Candid photography captures genuine moments, and at dfphoto.net, we help you master this art form to tell authentic stories through your lens. We provide the resources and inspiration needed to excel in natural and unposed photography. Ready to capture life as it unfolds with spontaneous shots and real-life photography?
1. What Exactly Is A Candid Photo?
A Candid Photo is an unposed and spontaneous image, capturing a person or scene in a natural and unrehearsed state. Think of it as a snapshot of real life, revealing genuine emotions and interactions. This differs sharply from posed portraits or staged photography. Candid photography is often referred to as documentary photography, emphasizing its role in visually narrating events as they unfold.
1.1. What Are the Key Characteristics of a Candid Photo?
A candid photograph distinguishes itself through several defining features:
- Spontaneity: Captured in the moment without prior arrangement.
- Naturalness: Subjects are unaware or unconcerned with the camera’s presence.
- Authenticity: Reflects genuine emotions and actions.
- Unposed: Avoids artificial poses or setups.
- Storytelling: Conveys a narrative or captures a fleeting moment in time.
1.2. How Does Candid Photography Differ from Traditional Portraiture?
Candid photography and traditional portraiture sit at opposite ends of the photographic spectrum. Here’s a table highlighting their key differences:
| Feature | Candid Photography | Traditional Portraiture |
|---|---|---|
| Subject Awareness | Often unaware or unbothered | Fully aware and engaged |
| Posing | Unposed, natural actions | Posed, directed by photographer |
| Setting | Real-life environments | Often a studio or carefully selected location |
| Goal | To capture genuine moments | To create a flattering or idealized image |
| Emotion | Authentic, spontaneous feelings | Can be staged or directed |
1.3. What are the Different Types of Candid Photography?
Candid photography spans various genres, each offering a unique lens through which to view the world. Here are a few notable types:
- Street Photography: Capturing everyday life in public spaces, often focusing on the interactions and emotions of people in urban environments.
- Documentary Photography: Aiming to record historical events or social issues, providing a visual record of significant moments in time.
- Photojournalism: Similar to documentary photography but often focuses on news events and current affairs, telling stories through images.
- Wedding Photography: Capturing unscripted moments during a wedding, preserving the emotions and events of the day in a natural way.
- Event Photography: Covering various events, from corporate gatherings to parties, focusing on candid interactions and key moments.
1.4. Why Is Candid Photography So Popular?
Candid photography resonates with people for its ability to capture authentic moments and emotions. In a world saturated with staged and filtered images, candid shots offer a refreshing glimpse into reality. Viewers connect with the genuine feelings and unrehearsed interactions depicted in these photographs.
2. What Are The Essential Techniques for Taking a Great Candid Photo?
Mastering candid photography requires a blend of technical skill and an eye for capturing authentic moments. Here’s a breakdown of essential techniques:
2.1. Understanding Your Camera Settings
- Aperture: Use a wide aperture (low f-number like f/1.8 or f/2.8) to create a shallow depth of field, which helps isolate your subject from the background.
- Shutter Speed: Choose a fast shutter speed (at least 1/200th of a second) to freeze motion and prevent blur, especially in dynamic environments.
- ISO: Adjust your ISO to balance image brightness and noise. Keep it as low as possible (ISO 100-400 in good light) to minimize graininess.
- Shooting Mode: Aperture Priority mode allows you to control the depth of field while the camera automatically adjusts the shutter speed. Manual mode gives you full control over both aperture and shutter speed, ideal for consistent lighting conditions.
2.2. Mastering the Art of Blending In
- Dress Appropriately: Avoid drawing attention to yourself by wearing neutral colors and comfortable clothing.
- Move Slowly and Deliberately: Sudden movements can alert your subjects and disrupt natural behavior.
- Use a Quiet Camera: Cameras with silent shutter options are ideal for candid photography as they minimize distractions.
- Be Respectful: Always be mindful of your subjects and avoid intruding on private moments.
2.3. Anticipating and Capturing the Moment
- Observe Your Surroundings: Pay attention to the environment and the interactions happening around you.
- Predict Key Moments: Anticipate potential emotional peaks or significant actions.
- Be Ready to Shoot: Keep your camera settings pre-adjusted and your finger on the shutter button.
- Shoot in Burst Mode: Capture a series of shots to increase your chances of getting the perfect moment.
