Are you curious about the hidden information within your photos? Do you want to learn how to efficiently organize, protect, and understand your image collection? At dfphoto.net, we’ll show you How To See Metadata On A Photo, unlocking a wealth of information about your digital images. By mastering photo metadata, you can enhance your photography skills, protect your copyright, and improve your digital asset management. Explore descriptive tags, technical details, and copyright notices and delve deeper into photography with dfphoto.net.
1. What Is Photo Metadata and Why Should You Care?
Photo metadata is the embedded information within a digital image file that provides details about the photo. This includes technical data, descriptive information, and copyright details. Photo metadata is essential because it helps you organize your photos, protect your copyright, and improve your workflow.
Think of photo metadata as the behind-the-scenes story of your images. It’s like the credits of a movie, revealing details that enhance your understanding and appreciation of the photograph. By understanding how to see metadata on a photo, you unlock a powerful tool for managing and optimizing your image library.
1.1 Understanding the Significance of Image Data
Image data carries a wealth of information that can significantly enhance your ability to organize, manage, and protect your visual content. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, metadata provides critical insights into the context and creation of an image, which is essential for both personal and professional use.
1.2 How Metadata Aids in Content Management
Metadata helps in content management by allowing users to categorize images based on different criteria. For instance, you can sort photos by location, date, camera settings, or keywords, making it easier to find specific images within a large collection. This efficient organization saves time and enhances productivity.
1.3 Copyright Protection Through Metadata
Copyright information embedded in metadata protects the rights of the image owner. By including copyright notices and contact information within the metadata, photographers can clearly assert their ownership and set usage guidelines, deterring unauthorized use and ensuring proper attribution.
2. Exploring the Key Categories of Photo Metadata
Metadata can be categorized into three main types: descriptive, structural, and administrative. Each category serves different purposes and provides unique information about the image.
 The three categories of metadata as icons with a woman on a laptop over a green background
The three categories of metadata as icons with a woman on a laptop over a green background
Understanding these categories will help you better navigate and utilize the information contained within your photo metadata.
2.1 Descriptive Metadata: Enhancing Image Discoverability
Descriptive metadata includes details like the title, author, keywords, and descriptions. This type of metadata is crucial for making images discoverable in search engines and digital asset management systems.
By adding relevant keywords and descriptive information, you can improve the SEO of your images and make them easier to find online.
2.2 Structural Metadata: Organizing Complex Digital Resources
Structural metadata outlines the organization and format of an image, detailing how different elements are arranged. This is particularly useful for complex digital resources, such as multi-page documents or image collections.
Structural metadata ensures that digital assets are presented and navigated effectively, maintaining the integrity of the content.
2.3 Administrative Metadata: Managing and Preserving Digital Assets
Administrative metadata provides essential details for managing a resource, including its creation time, file format, and information on access and rights. This category includes technical, preservation, and rights metadata.
2.3.1 Technical Metadata: Ensuring Continued Access to Digital Files
Technical metadata includes details about the technical aspects of an image, such as file types, compression algorithms, and file sizes. This information is crucial for digital preservation and ensuring continued access to digital files.
2.3.2 Preservation Metadata: Maintaining Digital Resources Over Time
Preservation metadata includes information needed to maintain and preserve a digital resource over time. It details the digital object’s history, condition, and any actions taken to ensure its preservation.
2.3.3 Rights Metadata: Managing Intellectual Property Rights
Rights metadata includes information about intellectual property rights and restrictions on access or use of the material. It helps organizations manage the legal aspects of digital asset usage, ensuring compliance and protecting copyright.
3. Popular Photo Metadata Formats: A Comprehensive Overview
Several formats are used to store photo metadata, each with its own capabilities and limitations. Here are some of the most common formats:
3.1 EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format): Capturing Camera Settings
EXIF format is standard for storing interchange information in digital photography. It includes details about the camera settings, such as shutter speed, aperture, ISO setting, and date/time the photo was taken, as well as information about the image itself like orientation.
