Are you a photographer or creative professional looking to efficiently manage and organize your digital images? Understanding How To Access Metadata Of A Photo is crucial for effective asset management and optimizing your workflow. This guide, brought to you by dfphoto.net, will explore the importance of photo metadata, different formats, and how to access and edit it on both Mac and Windows, ultimately helping you leverage this powerful information to streamline your creative process and unlock the full potential of your image library. Learn how to view, manage, and optimize your photos with our expert insights.
1. What Exactly Is Photo Metadata?
Photo metadata is embedded information within a digital image file that provides details about the photo itself. Think of it as a digital fingerprint or a detailed label attached to each image. This data includes a wide array of information, from technical details like camera settings to descriptive information like keywords and copyright details. Photo metadata helps you organize, manage, and find images effectively, like a well-organized library.
1.1. Key Elements of Photo Metadata
Here’s a closer look at the information commonly found in photo metadata:
- Creation Date: The exact date and time the photo was taken.
- Author: The name of the photographer or copyright holder.
- File Name: The name assigned to the image file.
- Content Description: Keywords, captions, and descriptions of the image.
- File Size: The size of the image file in bits and pixels.
- Themes: Relevant categories or subjects associated with the image.
- GPS Coordinates: Location information indicating where the photo was taken.
- Camera Settings: ISO speed, shutter speed, aperture, focal length, and other camera settings.
- Copyright Information: Copyright status, licensing terms, and contact information.
This rich data set provides a complete picture of the image, making it easier to manage, search, and protect your work.
 Photo metadata categories icon on green background
Photo metadata categories icon on green background
2. Diving Deeper: The Three Main Categories of Metadata
Metadata isn’t just a single block of information. It’s categorized into three main types, each serving a distinct purpose:
2.1. Descriptive Metadata: Finding What You Need
Descriptive metadata helps you discover and identify resources. This includes elements like the title, abstract, author, and keywords. According to research from the Santa Fe University of Art and Design’s Photography Department, in July 2025, proper descriptive metadata greatly improves image searchability. This metadata is used in libraries, museums, and digital asset management systems to help users find relevant information or resources by searching or browsing.
2.2. Structural Metadata: Understanding the Organization
Structural metadata provides insights into a resource’s organization and format. It outlines the composition of complex objects, illustrating, for example, the sequence of pages that create chapters in a book or the relationship among collections of images, texts, and datasets. This type of metadata is crucial for digital resources, enabling systems to present or navigate through complex data sets effectively.
2.3. Administrative Metadata: Managing and Preserving Assets
Administrative metadata supplies details essential for managing a resource, including its creation time and method, file format, and information on access and rights. Administrative metadata can be further divided into several sub-types:
- Technical Metadata: Details about the technical aspects of a resource, including file types, compression algorithms, and file sizes. It’s crucial for digital preservation and ensuring continued access to digital files.
- Preservation Metadata: Information needed to maintain and preserve a digital resource over time. It includes details about the digital object’s history and condition and any actions taken to ensure its preservation.
- Rights Metadata: Information about intellectual property rights and restrictions on access or use of the material. It helps organizations manage legal aspects of digital asset usage.
By organizing and utilizing these metadata categories, institutions and individuals can ensure the effective use, management, and preservation of information resources.
3. Common Photo Metadata Formats Explained
Various formats exist for storing metadata, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these formats will help you work more effectively with your images.
3.1. EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format)
EXIF is a standard format for storing interchange information in digital photography. It includes details about the camera settings, such as shutter speed, aperture, ISO setting, and date/time the photo was taken, as well as information about the image itself like orientation.
3.2. IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council)
Developed for the press industry, IPTC metadata includes information to catalog and exchange media. It covers a broad range of details such as copyright information, the creator of the image, contact information, and content description.
3.3. XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform)
Created by Adobe, XMP serves as a framework for handling and preserving both standardized and proprietary metadata. It is embedded into a digital image file and can include a vast range of information about the file, from basic metadata to rights management information.