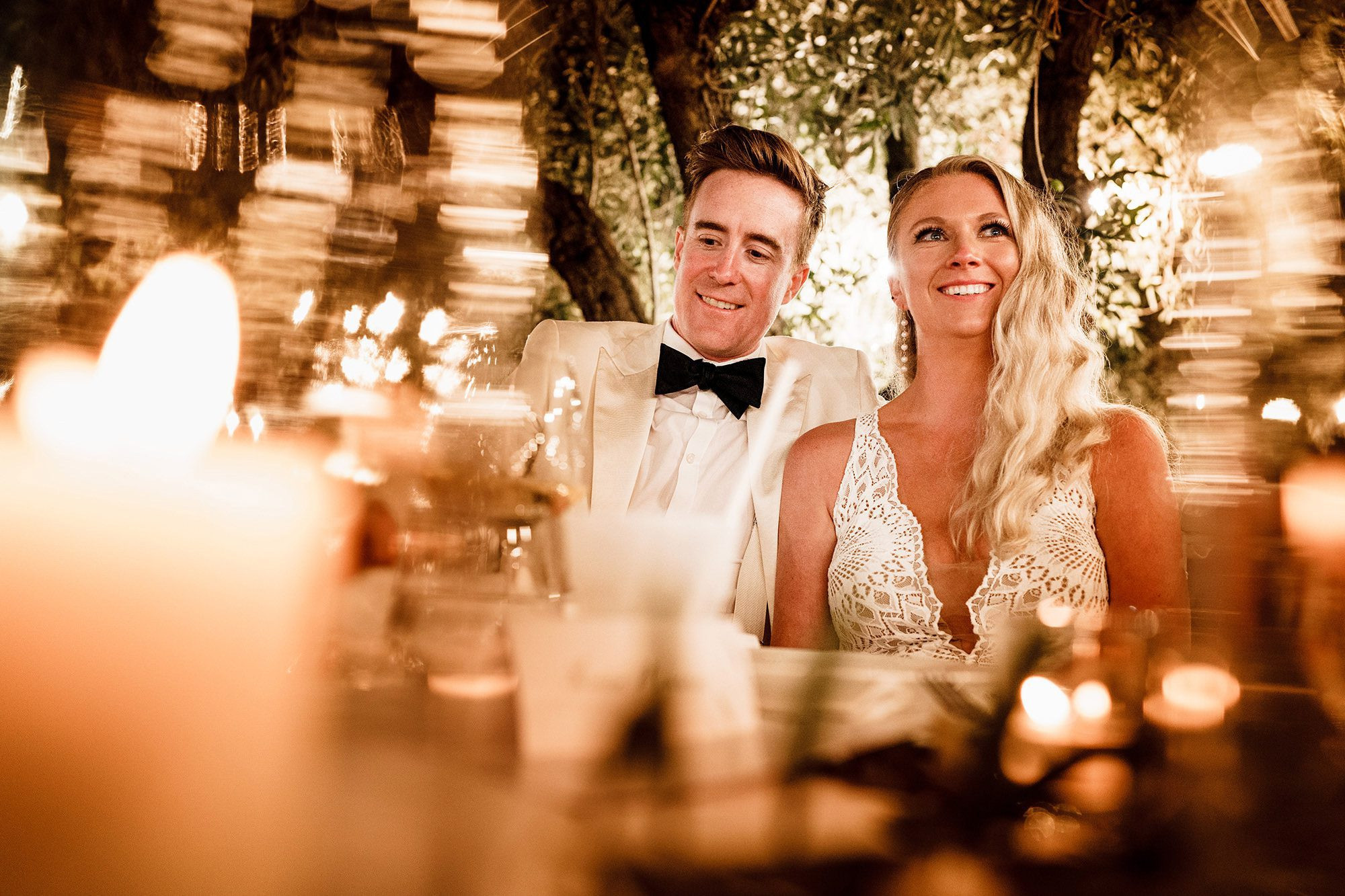 Candid wedding photography of a couple in Italy, capturing the natural joy and spontaneity of their destination wedding
Candid wedding photography of a couple in Italy, capturing the natural joy and spontaneity of their destination wedding
2.4. Using Natural Light Effectively
- Golden Hour: Shoot during the golden hour (shortly after sunrise and before sunset) for warm, soft light that enhances skin tones and adds a magical touch.
- Open Shade: Look for areas with open shade to avoid harsh shadows and create even lighting.
- Diffused Light: Overcast days or shaded areas provide naturally diffused light that minimizes harsh shadows.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Direct sunlight can create unflattering shadows and cause subjects to squint.
2.5. The Importance of Composition
- Rule of Thirds: Divide your frame into nine equal parts with two horizontal and two vertical lines, placing key elements along these lines or at their intersections.
- Leading Lines: Use lines to draw the viewer’s eye towards your subject.
- Framing: Use elements in the foreground to frame your subject and add depth to your image.
- Fill the Frame: Get close to your subject to eliminate distractions and emphasize their emotions.
2.6. Post-Processing Tips for Candid Photos
- Subtle Adjustments: Make subtle adjustments to exposure, contrast, and white balance to enhance the natural look of your photos.
- Color Correction: Correct any color imbalances to ensure accurate skin tones and natural colors.
- Sharpening: Apply a touch of sharpening to enhance details, but avoid over-sharpening, which can make the image look artificial.
