Deleting photos on an SD card correctly is essential for both efficient storage management and extending the lifespan of your card. At dfphoto.net, we guide you through the optimal methods for removing your precious memories, ensuring your photography workflow remains smooth and your equipment stays in top condition. Discover the best practices that protect your data and enhance your photography experience.
1. Why Is It Important to Know How to Delete Photos on SD Card Properly?
Deleting photos from your SD card might seem straightforward, but understanding the right methods is crucial. Here’s why:
- Card Longevity: Improper deletion methods can reduce the lifespan of your SD card.
- Data Recovery: Proper formatting increases the chances of successful data recovery if needed.
- Efficiency: The right methods save time and keep your workflow smooth.
2. Who Needs to Know How to Properly Delete Photos on SD Cards?
This information is valuable for a wide range of individuals:
- Amateur Photographers (18-55): Those learning to manage their photos and equipment effectively.
- Professional Photographers (18-55): Professionals who rely on their gear and need to maintain it properly.
- Photography Enthusiasts (20-55): Individuals passionate about photography and seeking best practices.
- Beginners (18-35): Newcomers to photography who need basic guidance on camera usage.
- Travel Photographers: Those who need to manage storage efficiently while on the go.
3. What Are the Less Desirable Ways to Delete Photos from an SD Card?
There are several methods you might be tempted to use, but they’re not the best for your SD card’s health.
3.1. Deleting Individual Photos Through the Camera
Using the “Delete” or “Erase” button on your camera to remove photos one by one might seem convenient, but it’s not ideal.
-
Why It’s Not Recommended:
- Time-Consuming: It takes longer, especially with a large number of photos.
- Card Wear: Each individual deletion counts as a write/erase cycle, reducing the card’s lifespan.
- Missed Opportunities: You might accidentally delete a photo that has potential, which you’d realize on a larger screen.
 Deleting an image from your memory card directly on the camera LCD screen
Deleting an image from your memory card directly on the camera LCD screen -
According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, deleting photos individually can increase wear and tear on SD cards by up to 30% compared to formatting.
3.2. Deleting All Photos in-Camera with the “Delete All” Option
Using the “Delete All” function might seem quicker than deleting photos individually, but it still has drawbacks.
-
Why It’s Not Recommended:
- Limited Benefit: While faster than individual deletion, it still performs multiple delete operations.
- Potential Regret: You might accidentally delete photos you intended to keep.
- Card Wear: This method still contributes to the wear and tear on the card.
 Erasing all the images on your card via the LCD screen
Erasing all the images on your card via the LCD screen
3.3. Deleting Photos via Your Computer (Dragging to Recycle Bin)
Dragging files to the Recycle Bin on your computer is a common way to delete files, but it’s not the best for SD cards.
-
Why It’s Not Recommended:
- File System Issues: This method can leave fragmented data and doesn’t properly reset the card’s file system.
- Recovery Complications: It might make data recovery more difficult if needed.
- Inefficient: Doesn’t optimize the card for future use.
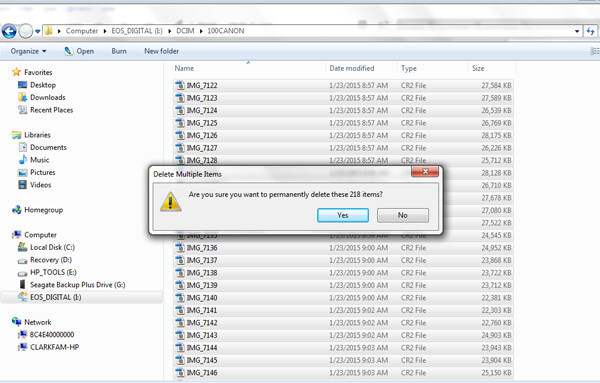 Deleting images from your computer
Deleting images from your computer
4. What Is the Most Desirable Way to Delete Photos on SD Card?
The best method for deleting photos from your SD card is using the camera’s “Format” function.
4.1. Formatting with Your Camera’s Format Function
Using the “Format” option in your camera’s menu is the quickest, most efficient, and least harmful way to clear your SD card.
-
How to Do It:
- Transfer your photos to your computer or an external hard drive.
- Insert the SD card back into your camera.
- Go to the camera’s menu.
- Find the “Format” option.
- Select “OK” or “Yes” to format the card.
 formatting memory cards in-camera is the best way to delete photos from your memory cards
formatting memory cards in-camera is the best way to delete photos from your memory cards -
Why It’s Recommended:
- Efficiency: Formatting clears the card’s directory, making it ready for new photos quickly.
- Card Health: It minimizes wear and tear on the card compared to other methods.