3.2 IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council): Cataloging and Exchanging Media
Developed for the press industry, IPTC metadata includes information to catalog and exchange media. It covers a broad range of details such as copyright information, the creator of the image, contact information, and content description.
3.3 XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform): Handling Standardized and Proprietary Metadata
Created by Adobe, XMP serves as a framework for handling and preserving both standardized and proprietary metadata. It is embedded into a digital image file and can include a vast range of information about the file, from basic metadata to rights management information.
3.4 DNG (Digital Negative): Enhancing Raw Image Files
DNG is a raw image file format created by Adobe, designed for use in digital photography. DNG metadata includes all the information found in EXIF, plus additional details specific to raw files, such as camera calibration data.
3.5 TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): Storing Raster Graphics
Primarily used for storing raster graphics and images, TIFF files can include a variety of metadata types stored in tags. These can describe image dimensions, resolution, and image data arrangement, among others.
3.6 PNG (Portable Network Graphics): Preserving Image Quality
PNG is a file format for raster graphics that allows for data compression without losing quality. PNG files can contain metadata such as textual information (titles, author, description, etc.) and image-specific data like gamma values, color profiles, and transparency information.
3.7 JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Compressing Digital Images
The JPEG format is a widely utilized technique for compressing digital images in a lossy manner. JPEG files can include EXIF, XMP, and ICC profile data, providing a wide range of information from camera settings to copyright and licensing information.
3.8 GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): Supporting Animations
A bitmap image format that supports animations. GIF files can include simple textual metadata, but their support for detailed metadata is limited compared to other formats.
4. Why Photo Metadata Matters: Key Benefits for Photographers and Creatives
Photo metadata is a key component for managing and organizing digital images effectively. Understanding the benefits of using photo metadata can transform your workflow and enhance your creative process.
4.1 Streamlining Image Organization
Metadata lets you categorize images based on criteria including location and keywords, making navigating large collections of images easier. By tagging your photos with relevant keywords and descriptive information, you can quickly find specific images without manually sifting through thousands of files.
4.2 Enhancing Searchability
With descriptive tags and keywords, users can quickly find specific images without manually sifting through thousands of files or relying on standard file naming nomenclature. Metadata ensures that your images are easily searchable, saving you valuable time and effort.
4.3 Protecting Copyright and Intellectual Property
Copyright information embedded in metadata protects the rights of the image owner and provides clear copyright-compliant image usage guidelines. This ensures that your work is protected and that you receive proper credit for your creations.
4.4 Facilitating Technical Analysis
Photographers and editors can use metadata to analyze camera settings and make informed decisions for post-processing and improving future shoots. By examining the technical metadata, you can gain valuable insights into your photography techniques and make adjustments to improve your results.
4.5 Preserving Context and Historical Value
Metadata ensures that important details about the image, such as the time and place it was taken, are preserved and accessible, maintaining the historical and contextual value of the photo. This is particularly important for archival purposes and for preserving the story behind your images.
5. How to See Metadata on a Photo: Step-by-Step Guides for Mac and Windows
Accessing photo metadata is straightforward, and with a few simple steps, you can unlock a wealth of information about your images. Here’s how to see metadata on a photo on Mac and Windows devices.
5.1 Viewing Metadata on Mac
For Apple users, macOS makes access to file metadata very simple:
- Locate the image you want to work on in ‘Finder.’
- Highlight the intended file using your mouse or keyboard and right-click.
- Click ‘Get Info.’
- A new window with relevant details will open. Cycle through the different tabs at the top to find the information needed.
 Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background
Image of Porto Houses with photo metadata displayed using a Mac over a blue background
5.2 Viewing Metadata on Windows
- Locate and right-click the intended digital image file.
- Select ‘Properties,’ and a small new window will open.
- Click the ‘Details’ tab at the top of the popup window.
- Scroll down until you find the desired metadata.