- Cropping: Use cropping to improve composition or remove distracting elements.
3. What Equipment Do You Need for Candid Photography?
Selecting the right equipment can significantly enhance your ability to capture stunning candid photos. Here’s a guide to essential gear:
3.1. Choosing the Right Camera
- DSLRs and Mirrorless Cameras: Offer excellent image quality, fast autofocus, and interchangeable lenses, making them ideal for candid photography.
- Compact Cameras: Provide a more discreet option with good image quality and portability, perfect for blending into crowds.
- Smartphones: Modern smartphones boast impressive camera capabilities and are incredibly convenient for capturing spontaneous moments.
3.2. Selecting the Best Lenses
- Prime Lenses (35mm, 50mm, 85mm): Offer wide apertures for shallow depth of field and excellent low-light performance, ideal for isolating subjects.
- Zoom Lenses (24-70mm, 70-200mm): Provide versatility for capturing both wide scenes and close-up moments without changing lenses.
3.3. The Importance of a Good Flash (or Lack Thereof)
- Natural Light: Rely on natural light whenever possible to maintain the authenticity of candid shots.
- External Flash: Use an external flash sparingly and with diffusion to soften the light and avoid harsh shadows.
- Flash Modifiers: Utilize diffusers or bounce flash techniques to create more natural-looking light.
3.4. Essential Accessories for Candid Photography
- Extra Batteries: Ensure you have enough power to last through long shooting sessions.
- Memory Cards: Carry multiple high-capacity memory cards to avoid running out of storage space.
- Camera Bag: Choose a comfortable and discreet camera bag to carry your gear.
3.5. Recommended Camera and Lens Combinations for Candid Photography
| Camera Type | Lens Recommendation | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mirrorless | Sony 50mm f/1.8 | Lightweight, excellent image quality, great low-light performance | Limited focal length |
| DSLR | Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8L II USM | Versatile zoom range, fast aperture, professional-grade quality | Can be heavy and expensive |
| Compact | Sony RX100 Series | Pocket-sized, excellent image quality, built-in zoom lens | Smaller sensor compared to DSLRs and mirrorless cameras |
4. Where Can You Find Inspiration for Candid Photography?
Finding inspiration is crucial to developing your unique style and vision in candid photography. Here are some resources to fuel your creativity:
4.1. Following Renowned Candid Photographers
- Henri Cartier-Bresson: A pioneer of candid photography, known for his decisive moment and capturing fleeting moments with precision.
- Garry Winogrand: Celebrated for his street photography, portraying the energy and chaos of urban life.
- Diane Arbus: Famous for her portraits of marginalized individuals, capturing raw and intimate moments.
4.2. Exploring Online Photography Communities
- Flickr: A platform for sharing and discovering photographs, offering a vast collection of candid images from photographers worldwide.
- Instagram: A visual social media platform where you can follow photographers and discover new trends in candid photography.
- 500px: A premium photography community showcasing high-quality images and offering opportunities for feedback and recognition.
4.3. Studying Photo Essays and Documentary Projects
- Magnum Photos: A renowned photo agency featuring documentary photography and photojournalism from around the world.
- National Geographic: Known for its compelling visual storytelling, covering a wide range of topics from culture to nature.
- The New York Times Lens Blog: Showcasing photo essays and documentary projects from talented photographers, providing insights into various subjects.
4.4. Visiting Art Galleries and Photography Exhibitions
- The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA), New York: Features a vast collection of photography, including iconic candid images. Address: 11 W 53rd St, New York, NY 10019, United States. Phone: +1 (212) 708-9400. Website: moma.org.
- The International Center of Photography (ICP), New York: Dedicated to photography and visual culture, offering exhibitions, education, and public programs. Address: 79 Essex St, New York, NY 10002, United States. Phone: +1 (212) 857-0001. Website: icp.org.
- The Getty Center, Los Angeles: Features a notable photography collection, showcasing works from various periods and styles. Address: 1200 Getty Center Dr, Los Angeles, CA 90049, United States. Phone: +1 (310) 440-7300. Website: getty.edu.
4.5. Reading Photography Books and Magazines
- Aperture Magazine: A quarterly publication featuring contemporary photography and critical writing, offering insights into the art and practice of photography.
- Magnum Contact Sheets: A book showcasing the contact sheets of Magnum photographers, revealing the process behind iconic images.
- The Decisive Moment by Henri Cartier-Bresson: A classic book on candid photography, illustrating the importance of capturing the perfect moment.