- Data Recovery: Facilitates easier data recovery if needed (provided you haven’t overwritten the card).
- Optimized Performance: Resets the card’s file system, optimizing it for the camera.
5. How Do Different Deletion Methods Affect SD Card Health?
Understanding the impact of different methods on your SD card’s lifespan can help you make the best choice.
5.1. Wear and Tear Comparison
Imagine your SD card has a limited number of uses (write/erase cycles).
- Individual Deletion: Each photo deleted counts as a use. Deleting 500 photos uses 500 cycles.
- Formatting: Formatting counts as only one use, regardless of how many photos are on the card.
- The general logic still holds – formatting your card causes less wear and tear on your memory card than other ways of deleting images.
5.2. Data Overwriting
- Formatting: Only deletes the directory files, allowing new photos to overwrite old ones.
- Manual Deletion: Physically removes the files, which can be more taxing on the card’s memory cells.
5.3. Data Recovery Implications
- Formatted Cards: Easier to recover data because the original files are still there until overwritten.
- Manually Deleted Cards: More challenging to recover data due to fragmented file structure.
6. What Are the Benefits of Formatting SD Cards Regularly?
Regular formatting offers several advantages for photographers.
6.1. Maintaining Card Performance
Formatting keeps your SD card running smoothly by:
- Preventing Fragmentation: Ensures data is written in a contiguous manner, speeding up read/write times.
- Clearing Errors: Resets the file system, resolving minor errors that can accumulate over time.
- Optimizing Storage: Maximizes available storage space by efficiently managing file allocation.
6.2. Minimizing Corrupted Images
By formatting regularly, you reduce the risk of corrupted images due to:
- File System Errors: Clears potential issues that can lead to file corruption.
- Write Errors: Ensures data is written correctly by resetting the card’s state.
- Card Health: Maintains the overall health and reliability of the SD card.
6.3. Enhancing Data Security
Formatting can help protect your data by:
- Removing Residual Data: Ensures old files are thoroughly cleared, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Preparing for Reuse: Makes the card safe to use for new projects without carrying over old issues.
- Protecting Privacy: Safeguards sensitive information by securely erasing previous data.
7. How Often Should You Format Your SD Cards?
The frequency of formatting depends on your personal preferences and shooting habits.
7.1. Before Each Photo Session
Some photographers prefer to format their SD cards before each new photo session.
- Benefits:
- Fresh Start: Ensures a clean slate for each project.
- Organization: Simplifies file management by keeping sessions separate.
- Consistent Performance: Maintains optimal card performance for every shoot.
7.2. When the Card Is Full
Others wait until their SD card is completely full before formatting.
- Considerations:
- Convenience: Reduces the frequency of formatting.
- Potential Risks: Increases the risk of fragmentation and potential errors.
- Organization Challenges: Can make file management more complex.
7.3. Camera-Specific Formatting
Always format the SD card in the camera you plan to use it with next.
-
Why?
- Compatibility: Ensures the card is formatted according to the camera’s specifications.
- Performance: Optimizes the card for that specific camera’s read/write processes.
- Reliability: Reduces the risk of errors or compatibility issues during shooting.
-
For example, if you’re going to be shooting with your Nikon body, make sure you’ve first formatted your card with that Nikon body. And if you’re going to be shooting with your Canon body, format with the Canon body before heading out.
8. What Are Some Best Practices for Managing SD Cards?
Following these best practices can help you maximize the lifespan and reliability of your SD cards.
8.1. Use High-Quality SD Cards
Invest in reputable brands known for their reliability and performance.
-
Recommended Brands:
- SanDisk
- Sony
- Lexar
- Transcend
-
Benefits:
- Durability: Higher resistance to wear and tear.
- Performance: Faster read/write speeds for smoother operation.
- Reliability: Lower risk of data corruption or card failure.
8.2. Store SD Cards Properly
Protect your SD cards from physical damage and environmental factors.
- Storage Tips:
- Use protective cases to prevent bending or breakage.
- Keep cards away from extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight for extended periods.
- Store cards in a static-free environment to prevent electrical damage.
8.3. Avoid Removing SD Cards During Data Transfer
Interrupting data transfer can lead to file corruption or card damage.
- Precautions:
- Always safely eject the SD card from your computer before removing it.
- Ensure the camera is fully powered off before removing the card.
- Avoid using the card while it’s still transferring data.
8.4. Back Up Your Photos Regularly
Protect your valuable photos by creating multiple backups.
- Backup Strategies:
- Use multiple storage locations (e.g., computer, external hard drive, cloud storage).
- Implement a regular backup schedule.