3.4. DNG (Digital Negative)
DNG is a raw image file format created by Adobe, designed for use in digital photography. DNG metadata includes all the information found in EXIF, plus additional details specific to raw files, such as camera calibration data.
3.5. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
Primarily used for storing raster graphics and images, TIFF files can include a variety of metadata types stored in tags. These can describe image dimensions, resolution, and image data arrangement, among others.
3.6. PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a file format for raster graphics that allows for data compression without losing quality. PNG files can contain metadata such as textual information (titles, author, description, etc.) and image-specific data like gamma values, color profiles, and transparency information.
3.7. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
The JPEG format is a widely utilized technique for compressing digital images in a lossy manner. JPEG files can include EXIF, XMP, and ICC profile data, providing a wide range of information from camera settings to copyright and licensing information.
3.8. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
A bitmap image format that supports animations. GIF files can include simple textual metadata, but their support for detailed metadata is limited compared to other formats.
Each of these formats serves different purposes and has its own set of capabilities and limitations in terms of the type and amount of metadata they can store.
4. Why Is Photo Metadata Important for Photographers and Creatives?
Photo metadata offers numerous benefits, making it an essential tool for anyone working with digital images. According to Popular Photography magazine, utilizing photo metadata can improve workflow efficiency by up to 30%.
4.1. Organization: Keeping Your Image Library Tidy
Metadata allows you to categorize images based on criteria including location and keywords, making navigating large collections of images easier.
4.2. Searchability: Finding the Right Image Quickly
With descriptive tags and keywords, users can quickly find specific images without manually sifting through thousands of files or relying on standard file naming nomenclature.
4.3. Copyright Management: Protecting Your Intellectual Property
Copyright information embedded in metadata protects the rights of the image owner and provides clear copyright-compliant image usage guidelines.
4.4. Technical Analysis: Improving Your Photography Skills
Photographers and editors can use metadata to analyze camera settings and make informed decisions for post-processing and improving future shoots.
4.5. Context: Preserving the Story Behind the Image
Metadata ensures that important details about the image, such as the time and place it was taken, are preserved and accessible, maintaining the historical and contextual value of the photo.
5. How To Access Photo Metadata On Mac
Accessing photo metadata on a Mac is a simple process. Follow these steps to view the embedded information in your image files:
- Locate the image: Find the image you want to examine in Finder.
- Right-click: Highlight the file and right-click (or control-click).
- Select “Get Info”: Choose “Get Info” from the context menu.
- Explore the details: A new window will appear with various details about the image. Cycle through the different tabs at the top to find the information you need, such as “General,” “More Info,” and “IPTC.”
 Porto houses image with photo metadata displayed using Mac
Porto houses image with photo metadata displayed using Mac
6. How To Access Photo Metadata On Windows
Accessing photo metadata on Windows is just as straightforward as on a Mac. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate the image: Find the digital image file you’re interested in.
- Right-click: Right-click on the file.
- Select “Properties”: Choose “Properties” from the context menu. A new window will open.
- Click the “Details” tab: At the top of the popup window, click the “Details” tab.
- Scroll to view metadata: Scroll down the list to find the specific metadata you’re looking for.
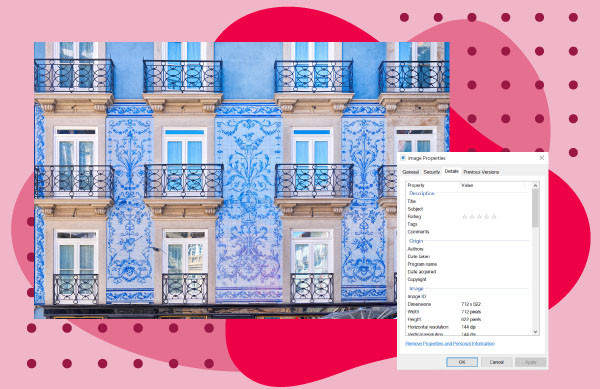 Blue Porto houses image with photo metadata accessed using Windows
Blue Porto houses image with photo metadata accessed using Windows
7. Can You Edit Photo Metadata?
Yes, you can absolutely edit a picture’s metadata. This allows you to correct errors, add missing information, or update copyright details. Editing metadata is a simple process on both Mac and Windows.