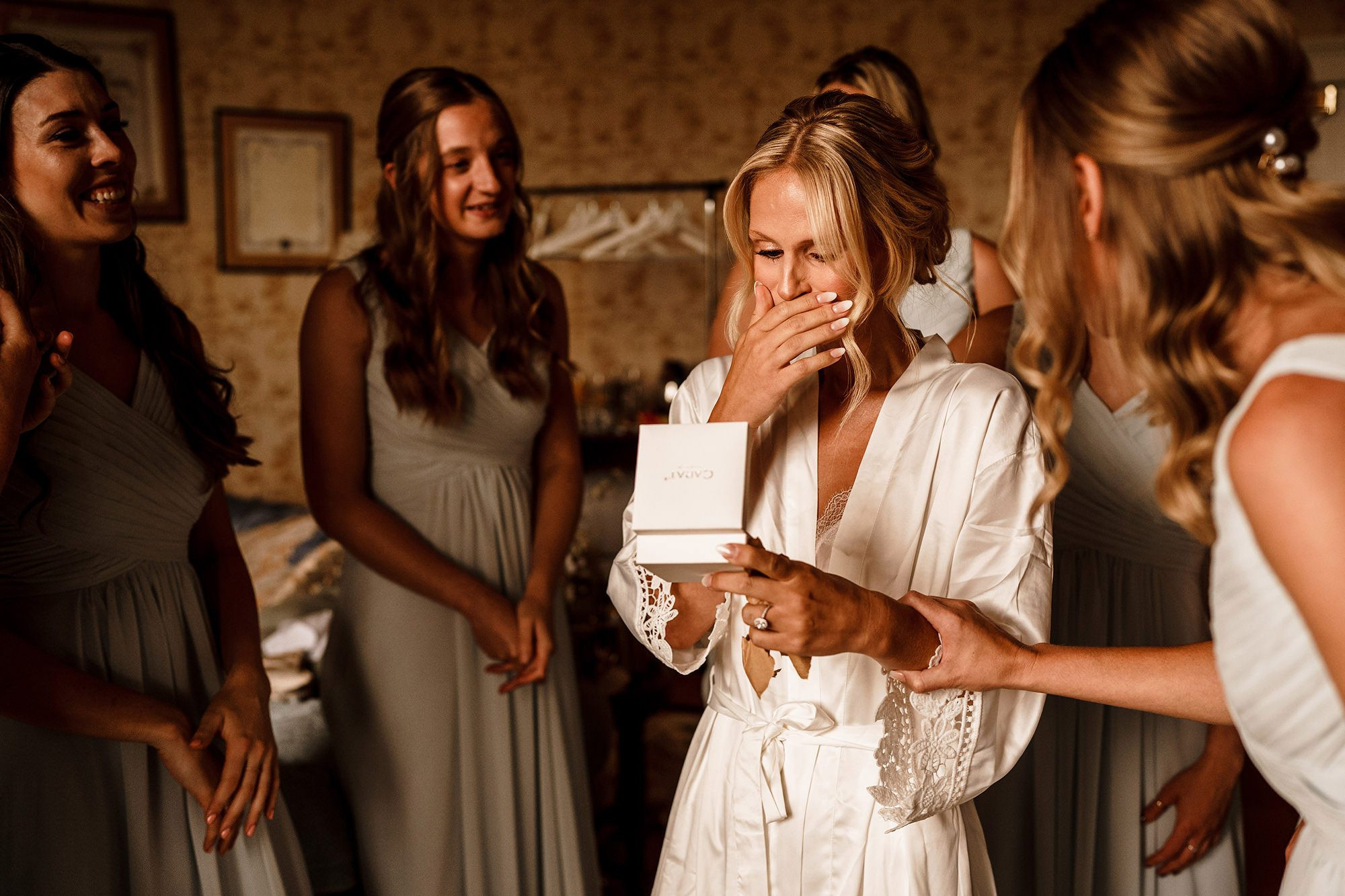 A candid moment of a bride opening her wedding gift, showcasing genuine surprise and emotion in a natural setting
A candid moment of a bride opening her wedding gift, showcasing genuine surprise and emotion in a natural setting
5. What Are Some Ethical Considerations in Candid Photography?
While candid photography captures authentic moments, it’s essential to consider the ethical implications of photographing people without their explicit consent. Here are some key considerations:
5.1. Respecting Privacy and Personal Space
- Public vs. Private: Be mindful of the location and whether it is considered a public or private space.
- Intrusive Behavior: Avoid photographing people in situations where they have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as inside their homes.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect local customs and traditions regarding photography, especially in culturally sensitive areas.
5.2. Obtaining Consent When Necessary
- When to Ask: If you plan to use a candid photograph for commercial purposes or display it prominently, it’s best to obtain consent from the subject.
- How to Ask: Approach the subject politely, explain your intentions, and be prepared to respect their decision if they decline.
- Model Releases: Use model release forms for commercial projects to ensure you have the legal right to use the images.
5.3. Avoiding Exploitation and Misrepresentation
- Vulnerable Individuals: Exercise caution when photographing vulnerable individuals, such as children, the elderly, or those in distress.
