In today’s digital age, creatives and marketers handle a vast number of images daily for various purposes. Organizing and searching through these large collections can quickly become overwhelming. Fortunately, photo metadata provides an efficient solution. Just like the index and chapter titles in a book guide you through its content, photo metadata offers key information embedded within your image files, making them easily searchable and manageable. This guide will explore How To Get Metadata From Photos, understand its importance, and leverage it to streamline your workflow.
Understanding Photo Metadata
Photo metadata is essentially hidden information nestled within a digital image file. It contains a wealth of details about the photo, ranging from technical specifications to descriptive content and copyright information. Think of it as the behind-the-scenes details that make managing your photo library much easier.
By accessing photo metadata, you can efficiently organize, sort, and locate specific images within your extensive collection. It typically includes elements such as:
- Date and time of creation
- Author or photographer
- File name
- Description of the content
- Image size (in bits and pixels)
- Keywords or tags
- GPS coordinates (location information)
- Camera settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture, focal length)
- Copyright details
Pro Tip: Metadata, in its simplest form, is “data about data.” It provides context and information that describes other data, making it more understandable and usable. To delve deeper into the concept of metadata, explore what metadata is.
Exploring the Categories of Metadata
Metadata isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s categorized into distinct types, each serving a unique purpose. Understanding these categories helps you appreciate the depth and breadth of information metadata can provide.
1. Descriptive Metadata
Descriptive metadata is designed to facilitate the discovery and identification of resources. It includes details like titles, abstracts, authors, and keywords. This type of metadata is widely used in libraries, museums, and digital asset management systems. By using descriptive metadata, users can effectively search and browse to find the information or images they need.
2. Structural Metadata
Structural metadata focuses on the organization and format of a resource. It clarifies how complex objects are structured. For instance, it can define the page order in a book’s chapters or the relationships between different images, texts, and datasets. This is especially vital for digital resources, enabling systems to effectively display and navigate intricate data collections.
3. Administrative Metadata
Administrative metadata provides essential details for managing a resource, including its creation specifics (time and method), file format, and access rights. It can be further broken down into sub-types:
- Technical Metadata: This covers the technical aspects of a resource, such as file types, compression methods, and file sizes. It’s crucial for digital preservation and ensuring long-term access to digital files.
- Preservation Metadata: This type of metadata is vital for maintaining and preserving digital resources over time. It includes details about the history and condition of a digital object and any preservation actions taken.
- Rights Metadata: This provides information about intellectual property rights and usage restrictions. It helps organizations manage the legal aspects of using digital assets.
By effectively organizing and utilizing these metadata categories, individuals and organizations can ensure the efficient use, management, and long-term preservation of their valuable information resources.
Common Photo Metadata Formats
Several formats exist for storing photo metadata, each with specific capabilities and industry applications. Knowing these formats can be helpful when working with different types of images and software.
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format)
EXIF is a standard format for storing interchange information in digital photography. It’s commonly used to record camera settings like shutter speed, aperture, ISO, date, and time, along with image details such as orientation.
IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council)
Developed for the press industry, IPTC metadata is designed for cataloging and exchanging media. It covers a broad spectrum of details, including copyright information, creator details, contact information, and content descriptions.
XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform)
Adobe created XMP as a versatile framework for handling both standardized and proprietary metadata. Embedded directly into digital image files, XMP can store a wide range of information, from basic metadata to comprehensive rights management details.
DNG (Digital Negative)
DNG, another Adobe creation, is a raw image file format designed for digital photography. DNG metadata encompasses all EXIF information plus additional details specific to raw files, such as camera calibration data.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
TIFF is primarily used for storing raster graphics and images. TIFF files can include diverse metadata types stored as tags, describing image dimensions, resolution, and data arrangement, among other properties.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a raster graphics file format known for lossless data compression. PNG files can contain metadata like textual information (titles, author, descriptions) and image-specific data such as gamma values, color profiles, and transparency information.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is a widely used lossy compression technique for digital images. JPEG files can include EXIF, XMP, and ICC profile data, providing a broad range of information from camera settings to copyright and licensing details.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
GIF is a bitmap image format that supports animations. While GIF files can include simple textual metadata, their capacity for detailed metadata is less extensive than other formats.