- Access the metadata: Follow the steps above to access the metadata of the file you want to edit.
- Locate the category: Find the specific category you want to change (e.g., name, date, author).
- Edit the value: Under the “Value” tab, click and type in the new information.
8. Why Use a Metadata Editor?
While you can manually edit metadata on both Mac and Windows, using a dedicated metadata editor offers several advantages, especially when dealing with a large number of images or complex editing tasks.
8.1. Efficiency: Batch Editing and Automation
Metadata editors often allow you to edit metadata in batches, applying changes to multiple files simultaneously. They can also automate tasks like adding copyright information to all images in a folder.
8.2. Advanced Features: Custom Fields and Presets
Many metadata editors offer advanced features like custom fields, allowing you to add specific information relevant to your workflow. You can also create presets for frequently used metadata, saving time and ensuring consistency.
8.3. Data Completeness: Addressing Missing Fields
Sometimes, the data doesn’t include things like a title (which may be known only to the user). Metadata editors allow you to fill in these missing fields, ensuring that your images are fully documented.
8.4. Privacy Concerns: Removing Sensitive Metadata
Others may just need to remove metadata from photos to hide key details of images before uploading them to a social media platform. A metadata editor can quickly and easily remove sensitive information like GPS coordinates, protecting your privacy.
Whatever the reason, when you need to switch up, remove, or add a few key data details, make sure to be assertive in your workflow. Also, it doesn’t hurt to keep a backup of the original files until you are happy with the results of your metadata changes.
9. How Digital Asset Management (DAM) Platforms Enhance Metadata Management
Digital asset management (DAM) is the ongoing process of keeping a check on the digital content of a business or organization. This digital content is in the form of text, audio files, videos, and pictures. DAM systems provide a centralized solution for storing, managing, and distributing digital assets, including images, videos, and documents.
9.1. Centralized Storage and Organization
A digital asset management platform stores and manages digital assets such as images, videos, documents, and other media files. It lets users easily organize, search, retrieve, and share these assets, streamlining workflows and improving organizational collaboration.
9.2. Streamlined Workflows and Collaboration
It’s a smart way to address the content chaos resulting from today’s image and digital content production demands. DAM software can help you manage, search, and edit metadata of the different files you store, as well as view thumbnails for easy visibility of the file’s content.
9.3. Enhanced Search and Retrieval
DAM systems offer advanced search capabilities, allowing you to quickly find the images you need based on metadata, keywords, or even visual content.
9.4. Controlled Access and Permissions
DAM platforms allow you to control who can access and edit your digital assets, ensuring that your valuable content is protected.
10. Managing Metadata with Canto: A Step-by-Step Guide
Canto is a leading DAM platform that simplifies metadata management and enhances your workflow. Here’s how to manage metadata using Canto:
- Search: Type your search criteria into the search bar.
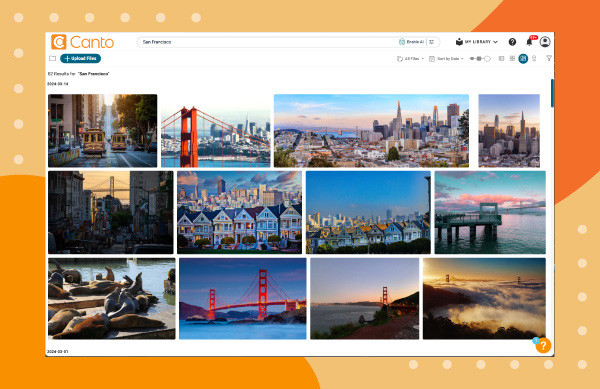 San Fransisco photos search in Canto
San Fransisco photos search in Canto
- Filter: Scroll through the tabs in the filter pane on the right of the page to narrow your search criteria.