- Contextual Integrity: Ensure that the context in which the photograph is presented does not misrepresent the subject or exploit their situation.
- Stereotypes: Avoid perpetuating stereotypes or using images in a way that could be discriminatory or offensive.
5.4. Legal Rights and Restrictions
- Public Spaces: In many countries, it is generally legal to photograph people in public spaces, but there may be restrictions on photographing certain subjects or in specific locations.
- Private Property: Photographing people on private property may require permission from the property owner.
- Defamation: Be aware of defamation laws and avoid publishing images that could harm a person’s reputation.
6. Candid Photography in Different Genres
Candid photography techniques can be applied across various genres, each offering unique opportunities and challenges.
6.1. Candid Wedding Photography: Capturing Authentic Moments
- Documenting the Day: Focus on capturing the natural flow of events, from the bride getting ready to the couple’s first dance.
- Emotional Moments: Be ready to capture spontaneous emotional moments, such as tears of joy, heartfelt speeches, and loving glances.
- Unobtrusive Approach: Blend into the background and avoid disrupting the natural interactions between guests.
- Candid Posed Shots: Use natural backgrounds while also capturing the posed family photos.
- Storytelling: Documenting is a key element of a fantastic wedding album.
6.2. Street Candid Photography: Documenting City Life
- Urban Landscapes: Explore the streets of cities and capture interesting people, interactions, and scenes that reflect the city’s culture and atmosphere.
- Decisive Moments: Watch for fleeting moments that tell a story or capture a unique aspect of city life.
- Blending In: Dress like a local and avoid drawing attention to yourself to capture more natural shots.
- Patience: Taking candid photos on the street requires a lot of patience and the ability to wait for the right moment.
6.3. Candid Portrait Photography: Capturing Authentic Personalities
- Environmental Portraits: Photograph people in their natural environments, whether it’s their home, workplace, or favorite hangout spot.
- Unposed Interactions: Engage with your subject in conversation and capture their natural expressions and gestures.
- Relaxed Atmosphere: Create a relaxed and comfortable atmosphere to help your subject feel at ease and be themselves.
- Connect: If you can connect with people then you will be able to put them at ease.
6.4. Candid Event Photography: Documenting Special Occasions
- Key Moments: Focus on capturing the key moments of the event, such as speeches, performances, and award presentations.
- Guest Interactions: Photograph guests interacting with each other, capturing their excitement and enjoyment.
- Behind-the-Scenes: Capture behind-the-scenes moments that give a glimpse into the event’s preparation and atmosphere.
- Always Be Ready: You never know when a memory will be made, therefore, always be ready to capture the moment.
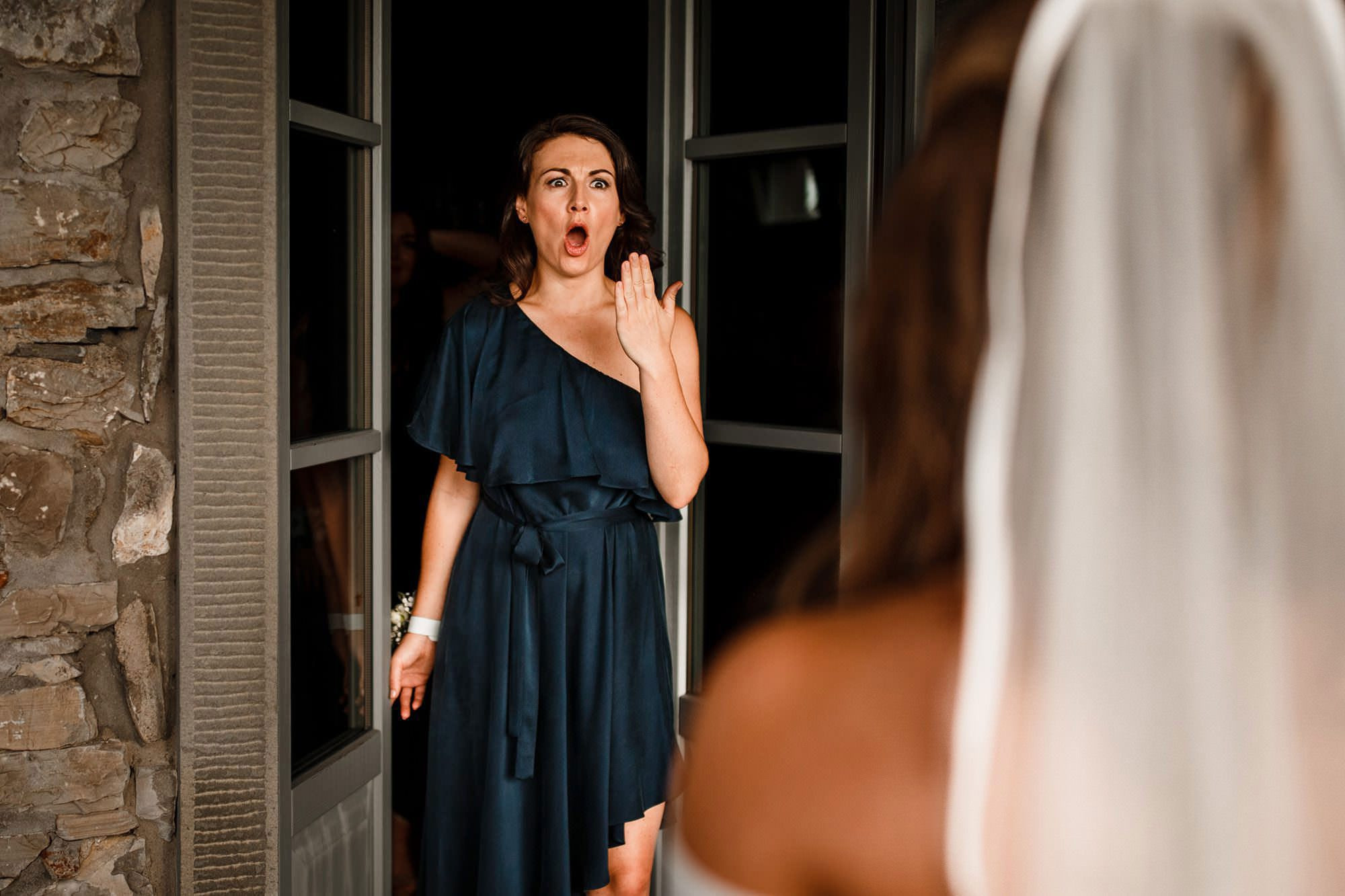 Candid wedding photography of a bride with her bridesmaids, showcasing a genuine moment of joy and camaraderie
Candid wedding photography of a bride with her bridesmaids, showcasing a genuine moment of joy and camaraderie