Each format has its strengths and limitations, influencing the type and amount of metadata it can store and how it’s used in different workflows.
The Importance of Photo Metadata
Why should you care about photo metadata? It offers significant benefits for anyone working with digital images.
Organization: Metadata enables you to categorize images based on location, keywords, and other criteria. This makes navigating large image collections significantly easier and more efficient.
Searchability: Descriptive tags and keywords embedded in metadata allow you to quickly find specific images without manually browsing through thousands of files or relying on generic file names.
Copyright Management: Embedding copyright information in metadata protects your rights as the image owner and clearly defines usage guidelines, crucial for professional photographers and content creators.
Technical Analysis: Photographers and editors can leverage camera setting metadata to analyze past shoots, inform post-processing decisions, and improve techniques for future projects.
Context: Metadata preserves essential details about an image, such as when and where it was taken, maintaining the historical and contextual value of the photo over time.
Now, let’s get to the core question: how to get metadata from photos. The process is quite simple and varies slightly depending on your operating system.
How to Access and View Photo Metadata on Mac
For Mac users, accessing file metadata is a straightforward process integrated into the operating system:
- Locate the Image: Open ‘Finder’ and find the image file you want to examine.
- Right-Click (or Control-Click): Highlight the image file, then right-click (or Control-click) on it.
- Select ‘Get Info’: From the context menu, choose the ‘Get Info’ option.
- Explore the Information Window: A new window will appear, displaying various details about the image. You can navigate through different tabs at the top of this window to find the specific metadata you need.
 Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background.
Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background.
Pro Tip: To enhance your metadata viewing capabilities, consider using dedicated photo metadata viewer tools. We’ve tested several and compiled a list of ten that offer excellent features and functionality.
How to Access and View Photo Metadata on Windows
Accessing photo metadata on Windows is equally simple:
- Locate the Image: Find the digital image file on your Windows computer.
- Right-Click: Right-click on the image file.
- Select ‘Properties’: From the context menu, choose ‘Properties’. A new window will pop up.
- Go to the ‘Details’ Tab: In the Properties window, click on the ‘Details’ tab located at the top.
- Scroll to View Metadata: Scroll down through the ‘Details’ tab to find and view the various metadata categories associated with your image.
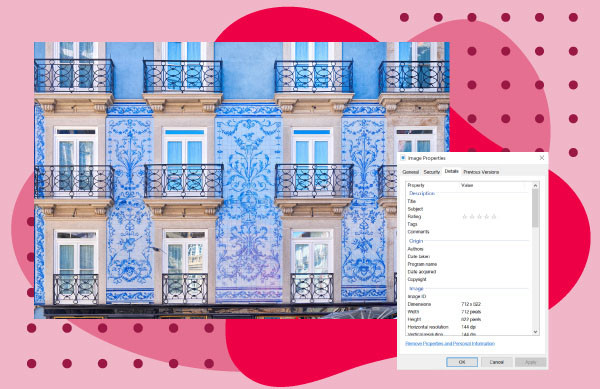 Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background.
Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background.
Pro tip: Viewing metadata in different file formats can sometimes be challenging. Exploring dedicated metadata viewer tools can provide more comprehensive support for various file types and offer enhanced viewing options.
Editing Photo Metadata
Beyond simply viewing metadata, you can also edit it to correct errors, add information, or customize your image organization.
Yes, image metadata is editable. Whether you’re using a Mac or Windows system, the process is quite similar to accessing the metadata:
- Navigate to Metadata: Follow the steps described above to access the metadata of the image you want to edit (using ‘Get Info’ on Mac or ‘Properties’ then ‘Details’ on Windows).
