Deleting SD card photos the right way is crucial for memory card health and data recovery. In this dfphoto.net guide, we’ll show you the best method to efficiently and safely remove images, extending the life of your storage and enabling easy data recovery. Discover how to format your SD cards, optimize storage, and ensure your images are properly handled. Let’s dive into the world of digital image management, image optimization, data security and photography workflow for photographers.
1. What Are the Less Desirable Ways to Delete SD Card Photos?
Avoid deleting SD card photos individually, using the “Delete All” option in-camera, or deleting them via your computer as these methods can be less efficient and potentially harmful to your card. These methods might seem convenient but can cause unnecessary wear and tear on your SD card.
1.1. Is Getting Rid of Each Photo Individually Through the Camera a Good Idea?
No, getting rid of each photo individually through the camera using the Delete or Erase button is not ideal because you might miss potential redeeming qualities in an image on a larger screen, and it’s not the most efficient way to maintain card health. Always review your images on a computer screen for details you might miss on the camera’s LCD. According to Popular Photography, reviewing images on a larger screen helps in making informed decisions about which photos to keep.
 Deleting an image from your memory card directly on the camera LCD screen
Deleting an image from your memory card directly on the camera LCD screen
1.2. Why Is Deleting All Photos In-Camera With the Delete All Option Not Recommended?
Deleting all photos in-camera with the Delete All option is not the best way to keep your card healthy because it still performs individual deletion processes, contributing to wear and tear. This method, while faster than deleting images one by one, is still less efficient than formatting.
 Erasing all the images on your card via the LCD screen
Erasing all the images on your card via the LCD screen
1.3. Is Deleting SD Card Photos Via Your Computer a Good Method?
Deleting via your computer, by dragging photos into the Recycle Bin, is convenient, but it is not the most desirable way to delete photos as it can be taxing on the memory card. This method doesn’t optimize the card’s file system as effectively as formatting.
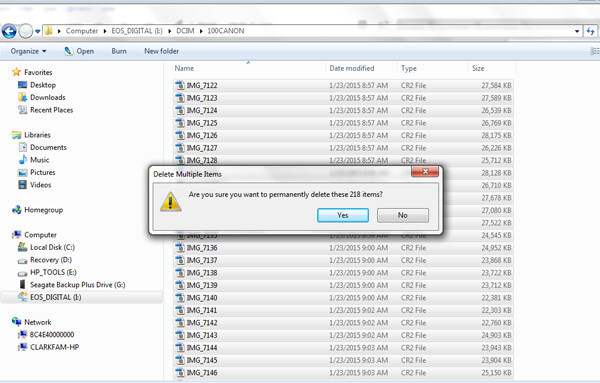 Deleting images from your computer
Deleting images from your computer
2. What Is the Most Desirable Way to Delete SD Card Photos?
The most desirable way to delete SD card photos is to use your camera’s Format function, which efficiently clears the card and maintains its health. This method ensures the quickest, most efficient, and least harmful way to erase images from your SD card.
2.1. How to Delete With Your Camera’s Format Function?
To delete with your camera’s Format function, follow these steps:
- Transfer your photos to your computer or an external hard drive.
- Insert the SD card back into your camera.
- Navigate to the Format option in the camera’s menu.
- Select OK to format the card.
This process is the suggested way of deleting photos off your memory card, and it is recommended every time you need to delete photos.
 formatting memory cards in-camera is the best way to delete photos from your memory cards
formatting memory cards in-camera is the best way to delete photos from your memory cards
2.2. What Are the Benefits of Formatting the SD Card Through the Camera?
Formatting the SD card through the camera offers several benefits, including:
- Efficiency: It quickly clears the card for reuse.
- Card Health: It minimizes wear and tear compared to other deletion methods.
- Data Recovery: It makes data recovery easier if needed, provided the card hasn’t been overwritten.
3. Why Are Some Methods Better Than Others for Deleting SD Card Photos?
Some methods are better because they affect the memory card differently. Formatting, unlike individual deletion, only clears the directory files, reducing wear and tear on the card.
3.1. How Does Formatting Affect the Lifespan of an SD Card?
Formatting extends the lifespan of an SD card by minimizing wear and tear. Unlike individually deleting photos, formatting only deletes the directory files, making it a more efficient method. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, formatting an SD card instead of individually deleting files significantly reduces the number of write cycles, thereby prolonging the card’s life.