7. What Are The Best Camera Settings For Candid Photography?
Mastering camera settings is essential for capturing high-quality candid photos in various situations. Here’s a guide to help you optimize your settings:
7.1. Aperture Priority Mode (Av or A)
- When to Use: Ideal for controlling depth of field, allowing you to blur backgrounds or keep everything in focus.
- Settings: Set your desired aperture (e.g., f/2.8 for shallow depth of field or f/8 for landscapes) and let the camera automatically adjust the shutter speed.
7.2. Shutter Priority Mode (Tv or S)
- When to Use: Ideal for freezing motion or creating motion blur, depending on your creative vision.
- Settings: Set your desired shutter speed (e.g., 1/200th of a second to freeze motion or 1/30th of a second for motion blur) and let the camera automatically adjust the aperture.
7.3. Manual Mode (M)
- When to Use: Ideal for consistent lighting conditions where you want full control over both aperture and shutter speed.
- Settings: Manually set both aperture and shutter speed based on your desired exposure and creative vision.
7.4. ISO Settings for Different Lighting Conditions
- Bright Sunlight (ISO 100-200): Keep ISO low to minimize noise and maximize image quality.
- Overcast Days (ISO 400-800): Increase ISO to compensate for lower light levels while maintaining a fast shutter speed.
- Indoor Lighting (ISO 800-3200+): Increase ISO further to capture images in dimly lit environments, but be mindful of noise levels.
7.5. Focusing Techniques for Candid Photography
- Single-Point Autofocus: Use a single autofocus point to precisely focus on your subject’s eyes or other key areas.
- Continuous Autofocus (AF-C or AI Servo): Use continuous autofocus to track moving subjects and keep them in focus.
- Back-Button Focus: Assign autofocus to a button on the back of your camera to separate focusing from the shutter release, giving you more control over focus.
7.6. Metering Modes for Candid Photography
- Evaluative Metering (Matrix Metering): The camera analyzes the entire scene and calculates the exposure based on the average light levels.
- Spot Metering: The camera measures the light only in a small area around your focus point, ideal for high-contrast situations.
- Center-Weighted Metering: The camera measures the light primarily in the center of the frame, with less emphasis on the edges.
8. How Can You Improve Your Candid Photography Skills?
Improving your candid photography skills requires practice, patience, and a willingness to learn from your experiences. Here are some actionable steps to help you hone your skills:
8.1. Practice Regularly
- Daily Shooting: Commit to taking at least a few candid photos every day to develop your eye and improve your timing.
- Diverse Environments: Practice shooting in different environments, from bustling city streets to quiet parks, to challenge yourself and expand your skills.
- Themed Projects: Create themed projects, such as “A Day in the Life” or “People at Work,” to focus your efforts and develop a cohesive body of work.
8.2. Seek Feedback and Critique
- Photography Groups: Join local photography groups or online forums to share your work and receive constructive feedback from other photographers.