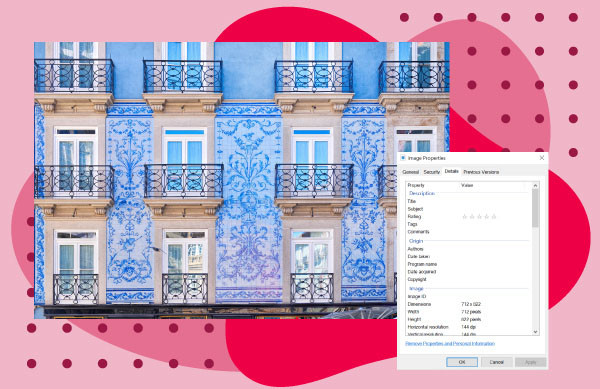 Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background
Image of blue Porto Houses with photo metadata accessed using Windows over a red background
6. Editing Photo Metadata: Adding, Modifying, and Removing Information
Yes, image metadata can be easily edited to correct errors, add missing information, or remove sensitive details. To edit the metadata of a digital photo on either Mac or Windows, follow these steps:
6.1 Editing Metadata on Mac
- Navigate to the metadata of the file you want to edit as described above (using the “Get Info” window).
- Locate the category that needs editing (name, date, author, etc.).
- Underneath the ‘Value’ tab, you’ll be able to input the new information (click and type).
6.2 Editing Metadata on Windows
- Navigate to the metadata of the file you want to edit as described above (using the “Properties” window).
- Click on the ‘Details’ tab.
- Click on the value field next to the property you want to edit.
- Enter the new information and click ‘OK’ to save the changes.
6.3 Using Metadata Editors for Advanced Editing
As easy as it looks, there are plenty of reasons why editing metadata manually isn’t ideal. Users in need of a large number of edits will prefer a metadata editor.
If you choose to use software, make sure it is suitable for the types of image files you will want to work with and can deal with the extensive editing tasks required.
Sometimes users need to edit metadata because of missing fields or unsatisfied parameters. For example, the data doesn’t include things like a title (which may be known only to the user).
Others may just need to remove metadata from photos (i.e.) to hide key details of images before uploading them to a social media platform.
Whatever the reason, when you need to switch up, remove, or add a few key data details, make sure to be assertive in your workflow. Also, it doesn’t hurt to keep a backup of the original files until you are happy with the results of your metadata changes.
7. Digital Asset Management (DAM): A Comprehensive Solution for Metadata Management
Digital asset management (DAM) is the ongoing process of keeping a check on the digital content of a business or organization. This digital content is in the form of text, audio files, videos, and pictures.
A digital asset management platform like Canto stores and manages digital assets such as images, videos, documents, and other media files. It lets users easily organize, search, retrieve, and share these assets, streamlining workflows and improving organizational collaboration.
It’s a smart way to address the content chaos resulting from today’s image and digital content production demands.
7.1 How DAM Platforms Simplify Metadata Management
DAM software can help you manage, search, and edit metadata of the different files you store, as well as view thumbnails for easy visibility of the file’s content.
7.2 Enhancing Workflow Efficiency with DAM
By centralizing your digital assets and providing powerful metadata management tools, DAM platforms streamline your workflow and improve collaboration across teams. This leads to increased productivity and better utilization of your digital resources.
8. Managing Metadata with Canto: A Practical Guide
Canto offers a range of features to help you efficiently manage your photo metadata. Here’s a practical guide to using Canto for metadata management:
8.1 Searching for Images Using Metadata
- Type your search criteria into the search bar.