3.2. What Is the Difference Between Deleting and Formatting an SD Card?
The difference between deleting and formatting an SD card lies in how the data is handled. Deleting removes files individually, whereas formatting clears the entire directory, making it quicker and less taxing on the card. Formatting only counts as one use, regardless of how many photos you’re deleting.
3.3. How Does Formatting Facilitate Easier Data Recovery?
Formatting facilitates easier data recovery because it only deletes the directory file instead of the images themselves. Images on a formatted card are typically easier to recover, assuming you did not overwrite the formatted images by taking more photos.
4. How Often Should You Format Your SD Card?
You should format your SD card based on personal preference, but it is generally recommended to format it before each new photo session to start fresh and keep files organized. Some prefer waiting until the card is totally full before formatting.
4.1. Is It Better to Format an SD Card Before Each Photo Session?
Yes, it is often better to format an SD card before each photo session because it helps keep your files organized and ensures a fresh start. This practice simplifies the process of uploading and managing your images.
4.2. How Does Formatting the SD Card in the Camera You Plan to Use Affect Performance?
Formatting the SD card in the camera you plan to use ensures optimal compatibility and performance. Different cameras may format cards slightly differently, so using the intended camera ensures the card is properly configured.
4.3. What Are the Best Practices for SD Card Maintenance?
The best practices for SD card maintenance include:
- Always format the card in the camera you intend to use.
- Avoid deleting photos individually on the card.
- Regularly back up your photos to a computer or external drive.
- Store SD cards in a safe, dry place.
5. How Do You Recover Photos From a Formatted SD Card?
Photos can be recovered from a formatted SD card using specialized data recovery software. These tools scan the card for residual data and attempt to reconstruct the deleted files.
5.1. What Software Can Be Used to Recover Photos From a Formatted SD Card?
Several software options can be used to recover photos from a formatted SD card:
- Recuva: A free and user-friendly option.
- Stellar Photo Recovery: A powerful tool for recovering various file types.
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard: A comprehensive solution for different data loss scenarios.
- Disk Drill: Offers both free and paid versions with advanced recovery features.
- PhotoRec: A free, open-source option that works with various operating systems.
5.2. What Is the Process of Using Data Recovery Software?
The process of using data recovery software typically involves these steps:
- Download and Install: Choose and install the data recovery software on your computer.
- Connect the SD Card: Insert the SD card into a card reader and connect it to your computer.
- Select the SD Card: Launch the software and select the SD card as the drive to be scanned.
- Scan the Card: Start the scanning process. The software will search for recoverable files.
- Preview Files: Once the scan is complete, preview the found files to ensure they are the ones you need.
- Recover Files: Select the files you want to recover and choose a location on your computer to save them.
- Save Files: Save the recovered files to your computer or another storage device.
5.3. What Factors Affect the Success of Data Recovery?
Several factors affect the success of data recovery:
- Time Since Formatting: The sooner you attempt recovery after formatting, the higher the chances of success.
- Overwriting: If new data has been written to the card after formatting, it can overwrite the old data, making recovery more difficult or impossible.
- Card Condition: The physical condition of the SD card can affect the recovery process. Damaged cards may be harder to recover data from.
- Software Quality: The effectiveness of the data recovery software plays a significant role in the success of the recovery.
- Type of Formatting: Quick formats are generally easier to recover from compared to full formats, which write over the entire card.
6. What Are the Different Types of SD Cards and Their Uses?
Different types of SD cards include SD, SDHC, and SDXC, each with varying capacities and uses. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right card for your needs.
6.1. What Is the Difference Between SD, SDHC, and SDXC Cards?
The primary differences between SD, SDHC, and SDXC cards are:
-
SD (Secure Digital):
- Capacity: Up to 2GB
- File System: FAT12, FAT16
- Use: Suitable for older devices and low-resolution images
-
SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity):
- Capacity: 2GB to 32GB
- File System: FAT32
- Use: Good for standard digital cameras and HD video recording
-
SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity):
- Capacity: 32GB to 2TB
- File System: exFAT
- Use: Ideal for high-resolution photography and 4K video recording
6.2. How Do I Choose the Right SD Card for My Camera?
Choosing the right SD card for your camera depends on several factors:
-
Camera Compatibility:
- Check your camera’s manual for the types of SD cards it supports (SD, SDHC, or SDXC).
- Ensure the card type is compatible with your camera to avoid compatibility issues.
-
Capacity:
- Consider the resolution of your camera and the types of files you’ll be saving (photos or videos).
- For high-resolution photos and 4K videos, opt for SDXC cards with larger capacities (64GB or more).