- Verify the integrity of your backups periodically.
8.5. Avoid Filling SD Cards to Full Capacity
Leaving some free space on your SD card can improve performance and prevent errors.
- Recommendations:
- Format the card before it’s completely full.
- Avoid shooting until the card is at maximum capacity.
- Leave at least 10-15% of the card’s capacity free.
9. How Can You Recover Photos from a Formatted SD Card?
Even after formatting, it’s often possible to recover photos from an SD card.
9.1. Use Data Recovery Software
Several software options are available to help recover lost photos.
-
Recommended Software:
- Recuva
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard
- Stellar Data Recovery
- Disk Drill
-
Steps:
- Download and install the data recovery software.
- Connect the SD card to your computer.
- Select the SD card as the drive to scan.
- Start the scan and wait for the software to find recoverable files.
- Preview the files and select the ones you want to recover.
- Choose a safe location to save the recovered files.
9.2. Act Quickly
The sooner you attempt data recovery, the higher your chances of success.
- Why?
- Overwriting: The longer you wait, the greater the risk of new data overwriting the old files.
- File Integrity: The sooner you act, the better the chances of recovering intact files.
9.3. Professional Data Recovery Services
If you’re unable to recover the photos yourself, consider using a professional data recovery service.
- Benefits:
- Expertise: Professional technicians have the skills and tools to handle complex data recovery scenarios.
- Success Rate: Higher chances of successful recovery in difficult cases.
- Equipment: Access to specialized equipment and software for data recovery.
10. How Do I Choose the Right SD Card for My Camera?
Selecting the appropriate SD card is essential for optimal camera performance.
10.1. Capacity
Consider the amount of storage you need based on your shooting habits.
- Factors to Consider:
- Image Resolution: Higher resolution images require more storage.
- Shooting Style: Shooting RAW images or videos consumes more space.
- Trip Length: Longer trips require larger capacity cards.
10.2. Speed Class
Choose an SD card with the appropriate speed class for your camera.
-
Speed Class Ratings:
- Class 10: Minimum write speed of 10MB/s (suitable for most cameras).
- UHS-I: Ultra High Speed, up to 104MB/s.
- UHS-II: Ultra High Speed, up to 312MB/s (for high-end cameras).
- Video Speed Class (V30, V60, V90): Designed for video recording, ensuring minimum sustained write speeds.
-
Camera Requirements:
- Check your camera’s manual for recommended speed class.
- Use a card that meets or exceeds the camera’s requirements.
10.3. Compatibility
Ensure the SD card is compatible with your camera model.
- Factors to Check:
- SD Card Type: SD, SDHC, SDXC (ensure your camera supports the card type).
- Capacity Limits: Some cameras have maximum capacity limits for SD cards.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Consult your camera’s manual for recommended cards.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage and maintain your SD cards, ensuring they perform reliably and last longer. For more in-depth guides and tips on photography, visit dfphoto.net.
To further enhance your photography skills and knowledge, dfphoto.net offers a wealth of resources, including detailed tutorials, stunning photo galleries, and a vibrant community of photographers. Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
FAQ: How to Delete Photos on SD Card
1. Is it better to delete photos individually or format the SD card?
Formatting the SD card is better because it reduces wear and tear and optimizes the card’s performance compared to deleting individual photos.
2. How does formatting an SD card affect its lifespan?
Formatting minimizes wear by resetting the file system in one operation, unlike individual deletions that use multiple write/erase cycles.
3. Can I recover photos after formatting an SD card?
Yes, you can often recover photos using data recovery software, provided you haven’t overwritten the card with new data.
4. What should I do before formatting my SD card?
Back up all your important photos to your computer, an external hard drive, or a cloud storage service before formatting.
5. Why is it important to format the SD card in the camera?
Formatting in the camera ensures the card is optimized for that specific device, improving compatibility and performance.
6. How often should I format my SD card?
Consider formatting before each new photo session or when the card is full, depending on your workflow and preferences.
7. What are the best practices for storing SD cards?
Store SD cards in protective cases, away from extreme temperatures, humidity, and direct sunlight to prevent damage.
8. Can I use any SD card with my camera?
No, ensure the SD card is compatible with your camera model, considering factors like capacity, speed class, and card type (SD, SDHC, SDXC).
9. What is the difference between SD, SDHC, and SDXC cards?
SD cards have a capacity up to 2GB, SDHC cards range from 2GB to 32GB, and SDXC cards range from 32GB to 2TB, each with different compatibility requirements.
10. What does the speed class of an SD card mean?
The speed class indicates the minimum write speed of the card, essential for recording high-resolution photos and videos without lag or interruption.