- Online Communities: Participate in online photography communities, such as Flickr or 500px, to showcase your images and receive comments and critiques.
- Mentorship: Seek out a mentor who can provide guidance and support as you develop your skills.
8.3. Analyze Your Own Work
- Review Your Images: Regularly review your images and identify what works well and what could be improved.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns in your successes and failures to understand your strengths and weaknesses.
- Keep a Journal: Keep a journal to record your thoughts, observations, and lessons learned from each shooting session.
8.4. Take Workshops and Classes
- Local Workshops: Attend local photography workshops to learn new techniques and receive hands-on instruction from experienced photographers.
- Online Courses: Enroll in online photography courses to learn at your own pace and expand your knowledge on specific topics.
- University Programs: Consider taking photography classes at a local university or community college to gain a more formal education in photography.
- Santa Fe University of Art and Design: According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, P provides Y.
8.5. Experiment with Different Styles and Techniques
- Try New Approaches: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different styles and techniques to find what works best for you.
- Push Your Boundaries: Push your boundaries by trying new things and challenging yourself to step outside of your comfort zone.
- Find Your Voice: Develop your unique voice and style by incorporating your personal interests and perspective into your photography.
8.6. Stay Inspired and Motivated
- Visit Galleries: Regularly visit art galleries and photography exhibitions to see the work of other photographers and gain inspiration.
- Read Books: Read books and magazines on photography to learn about different styles, techniques, and photographers.
- Follow Blogs: Follow photography blogs and websites to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and techniques.
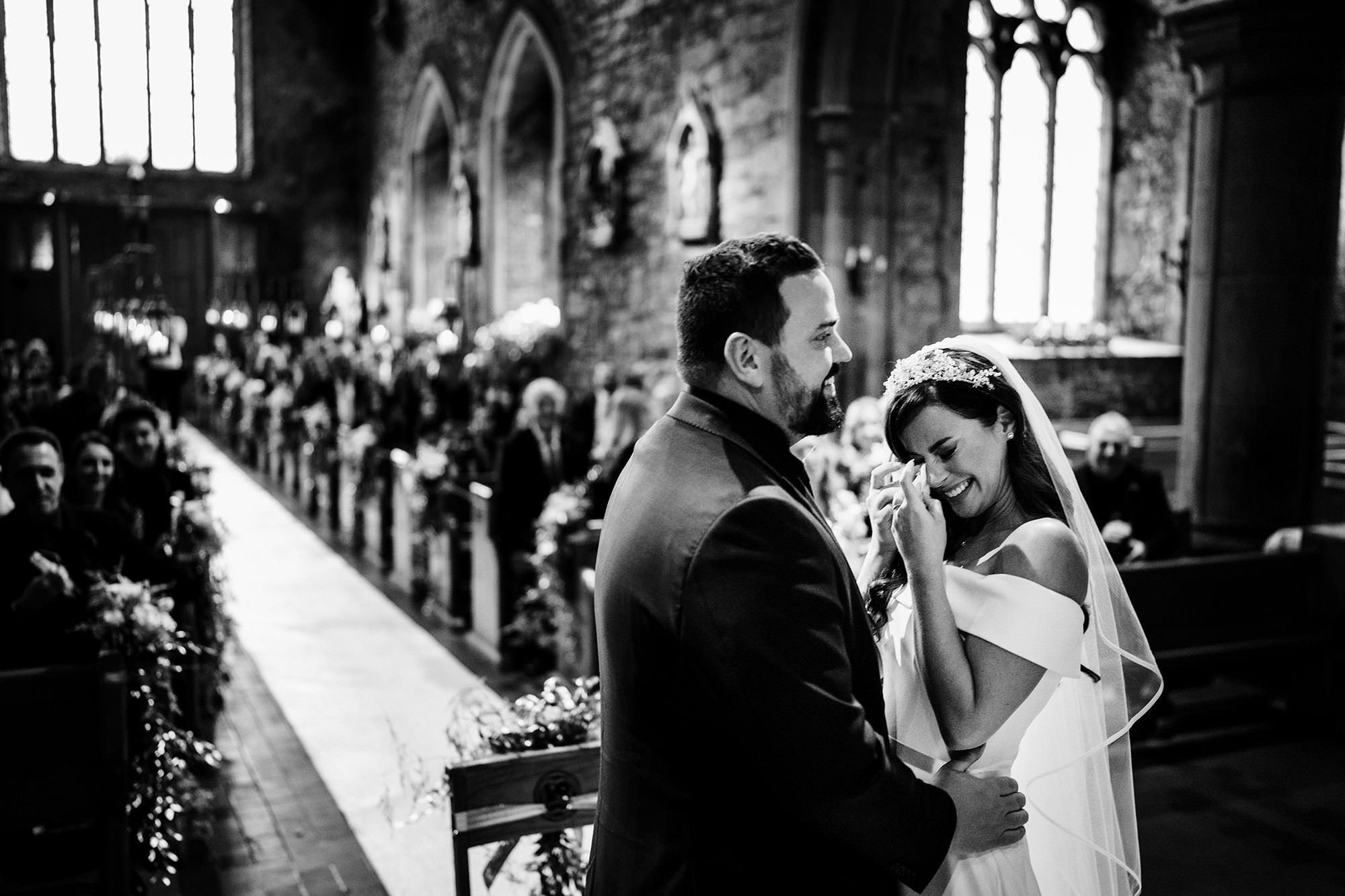 Candid moment captured at Adare Manor of a bride and groom, showcasing natural affection and joy
Candid moment captured at Adare Manor of a bride and groom, showcasing natural affection and joy
9. Candid Photography Tips for Beginners
Starting out in candid photography can feel daunting, but with the right guidance, you can quickly develop your skills and capture stunning, authentic moments. Here are some essential tips for beginners:
9.1. Start with a Simple Setup
- Basic Camera: Begin with a basic camera, such as a smartphone or entry-level DSLR or mirrorless camera, to learn the fundamentals of photography.