- For standard photography, SDHC cards (16GB to 32GB) may suffice.
-
Speed Class:
- Look for the speed class rating on the card, which indicates the minimum write speed.
- Speed Class: Indicates the minimum write speed in MB/s (e.g., Class 10 = 10MB/s).
- UHS Speed Class: Indicates the minimum write speed for UHS (Ultra High Speed) cards (U1 = 10MB/s, U3 = 30MB/s).
- Video Speed Class: Designed for video recording (V30 = 30MB/s, V60 = 60MB/s, V90 = 90MB/s).
- For 4K video recording, a card with a U3 or V30 speed class is recommended.
- For high-speed continuous shooting, choose a card with a higher speed class.
-
Brand and Reliability:
- Opt for reputable brands known for their reliability (e.g., SanDisk, Sony, Samsung, Lexar).
- Read reviews and check user feedback to ensure the card performs well under different conditions.
-
File System:
- SD cards use different file systems (FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, exFAT).
- Ensure your camera supports the file system of the SD card you choose.
- SDXC cards use the exFAT file system, which is necessary for handling large files and capacities.
Here’s a table summarizing the key considerations:
| Factor | Consideration | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Camera’s supported card types (SD, SDHC, SDXC) | Check the camera manual for compatibility. |
| Capacity | Resolution and file types (photos, videos) | SDXC (64GB+) for high-res and 4K video; SDHC (16GB-32GB) for standard photography. |
| Speed Class | Minimum write speed requirements | U3/V30 for 4K video; higher speed class for continuous shooting. |
| Brand/Reliability | Card performance and user feedback | Choose reputable brands with positive reviews. |
| File System | Camera’s support for FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, exFAT | Ensure camera supports the card’s file system. |
6.3. What Are the Speed Classes and UHS Ratings for SD Cards?
Speed Classes and UHS (Ultra High Speed) ratings indicate the minimum write speed of an SD card:
-
Speed Class:
- Class 2: 2MB/s (suitable for standard video recording)
- Class 4: 4MB/s (suitable for HD video recording)
- Class 6: 6MB/s (suitable for HD video recording and photography)
- Class 10: 10MB/s (suitable for full HD video recording and high-speed photography)
-
UHS (Ultra High Speed):
- UHS-I: Supports speeds up to 104MB/s
- UHS-II: Supports speeds up to 312MB/s
-
UHS Speed Class:
- U1: 10MB/s (minimum write speed for UHS)
- U3: 30MB/s (minimum write speed for UHS, recommended for 4K video)
-
Video Speed Class:
- V6: 6MB/s
- V10: 10MB/s
- V30: 30MB/s (suitable for high-quality video recording)
- V60: 60MB/s (suitable for 8K video recording)
- V90: 90MB/s (suitable for high-end 8K video recording)
The speed class and UHS rating you choose should match the requirements of your camera and the type of media you plan to record.
7. How Do You Protect Your SD Card From Damage and Data Loss?
Protecting your SD card involves physical care and following best practices to prevent data loss. Proper handling and storage are essential.
7.1. What Are the Physical Precautions to Protect an SD Card?
Physical precautions to protect an SD card include:
- Storage: Store SD cards in a protective case to prevent physical damage.
- Handling: Avoid bending or applying excessive pressure to the card.
- Environment: Keep cards away from extreme temperatures, moisture, and direct sunlight.
- Contacts: Avoid touching the gold contacts on the card to prevent corrosion or damage.
7.2. How Do You Prevent Data Loss on an SD Card?
To prevent data loss on an SD card:
- Proper Ejection: Always eject the card properly from your camera or computer before removing it.
- Avoid Interruptions: Do not remove the card during read or write operations.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up the data on your SD card to multiple locations.
- Virus Scans: Scan the card for viruses if you use it on multiple devices.
- Avoid Filling the Card Completely: Leaving some free space on the card can help prevent data corruption.
7.3. What Are Common Causes of SD Card Failure?
Common causes of SD card failure include:
- Physical Damage: Bending, breaking, or water damage.
- Electrical Issues: Power surges or static electricity.
- Improper Handling: Removing the card during data transfer.
- File System Corruption: Caused by viruses or improper formatting.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the card’s memory cells can degrade.
8. What Are the Best Practices for Storing SD Cards?
Best practices for storing SD cards include using protective cases, keeping them away from extreme conditions, and labeling them for easy identification. Proper storage helps maintain the card’s integrity and lifespan.
