail, adjusting color balance, and sharpening to bring out fine features. Specialized software like RegiStax and AutoStakkert! are commonly used for these tasks.
4.1 What Is Image Stacking And Why Is It Important?
Image stacking combines multiple exposures of the same object to reduce noise and enhance signal. This technique is crucial for revealing faint details that would otherwise be lost in the noise. According to Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department research from July 2025, stacking can dramatically improve the clarity and detail in astrophotography.
4.2 What Software Is Commonly Used For Processing Solar System Images?
Popular software includes:
- RegiStax: Free software designed for stacking and processing planetary images.
- AutoStakkert!: Another free option known for its advanced stacking algorithms.
- Adobe Photoshop: Used for final adjustments, color correction, and sharpening.
4.3 How Do You Adjust Color Balance and Sharpen Images?
Adjusting color balance ensures that the planets appear in their natural colors, while sharpening brings out fine details and enhances contrast. These steps require careful adjustments and a good understanding of the software’s tools.
5. Where Can You Find The Best Photos Of The Solar System?
The best photos of the solar system can be found on NASA’s websites, astronomy journals, and astrophotography communities. These sources showcase stunning images captured by both professional and amateur astronomers.
5.1 What Are Some Reputable Sources For High-Quality Images?
- NASA’s Image Galleries: Offer a vast collection of images from various missions and telescopes.
- Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD): Features a different image each day, often showcasing stunning solar system views.
- Space.com: Provides news and images from space exploration and astronomy.
5.2 How Can You Find Images Taken By Amateur Astrophotographers?
Websites like Astrobin and Cloudy Nights host forums and galleries where amateur astrophotographers share their work and techniques. These communities are excellent resources for inspiration and learning.
5.3 Are There Any Ethical Considerations When Sharing Or Using These Photos?
When sharing or using these photos, it’s essential to respect copyright and give credit to the original photographers. Many images are available under Creative Commons licenses, which allow for sharing and adaptation with proper attribution.
6. What Are Some Iconic Photos Of The Solar System?
Iconic photos of the solar system include Voyager 1’s “Pale Blue Dot,” which shows Earth as a tiny speck in the vastness of space, and the first images of Pluto taken by the New Horizons spacecraft.
6.1 What Is The Story Behind The “Pale Blue Dot” Image?
The “Pale Blue Dot” was taken by Voyager 1 in 1990, as it was leaving the solar system. Carl Sagan, the famous astronomer, championed the idea of turning the camera back towards Earth to capture this poignant image. It serves as a reminder of our planet’s fragility and insignificance in the cosmic scale.
 Earth appears as a tiny speck of light suspended in a sunbeam against the vastness of space.
Earth appears as a tiny speck of light suspended in a sunbeam against the vastness of space.
6.2 Why Are The New Horizons Images Of Pluto So Significant?
The New Horizons images of Pluto were the first close-up views of this dwarf planet, revealing its complex surface features, including mountains, glaciers, and plains. These images revolutionized our understanding of Pluto and its place in the solar system.
6.3 What Other Images Have Significantly Impacted Our Understanding Of The Solar System?
Other impactful images include:
- The Pillars of Creation (Eagle Nebula): Captured by the Hubble Space Telescope, showcasing star formation in stunning detail.
- Earthrise: Taken by the Apollo 8 astronauts, showing Earth rising above the lunar horizon, a powerful symbol of our planet’s beauty and fragility.
- Jupiter’s Great Red Spot: Continuous observation of this long-lived storm helps scientists understand atmospheric dynamics.
7. How Has Technology Advanced Solar System Photography?
Technology has revolutionized solar system photography, with advancements in telescopes, cameras, and image processing software enabling astronomers to capture more detailed and stunning images than ever before.
7.1 How Have Telescopes Improved Over Time?
Telescopes have evolved from simple refracting lenses to sophisticated reflecting systems with computer-controlled tracking and adaptive optics. These improvements have significantly increased the resolving power and light-gathering ability of telescopes.
- Larger Apertures: Allow telescopes to collect more light, revealing fainter objects.
- Adaptive Optics: Correct for atmospheric distortion, producing sharper images.
- Computerized Tracking: Precisely follow celestial objects as they move across the sky.
7.2 What Are The Latest Innovations In Astronomical Cameras?
The latest astronomical cameras feature larger sensors, higher resolutions, and lower noise levels, allowing for more detailed and sensitive imaging. Cooled CCD and CMOS cameras are now standard for serious astrophotography.