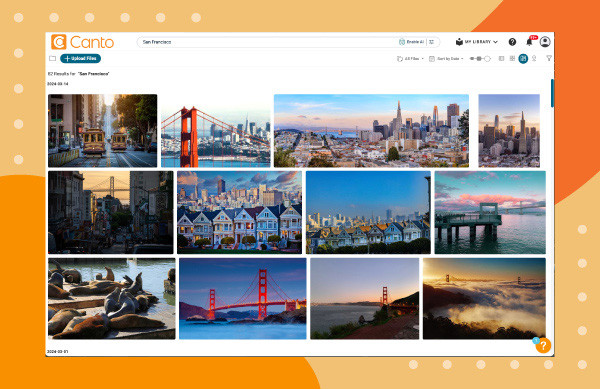 A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background
A search for San Fransisco photos in Canto over an orange background
- Scroll through the tabs in the filter pane on the right of the page to narrow your search criteria.
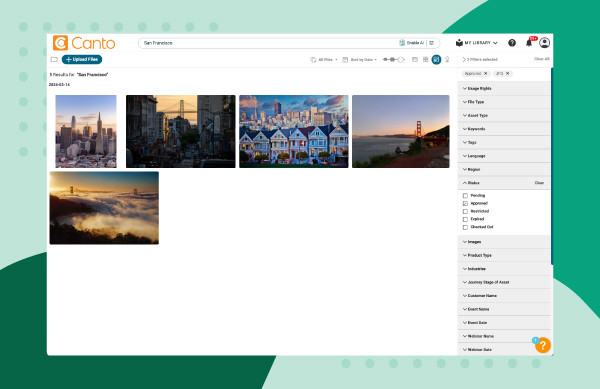 Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background
Image showing how to search metadata with Canto filters over a green background
8.2 Viewing Embedded Metadata in Canto
- Click on the image you are searching for, and the embedded image metadata will appear in the right pane.
- Looking for all image metadata? Click the double arrows at the top right to display all embedded image metadata.
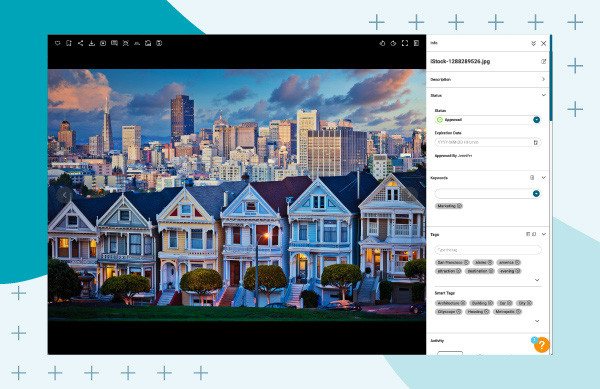 Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background
Image of San Fransisco houses with photo metadata displayed in Canto over a blue background
8.3 Accessing Detailed Metadata Information
- Scroll down the page and find metadata details like the date created, dimensions, and resolution.
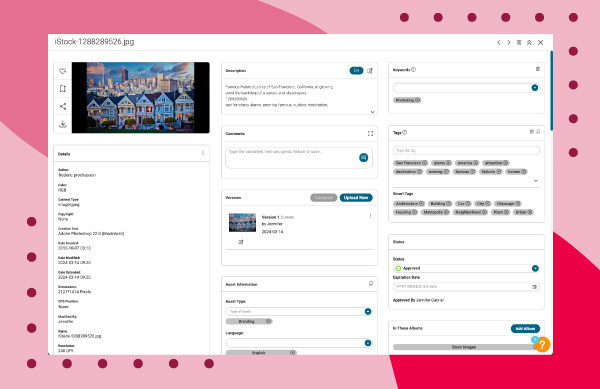 Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background
Image of San Fransisco houses and all image metadata using Canto over a red background
9. Leveraging AI Visual Search for Efficient Image Discovery
For users who have incorrect, incomplete, or missing metadata on their photos or those who simply wish to reduce metadata management, Canto AI Visual Search is the answer. Canto’s AI-powered search uses natural language when visually scanning your images inside your Canto library to find the most relevant photos without relying on metadata.