8.1. What Type of Cases Are Best for Storing SD Cards?
The best types of cases for storing SD cards are:
- Hard Plastic Cases: These provide excellent protection against physical damage.
- Waterproof Cases: These protect against moisture and water damage.
- Anti-Static Cases: These protect against static electricity.
- Compact Cases: These keep cards organized and prevent them from getting lost.
8.2. How Should SD Cards Be Labeled for Easy Identification?
SD cards should be labeled with:
- Capacity: Indicate the storage capacity (e.g., 64GB, 128GB).
- Content Type: Specify the type of data stored (e.g., “Vacation Photos,” “Project X”).
- Date Range: Include the date range of the photos or videos stored on the card.
- Camera Used: Note the camera used to record the data.
Use a fine-tip permanent marker or adhesive labels to write the information on the card or its case.
8.3. Where Should SD Cards Be Stored to Prevent Damage?
SD cards should be stored in:
- Cool, Dry Place: Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Protective Case: To prevent physical damage.
- Away From Magnetic Fields: To prevent data corruption.
- Safe From Dust and Debris: To keep the contacts clean.
9. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Deleting Photos From an SD Card?
Ethical considerations when deleting photos involve respecting privacy, ensuring proper consent, and adhering to legal requirements. Always consider the implications of deleting sensitive or personal information.
9.1. How Do You Ensure Privacy When Deleting Photos of Others?
To ensure privacy when deleting photos of others:
- Obtain Consent: Always get permission from individuals before taking and deleting their photos.
- Secure Deletion: Use secure deletion methods to ensure the photos cannot be recovered.
- Respect Boundaries: Avoid taking or keeping photos of individuals in private or sensitive situations without their explicit consent.
9.2. What Are the Legal Considerations When Deleting Photos?
Legal considerations when deleting photos include:
- Copyright: Ensure you have the right to delete or use the photos, especially if they are not your own.
- Privacy Laws: Comply with privacy laws and regulations regarding the handling of personal data.
- Data Retention Policies: Adhere to any data retention policies that may apply to the photos.
9.3. How Do You Handle Sensitive or Confidential Photos?
To handle sensitive or confidential photos:
- Encryption: Encrypt the photos to protect them from unauthorized access.
- Secure Storage: Store the photos in a secure location with limited access.
- Secure Deletion: Use secure deletion methods to permanently remove the photos when they are no longer needed.
10. FAQ About Deleting SD Card Photos
Here are some frequently asked questions about deleting SD card photos.
10.1. Is it safe to delete photos directly from my camera?
Yes, it is generally safe to delete photos directly from your camera, but using the format function is better for card health. Deleting photos individually can cause more wear and tear on the card.
10.2. Will formatting my SD card erase everything?
Yes, formatting your SD card erases all the data on the card, including photos and videos. Always back up important files before formatting.
10.3. Can deleted photos be recovered from an SD card?
Yes, deleted photos can often be recovered from an SD card using data recovery software, unless the card has been overwritten with new data.
10.4. How do I securely delete photos from my SD card?
To securely delete photos, use the format function on your camera or a secure deletion tool on your computer that overwrites the data multiple times.
10.5. Does formatting my SD card improve its performance?
Yes, formatting your SD card can improve its performance by clearing fragmented files and reorganizing the file system.
10.6. Can viruses affect my SD card?
Yes, viruses can affect your SD card if it is used on infected devices. Always scan your SD card with antivirus software.
10.7. How do I know when my SD card is failing?
Signs of SD card failure include corrupted files, slow performance, and the inability to read or write data.
10.8. What is the best way to store my SD cards?
The best way to store your SD cards is in a protective case, away from extreme temperatures, moisture, and magnetic fields.
10.9. Can I use the same SD card for different cameras?
Yes, you can use the same SD card for different cameras, but it is best to format the card in the camera you plan to use it with to ensure compatibility.
10.10. How often should I back up my SD card?
You should back up your SD card regularly, ideally after each photo session, to prevent data loss.
Conclusion
Mastering How To Delete Sd Card Photos correctly ensures your memory cards last longer, perform better, and keep your data safe. Whether you’re a professional photographer or a hobbyist, understanding the best practices for managing your storage is essential. Remember to always format your card in-camera and take precautions to protect your valuable images.
Ready to elevate your photography skills? Explore a wealth of tutorials, stunning photo galleries, and connect with a vibrant community of photographers at dfphoto.net. Visit us at 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States, or call +1 (505) 471-6001. Start your journey to photographic excellence today! Check out dfphoto.net now for inspiration, learning, and connection.