- Locate the Category to Edit: Identify the metadata category you want to change (e.g., name, date, author, keywords).
- Edit the ‘Value’ Field: Underneath the ‘Value’ column for the chosen category, you’ll find an editable field. Simply click in this field and type in the new information.
Using a Metadata Editor for Advanced Tasks
While manual editing within your operating system is convenient for minor changes, dedicated metadata editor software offers more advanced capabilities, especially when dealing with large batches of images or complex editing tasks.
Reasons to use a metadata editor include:
- Batch Editing: Efficiently edit metadata for multiple images simultaneously, saving significant time.
- Advanced Features: Access more sophisticated editing options and metadata fields than those available in basic operating system tools.
- Format Support: Ensure compatibility with a wider range of image file formats and metadata standards.
- Workflow Efficiency: Streamline metadata management as part of a professional photography or content creation workflow.
Users often need to edit metadata to fill in missing fields, correct inaccuracies, or add specific details like titles or keywords that weren’t automatically included. Conversely, some users need to remove metadata from photos for privacy reasons before sharing images online, especially on social media platforms.
Regardless of your specific needs, when editing metadata, it’s always wise to be methodical and maintain backups of your original files until you’re satisfied with the changes.
Digital Asset Management (DAM) Platforms and Metadata
For organizations managing vast libraries of digital assets, including images, Digital Asset Management (DAM) platforms provide a centralized and powerful solution. DAM systems are designed to manage, organize, and distribute digital content effectively.
A DAM platform like Canto excels at storing and managing digital assets such as images, videos, documents, and more. It empowers users to easily organize, search, retrieve, and share these assets, significantly improving workflow efficiency and team collaboration. DAM systems are essential for overcoming the content chaos that arises from today’s high demands for image and digital content production.
DAM software offers robust metadata management features, enabling you to:
- Manage Metadata: Efficiently view, edit, and standardize metadata across your entire image library.
- Search with Metadata: Utilize metadata to perform advanced searches and quickly locate specific assets based on various criteria.
- Automate Metadata Processes: Automate metadata tagging and organization to streamline workflows.
- Visualize Content: View image thumbnails and previews for easy content identification.
Managing Metadata with Canto: A Practical Example
Let’s illustrate how Canto simplifies metadata management:
- Keyword Search: Type your search terms into Canto’s search bar to initiate a metadata-driven search.
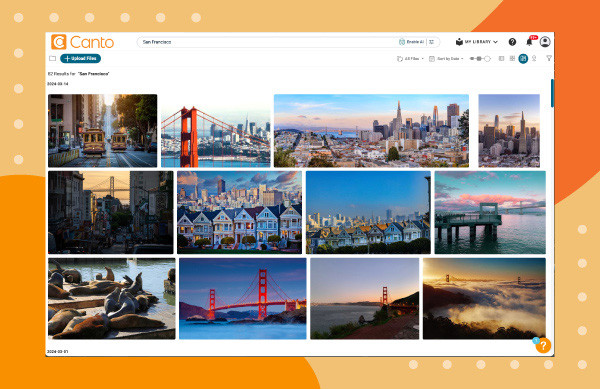 A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background.
A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background.
- Filter and Refine: Use the filter pane on the right side to narrow down your search based on specific metadata criteria.
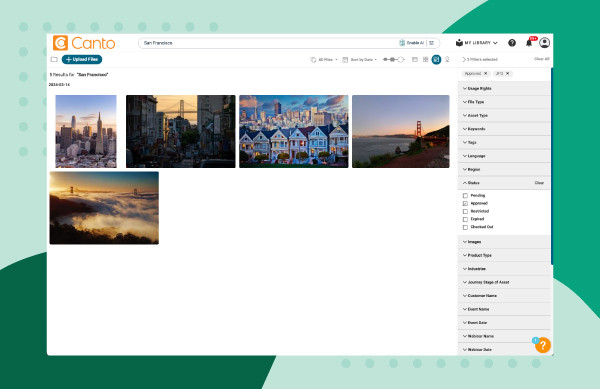 Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background.
Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background.
- View Embedded Metadata: Click on an image to display its embedded metadata in the right pane. For a comprehensive view, click the double arrows to show all metadata fields.
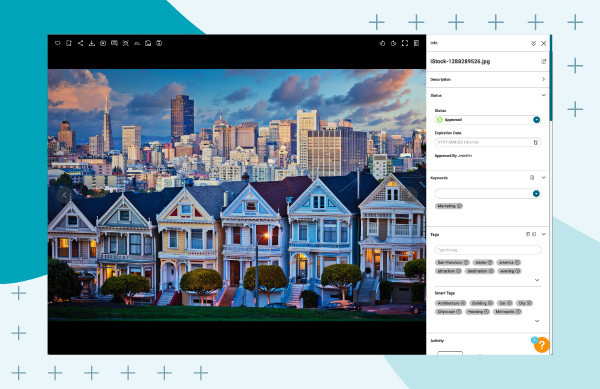 Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background.
Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background.
- Access Detailed Metadata: Scroll down to find detailed metadata information like creation date, dimensions, and resolution.
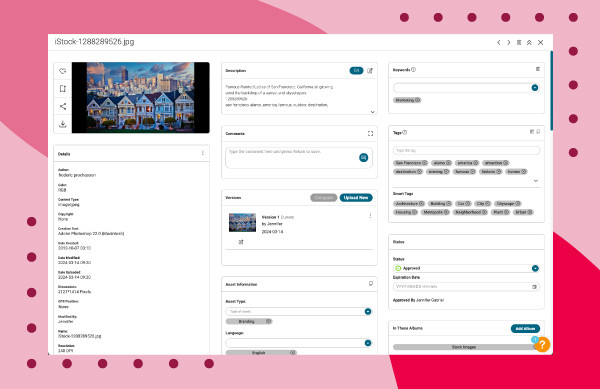 Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background.
Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background.
Canto: Simplifying Image Metadata Management with AI
Canto takes metadata management a step further with AI Visual Search. For users struggling with incorrect, incomplete, or missing metadata, or those seeking to minimize manual metadata work, Canto AI offers a powerful solution.
Canto’s AI-powered search uses natural language processing to visually analyze images within your Canto library. This allows you to find relevant photos based on visual content, without relying solely on metadata. You can search using everyday language, just as you would with your favorite internet search engine, eliminating the need for complex search terms or specific keywords.
The advantage of AI Visual Search is its ability to discover valuable, yet potentially forgotten, photography that can be repurposed and generate new value for you and your organization, even if the metadata is lacking.
Start Optimizing Your Photo Workflow with Canto
Canto stands as a leader in digital asset management, making it exceptionally easy to organize, locate, and share content using image metadata and AI-driven visual search. By leveraging Canto, you can revolutionize your workflows and make photo organization and retrieval effortless.
Ready to enhance your photo management? Discover how to begin with a digital asset management platform today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I ensure my photo metadata is secure when sharing images online?
To protect sensitive information, consider removing metadata like location data before sharing images online. Many platforms automatically strip metadata for privacy, but it’s wise to check and take control when needed.
What are the legal considerations when altering or removing metadata, especially copyright related?
Modifying or removing metadata, particularly copyright information on images you don’t own, can have legal repercussions. Digital rights management (DRM) tools help manage and track essential digital rights metadata. Always seek legal advice if you are uncertain about copyright or digital rights issues.
How does metadata impact image SEO when uploading to websites or social media?
Metadata like keywords, alt text, and titles significantly influence how search engines index images, improving online discoverability. Optimizing this data through proper tagging and relevant keywords enhances image visibility in search results.