- Prime Lens: Use a prime lens, such as a 50mm f/1.8, to develop your eye for composition and depth of field.
- Minimal Gear: Keep your gear to a minimum to stay mobile and avoid drawing attention to yourself.
9.2. Focus on Composition and Lighting
- Rule of Thirds: Use the rule of thirds to create balanced and visually appealing compositions.
- Natural Light: Utilize natural light whenever possible to create soft, flattering images.
- Avoid Backlighting: Avoid shooting directly into the sun, which can create harsh shadows and cause your subject to squint.
9.3. Be Patient and Observant
- Wait for the Moment: Be patient and wait for the right moment to capture a genuine expression or interaction.
- Observe Your Surroundings: Pay attention to the environment and the people around you to anticipate potential photo opportunities.
- Stay Hidden: Stay hidden or blend into the background to avoid alerting your subjects to your presence.
9.4. Take Lots of Photos
- Practice Makes Perfect: The more photos you take, the better you will become at anticipating and capturing candid moments.
- Experiment with Angles: Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find unique and interesting compositions.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Fail: Don’t be afraid to make mistakes and learn from your experiences.
9.5. Edit Your Photos Carefully
- Subtle Adjustments: Make subtle adjustments to exposure, contrast, and white balance to enhance the natural look of your photos.
- Crop for Composition: Crop your photos to improve composition or remove distracting elements.
- Sharpen Sparingly: Sharpen your photos sparingly to enhance details without making them look artificial.
9.6. Get to Know Your Camera
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with your camera’s features and functions by reading the manual.
- Experiment with Settings: Experiment with different settings to understand how they affect your images.
- Practice in Different Modes: Practice shooting in different modes, such as aperture priority, shutter priority, and manual mode, to gain full control over your camera.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Candid Photography
10.1. What is the difference between candid and posed photography?
Candid photography involves capturing spontaneous, unposed moments, while posed photography involves directing subjects to create a specific image.
10.2. What equipment is best for candid photography?
A camera with good low-light performance and a fast lens (e.g., 50mm f/1.8) is ideal. A discreet camera bag and extra batteries are also essential.
10.3. How can I blend in while taking candid photos?
Dress casually, move slowly, and avoid making direct eye contact. Use a quiet camera and be respectful of your subjects.
10.4. What are the best camera settings for candid photography?
Use aperture priority mode with a wide aperture (e.g., f/2.8) for shallow depth of field. Adjust ISO as needed for proper exposure.
10.5. How can I improve my timing for candid shots?
Practice regularly, observe your surroundings, and anticipate key moments. Shoot in burst mode to increase your chances of capturing the perfect shot.
10.6. What are some ethical considerations in candid photography?
Respect privacy, obtain consent when necessary, and avoid exploitation or misrepresentation. Be aware of local laws and customs.
10.7. How can I find inspiration for candid photography?
Follow renowned candid photographers, explore online photography communities, and study photo essays and documentary projects.
10.8. How do I handle low-light situations in candid photography?
Use a fast lens, increase ISO, and stabilize your camera with a tripod or monopod. Consider using an external flash with diffusion.
10.9. How important is post-processing in candid photography?
Subtle post-processing adjustments can enhance the natural look of candid photos. Focus on exposure, contrast, white balance, and sharpening.
10.10. Can I take candid photos with my smartphone?
Yes, modern smartphones have excellent camera capabilities and are great for capturing spontaneous moments. Use the tips above to optimize your settings and technique.
Visit dfphoto.net today to discover more insightful articles, stunning photo galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers. Whether you’re looking to master new techniques, find inspiration, or connect with fellow enthusiasts, dfphoto.net is your ultimate resource for all things photography. Start your journey now and capture the world through your unique lens! Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.