7.3 How Has Software Enhanced Image Processing?
Software has transformed image processing, with advanced algorithms for stacking, deconvolution, and noise reduction enabling astronomers to extract maximum detail from their images.
8. What Are Some Tips For Aspiring Solar System Photographers?
Aspiring solar system photographers should start with a solid understanding of basic astronomy and photography principles, invest in quality equipment, and practice regularly to hone their skills.
8.1 How Can Beginners Get Started In Astrophotography?
Beginners can start with a simple telescope and camera, focusing on capturing bright objects like the Moon and planets. Joining a local astronomy club can provide valuable guidance and support.
8.2 What Are Some Essential Techniques To Learn?
Essential techniques include:
- Focusing: Achieving precise focus is critical for capturing sharp details.
- Tracking: Compensating for Earth’s rotation to prevent blurring.
- Image Stacking: Combining multiple exposures to reduce noise and enhance detail.
8.3 How Important Is Post-Processing?
Post-processing is crucial for bringing out the best in solar system images. Learning to use software like RegiStax, AutoStakkert!, and Photoshop can dramatically improve the final result.
9. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Photos Of The Solar System?
Common misconceptions include the belief that planets always appear brightly colored and that amateur equipment cannot capture impressive images.
9.1 Do Planets Always Appear As Brightly Colored As They Do In Pictures?
While some planets do have vibrant colors, many appear more subdued to the naked eye. The enhanced colors in many images are achieved through careful processing and are often used to highlight subtle details and atmospheric phenomena.
9.2 Can You Really Capture Good Solar System Photos With Amateur Equipment?
Yes, with the right equipment and techniques, amateur astronomers can capture stunning images of the solar system. Many amateurs have made significant contributions to our understanding of the cosmos.
9.3 Is It Possible To See The True Colors Of Planets With The Naked Eye?
While you can see the general color of some planets with the naked eye (Mars appears reddish, for example), the subtle nuances and details are usually only visible through telescopes and cameras.
10. The Future Of Solar System Photography
The future of solar system photography is bright, with new telescopes, cameras, and techniques promising to reveal even more stunning details and insights into our cosmic neighborhood.
10.1 What New Technologies Are On The Horizon?
New technologies include:
- Extremely Large Telescopes (ELTs): Giant telescopes with unprecedented light-gathering ability and resolving power.
- Advanced Space Telescopes: Next-generation space telescopes designed to observe the universe with greater clarity and sensitivity.
- Improved Adaptive Optics: More sophisticated systems for correcting atmospheric distortion.
10.2 How Will These Advancements Impact Our Understanding Of The Solar System?
These advancements will enable astronomers to study the solar system in greater detail, revealing new insights into planetary formation, atmospheric dynamics, and the potential for life beyond Earth.
10.3 What Role Will AI Play In Future Image Processing?
AI is already playing a role in image processing, with algorithms for automated stacking, deconvolution, and noise reduction. In the future, AI may be able to identify subtle patterns and features in images that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Capturing a photo of the solar system is a challenging but rewarding endeavor that combines art and science. With the right equipment, techniques, and a passion for exploration, anyone can contribute to our understanding and appreciation of the cosmos.