9.1 Simplifying Image Searches with AI
There’s no need for complex search terms or specific keywords used for a normal photo metadata search. AI Visual Search has no learning curve. You can search your images similarly to how you search your favorite internet search engine.
9.2 Rediscovering Valuable Photography with AI
The best part of using AI Visual Search is finding old, forgotten, and valuable photography that can be reused to create more value for you and your organization.
10. Key Considerations and Best Practices for Photo Metadata
To maximize the benefits of photo metadata, it’s important to follow some key considerations and best practices. These guidelines will help you ensure that your metadata is accurate, consistent, and effective.
10.1 Ensuring Metadata Security and Privacy
To avoid sharing metadata you don’t want to make public, you should consider stripping sensitive information like location data before uploading or sharing. Some platforms may also automatically remove metadata for privacy reasons.
10.2 Understanding Legal Considerations
For images you don’t own the rights to, altering or removing metadata (especially copyright information) can have serious consequences, including potential legal liability for infringement. Digital rights management tools can help store and track essential digital rights metadata. Always get expert legal advice if you’re unsure about copyright or digital rights issues.
10.3 Optimizing Metadata for SEO
For SEO, metadata like keywords, alt text, and titles can significantly impact how images are indexed by search engines, making them more discoverable online. Properly tagging and optimizing this data enhances visibility.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your photo metadata is accurate, secure, and optimized for discoverability. This will help you manage your images more effectively and protect your intellectual property rights.
Ready to take your photography skills to the next level? Visit dfphoto.net to explore our comprehensive guides, stunning photo collections, and vibrant photography community. Discover expert tips, find inspiration, and connect with fellow photographers. Don’t just capture moments, master them with dfphoto.net. Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How Do I Add Metadata to a Photo?
You can add metadata to a photo using photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom. In these programs, you can access the metadata panel and manually enter information such as the title, description, keywords, and copyright details.
2. Can I View Metadata on My Smartphone?
Yes, many smartphone apps allow you to view metadata. On iPhones, you can use the built-in Photos app to view basic metadata. On Android devices, you can use apps like Google Photos or dedicated metadata viewer apps.
3. What Is the Difference Between EXIF and IPTC Metadata?
EXIF metadata primarily contains technical information about the camera settings used to capture the photo, such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. IPTC metadata, on the other hand, contains descriptive information about the photo, such as the title, author, and keywords.
4. How Can Metadata Help Me Organize My Photos?
Metadata allows you to categorize and sort your photos based on various criteria, such as date, location, keywords, and camera settings. By adding relevant metadata to your photos, you can easily find specific images within a large collection.
5. Is It Possible to Remove Metadata from a Photo?
Yes, you can remove metadata from a photo using photo editing software or dedicated metadata removal tools. This is often done to protect privacy or reduce file size before sharing images online.
6. Why Is It Important to Include Copyright Information in Metadata?
Including copyright information in metadata helps protect your intellectual property rights. It clearly indicates that you are the owner of the photo and sets the terms for its usage, deterring unauthorized use and ensuring proper attribution.
7. How Does Metadata Affect the SEO of My Images?
Metadata, such as keywords and alt text, plays a crucial role in how search engines index and rank your images. By optimizing your metadata with relevant keywords, you can improve the visibility of your images in search results.
8. What Are Some Common Metadata Editing Tools?
Some popular metadata editing tools include Adobe Bridge, ExifTool, and online metadata editors like Metadata2go. These tools allow you to view, edit, and remove metadata from your photos.
9. How Can I Ensure My Metadata Is Accurate and Consistent?
To ensure your metadata is accurate and consistent, establish a standardized workflow for adding and editing metadata. Use consistent terminology for keywords and descriptions, and regularly review and update your metadata as needed.
10. What Should I Do If My Photo Metadata Is Missing or Incorrect?
If your photo metadata is missing or incorrect, you can manually add or edit the metadata using photo editing software or metadata editing tools. Refer to the photo’s original source or documentation for accurate information.