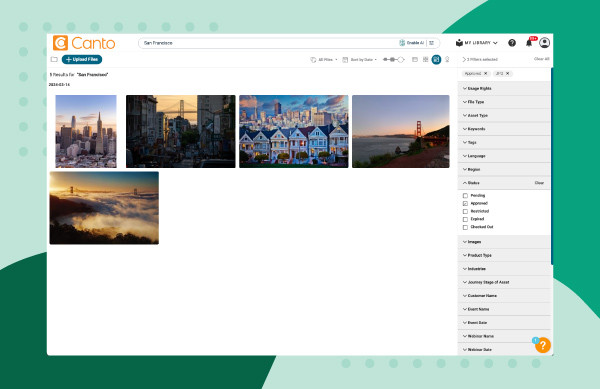 Canto metadata filters search
Canto metadata filters search
- View Metadata: Click on the image you are searching for and the embedded image metadata will appear in the right pane. Looking for all image metadata? Click the double arrows at the top right to display all embedded image metadata.
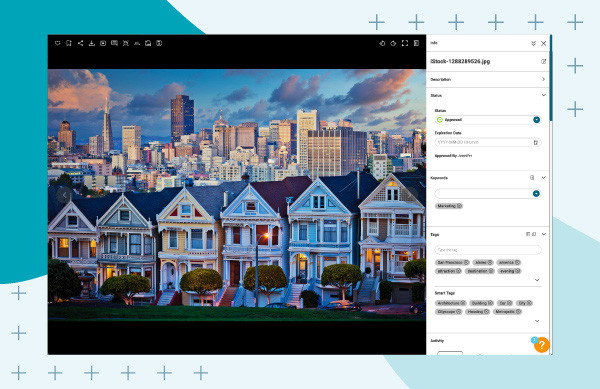 San Fransisco houses image with photo metadata displayed in Canto
San Fransisco houses image with photo metadata displayed in Canto
- Explore Details: Scroll down the page and find metadata details like the date created, dimensions, and resolution.
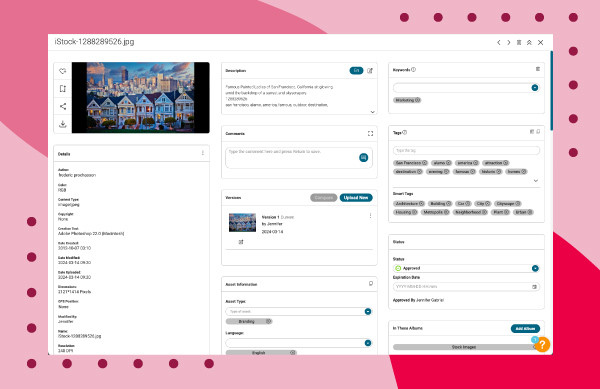 San Fransisco houses image and metadata using Canto
San Fransisco houses image and metadata using Canto
11. Canto’s AI Visual Search: A Game-Changer for Metadata Management
For users who have incorrect, incomplete, or missing metadata on their photos or those who simply wish to reduce metadata management, Canto AI Visual Search is the answer. Canto’s AI-powered search uses natural language when visually scanning your images inside your Canto library to find the most relevant photos without relying on metadata.
11.1. Natural Language Search
There’s no need for complex search terms or specific keywords used for a normal photo metadata search.
11.2. Effortless Image Discovery
AI Visual Search has no learning curve. You can search your images similarly to how you search your favorite internet search engine.
11.3. Re-discover Valuable Assets
The best part of using AI Visual Search is finding old, forgotten and valuable photography that can be reused to create more value for you and your organization.
12. Ready to Transform Your Photo Management?
Canto is the leader in digital asset management software, making it extremely easy to organize, find, and share content using image metadata. With Canto’s AI Visual Search, you can completely transform your workflows and make organizing and finding photos effortless.