Ready to embark on your own journey into astrophotography? Visit dfphoto.net for in-depth tutorials, gear reviews, and inspiration to capture the wonders of the universe. Explore our extensive collection of breathtaking images and connect with a thriving community of fellow photography enthusiasts. Let’s capture the cosmos together. Contact us at Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
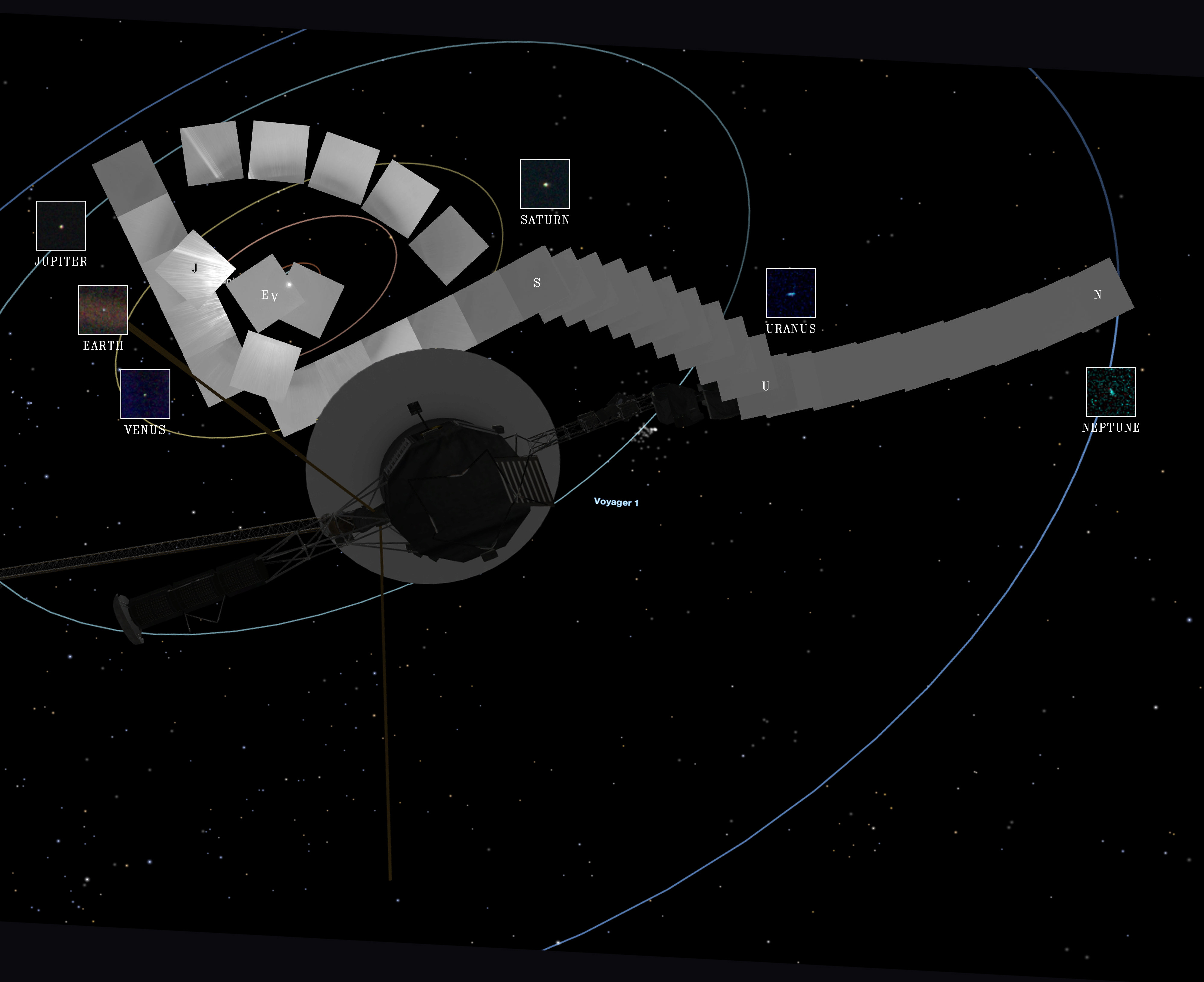 Voyager 1 is superimposed against a background showing the frames that make up the family portrait.
Voyager 1 is superimposed against a background showing the frames that make up the family portrait.
FAQ: Solar System Photography
1. Can I see planets with my naked eye?
Yes, some planets like Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn can be seen without a telescope under the right conditions.
2. What is the best time to photograph the solar system?
The best time is during clear, dark nights when the planets are favorably positioned in the sky.
3. How do I find out when planets are visible?
Astronomy apps and websites can provide information on planetary positions and visibility.
4. Do I need a dark sky to photograph planets?
While a dark sky is ideal, you can still capture planets from moderately light-polluted areas with the right equipment and techniques.
5. What is image stacking, and why is it important?
Image stacking combines multiple images to reduce noise and enhance detail, crucial for revealing faint features.
6. What software is best for processing solar system images?
Popular options include RegiStax, AutoStakkert!, and Adobe Photoshop.
7. How do I compensate for Earth’s rotation during long exposures?
Use a tracking mount to keep celestial objects centered in the frame.
8. Can I use a smartphone to photograph planets?
While challenging, you can capture basic images of bright planets like Venus and Jupiter with a smartphone and a small telescope adapter.
9. Where can I find inspiration for solar system photography?
NASA’s image galleries, astronomy journals, and astrophotography communities are great resources.
10. How can I improve my astrophotography skills?
Practice regularly, join an astronomy club, and study the techniques used by experienced astrophotographers.