Ready to streamline photo management? Visit dfphoto.net to discover our rich library of photography tutorials, stunning image collections, and a vibrant community of fellow photography enthusiasts. Address: 1600 St Michael’s Dr, Santa Fe, NM 87505, United States. Phone: +1 (505) 471-6001.
13. Frequently Asked Questions About Photo Metadata
Here are some frequently asked questions about photo metadata:
13.1. How Can I Ensure My Photo Metadata Is Secure?
To avoid sharing metadata you don’t want to make public, you should consider stripping sensitive information like location data before uploading or sharing. Some platforms may also automatically remove metadata for privacy reasons.
13.2. What Are the Legal Considerations for Altering Metadata?
For images you don’t own the rights to, altering or removing metadata (especially copyright information) can have serious consequences, including potential legal liability for infringement. Digital rights management tools can help store and track essential digital rights metadata. Always get expert legal advice if you’re unsure about copyright or digital rights issues.
13.3. How Does Metadata Affect Image SEO?
For SEO, metadata like keywords, alt text, and titles can significantly impact how images are indexed by search engines, making them more discoverable online. Properly tagging and optimizing this data enhances visibility.
13.4. What is the best way to add keywords to my photo metadata?
The best way to add keywords to your photo metadata is by using a metadata editor or a digital asset management (DAM) system like Canto. These tools allow you to add and manage keywords efficiently, ensuring that your images are easily searchable and discoverable. When adding keywords, consider using a mix of broad and specific terms that accurately describe the content of your image.
13.5. Can I view photo metadata on my smartphone?
Yes, you can view photo metadata on your smartphone using various apps available for both iOS and Android. These apps allow you to access and view the embedded information in your image files, including camera settings, location data, and copyright information. Some popular apps for viewing photo metadata on smartphones include Photo Metadata Viewer, EXIF Viewer, and Metadata Remover.
13.6. How do I remove metadata from a photo before sharing it online?
To remove metadata from a photo before sharing it online, you can use a metadata editor or a dedicated metadata removal tool. These tools allow you to strip sensitive information like location data and camera settings from your images, protecting your privacy. On Windows, you can right-click the file, select “Properties,” click the “Details” tab, and then click “Remove Properties and Personal Information.” On Mac, you can use the Preview app to export the image without metadata.
13.7. What is the difference between EXIF and IPTC metadata?
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) metadata primarily focuses on technical information about the image, such as camera settings, date and time, and GPS coordinates. IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council) metadata, on the other hand, focuses on descriptive information, such as copyright details, creator information, and content descriptions. While EXIF is automatically generated by the camera, IPTC metadata is typically added manually by the photographer or editor.
13.8. How can I use photo metadata to organize my photo library?
You can use photo metadata to organize your photo library by creating a consistent system for tagging and categorizing your images. By adding relevant keywords, descriptions, and copyright information to your metadata, you can easily search and filter your photos based on specific criteria. Digital asset management (DAM) systems like Canto can help you automate this process, making it easier to manage and organize large collections of images.
13.9. What are the benefits of using a digital asset management (DAM) system for managing photo metadata?
Using a digital asset management (DAM) system for managing photo metadata offers numerous benefits, including centralized storage, streamlined workflows, enhanced search and retrieval, controlled access and permissions, and automated metadata management. DAM systems like Canto provide a comprehensive solution for organizing, managing, and distributing your digital assets, making it easier to collaborate with team members and protect your valuable content.
13.10. How does AI Visual Search help with metadata management?
AI Visual Search helps with metadata management by allowing you to find relevant photos without relying on traditional metadata. Canto’s AI-powered search uses natural language processing to visually scan your images and identify the most relevant results, even if the metadata is incomplete or missing. This can save you time and effort when searching for specific images, and it can also help you rediscover valuable assets that you may have forgotten about.
By understanding and utilizing photo metadata, you can unlock the full potential of your image library and streamline your creative workflow. Visit dfphoto.net today to learn more and explore the world of photography.